Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Major Inventions in Control Systems
Transféré par
Ali AkhterTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Major Inventions in Control Systems
Transféré par
Ali AkhterDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SYSTEM DYNAMICS AND CONTROLS (ME-464)
[Dr. Shaukat Ali]
Assignment # 1
The major inventions and developments in control Systems in history
ALI AKHTER 2 0 0 9 0 3 2 FME
G H U L A M I S H A Q K H A N I N S T I T U T E OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & TECHNOLOGY www.giki.edu.pk
Inventions and developments in control systems
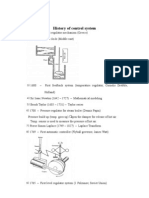
Ctesibius (B.C.270) Float regulator mechanism: In about 270 BC the Greek Ctesibius invented a float regulator for a water clock. Water was allowed to flow in a small stream into a measuring container at a constant rate. The level of water was used to tell the time. To keep the level of supply tank constant, a float valve was used similar to that used in flush toilets. Cornelis Drebbel (17th Century) Temperature regulator: In 17th century, Cornelis Drebbel in Holland invented a purely mechanical temperature control system for hatching eggs. The device used a vial of alcohol and mercury with floater inserted in it which was connected to a damper controlling flame. Alcohol and mercury expanded on increased heat, raising the floater, closing the damper, reducing the flame. Sir Isaac Newton (1642 1727) Mathematical modeling: A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. Brook Taylor (1685 1731) Taylor series: The concept of a Taylor series was formally introduced by the English mathematician Brook Taylor in 1715. Dennis Papin (1700) Pressure regulator for steam boiler: Pressure build up (temp. goes up) open the damper for release of hot air. Temperature sensor is used to measure the pressure of hot air. Pierse Simon Laplace (1749 1827) Laplace Transform: The Laplace transform is named after mathematician and astronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who used a similar transform (now called z transform) in his work on probability theory. James Watt (1788) Flyball governer: In 1788 Watt completed the design of the centrifugal flyball governor for regulating the speed of the rotary steam engine.
Polzunov (1765) First level regulator system: Polzunov's water float regulator was used to control the amount of water flowing into the boiler of the engine.
Edward John Routh (1831 1907) Routh criterion: It is a necessary and sufficient method to establish the stability of a control system. Oliver Heaviside (1859 1925) mathematical analysis: Oliver Heaviside invented mathematical techniques to the solution of differential equations (later found to be equivalent to Laplace transforms) J.C. Maxwell 1868 Mathematical theory for control system: In the mid 1800's mathematics was first used to analyze the stability of feedback control systems. Liapunov (1890) Stability theory: The work of A.M. Lyapunov was seminal in control theory. He studied the stability of nonlinear differential equations using a generalized notion of energy in 1892 [Lyapunov 1893]. Nyquist, Bode, Black (1930) Electronic feedback amplifier: The Bell Telephone system was developed. Harry Nyquist (1889 1976) Nyquist criterion: Nyquist published a classic paper on stability of feedback amplifiers called Nyquist stability criterion. Harold Black (1898 1981) Negative feedback amp: The negative feedback amplifier was invented by Harold Stephen Black on August 2, 1927. Black had been toiling at reducing distortion in repeater amplifiers used for telephone transmission.
Hendrik Bode (1905 1982) Bode diagram: Bode plot was invented by Hendrik Wade Bode. WWII period Automatic airplane pilot: Gun-positioning system, radar Antenna control system Military systems Post War Frequency domain analysis: Laplace transform method John Von Neumann (1903 1957) Basic operation of digital computer: Neumann introduced the basic operation of digital computer. 1950 Root locus method: Computer age open (digital control) Space age (Sputnik, Soviet Union) Maximum principle (Pontryagin) Optimal control Adaptive control system (Draper) Bellman (1960) Dynamic programming: State space method 1970 Microprocessor based control system: Digital control system 1980 Neural network: AI Fuzzy control Predictive control Doyle & stein : LQG / LTR Remote diagnostic control system
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1.1 A BRIEF HIS-WPS OfficeDocument10 pages1.1 A BRIEF HIS-WPS OfficeLiezel Pura EugerioPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Definition and History of Feedback and Control Systems Group 1Document16 pages1.1 Definition and History of Feedback and Control Systems Group 1K yEPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Control SystemDocument3 pagesHistory of Control SystemBojan MarkovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview and History of Feedback ControlDocument4 pagesOverview and History of Feedback ControlJeremiah MalagueñoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Automatic Control: Stuart BennettDocument9 pagesA Brief History of Automatic Control: Stuart BennettMUhammad HafidhPas encore d'évaluation
- Resumen Ingenieria de ControlDocument5 pagesResumen Ingenieria de ControlIsaudRodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems TimelineDocument34 pagesControl Systems Timelinepedrohcg100% (1)
- HistoriDel Control StuartBennetDocument9 pagesHistoriDel Control StuartBennetERICA JOHANA FIGUEROA DURANGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems TimelineDocument5 pagesControl Systems TimelinenikkiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 ArticuloDeInvestigación1-1Document6 pages2 ArticuloDeInvestigación1-1Jorge Luis Rodríguez GonzálezPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivek AssignmentDocument5 pagesVivek AssignmentcparroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Historia Del ControlDocument19 pagesHistoria Del ControljefersonPas encore d'évaluation
- History of ACEDocument2 pagesHistory of ACEm1nitk 19Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Introduction To Control Chapter OneDocument13 pages1 - Introduction To Control Chapter Onesythepaul24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hap ReviewerDocument7 pagesHap ReviewerNoceja, Mark Allen L.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Physics (PHY831) : Part 1 - The Foundations Phillip M. Duxbury, Fall 2012Document38 pagesStatistical Physics (PHY831) : Part 1 - The Foundations Phillip M. Duxbury, Fall 2012Prince MensahPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary ESE623 For EE241Document1 pageSummary ESE623 For EE241Afeef Abu BakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hap ReviewerDocument7 pagesHap ReviewerNoceja, Mark Allen L.Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Feedback Control - LewisDocument19 pagesA Brief History of Feedback Control - LewisLuis ZambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtb 141Document7 pagesNewtb 141proxywarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Feedback Control Lewis PDFDocument19 pagesA Brief History of Feedback Control Lewis PDFAnonymous VfH06fQXbAPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesA Brief History of ThermodynamicsKelvin Law100% (1)
- Script ZapantaDocument2 pagesScript ZapantaSiN XPas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Timeline 293Document2 pagesHVAC Timeline 293rohitPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of Feedback ControlDocument20 pagesA Brief History of Feedback ControlJuan CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes PHY3Document3 pagesNotes PHY3Ako ToPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Control SystemsDocument1 pageHistory of Control SystemsNicca PolitadoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief History of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesA Brief History of ThermodynamicsŞükrü_talaşPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 11 CBSE'Document11 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 11 CBSE'Anirudh G67% (3)
- Famous Physicis-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesFamous Physicis-WPS OfficeAbhishek B Kumar VfcPas encore d'évaluation
- Basicsofthermodynamics 151006214440 Lva1 App6891Document30 pagesBasicsofthermodynamics 151006214440 Lva1 App6891Shahdura Hammad ThauriPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic ControlDocument6 pagesAutomatic ControlEdgar Andres Bustos GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ludwig Prandtl (1875-1953)Document3 pagesLudwig Prandtl (1875-1953)christian roy camasisPas encore d'évaluation
- AUTO506 Lecture 2 History of Control Systems EngineeringDocument8 pagesAUTO506 Lecture 2 History of Control Systems EngineeringWalid YahiaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Classical Period: Famous PhysicistsDocument18 pagesClassical Period: Famous PhysicistsWebon RelatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction, History and Applications: Engr. Shakeel AhmadDocument13 pagesIntroduction, History and Applications: Engr. Shakeel AhmadShakeel MohmandPas encore d'évaluation
- Historia Del Control OptimoDocument8 pagesHistoria Del Control OptimoRaul Gil BayardoPas encore d'évaluation
- 347Document19 pages347jikurPas encore d'évaluation
- DK2135 ch08Document137 pagesDK2135 ch08Mohamed Anouar Nciri100% (1)
- Robert LDocument7 pagesRobert LEricPas encore d'évaluation
- Twentieth Century Developments On Control SystemsDocument6 pagesTwentieth Century Developments On Control SystemsIncohatusFormlessPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-01 IntroductionDocument35 pagesLecture-01 Introductionvasu sainPas encore d'évaluation
- Archimedes: F38Amlec8BrsDocument4 pagesArchimedes: F38Amlec8BrsYeddaMIlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Timeline of ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesTimeline of ThermodynamicsBob JoePas encore d'évaluation
- Inventors, Scientists & MathematiciansDocument4 pagesInventors, Scientists & MathematiciansKimberly Joy FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Water Distrubution System Final1Document60 pagesAdvance Water Distrubution System Final1Suraj RaghuwanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Chemical Engineering TimelineDocument24 pagesA Chemical Engineering TimelineZack LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Scientists and Their InventionsDocument11 pagesScientists and Their InventionsCathyPas encore d'évaluation
- History and Development: Pre-IndustrialDocument2 pagesHistory and Development: Pre-IndustrialdrbstesbtabtbatPas encore d'évaluation
- GEC 8 Sigbificant Discoveries and InventionsDocument36 pagesGEC 8 Sigbificant Discoveries and InventionsNICASIO PIMENTELPas encore d'évaluation
- History and Innovations of Control SystemsDocument5 pagesHistory and Innovations of Control SystemsMark Anthony Salazar ArcayanPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesHistory of Fluid MechanicsZetsu Black100% (1)
- Inventors & Their Inventions 2Document6 pagesInventors & Their Inventions 2paglafou100% (1)
- A Thermodynamics HistoryDocument8 pagesA Thermodynamics HistoryJaster Monloise Baña SanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Famous ScientistsDocument118 pagesFamous Scientistsmarife gupaalPas encore d'évaluation
- Science History TimelineDocument8 pagesScience History TimelineCurt UlandayPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Technology and Society PPT Study Guide Lesson 2 Part 1Document25 pagesScience Technology and Society PPT Study Guide Lesson 2 Part 1nashcasunggay511Pas encore d'évaluation
- Author ProfileDocument9 pagesAuthor ProfileGCVishnuKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Need Identification and Problem DefinitionDocument17 pagesNeed Identification and Problem DefinitionAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire Hip ImplantDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire Hip ImplantAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2Document14 pagesCH 2Ali AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Design and Design ProcessDocument61 pagesProduct Design and Design ProcessAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- LECT-Ch 2-Design and Concurrent EnggDocument20 pagesLECT-Ch 2-Design and Concurrent EnggAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Design ProcessDocument1 pageProduct Design ProcessAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste 2 Water Food Waste Digester BrochureDocument4 pagesWaste 2 Water Food Waste Digester BrochureAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Timetable Spring 2013Document3 pagesTimetable Spring 2013Ali AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Mos Projects: DeadlinesDocument1 pageMos Projects: DeadlinesAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Students Allotment ListDocument17 pagesCurrent Students Allotment ListAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total 0 0: Semester Sgpa Credit HoursDocument1 page1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total 0 0: Semester Sgpa Credit HoursAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Project CharterDocument3 pagesProject CharterAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Dawat-E-Islami: Namaz Timings: Topi, PakistanDocument12 pagesDawat-E-Islami: Namaz Timings: Topi, PakistanAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime TableAli AkhterPas encore d'évaluation
- Billing System of MEPCO by Iqrash AwanDocument27 pagesBilling System of MEPCO by Iqrash AwanMuhammad Iqrash Awan100% (1)
- Calling Sheet Status 03-10-2023Document18 pagesCalling Sheet Status 03-10-2023bokoto9929Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arrow Product OverviewDocument13 pagesArrow Product OverviewRafael Zurita100% (1)
- Symantec Data Center Security Server Monitoring Edition and Server Advanced 6.8 Overview GuideDocument20 pagesSymantec Data Center Security Server Monitoring Edition and Server Advanced 6.8 Overview GuideĐình Khánh BùiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cnes / Esa: RF / Microwave Printed Circuit Boards For Space ApplicationsDocument29 pagesCnes / Esa: RF / Microwave Printed Circuit Boards For Space ApplicationsMehmet KibarPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 240105 063345 933Document6 pagesNotes 240105 063345 933Rachel MaharaniPas encore d'évaluation
- David 2105 PrelimExamsDocument10 pagesDavid 2105 PrelimExamsJAZPER DAVIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Dvp-Plc-Program o en 20101119Document618 pagesDvp-Plc-Program o en 20101119Mohammed MagdyPas encore d'évaluation
- B-63833en 02 (Hardware)Document338 pagesB-63833en 02 (Hardware)MANI KANDAN100% (1)
- Rectt PS Group B Notification 2023Document16 pagesRectt PS Group B Notification 2023MANOJ VIJAYANPas encore d'évaluation
- P0903, P0915Document1 pageP0903, P0915Joanmanel Sola QuintanaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB 5SYA 2091 01 - Banding of DevicesDocument7 pagesABB 5SYA 2091 01 - Banding of DevicesFaisal WaseemPas encore d'évaluation
- Driving To Outcomes - Success Plans & ScorecardsDocument59 pagesDriving To Outcomes - Success Plans & Scorecardshkulkarni100% (1)
- WAE28366GB Bosch Washing Machine ManualDocument8 pagesWAE28366GB Bosch Washing Machine ManualDmitrii PanasiukPas encore d'évaluation
- SG 247757Document478 pagesSG 247757ahmedalyPas encore d'évaluation
- SQS Practice QuestionsDocument39 pagesSQS Practice QuestionsLEAH DJEUKAMPas encore d'évaluation
- A122 DVB-T2 Spec PDFDocument187 pagesA122 DVB-T2 Spec PDFWilson OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- DG 03 001-E 04-03 ARGOSDocument35 pagesDG 03 001-E 04-03 ARGOSrickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Spec AgitatorDocument74 pagesTechnical Spec Agitatornaresh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Five Networking in JavaDocument44 pagesChapter Five Networking in JavaabdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 18/07/2022 Java Homework-1: Core Java Test Papers - Day 1 (Class, Objects, Methods)Document13 pages18/07/2022 Java Homework-1: Core Java Test Papers - Day 1 (Class, Objects, Methods)praveen murugesanPas encore d'évaluation
- ABAP Proxy (Complete Developments On SAP-PI &am..Document7 pagesABAP Proxy (Complete Developments On SAP-PI &am..saranpcPas encore d'évaluation
- Undergraduate Certificate in Information Technology: Document NumberDocument10 pagesUndergraduate Certificate in Information Technology: Document NumberMega Services CoparationPas encore d'évaluation
- P2M BookletDocument20 pagesP2M BookletAkaninyenePas encore d'évaluation
- CV of MD Moshiur RahamanDocument3 pagesCV of MD Moshiur RahamanMoshiur RahamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Title: OWASP Top 10 Threats and Mitigation Exam Questions - Single SelectDocument12 pagesCourse Title: OWASP Top 10 Threats and Mitigation Exam Questions - Single SelectBriar WoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrawise Manual - TroubleshootingDocument15 pagesHydrawise Manual - TroubleshootingBalazs LosoncziPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC Adderss:ABC India PVT Ltd. Bengaluru (Ready To Relocate)Document5 pagesABC Adderss:ABC India PVT Ltd. Bengaluru (Ready To Relocate)ruby guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Connection User GuideDocument10 pagesWave Connection User GuideAromal SPas encore d'évaluation
- Linux Administration: Unit 1Document59 pagesLinux Administration: Unit 1DerenPas encore d'évaluation