Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
4d94e Shop Manual
Transféré par
yeudysDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
4d94e Shop Manual
Transféré par
yeudysDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
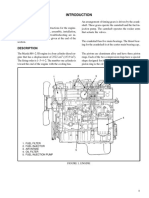
INTRODUCTION
ENGINE BODY
3.1 Introduction Prepare the following prior to starting inspections and maintenance of the engine. (1) Fix the engine on a horizontal table. CAUTION Fix it firmly because it may fall down and injure you or damage the parts during work.
(2) Remove the cooling water hose, fuel oil pipe, wire harness, and so on connecting the engine to the forklift truck body to drain the cooling water, oil, and fuel. (3) Use detergent, air, steam, and so on to clean the engine by washing away earth, oil, dust, and so on adhered to it. When this is done, be careful not to allow foreign substances into the engine. CAUTION When using the air, steam, and so on, foreign substances may be scattered and damage your eye, and so on. Be sure to wear a protective wear such as goggles.
3-2
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER HEAD
3.2 Cylinder Head
(1) Component Parts
1st time T = 53.9 Nm (5.5 kgf-m) <39.8 ft-lb> 2nd time T = 107.8 Nm (11 kgf-m) <79.6 ft-lb>
CAUTION At the time of disassembly, the packings, O-rings, and oil seals must be all replaced by new parts; they are not reusable. Particularly, if a head gasket packing is reused, a blow-by of the combustion gas may damage the explosion surfaces of the cylinder and cylinder head, and it is feared that you will not be able to reuse them.
3-3
CYLINDER HEAD
ENGINE BODY
(2) Disassembly and Aassembly of Cylinder Head
(3) Disassembly Procedure Disassemble in order of the numbers shown in the drawing. Remove the alternator assembly. (Note 1) Remove the fan, pulley, and V-belt. Remove the water pump assembly. Remove the fuel filter and fuel oil pipe. Remove the oil gauge assembly. Remove the fuel injection pipe. (Note 2) Remove the intake manifold assembly, Remove the exhaust manifold assembly. Remove the cylinder head cover assembly. Remove the lever shaft assembly, push rod, and valve head protector. (Note 3) Remove the cylinder head assembly and head gasket. (Note 4) Remove the fuel injection valve and fuel return oil pipe. (Note 5) Remove the glow plug and lead wires. Remove the intake/exhaust valve and valve spring. (Note 6) Remove the valve lever from the lever shaft.
3-4
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER HEAD
(4) Assembly Procedure Assemble in the reverse order of disassembiy. (Note 1) Alternator Disassembly: Supporting the alternator, loosen the mounting bolts. Assembly: Belt tension is 10 - 15 mm (0.39 - 0.59 in) (7 - 9 mm (0.28 0.35 in) for a new belt) at finger pressure of 98 N(10 kgf) <22 lb>.
CAUTION Support the alternator firmly. Otherwise, you may have your finger caught or damage the parts. (Note 2) Fuel injection pipe Disassembly and assembly: Note combinations of the pumps A, B, C, and D marks with the cylinder numbers. A-4, B-2, C-1, D-3 Pump: Marked on the delivery section of the main body Cylinders: Numbered in order of 1, 2, 3, and 4 from the flywheel side (Note 3) Push rod Assembly: Be sure to apply oil to the contact with a valve clearance adjusting screw. (Note 4) Cylinder head Disassembly 1) Loosen the head bolts sequentially in two times. 2) Be careful not to scratch the combustion) surface. Assembly 1) Apply oil to the threads and seat surface of the head bolts and set them uniformly. 2) When tightening them, do so in two times in reverse order of disassembly. 1st-time torque T=53.9Nm (5.5kgf-m) <39.8 ft-lb> 2nd-time torque T=107.8Nm (11kgf-m) <79.6 ft-lb>
3-5
CYLINDER HEAD
ENGINE BODY
(Note 5) Fuel injection valve Disassembly: Note that the protector at the nose will remain in the cylinder head Assembly: Unless there is a gas leak, replace only the copper washer between the nozzle and protector by a new one and assemble. (Note 6) Intake/exhaust valve Disassembly: When there is a cotters burr at the shaft of the intake/exhaust valve, eliminate it with an oilstone, and so on, and then, remove the valve from the cylinder head Assembly: 1) Apply oil and assemble it, paying attention not to damage the stem seal. 2) After assembling the intake/exhaust valve, valve spring, holder, and cotter, fit in the spring by lightly hitting the head of the valve stem.
(5) Inspection and Measurement of Parts (i) Cylinder head 1) Inspection of the combustion surface and measurement of distortion. a) Distortion of the combustion surface Clean the combustion surface, apply a straight edge to two diagonal directions and four peripheral directions and use a thickness gauge to measure deformation of the combustion surface.
b) Inspection of the combustion surface When cracks are suspected, examine by a color check. 2) Wear measurement of the intake/exhaust valve seat Clean the valve seat and measure valve sinking and seat width. Depending on the circumstances, paint the valve in blue and check for a contact. a) Measurement of valve sinking
3-6
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER HEAD
b) Measurement of seat width
(ii) Intake/exhaust valve and valve guide 1) When the intake/exhaust valve shaft is bent or greatly worn, replace it together with the valve guide. 2) Measurement of the outer diameter of the valve shaft and inner diameter of the valve guide
(iii) Valve spring 1) Replace it if it has any abnormality such as damage, corrosion. 2) Measurement of free length, inclination, and spring tension
(iv) Locker arm, shaft, spring, push rod, valve head protector, and valve clearance adjusting screw 1) Replace them if they have any abnormality such as damage, corrosion. Pay additional attention to the contact area between the locker arm and valve head protector, corrosion and damage of the spring, bent of the push rod, and contact of both ends.
3-7
CYLINDER HEAD
ENGINE BODY
(2) Measurement of the inner diameter of the locker shaft hole and outer diameter of the shaft
(6)
Correction of Valve Seat
IMPORTANT: When correcting the valve seat, check the clearance between the valve and valve guide first. If it is larger than the specified limit, replace the valve or valve guide to normalize the clearance, and then, correct the valve seat. After correcting the valve seat, wash the valve and cylinder head fully with light oil, and so on to completely eliminate grinding powder, compound, and so on. (i) When the seat is slightly rough: Perform [A] and [B] below. (ii) When the seat is considerably rough, but the seat width is normal, correct with a seat grinder or seat cutter, and then, perform [A] and [B] below.
(iii) When the seat is considerably rough and the seat width is too large, grind or cut the seat surface with a 40 seat grinder or seat cutter, finish the seat width to the reference dimension with a 150 seat grinder, perform seat correction described in (ii) above, and then, perform [A] and [B] below.
[A]: Knead the valve compound and engine oil together, and fit the valve to the seat. [B]: Fit with the engine oil alone.
3-8
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER HEAD
(7) Replacement of Valve Guide (i) Using a drawout tool, draw out the valve guide from the cylinder head. (ii) Put liquid nitrogen or ether/alcohot plus dry ice in a container to cool a replacement valve guide, and drive in with a valve guide inserting tool. (iii)Finish to a reference inner diameter with a reamer. (iv) Check a projection amount from the cylinder head. Projection amount: 15 mm (0.59 in)
CAUTION Do not touch a cooled valve guide with a naked hand. The skin may be damaged. (8) Replacement of Valve Stem Seal (i) Whenever the intake/exhaust valve is disassembled, be sure to replace it by a new one. (ii) To reassemble it, apply grease to a stem seal, push it in with an inserting tool to install it. Only the exhaust side is painted in yellow. Be careful not to mistake the intake side for the exhaust side.
3-9
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
ENGINE BODY
3.3 Gear Train and Cam Shaft
(1) Component Parts
Crank pulley Fuel injection pump gear Flywheel Non-reusable part pply liquid packing Apply grease
T = 117.6 Nm(12 kgf-m) <86.8 ft-lb> T = 63.7 Nm(6.5 kgf-m) <47.0 ft-lb> T = 196 Nm(20 kgf-m) <144.7 ft-lb>
3-10
ENGINE BODY
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
(2) Disassembly and Assembly of Gear Train and Cam Shaft
(3) Disassembly Procedure Disassemble in order of the numbers shown in the drawing. Take the cylinder head disassembly procedural steps through Remove the fuel injection pump drive gear cover. Remove the fuel injection pump. (Note 1) Remove the crank shaft pulley. (Note 2) Remove the gear case cover. (Note 3) Remove the idle gear assembly. (Note 4) Remove the PTO drive gear. (Note 5) Remove the PTO injection pipe. Remove the starting motor. Remove the flywheel. (Note 6) Remove the cam shaft assembly. (Note 7) Remove the gear case. (Note 8) Remove the oil seal from the gear case cover. (Note 9) (4) Assembly Procedure Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
11 .
3-11
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
ENGINE BODY
(Note 1) Fuel injection pump Disassembly: Remove fuel injection pump drive gear mounting nuts. Remove the gear by a gear puller, using an M8 forcing screw. Loosen and remove fuel injection pump mounting nuts. Remember to remove the rear stay. Assembly: 1) Make sure that an O-ring is set, and adjust the fuel injection pump to a timing mark. 2) Adjust the top mark to 6 (ATDC) past the top. 3) Make sure that a plunger lift is 1 mm (0.039 in). 4) If it is not 1 mm (0.039 in), adjust a pump body setting angle. 5) Set the fuel injection pump drive gear. Tightening torque T = 63.7 Nm(6.5 kgf-m) <47.0 ft-lb>
(Note 2) Crank pulley Disassembly: Remove the crank pulley after removing pulley mounting bolts. Assembly: Apply engine oil and assemble the crank pulley, paying attention not to damage the oil seal. Tightening torque T = 117.6 Nm(12 kgf-m) (Note 3) Gear case cover Disassembly: Remember to remove two middle reinforcing bolts. Assembly: 1) Measure a backlash for each gear. 2) Apply liquid packing and set two knock pins together.
3-12
ENGINE BODY
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
(Note 4) Idle gear Assembly: 1) Assemble the crank gear A, fuel injection pump B, and cam gear C to the idle gears A, B, and C respectively at the same time. 2) Install the idle gear shaft with its oil hole facing upward. (Note 5) PTO drive gear Assembly: Set the inner spline side to the flywheel side. (Note 6) Flywheel Disassembly/Assembly: Set a bolt in an M8 threaded hole in the end face of the wheel and use it as a handle. Be careful not to damage the ring gear. (Note 7) Cam shaft Disassembly 1) Measure a side gap.
2) When the side gap is excessive, replace a thrust bearing. As the gear is shrink-fit, heat it to 180 to 200C to remove it. 3) Put up the engine with the mounting flange facing down. Remove a cam shaft thrust bearing mounting bolt through a cam gear hole. Paying attention not to damage the bearing bush, remove the cam shaft. Turn the cam shaft a couple of times before removing it, so that the tappet will not be caught by the cam. Assembly: After assembling the cam shaft, put back the engine horizontally and fix it onto the table.
CAUTION When putting up the engine vertically or putting it back horizontally, it may fall down and injure you. Work carefully so that it will not lose stability.
3-13
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
ENGINE BODY
(Note 8) Gear case Disassembly: Remember to remove oil pan mounting bolts from below. Assembly: Apply a liquid packing (No. 977770-01212) and set two knock pins together. (Note 9) Oil seal Assembly: When assembling, apply lithium grease. Inspection and Measurement of Parts (i) Cam shaft Check for a contact of the tappet with the cam surface, seizure of the bearing, wear, damage on the gear, and so on. 1) Measurement of the shaft bent
2) Measurement of Cam Height
3) Cam shaft outer diameter and bearing inner diameter
3-14
ENGINE BODY
GEAR TRAIN AND CAM SHAFT
(ii) Idle gear Measurement of the idle gear shaft outer diameter and bushing inner diameter
(iii) PTO drive gear Check both bearings for backlash and hitch, and gear shaft for any abnormality. (6) Replacement of Oil Seal 1) Remove the used oil seal. 2) Insert a new one, using an oil seal inserting tool. 3) Apply lithium grease.
3-15
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
3.4 Cylinder Block
(1) Component Parts
Rod bolt T = 53.9 Nm(5.5 kgf-m) <39.8 ft.-lb> Metal cap T = 112.7 Nm(11.5 kgf-m) <83.2 ft-lb> Non-reusable Part Apply liquid packing Apply grease
3-16
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
(2) Disassembly and Assembly of Cylinder Block
(3) Disassembly Procedure Disassemble in order of the numbers shown in the drawing. Take the cylinder head disassembly procedural steps through 11 . Take the gear train disassembly procedural steps through 12. . Remove the oil pan. (Note 1) Remove the lubricant suction pipe. Remove the piston W/rod. (Note 2) Remove the flywheel housing. (Note 3) Remove the metal cap. (Note 4) Remove the crank shaft. (Note 5) Remove the tappet. Remove the piston pin and ring. (Note 6) Remove the oil filter assembly. (Note 7) Remove the oil seal from the flywheel housing. (Note 8) (4) Assembly Procedure Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
3-17
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
(Note 1) Oil pan Disassembly: The liquid packing has been applied to its mounting surface to the block. Be careful not to cause a damage or distortion on the adhering surface. Assembly: Apply the liquid packing (code No. YM977770-01212) and assernble. (Note 2) Piston W/rod Disassembly: 1) Measure the side gap of the rod. Standard mm (in) 2) 3) 4) 0.10-0.20 (0.004-0.008)
Eliminate the carbon deposit accumulated on the cylinder carefully not to damage the interior of the cylinder. Set the piston to BDC and remove the rod cap. Next, set the piston to TDC and push out the rod larger end, using the wooden handle of a hammer. Care should be taken so that the rod larger end will not be caught by the cylinder block. Set the rod cap and metal and assemble them.
Assembly: 1) Apply oil elaborately to the slideways of the piston, rod, and ring. 2) Incorporate into the block, using a piston inserting tool, and install the metal cap. Tightening torque T = 53.9 Nm (5.5 kgf-m) <39.8 ft-lb> (Note 3) Flywheel housing Disassembly: Paying attention not to damage, put the engine on the stable table with its explosion surface facing down, and remove the flywheel housing. Assembly: Apply the liquid packing (code No. YM977770-01212) and set two knock pins together. After assembling, put up the engine with the flywheel housing facing down. CAUTION When putting up the engine, it may fall down and injure you. Pay attention to its stability.
3-18
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
(Note 4) Journal metal cap Disassembly 1) Prior to removing the journal metal cap, measure the side gap of the crank shaft. Standard 0.11-0.21 mm (0.004-0.008 in) 2) When the side gap is beyond the above-mentioned limits, apply a thrust metal oversize.
3) Remove the metal cap, metal cap-side metal, and thrust metal. Put the thrust metal in such a manner that you can tell its position and direction. Assembly 1) When assembling the thrust metal, its slotted side shoulld be outside to the cap. 2) Note that the upper metal (block side) has an oil hole and the lower metal (cap side) does not. 3) Install the metal cap with its wheel, arrow mark facing the flywheel. Metal cap bolt tightening torque T = 112.7 Nm(11.5kgf-m)<83.2 ft-lb>
(Note 5) Crank shaft Disassembly 1) Remove the crank shaft. 2) Remove the upper metal (block side) and assemble it to the metal cap. CAUTION The crank shaft is heavy. When installing it, be careful not to damage the metal or injure your fingers.
3-19
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
(Note 6) Piston pin and ring Disassembly: 1) Remove the rings with a piston ring tool. 2) Remove a circlip and push out the piston pin to remove it. Assembly: 1) Install the rings to the piston with their makers mark facing up. Shift ring splits by about 120 from each other. 2) When assembling the piston pin to the rod and piston, the marking on the rod larger end and the size marking on the crest of the piston should be on the opposite sides, respectively. 3) Assemble to the block in such a manner that the marking at the rod larger end will face the fuel injection pump. (The embossed marking on the rod body faces the flywheel)
(Note 7) Oil filter Assembly: Close fully with hand, and then, tighten additionally by 3/4 turn with a filter wrench. (Note 8) Oil seal: Assembly: Apply lithium grease at the time of assembly. (5) Inspection and Measurement of Parts (i) Cylinder block 1) Eliminate dirt, rust, adhesive agent, and so on. The oil hole should be cleaned thoroughly so that it will not be blocked. When any cracks are suspected, make a color check to judge.
3-20
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
2) Measurement of the cylinder inner diameter and distortion amount
Use a cylinder gauge to measure the inner diameter of each cylinder. Measure at the crest, position 20 mm (0.29 in) from the lower end, and three central dimensions, a, b, and c. Roundness: Difference between the maximum and minimum dimensions of a, b, and c Cylindricity: Difference in the respective dimensions, a, b, and c, in the directions, A and B. 3) When the dimension exceeds the abovementioned limits or the cylinder is damaged, repair it by boring or honing, and use an oversize piston as required.
[Note] Measure the dimensions at a, b, and c in both A- and B-directions.
3-21
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
(iii) Crank shaft The crank gear has been shrink-fit. When it is necessary to remove it, heat it to 180 to 200 C. 1) Check for cracks by a color check, or with a magnetic defectoscope depending on the case. 2) Measurement of bent 1/2 of reading of the dial gauge Limit: 02 mm (0.0008 in) or less
3) Measurement of the journal
When the oil clearance exceeds its limits, apply an undersize metal.
3-22
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
4) Measurement of the crank pin
When the oil clearance exceeds the limits, use an undersize metal.
IMPORTANT 1) When thickness of the journal metal and crank pin metal is normal and the oil clearance is excessive, or when local eccentric wear is recognized, regrind the crank shaft and use an oversize metal. 2) When the back of the metal is rusty or coarse, apply blue color or minium, assemble with a specified torque and check for a contact. It is normal if there is a contact of 3/4 or more. If there is not a sufficient contact, a metal interference is not enough. Replace the metal.
(iii) Thrust metal
When the side cap exceeds the limits, use an oversize metal.
(iv) Piston 1) Eliminate the deposit on the exposition surface, outer circumference, and ring slots, not damaging the piston. If the ring slots or snap ring slots have burr, deburr them. If cracks are suspected, make a color check to examine.
3-23
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
2) Measurement of the piston large diameter Measure at a position about 20 mm (0.8 in) from the lower end in the right-angled direction of the piston pin.
When the clearance from the cylinder exceeds the limit, use an oversize piston.
3) Measurement of the piston pin hole
(v) Piston rings
3-24
ENGINE BODY
CYLINDER BLOCK
Except the top ring, when measuring the ring groove width, measure the ring width and put the ring in its groove. Use a thickness gauge to measure the clearance between the groove and ring. Add the measured value to the ring width and assume the sum to be the groove width. To measure the clearance of the slit, push the ring into the cylinder by the head of the piston and measure it with the thickness gauge. Push it in as far as about 20 mm (0.8 in) from the lower end of the cylinder. (vi) Connecting rod 1) Care should be taken when the piston bushing, crank pin metal, or both rod larger and smaller ends have an extreme local contact. 2) Measurement of the piston pin
When the oil clearance exceeds its limit and you need to replace the bushing, use a replacement part, No. 12990023910. (vii) Tappet 1) Pay attention to a contact with the cam and push rod. If it has burr, eliminate it. 2) Measurement of the outer diameter
3-25
CYLINDER BLOCK
ENGINE BODY
(6) Honing 1) When satisfactory repair cannot be done only by honing, judging from the conditions of local eccentric wear, damage, and so on, perform boring first. 2) Prepare a flexible hone (code No. 129400-92430), electric drill, and honing liquid (mixed liquid of the engine oil and light oil). 3) Apply the honing liquid to the flexible hone. Running the electric drill at 300 to 1,200 rpm, insert it into the cylinder bore and move up and down the flexible hone to hone the cylinder bore at 30 to 40. IMPORTANT 1) Do not run the drill at a higher rpm because it will lead to a breakage. 2) Do not put in/out the flexible hone in its stopping state. 3) The cylinder will be damaged. Each grinding allowance should be about 1/1,000 mm (1/25,000 in).
(7) Replacement of Cam Shaft Bushing and Connecting Rod Bushing Replace them by using their respective special purpose tools. (8) Replacement of Oil Seal 1) Draw out the used oil seal. 2) Use an oil seal inserting tool to set a new oil seal. 3) Apply lithium grease.
3-26
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mazda FE y F2Document27 pagesMazda FE y F2jads30117971% (14)
- Service Manual for 4D94E-BE4 EPA Compliant Diesel EnginesDocument14 pagesService Manual for 4D94E-BE4 EPA Compliant Diesel EnginesDixon JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Shop Manual FD10,15,30Document340 pagesShop Manual FD10,15,30Budi Waskito100% (2)
- Engine 4d94e-Be3Document159 pagesEngine 4d94e-Be3little khansa83% (6)
- HINSHI Diesel Engine Direct Ignition System Service Manual 2000Document184 pagesHINSHI Diesel Engine Direct Ignition System Service Manual 2000Anonymous zw7gMoUN7TPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual Diesel Engine DB33ADocument78 pagesService Manual Diesel Engine DB33ADVHHTC100% (4)
- S 6 SDocument33 pagesS 6 Sdjpolhn1750% (6)
- Shop Manual: 4D98E 4D106 S4D106Document204 pagesShop Manual: 4D98E 4D106 S4D106Julio Alvarado MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nissan BD30 Valve Adjustment Procedure, Valve Lash Clearance Specifications, Nissan BD30 Engine Parts ContactDocument1 pageNissan BD30 Valve Adjustment Procedure, Valve Lash Clearance Specifications, Nissan BD30 Engine Parts ContactLuis BastardesPas encore d'évaluation
- Perkins 900 Series CR 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine Service Repair ManualDocument35 pagesPerkins 900 Series CR 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine Service Repair ManualBobCav57% (7)
- Fd30t3 ServiceDocument150 pagesFd30t3 ServicePyae Phyoe Aung100% (1)
- Nissan H20 Engine SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNissan H20 Engine SpecificationsAwal Asri100% (2)
- 4d94e17 Be2 1Document160 pages4d94e17 Be2 1dend juandi100% (2)
- SM-Toyota 5FG33-45, 5FD33-45, 5FGE35, 5FDE35 Forklift Service Repair Manual PDFDocument559 pagesSM-Toyota 5FG33-45, 5FD33-45, 5FGE35, 5FDE35 Forklift Service Repair Manual PDFvadim vadim71% (7)
- Torque Specifications For KubotaDocument1 pageTorque Specifications For Kubotasaulomachado8262Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Forklift Engine 1dz II Model Service Repair ManualDocument21 pagesToyota Forklift Engine 1dz II Model Service Repair ManualMohammed SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota 6FG 6FD 10-30 Forklift Trucks Service Repair Manual PDFDocument40 pagesToyota 6FG 6FD 10-30 Forklift Trucks Service Repair Manual PDFJoaquinPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdocuments - in Toyota 02 5fd30 Forklift Service Repair ManualDocument15 pagesFdocuments - in Toyota 02 5fd30 Forklift Service Repair ManualFebrian SyahputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Foreword: Toyota Motor CorporationDocument11 pagesForeword: Toyota Motor CorporationAryo Wicaksono0% (2)
- Engine Repair InstructionsDocument35 pagesEngine Repair InstructionsArmando Orta100% (1)
- 4d84e-5 Sebm035103Document197 pages4d84e-5 Sebm035103PHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ100% (11)
- Motor Diesel C240Document235 pagesMotor Diesel C240colive1100% (1)
- Service Manual Engine Mitsubishi Canter 4d34Document1 pageService Manual Engine Mitsubishi Canter 4d34Stif B. Marengo50% (2)
- Komatsu 6bg1t-Be2 - A4Document166 pagesKomatsu 6bg1t-Be2 - A4George Jhonson90% (10)
- 1y 2y 3y 4yDocument5 pages1y 2y 3y 4yBelofortePas encore d'évaluation
- Mitsubishi 6DB1 Engine PartsDocument5 pagesMitsubishi 6DB1 Engine PartsEngineParts250% (6)
- Yale Parts Catalogue MAZDA FE/F2, YANMAR 4TNE92/4TNE98Document154 pagesYale Parts Catalogue MAZDA FE/F2, YANMAR 4TNE92/4TNE98Петр100% (2)
- Hyundai D4BBDocument232 pagesHyundai D4BBYew Lim83% (6)
- DV15TIS Maintenance ManualDocument147 pagesDV15TIS Maintenance ManualEdgar Gonzalez100% (4)
- Isuzu C240 Engine Repair ManualDocument1 pageIsuzu C240 Engine Repair ManualRovell Raim Quijano Diaz100% (2)
- Manual Isuzu C240 Diesel Engine PDFDocument5 pagesManual Isuzu C240 Diesel Engine PDFSajid Jatt14% (7)
- Yanmar 4tne88 TNE Series PDFDocument15 pagesYanmar 4tne88 TNE Series PDFluna281068Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cummins 6LT9.3 162 KW (220 HP) at 2,200 RPM 146 KW (199 HP) at 2,200 RPM 16,700 KG 3.6 M 155 KN 2,950 MMDocument2 pagesCummins 6LT9.3 162 KW (220 HP) at 2,200 RPM 146 KW (199 HP) at 2,200 RPM 16,700 KG 3.6 M 155 KN 2,950 MMTalita Yasmin Talita100% (5)
- Nissan TD Diesel Engine Workshop Manual Td23 Td25 Td27 Td27tDocument5 pagesNissan TD Diesel Engine Workshop Manual Td23 Td25 Td27 Td27tJuan Diego Vergel Rangel0% (1)
- Caterpillar 3204 Engine Service Manual for 215 ExcavatorDocument9 pagesCaterpillar 3204 Engine Service Manual for 215 ExcavatorFernando Ortiz40% (5)
- 4D30 31Document4 pages4D30 31VictorDjChiqueCastillo50% (2)
- 002-004 Cylinder Head Cummins 6BTA5.9 G2Document10 pages002-004 Cylinder Head Cummins 6BTA5.9 G2AleksaPas encore d'évaluation
- Servicing Specifications: (1) Engine BodyDocument17 pagesServicing Specifications: (1) Engine BodyСергей100% (3)
- 1dz-Ii GB1Document144 pages1dz-Ii GB1lm82% (17)
- Manual de Taller Serie 900 PDFDocument240 pagesManual de Taller Serie 900 PDFhecazorla100% (1)
- Mazda T3000 T3500 T4000 Workshop Repair ManualDocument905 pagesMazda T3000 T3500 T4000 Workshop Repair ManualBestManuals4u87% (15)
- 1DZ EngineDocument181 pages1DZ EngineGonçalo SousaPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual: Diesel EngineDocument152 pagesService Manual: Diesel EngineggpetPas encore d'évaluation
- Isuzu 2AA1 To 3AB1 Workshop ManualDocument134 pagesIsuzu 2AA1 To 3AB1 Workshop ManualNam Won Hong75% (4)
- Mechanical injection D5D, checking and adjustingDocument23 pagesMechanical injection D5D, checking and adjustingJason Pignotti100% (1)
- Nissan PE6Document2 pagesNissan PE6Adam Olow88% (8)
- Forklift Truck Specs and Service ManualDocument114 pagesForklift Truck Specs and Service ManualPyae Phyoe Aung71% (7)
- CAT Transmission Parts for P6000 Lift TrucksDocument3 pagesCAT Transmission Parts for P6000 Lift TrucksGuillermo Reyes Villarruel100% (4)
- Service Manual: H2.0UT, H2.5UT, H3.0UT, H3.5UTDocument100 pagesService Manual: H2.0UT, H2.5UT, H3.0UT, H3.5UTThuong Hoang75% (4)
- D20 25 30 33S-5 D35C-5 (Sb1109e06) PDFDocument424 pagesD20 25 30 33S-5 D35C-5 (Sb1109e06) PDFGORD100% (8)
- 2010 D 2.5 TCI-4D56 Sistema Mecanico de Motor Conjunto Culata Motor Conjunto Culata Motor Procedimientos de Reparaci ÓnDocument8 pages2010 D 2.5 TCI-4D56 Sistema Mecanico de Motor Conjunto Culata Motor Conjunto Culata Motor Procedimientos de Reparaci Óncarlos Gutierrez De La HozPas encore d'évaluation
- Oilpump4afe PDFDocument7 pagesOilpump4afe PDFhanzhio elPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5l 4 Cyl Vin HDocument17 pages2.5l 4 Cyl Vin HFrank MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.6l 4 CylDocument29 pages1.6l 4 Cyl25912530100% (1)
- Timing Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalDocument7 pagesTiming Chain Components & Instalation Toyota Hilux 22R-E: Preparation of RemovalPablo FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Install The ATF (Automatic Transaxle Fluid) Oil Cooler Hoses (C) - Page 116 of 138Document15 pagesInstall The ATF (Automatic Transaxle Fluid) Oil Cooler Hoses (C) - Page 116 of 138flash_24014910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oil Pan Service RepairDocument8 pagesOil Pan Service RepairFernando vungePas encore d'évaluation
- AC Compressor ServicingDocument28 pagesAC Compressor Servicinggentiles mdqPas encore d'évaluation
- 78 Dt400e DT250E ManualDocument18 pages78 Dt400e DT250E Manualdisgustipate0% (1)
- Cam Shaft Removal and InstallationDocument9 pagesCam Shaft Removal and InstallationAlexander Dominguez0% (1)
- Euro-III Parts ListDocument452 pagesEuro-III Parts ListAnbarasan0% (1)
- Caterpillar Cat 330B L Excavator (Prefix 6DR) Service Repair Manual (6DR00001 and Up)Document27 pagesCaterpillar Cat 330B L Excavator (Prefix 6DR) Service Repair Manual (6DR00001 and Up)kfm8seuuduPas encore d'évaluation
- Komatsu Manual Partes - PC200lc-8 PDFDocument921 pagesKomatsu Manual Partes - PC200lc-8 PDFsergio blandon l100% (3)
- Rezervni dijelovi za traktore TafeDocument20 pagesRezervni dijelovi za traktore TafeMilos BogicevicPas encore d'évaluation
- 580 M Series 3 F4C Engine Service Training Manual 0407 87630273Document109 pages580 M Series 3 F4C Engine Service Training Manual 0407 87630273josue100% (6)
- Passenger 6etiDocument283 pagesPassenger 6etiMohan Preeth100% (1)
- Reparacion de CabezasDocument23 pagesReparacion de CabezasLuis TepezanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maintenance Manual For WP2.1C/WP3.9C Marine DieselDocument28 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual For WP2.1C/WP3.9C Marine DieselVladis0710Pas encore d'évaluation
- wsm124 Sunbeam Alpine Series I-Iv PDFDocument413 pageswsm124 Sunbeam Alpine Series I-Iv PDFIshit AminPas encore d'évaluation
- 10198-Kubota - KH-191 - EPC 2Document391 pages10198-Kubota - KH-191 - EPC 2Jade Lavoie0% (1)
- Vortec Lh6 5.3l v8 MT OrgDocument837 pagesVortec Lh6 5.3l v8 MT Orggabriel megaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yanmar 4TNV84T (Himoinsa 28kVA)Document40 pagesYanmar 4TNV84T (Himoinsa 28kVA)omarpat100% (7)
- SEBF 8380 перечень инструкции по ремонту головокDocument8 pagesSEBF 8380 перечень инструкции по ремонту головокЕвгений АбрамовPas encore d'évaluation
- Vedlikeholds Skjema Cat 3500 A, B Og C Cat Vs Pon Power 5 20Document7 pagesVedlikeholds Skjema Cat 3500 A, B Og C Cat Vs Pon Power 5 20Deividas BPas encore d'évaluation
- SML Final Training ReportDocument63 pagesSML Final Training ReportArjun BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- PARTS CATALOG FOR FERRIS 3TNM72-AFS ENGINEDocument27 pagesPARTS CATALOG FOR FERRIS 3TNM72-AFS ENGINErezandriansyah0% (1)
- Parts Catalogue: CD DeluxeDocument52 pagesParts Catalogue: CD DeluxeJonathan FiquitivaPas encore d'évaluation
- v2c 650s - T Parts Book CrusierDocument66 pagesv2c 650s - T Parts Book CrusierSebastian RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- M05100028 200 KW Valve Recession (NGE 14 6 L) PDFDocument17 pagesM05100028 200 KW Valve Recession (NGE 14 6 L) PDFManuel IzaquitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-ICE UpdateDocument69 pagesChapter 1-ICE UpdateMahesh LohanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Foton Operation and Miantenance Manuai For View Series Light BusDocument575 pagesFoton Operation and Miantenance Manuai For View Series Light BusJp Braulio80% (5)
- 4202-6 CompresorDocument34 pages4202-6 CompresorIgnacio jara gallegosPas encore d'évaluation
- 3736a G9T Common Rail SystemDocument180 pages3736a G9T Common Rail Systemplamenvp21100% (1)
- SOP - Bob CatDocument37 pagesSOP - Bob CatvozefjadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Component ManualDocument632 pagesEngine Component ManualHelioPas encore d'évaluation
- MT VICTORY Report On Decarbonization of Auxiliary EnginesDocument3 pagesMT VICTORY Report On Decarbonization of Auxiliary Engineskailash behera100% (1)
- 82 5KVAto125KVADocument53 pages82 5KVAto125KVALU YOPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Mehanika HD-120 PDFDocument119 pagesMotor Mehanika HD-120 PDFанджелаPas encore d'évaluation
- '04 '05 EJ650-C6P/C7P Title: This Catalog Covers: Grid No. This Grid CoversDocument87 pages'04 '05 EJ650-C6P/C7P Title: This Catalog Covers: Grid No. This Grid CoversOliverPas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar d7g Crawler Parts Manual S N 72w1 and 72w607Document7 pagesCaterpillar d7g Crawler Parts Manual S N 72w1 and 72w607Hevy MulyokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesD'EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- ISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemD'EverandISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignD'EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Way Home: Tales from a life without technologyD'EverandThe Way Home: Tales from a life without technologyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsD'EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureD'EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (48)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentD'EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionD'EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresD'EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresPas encore d'évaluation
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesD'EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionD'EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridD'EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyD'EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressD'EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualD'EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (7)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemD'EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsD'EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandEnergy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsD'EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (10)
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AD'EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialD'EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPas encore d'évaluation