Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Jundice
Transféré par
JanineLingayoCasilenTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Jundice
Transféré par
JanineLingayoCasilenDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
What is obstructive jaundice? Obstructive jaundice is a condition in which there is blockage of the flow of bile out of the liver.
This results in an overflow of bile and its by-products into the blood, and bile excretion from the body is incomplete. Bile contains many by-products, one of which is bilirubin, a pigment derived from dead red blood cells. Bilirubin is yellow, and this gives the characteristic yellow appearance of jaundice in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Symptoms of obstructive jaundice include yellow eyes and skin, abdominal pain, and fever. Any type of obstruction that blocks the flow of bile from the liver can cause obstructive jaundice. Most commonly, gallstones create the blockage. Other causes of obstruction include inflammation, tumors, trauma,pancreatic cancer, narrowing of the bile ducts, and structural abnormalities present at birth. The signs and symptoms of obstructive jaundice differ depending on the completeness of the blockage, and the disease course varies among individuals. Some people with obstructive jaundice may have no symptoms initially, but if the condition persists, they may have severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting. Complete blockage may also occur, posing a risk of infection leading to liver and gallbladder damage. Fortunately, in most cases, obstructive jaundice can be treated with intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and surgical removal of the obstruction. What are the symptoms of obstructive jaundice? Obstructive jaundice can cause many different types of symptoms, which vary in intensity among individuals. Common symptoms of obstructive jaundice Obstructive jaundice can cause any of the following symptoms, and at times, any of these symptoms can be severe: Abdominal pain (typically occurs in the right upper quadrant of the body) Dark-colored urine Diarrhea Easy bleeding or bruising Fever and chills Itchy skin Loss of appetite (anorexia) Malaise or lethargy Pale stools Unintentional weight loss Yellow coloration of the eyes and skin (jaundice) Serious symptoms that might indicate a lifethreatening condition In some cases, obstructive jaundice can be life threatening. Seek immediate medical care (call 911)if you, or someone you are with, have any of these life-threatening symptoms including:
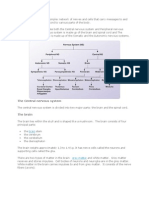
Abdominal swelling, distension and bloating High fever (higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit) Nausea with or without vomiting Severe abdominal pain What causes obstructive jaundice? Obstructive jaundice is a condition in which there is a blockage of the flow of bile out of the liver. This results in an overflow of bile and its byproducts into the blood, and bile excretion from the body is incomplete. Bilirubin, a component of bile, is yellow, which gives the characteristic yellow appearance of jaundice in the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. The most common cause of obstructive jaundice is the presence of gallstones (cholelithiasis). Other causes of obstructive jaundice are tumors, trauma, cysts, and inflammation in the bile ducts. Causes of obstructive jaundice Obstructive jaundice is caused by conditions that block the normal flow of bile from the liver into the intestines including: Biliary stricture (narrowing of the bile duct) Cancer of the gallbladder or pancreas Cholangitis (infection or inflammation of the common bile duct) Cholelithiasis (gallstones) Congenital structural defects Cysts of the bile duct Lymph node enlargement Pancreatitis Parasitic infection Trauma, including surgical complications What are the risk factors for obstructive jaundice? A number of factors increase your risk of developing obstructive jaundice. Not all people with risk factors will get obstructive jaundice. Risk factors for obstructive jaundice include: Abdominal injury Gallstones Pancreatic cancer Tumors in the area of the common bile duct How is obstructive jaundice treated? Your health care professional can develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs. It is important to precisely follow your treatment plan for obstructive jaundice to help minimize your symptoms and decrease the chance of your symptoms recurring over time. To determine if you have obstructive jaundice, your health care provider may ask you to provide blood samples and undergo diagnostic tests. Treatment options for obstructive jaundice Treatment options for obstructive jaundice depend on the exact cause of the jaundice and on the severity of the disease. Examples include:
Antibiotic therapy (if indicated for infection) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an imaging procedure that allows treatment of some bile duct problems, including removal of gallstones that are causing obstruction Intravenous fluids and pain medications Nutritional support Surgery or other procedures to repair anatomical defects or create alternative pathways for the flow of bile
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument24 pagesNephrotic SyndromeJawad SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia سمنار 2023Document25 pagesAnemia سمنار 2023Hesham IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument21 pagesCirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDan ChicinasPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Liver FunctionDocument64 pagesEvaluation of Liver FunctionMustafa KhandgawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Megaloblastic AnaemiaDocument11 pagesMegaloblastic AnaemiaJesmin_36Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Management of Hyperkalemia in CKD PatientsDocument49 pages1 Management of Hyperkalemia in CKD PatientsTelli KoromaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument15 pagesAnaemiaAnik SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaemiaDocument83 pagesAnaemiadoc19019696Pas encore d'évaluation
- NocturiaDocument10 pagesNocturiaKousik AmancharlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument28 pagesAcid-Base Balanceps4only100% (1)
- Case Study 1Document6 pagesCase Study 1rajambal_ayyasamy0% (1)
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument12 pagesCirrhosis of The LiverherlindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsDocument56 pagesKidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsPaulina Paskeviciute100% (1)
- An Introduction To AnaemiaDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Anaemiaمجاهد إسماعيل حسن حسينPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument51 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseaseTeena Chandran100% (1)
- 01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersDocument51 pages01 - Signs and Symptoms of Git DisordersRere AnugrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanDocument30 pagesAcute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanHandre Putra100% (1)
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) : Where Are We Today?Document32 pagesNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) : Where Are We Today?Saad MotawéaPas encore d'évaluation
- PresentationDocument11 pagesPresentationShravan TuragaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument49 pagesNephrotic SyndromeAMA237Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateDocument8 pagesCBC Test - What Is The Normal Range, What Do Abnormal Levels IndicateRedcliffe LabsPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinalysis 150313040235 Conversion Gate01Document30 pagesUrinalysis 150313040235 Conversion Gate01AbhishiktaAbhi100% (1)
- Lets Get Started - Urinalysis PDFDocument3 pagesLets Get Started - Urinalysis PDFSatya PramanaPas encore d'évaluation
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundiceAbo Omar Ahmed100% (1)
- Edema: Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDocument55 pagesEdema: Dr. Bernardo Dámaso MataDeivis Dan ErickPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAcute Renal Failurearif kurnia timurPas encore d'évaluation
- MIDocument22 pagesMIGagauz SiliviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Normocytic Anemia'sDocument14 pagesNormocytic Anemia'sbrown_chocolate87643Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renal DisordersDocument77 pagesRenal Disorderslorelee_espaldon100% (1)
- Poisoning II FinalDocument45 pagesPoisoning II FinalBi PinPas encore d'évaluation
- Colon Cancer: Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesColon Cancer: Risk FactorsAshley VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuDocument65 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy: Assisstant Professor Dr. Mihaela-Dora DonciuFloreaAndreiPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Protein Nitrogenous Constituents of Blood - Urea, Uric Acid EtcDocument50 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogenous Constituents of Blood - Urea, Uric Acid EtcBobskinnyPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Changes in Drug and Electrolyte AbnormalitiesDocument28 pagesECG Changes in Drug and Electrolyte AbnormalitiesNachiket Vijay PotdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesAcute On Chronic Kidney DiseaseElizabeth LiePas encore d'évaluation
- National Program of Cancer Registries Education and Training SeriesDocument93 pagesNational Program of Cancer Registries Education and Training SeriesNADEEMPas encore d'évaluation
- SepsisDocument33 pagesSepsisv_vijayakanth7656Pas encore d'évaluation
- Urolithiasis: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesUrolithiasis: ObjectivesOkki Masitah Syahfitri NasutionPas encore d'évaluation
- Ugib &lgibDocument41 pagesUgib &lgibDawex IsraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenal DisordersDocument32 pagesAdrenal DisordersJyoti ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- HepatomegalyDocument2 pagesHepatomegalyFuyumi RiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gi Bleeding 6th Year Seminar GRP BB PDFDocument32 pagesGi Bleeding 6th Year Seminar GRP BB PDFmohamedeen hamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes NotesDocument10 pagesDiabetes Notestripj33Pas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Document58 pagesGlomerulonephritis-1 (Dr. Soffa)Rahmailla Khanza Diana FebriliantriPas encore d'évaluation
- AnemiaDocument11 pagesAnemiacentrino1780% (5)
- Anmol's Investigatory Project 1Document7 pagesAnmol's Investigatory Project 1Anmol KatariaPas encore d'évaluation
- AKI in SepsisDocument45 pagesAKI in SepsisIkeBundaAdellulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The KidneysDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The KidneysSanthu SuPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE STUDY FORMAT (Kidney Transplantation)Document12 pagesCASE STUDY FORMAT (Kidney Transplantation)ashnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Overdose and PoisoningDocument4 pagesOverdose and PoisoningMahmoud SelimPas encore d'évaluation
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- Hyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismDocument12 pagesHyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismCésar Augusto Sánchez SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Stones A Clinical Review PDFDocument6 pagesRenal Stones A Clinical Review PDFNurholis MajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Guide To ECGDocument78 pagesComplete Guide To ECGAnas YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Swollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandSwollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyanosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandCyanosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Hypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandHypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma in the 21st Century: New Research AdvancesD'EverandAsthma in the 21st Century: New Research AdvancesRachel NadifPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Phone and Risk of Developing Meningioma Brain Cancer Hartselle ALDocument3 pagesCell Phone and Risk of Developing Meningioma Brain Cancer Hartselle ALJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Animals Without BackbonesDocument10 pagesAnimals Without BackbonesJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Tests Why Is It Done? Patient's Test ResultsDocument3 pagesTests Why Is It Done? Patient's Test ResultsJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastritis Is An Inflammation of The Gastric MucosaDocument6 pagesGastritis Is An Inflammation of The Gastric MucosaJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- JaundiceDocument3 pagesJaundiceJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- CUSHING'sDocument3 pagesCUSHING'sJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearancemishyjayPas encore d'évaluation
- 55043153Document9 pages55043153JanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Document2 pagesCh50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Caress Mae Gubaton CabudoyPas encore d'évaluation
- JaundiceDocument3 pagesJaundiceJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Assisted TherapyDocument5 pagesAnimal Assisted TherapyJanineLingayoCasilenPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document2 pages1Amran Cleo SPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles of Mastication Saurav 2Document79 pagesMuscles of Mastication Saurav 2FourthMolar.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles - of - Genetics 6th Ed by Snustad - 20 (PDF - Io) (PDF - Io) - 12-14-1-2Document2 pagesPrinciples - of - Genetics 6th Ed by Snustad - 20 (PDF - Io) (PDF - Io) - 12-14-1-2Ayu JumainPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Container Form Lab Process Remarks HKL (Hospital Appointment Date - Specialist's SignatureDocument9 pagesTest Container Form Lab Process Remarks HKL (Hospital Appointment Date - Specialist's SignaturesyasyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumor Marker Tests - CancerDocument4 pagesTumor Marker Tests - CancerMonna Medani LysabellaPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Ololade 038Document13 pagesDR Ololade 038Andrawus DanjumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wallstreetjournal 20230401 TheWallStreetJournalDocument64 pagesWallstreetjournal 20230401 TheWallStreetJournalNJBHVGCFPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Jaggery? Is Jaggery Healthy? What Is Better: Jaggery or Sugar? Can Jaggery Cure Ailments?Document5 pagesWhy Jaggery? Is Jaggery Healthy? What Is Better: Jaggery or Sugar? Can Jaggery Cure Ailments?satheb319429Pas encore d'évaluation
- ETT IntubationDocument27 pagesETT IntubationGilbert Sterling Octavius100% (1)
- Neurobiology of Sleep: Madhu Kalia4Document5 pagesNeurobiology of Sleep: Madhu Kalia4Julian ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesBahasa InggrisSofi SusantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual Blood Derived Stem Cells and Their Scope in Regenerative Medicine A Review ArticleDocument6 pagesMenstrual Blood Derived Stem Cells and Their Scope in Regenerative Medicine A Review ArticleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument31 pagesCarbon Monoxide PoisoningDheerajPas encore d'évaluation
- IMTX PatentDocument76 pagesIMTX PatentCharles GrossPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxime Gorky and KingstonDocument433 pagesMaxime Gorky and KingstonBasil FletcherPas encore d'évaluation
- Unilever Lifebuoy in India Implementing The Sustainability PlanDocument14 pagesUnilever Lifebuoy in India Implementing The Sustainability PlanMira Sesaria50% (2)
- 24 Bio Fertilization of BananaDocument6 pages24 Bio Fertilization of Bananamiceli57Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3yc CrVlEemddAqBQMk Og 1.4 Six Artifacts From The Future of Food IFTF Coursera 2019Document13 pages3yc CrVlEemddAqBQMk Og 1.4 Six Artifacts From The Future of Food IFTF Coursera 2019Omar YussryPas encore d'évaluation
- LAN Party Skate Park by Shane Jesse ChristmassDocument91 pagesLAN Party Skate Park by Shane Jesse ChristmassPatrick TrottiPas encore d'évaluation
- CHCCCS023 Support Independence and WellbeingDocument22 pagesCHCCCS023 Support Independence and WellbeingSushma karkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinchers: RheumatologyDocument22 pagesClinchers: RheumatologyvarrakeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in MCNDocument16 pagesReviewer in MCNChristian Clyde Noel JakosalemPas encore d'évaluation
- LP MAPEH 9 (Health)Document4 pagesLP MAPEH 9 (Health)Delima Ninian100% (2)
- BTS Sarcoidosis Clinical StatementDocument17 pagesBTS Sarcoidosis Clinical StatementDarrin WiebePas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPclaidelynPas encore d'évaluation
- GIEEE TGMP Policy Terms For 2022-23Document5 pagesGIEEE TGMP Policy Terms For 2022-23Janardhan Reddy TPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical FlyerDocument2 pagesMedical FlyerThana PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal Exam TipayEmelieDocument4 pagesRizal Exam TipayEmelieEmelie TipayPas encore d'évaluation
- National Geographic USA - January 2016Document148 pagesNational Geographic USA - January 2016stamenkovskib100% (4)
- Para Lab 11Document3 pagesPara Lab 11api-3743217Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHCCCS015 Student Assessment Booklet Is (ID 97088) - FinalDocument33 pagesCHCCCS015 Student Assessment Booklet Is (ID 97088) - FinalESRPas encore d'évaluation