Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Solution 1
Transféré par
searock25decDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Solution 1
Transféré par
searock25decDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Solution 1 :Retail banking is, however, quite broad in nature - it refers to the dealing of commercial banks with individual
customers, both on liabilities and assets sides of the balance sheet. Fixed, current / savings accounts on the liabilities side; and mortgages, loans (e.g., personal, housing, auto, and educational) on the assets side, are the more important of the products offered by banks. Related ancillary services include credit cards, or depository services. Todays retail banking sector is characterized by three basic characteristics:
multiple products (deposits, credit cards, insurance, investments and securities); multiple channels of distribution (call centre, branch, Internet and kiosk); and multiple customer groups (consumer, small business, and corporate).
Retail banking in India is not a new phenomenon. It has always been prevalent in India in various forms. For the last few years it has become synonymous with mainstream banking for many banks.The typical products offered in the Indian retail banking segment are housing loans, consumption loans for purchase of durables, auto loans, credit cards and educational loans. The loans are marketed under attractive brand names to differentiate the products offered by different banks. As the Report on Trend and Progress of India, 2003-04 has shown that the loan values of these retail lending typically range between Rs.20,000 to Rs.100 lakh. The loans are generally for duration of five to seven years with housing loans granted for a longer duration of 15 years. Credit card is another rapidly growing sub-segment of this product group. In recent past retail lending has turned out to be a key profit driver for banks with retail portfolio constituting 21.5 per cent of total outstanding advances as on March 2004. The overall impairment of the retail loan portfolio worked out much less then the Gross NPA ratio for the entire loan portfolio. Within the retail segment, the housing loans had the least gross asset impairment. In fact, retailing make ample business sense in the banking sector. While new generation private sector banks have been able to create a niche in this regard, the public sector banks have not lagged behind. Leveraging their vast branch network and outreach, public sector banks have aggressively forayed to garner a larger slice of the retail pie. By international standards, however, there is still much scope for retail banking in India. After all, retail loans constitute less than seven per cent of GDP in India vis--vis about 35 per cent for other Asian economies South Korea (55 per cent), Taiwan (52 per cent), Malaysia (33 per cent) and Thailand (18 per cent). As retail banking in India is still growing from modest base, there is a likelihood that the growth numbers seem to get somewhat exaggerated. One, thus, has to exercise caution is interpreting the growth of retail banking in India.
DRIVERS OF RETAIL BUSINESS IN INDIA
The Indian players are bullish on the retail business and this is not totally unfounded. As the face of the Indian consumer is changing, that is reflected in a change in the urban household income pattern, the direct fallout of such change is on the consumption pattern and hence on the banking habits of Indians, which is now skewed towards retail products. Following changing consumer demographics have led to the need for expansion of retail banking activities in India. INCREASINGLY AFFLUENT AND BULGING MIDDLE CLASS: About 320 million people will be added in the middle-income group in a period of 15 years approximately. YOUNGEST POPULATION IN THE WORLD: Changing consumer demographics indicate vast potential for growth in consumption both qualitatively and quantitatively, due to increasing affluent with bulging middle class and youngest people in the world. 70% of Indian population is below 35 years of age which means that there is tremendous opportunity of 130 million people being added to working population. The BRIC report of the GoldmanSachs, which predicted a bright future for Brazil, Russia, India and China, mentioned Indian demographic advantage as an important positive factor for India. INCREASING LITERACY LEVELS: Due to increase in the literacy ratio, people have developed a taste for latest technology and variety of products and services. It will lead to greater demand for retail activities specially retail banking activities. HIGHER ADAPTABILITY TO TECHNOLOGY: Convenience banking in the form of debit cards, internet and phone-banking, anywhere and anytime banking has attracted
many new customers into the banking field. Technological innovations relating to increasing use of credit / debit card, ATMs, direct debits and phone banking have contributed to the growth of retail banking in India. CONTINUING TREND IN URBANIZATION: Urbanization of Indian population is also an important feature influencing the retail banking. INCREASING CONSUMPTION MINDSET OF INDIANS: Economic prosperity and the consequent increase in purchasing power have given a fillip to a consumer boom. During the 10 years after 1997, India's economy grew at an average rate of 6.8 percent and continues to grow at the almost the same rate not many countries in the world match this erformance. It means that Indian consumers are now shifting from the tendency of buying more and better quality to new services and products. DECLINING TREASURY INCOME OF THE BANKS: The Treasury income of the banks, which had strengthened the bottom lines of banks for the past few years,has been on the decline during the last two years. In such a scenario, retail business provides a good vehicle of profit maximisation. Considering the fact that retails share in impaired assets is far lower than the overall bank loans and advances, retail loans have put comparatively less provisioning burden on banks apart from diversifying their income streams. DECLINE IN INTEREST RATES: Finally, decline in interest rates has a also contributed to the growth of retail credit by generating the demand for such credit.
Future Scope of Retail Banking in India
As the growth story gets unfolded in India, retail banking is going to emerge astonishingly. A. T. Kearney, a global management consulting firm, recently identified India as the "second most attractive retail destination" of 30 emergent markets. The rise of the Indian middle class is an important contributory factor in this regard. The percentage of middle to high income Indian households is expected to continue rising. The younger population not only wields increasing purchasing power, but as far as acquiring personal debt is concerned, they are perhaps more comfortable than previous generations. Improving consumer purchasing power, coupled with more liberal attitudes toward personal debt, is contributing to India's retail banking segment. The combination of the above factors promises substantial growth in the retail sector, which at present is in the nascent stage. Due to bundling of services and delivery channels, the areas of potential conflicts of interest tend to increase in universal banks and financial conglomerates. Some of the key policy issues relevant to the retail banking sector are: financial inclusion, responsible lending, access to finance, long-term savings, financial capability, consumer protection, regulation and financial crime prevention. The rise of the Indian middle class is an important contributory factor in this regard. The percentage of middle to high income Indian households is expected to continue rising. The younger population not only wields increasing
purchasing power, but as far as acquiring personal debt is concerned, they are perhaps more comfortable than previous generations. Improving consumer purchasing power, coupled with more liberal attitudes toward personal debt, is contributing to India's retail banking segment. The combination of the above factors promises substantial growth in the retail sector, which at resent is in the nascent stage. Due to bundling of services and delivery channels, the areas of potential conflicts of interest tend to increase in universal banks and financial conglomerates. Some of the key policy issues relevant to the retail banking sector are: financial inclusion, responsible ending, access to finance, long-term savings, financial capability, consumer protection, regulation and financial crime prevention.
****************************************************************************** Solution 2 :Major Challenge for Retail Banking in India:A). Retention of customers is going to be a major challenge. According to a research by Reichheld and Sasser in the Harvard Business Review, 5 per cent increase in customer retention shall increase profitability by 35 per cent in banking business, 50 per cent in insurance and brokerage, and 125 percent in the consumer credit card market. Thus, banks need to emphasise retaining customers and increasing market share.
B). Rising indebtedness could turn out to be a cause for concern in the future. India's position, of course, is not comparable to that of the developed world where household debt as a proportion of disposable income is much higher. Such a scenario creates high uncertainty. Expressing concerns about the high growth witnessed in the consumer credit segments the Reserve Bank has, as a temporary measure, put in place risk containment measures and increased the risk weight from 100 per cent to 125 per cent in the case of consumer credit including personal loans and credit cards (Midterm Review of Annual Policy, 2004-05). C). Information technology poses both opportunities and challenges. Inspite of availing the services of ATMs and Internet Banking, many consumers still prefer the personal touch of their neighborhood branch bank. Technology has made it possible to deliver services throughout the branch bank network, providing instant updates to checking accounts and rapid movement of money for stock transfers. However, this dependency on the network has brought IT departments additional responsibilities and challenges in managing, maintaining and optimizing the performance of retail banking networks. Illustratively, ensuring that all bank products and services are available, at all times, and across the entire organization is essential for todays retails banks to generate revenues and remain competitive. Besides, there are network management challenges, whereby keeping these complex, distributed networks and applications operating properly in support of business objectives becomes essential. Specific challenges include ensuring that account transaction applications run efficiently between the branch offices and data centers. D). KYC issues and money laundering risks in retail banking is yet another important issue. Retail lending is often regarded as a low risk area for money laundering because of the perception of the sums involved. However, competition for clients may also lead to KYC procedures being waived in the bid for new business. Banks must also consider seriously the type of identification documents they will accept and other processes to be completed. The most significant challenge is to devise appropriate pricing mechanism. The industry today is witnessing a price war, with each bank competing to have a large slice of the cake of the market, without much of a scientific study into the cost of funds involved, margins etc,. Most of the banks that use rating models for determining the health of the retail portfolio do not use them for pricing the products. This issue will be gaining more importance in the near future.While retail banking offers phenomenal opportunities for growth, the challenges are equally daunting. How far the retail banking is able to lead growth of the banking industry in future would depend upon the capacity building of the banks to meet the challenges and make use of the opportunities profitably. However, the kind of technology used and the efficiency of operations would provide the much needed competitive edge for success in retail banking business.
Step taken by Regulator / Market / Bankers :By Banks :- 1. Presence and availability. 2. Core Banking
3. Extended hours , quality and quickness in delivery. 4. Better Infrastructure. 5. Make routine tasks easier and less time consuming like (ATM, Fund Trnasfer,Net banking) 6. Merger and Acquisition . like (Satate bank of Indore) 7. Service , Product Range, Group Companies. (Capital Market, Mutual Funds) ******************************************************************************
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Study On Customer Perception Towards The Services Offered in Retail Banking by South Indian Bank, Vennikulam Branch (Kerala)Document71 pagesA Study On Customer Perception Towards The Services Offered in Retail Banking by South Indian Bank, Vennikulam Branch (Kerala)Lini Susan John100% (4)
- Banking Module 1Document26 pagesBanking Module 1mansisharma8301Pas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking JUNE 2022Document10 pagesRetail Banking JUNE 2022Rajni KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Shyamala Gopinath: Retail Banking - Opportunities and ChallengesDocument5 pagesShyamala Gopinath: Retail Banking - Opportunities and ChallengesAmol ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- Retail BankingDocument15 pagesRetail BankingjazzrulzPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail BankingDocument10 pagesRetail BankingAtul MadPas encore d'évaluation
- ChapterDocument16 pagesChapterAjay YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Lending Business Importance & Strategies For Maintaining GrowthDocument21 pagesRetail Lending Business Importance & Strategies For Maintaining Growthjpradnya4451Pas encore d'évaluation
- Retail BakingDocument29 pagesRetail BakingdarshpujPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking Retail ProductsDocument7 pagesBanking Retail ProductsaadisssPas encore d'évaluation
- Synopsis 1Document16 pagesSynopsis 1Vipul GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Retail Banking Industry: Drivers & Dooms - An Empirical StudyDocument16 pagesIndian Retail Banking Industry: Drivers & Dooms - An Empirical StudyApoorva PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges To Retail Banking in IndiaDocument2 pagesChallenges To Retail Banking in IndiapadmajammulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking in IndiaDocument17 pagesRetail Banking in Indianitinsuba198050% (2)
- Impact of Retail Banking in Indian Economy: Research Article Parmanand Barodiya and Anita Singh ChauhanDocument5 pagesImpact of Retail Banking in Indian Economy: Research Article Parmanand Barodiya and Anita Singh ChauhanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Akshu Full ProjectDocument73 pagesAkshu Full ProjectAshwini VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking - A Real Growing Concept in The Present Scenario Dr.A.SelvarajDocument8 pagesRetail Banking - A Real Growing Concept in The Present Scenario Dr.A.Selvarajrajeshraj0112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Retail BankingDocument44 pagesProject On Retail BankingabhinaykasarePas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation Project IqbalDocument85 pagesDissertation Project Iqbalsunnychauhan89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Topic Meaning of Retail BankingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Topic Meaning of Retail Bankingpriyanka guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Full)Document60 pagesFull)Neeraj BhatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1Document8 pagesChapter - 1rajkumariPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities of Retail Banking in IndiaDocument12 pagesA Study On Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities of Retail Banking in IndiakokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking IndustryDocument30 pagesBanking IndustrySagar Damani100% (1)
- Page 11-37Document28 pagesPage 11-37Preeti MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- BANKING INDUSTRY-Fundamental AnalysisDocument19 pagesBANKING INDUSTRY-Fundamental AnalysisGopi Krishnan.nPas encore d'évaluation
- BANKING INDUSTRY-Fundamental AnalysisDocument19 pagesBANKING INDUSTRY-Fundamental AnalysisGopi Krishnan.nPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Jay Ketanbhai Changela Enrollment No.: 20fomba11508 For The Submission Of: SeeDocument26 pagesName: Jay Ketanbhai Changela Enrollment No.: 20fomba11508 For The Submission Of: SeeMAANPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.0 Introduction To Retail Banking: The Retail Banking Environment Today Is Changing Fast. The ChangingDocument45 pages2.0 Introduction To Retail Banking: The Retail Banking Environment Today Is Changing Fast. The ChangingViraat Ashok SudPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking An Introduction Research Methodology: Title of Project Statement of The Problem Objective of The StudyDocument9 pagesRetail Banking An Introduction Research Methodology: Title of Project Statement of The Problem Objective of The StudySandeep KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Finance (ANALYSIS OF HDFC CAR LOAN'S FINANCE)Document40 pagesFinance (ANALYSIS OF HDFC CAR LOAN'S FINANCE)AneesAnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Kotak FinalDocument46 pagesKotak FinalRahul FaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking Front Office Management ActivityDocument66 pagesRetail Banking Front Office Management ActivitysargunkaurPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Customer Perception Towards The Services Offered in Retail Banking by South Indian Bank Vennikulam Branch KeralaDocument71 pagesA Study On Customer Perception Towards The Services Offered in Retail Banking by South Indian Bank Vennikulam Branch KeralaRajasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Comm ReportDocument5 pagesComm ReportvarunsalwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking Front Office Management Activity For HDFC Bank by Nisha Wadekar This Project Is Very Useful To StudentDocument51 pagesRetail Banking Front Office Management Activity For HDFC Bank by Nisha Wadekar This Project Is Very Useful To Studentganeshkhale7052Pas encore d'évaluation
- Banking ProjectDocument35 pagesBanking Projectvarun_varunsharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge ManagementDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Managementrakeshkmr1186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study On Retail BankingDocument47 pagesStudy On Retail Bankingzaru1121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges and Opportunities To Commercial Banks in RuralDocument16 pagesChallenges and Opportunities To Commercial Banks in RuralRaghav guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancillary Services Provided by BankersDocument17 pagesAncillary Services Provided by BankersLogan Davis100% (2)
- The Indian Kaleidoscope: Emerging Trends in RetailDocument52 pagesThe Indian Kaleidoscope: Emerging Trends in RetailSwati Agarwal100% (1)
- Retail Fs MarketDocument6 pagesRetail Fs MarketAvikalmmPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Banking at HDFCDocument56 pagesRetail Banking at HDFCutkarsh jaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- I. Overall Market Size: Question-4Document4 pagesI. Overall Market Size: Question-4Himanshu ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Nishith Devraj Paper For Jbfsir 1 PDFDocument10 pages10 Nishith Devraj Paper For Jbfsir 1 PDFpareek gopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Yes Bank Mainstreaming Development Into Indian BankingDocument20 pagesYes Bank Mainstreaming Development Into Indian Bankinggauarv_singh13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synopsis Cannra BankDocument3 pagesSynopsis Cannra BankGagan KauraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sector Project 1Document5 pagesSector Project 12k20dmba102 RiyaGoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Credit Score EssayDocument24 pagesCredit Score EssaypavistatsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.10 Retail BankingDocument14 pages2.10 Retail BankingSrinivas RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Meaning of Retail: Banking Regulation Act 1949Document22 pagesMeaning of Retail: Banking Regulation Act 1949chinu1303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Banking Sector: 1.1 Introduction To The TaskDocument23 pagesBanking Sector: 1.1 Introduction To The TaskRIYA CHALKEPas encore d'évaluation
- Industry Profile: Excellence in Indian Banking', India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth Will Make TheDocument27 pagesIndustry Profile: Excellence in Indian Banking', India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth Will Make TheNekta PinchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingD'EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingPas encore d'évaluation
- T R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)D'EverandT R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)Pas encore d'évaluation
- JAIIB Legal Sample Questions by MuruganDocument63 pagesJAIIB Legal Sample Questions by MuruganRizz Ahammad80% (5)
- Hand Book On Know Your Circular Andhra Bank PromotionDocument81 pagesHand Book On Know Your Circular Andhra Bank PromotionSubrat Satyaranjan KanungoPas encore d'évaluation
- Monetary Policy and CB Module-7Document18 pagesMonetary Policy and CB Module-7Eleine Taroma AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Libra To Vashu TradingDocument1 pageLibra To Vashu TradingLL Lawwise Consultech India Pvt LtdPas encore d'évaluation
- Incoming Payment InstructionDocument2 pagesIncoming Payment InstructionCapitol COPas encore d'évaluation
- The Roman Eagle On A Red ShieldDocument2 pagesThe Roman Eagle On A Red ShieldARBITRAJ COMERCIAL -Mircea Halaciuga,Esq. aka. Mike SerbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Contract Account FormatDocument3 pagesContract Account FormatVishakh Nag100% (1)
- Statement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument21 pagesStatement of Account: Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing Balancemani kantaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Non-Scheduled Urban Co-Operative Banks Sr. No. Bank Name RO NameDocument102 pagesList of Non-Scheduled Urban Co-Operative Banks Sr. No. Bank Name RO NameSusanPas encore d'évaluation
- Deposit Mobilization of Nabil Bank LimitedDocument41 pagesDeposit Mobilization of Nabil Bank Limitedram binod yadav76% (38)
- Classroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersDocument4 pagesClassroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersJohn Cedfrey Narne100% (1)
- Proc No. 129-155 dt.14.12.2018Document7 pagesProc No. 129-155 dt.14.12.2018Maku RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Moi Chapter I Simple InterestDocument17 pagesMoi Chapter I Simple InterestBadtuan Asliya E.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Banking System of India: Presented By-Sohini MukherjeeDocument31 pagesBanking System of India: Presented By-Sohini MukherjeeShivam AgarwalITF43Pas encore d'évaluation
- Total: Tax Invoice For..Document10 pagesTotal: Tax Invoice For..Sarun SunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Coldwell Banker Home Buyer's GuidebookDocument25 pagesColdwell Banker Home Buyer's GuidebookLani Rosales100% (2)
- Chanda KochharDocument39 pagesChanda KochharviveknayeePas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting For Musyarakah FinancingDocument16 pagesAccounting For Musyarakah FinancingHadyan AntoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Samudra Milk Bill 01.04.19 To 10.04.19Document102 pagesSamudra Milk Bill 01.04.19 To 10.04.19SanjayVermaPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN435 Asgmnt UpdatedDocument10 pagesFIN435 Asgmnt UpdatedNazirah Mohamed KauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Split 162013 190909 - 20220331Document5 pagesSplit 162013 190909 - 20220331NUR FASIHAH BINTIPas encore d'évaluation
- Amtb Eft Format SpaDocument7 pagesAmtb Eft Format SpaDavid GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- Statement EUDocument41 pagesStatement EUuyên đỗPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz On Audit of CashDocument11 pagesQuiz On Audit of CashY JPas encore d'évaluation
- OpTransactionHistoryTpr09 04 2019 PDFDocument9 pagesOpTransactionHistoryTpr09 04 2019 PDFSAMEER AHMADPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Customer Prefernces Towards Credit Cards in HDFC BankDocument40 pagesA Study On Customer Prefernces Towards Credit Cards in HDFC BankSharathPas encore d'évaluation
- Fees Structure For Kabojja International SchoolDocument2 pagesFees Structure For Kabojja International SchoolTheCampusTimes100% (1)
- IBPS (Institute of Banking and Personal Selection)Document3 pagesIBPS (Institute of Banking and Personal Selection)Nikhil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Financial System in NepalDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Financial System in NepalMukul Bhatia67% (6)
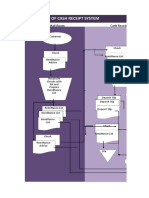
- Flowchart of Cash Receipt System: Mail Room Cash ReceiptsDocument17 pagesFlowchart of Cash Receipt System: Mail Room Cash ReceiptsStephanie Diane SabadoPas encore d'évaluation