Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mathflipchart 5 G
Transféré par
kvinodan73Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mathflipchart 5 G
Transféré par
kvinodan73Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Kansas State Mathematics Standards and Assessment Guide
Based on the 2005 Kansas State Curricular Standards for Mathematics adopted by the Kansas State Board of Education on July 8, 2003
Grade 5
Developed by the Kansas State Department of Education and Mathematics Specialists in the Private Sector from Kansas
2005
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.1.1.K1a-c N Standard: Number and Computation Benchmark: Number Sense Indicator: Knows, explains, and uses equivalent representations for: a) whole numbers from 0 through 1,000,000; b) fractions greater than or equal to zero (including mixed numbers); c) decimals greater than or equal to zero through hundredths place and when used as monetary amounts Explanation of Indicator
is the same as 1/4, which is the same as .25, which is the same as 4/16, etc.. Instructional Example 1. If you have two same size pizzas, one cut into eights and the other into twelfths, determine how many slices of each pizza you would need to have the same amount. 2. Writes a whole number in expanded form. For example: 125,349 is equal to 100,000 + 20,000 + 5,000 + 300 + 40 + 9. 3. If you ordered 3 pizzas, each cut into eighths, and each person gets one-eighth of a pizza. How many people can you serve? Item Specification Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2a. Uses numbers to count, order, or denote 2b. Do computational procedures or algorithms Category 3: Demonstrates an Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3b. Use representations to model mathematical ideas, 3e. Shows and/or explains relationship between models/diagrams and/or other representations Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4a. Determines the truth of a mathematical pattern, a mathematical statement, and/or proposition or make predictions Assessment Item Example Which is ANOTHER way to write 809,260? A. B. C. D. 8 hundred thousand + 9 thousand + 2 hundred + 60 809 thousand, 260 hundred eight hundred ninety thousand, two hundred sixty 800,000 + 9,000 + 200 + 6
Correct Answer: A
Indicator M.5.1.1.K1a-c
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.1.3.K2 N Standard: Number and Computation Benchmark: Estimation Indicator: Uses various estimation strategies to estimate whole number quantities from 0 through 100,000; fractions greater than or equal to zero (including mixed numbers); decimals greater than or equal to zero through hundredths place; and monetary amounts to $10,000 and explains how various strategies are used Explanation of Indicator Estimates using whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and money. Instructional Example 1. Record the number of pages read in a novel for the first two days. Estimate how many pages could be read in a week. 2. Estimates the total cost of the groceries purchased and asks how they got their estimate. 3. Determine if the pocket full of change is enough to buy a wanted item. 4. Select 5 items from a catalog, estimate the total cost. Explain how they got their estimate. Item Specification Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2c. Follows procedures and/or instructions Category 3: Demonstrates an Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3a. Communicates mathematical ideas or rules and/or explains the process, 3d. Develops and/or explains relationships among concepts Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4f. Identify faulty arguments or identify misrepresentations of data Assessment Item Example The art supplies Tim wants to buy total $11.68. Tim has only bills and does not have any coins. To ESTIMATE how much money to give to the clerk, Tim should A. B. C. D. round up to $11.70. round up to $12.00. round down to $11.00. round down to $11.50.
Correct Answer: B
Indicator M.5.1.3.K2
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.1.4.K4 N Standard: Number and Computation Benchmark: Computation Indicator: Identifies, explains, and finds the greatest common factor and least common multiple of two or more whole numbers through the basic multiplication facts from 1 x 1 through 12 x 12 Explanation of Indicator Greatest Common Factor Find the greatest number that will divide evenly into two different numbers (For example: 24 and 30 the greatest common factor is 6) Least Common Multiple When skip counting by the two different numbers, what is the first number will appear in both patterns. (For example: 8,16,24,32 12, 24, 36; 8 and 12 the least common factor is 24) Instructional Example Fencing comes in 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 15 unit lengths. You want to make two areas in your backyard. One area will be 24 square units and the other 30 square units. Which is the longest length of fence to do both jobs? Item Specification Category 1: Memorize Facts/Definitions/ Formulas: 1b. Recite or recall basic mathematics facts Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2c. Follows procedures or instructions Assessment Item Example The least common multiple (LCM) of 6 and 12 is A. B. C. D. the smallest non-zero number that divides both 6 and 12 evenly. the greatest number that divides both 6 and 12 evenly. the smallest non-zero number that is a multiple of both 6 and 12. the greatest number that is a multiple of both 6 and 12.
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.1.4.K4
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.2.2.K1 Standard: Algebra Benchmark: Variables, Equations, and Inequalities Indicator: Explains and uses variables and symbols to represent unknown whole number quantities from 0 through 1,000 and variable relationships Explanation of Indicator A variable is a shape, letter, symbol to represent an unknown value. For example, if a dog eats pound of food, he would eat d in d days. Instructional Example 1. Have student write in their own words what a variable is and what its purpose is. 2. Have student write a variable expression representing something that would be happening around the house such as if your get 6 chicken nuggets from McDonalds, how many would eat in a year if your went to Mcdonalds n times. Item Specification Category 3: Demonstrates an Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3b. Use representations to model mathematical ideas, 3e. Shows and/or explains relationship between models/diagrams and/or other representations Assessment Item Example Which equation shows that there are four quarters (q) in one dollar? A. B. C. D. Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.2.2.K1
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.2.2.K2 N Standard: Algebra Benchmark: Variables, Equations, and Inequalities Indicator: Solves one-step linear equations with one variable and a whole number solution using addition and subtraction with whole numbers from 0 through 100 and multiplication with the basic facts Explanation of Indicator A one step equation requires only on operation (addition, subtraction, or multiplication in this indicator) to solve for an unknown (variable). Student should solve one-step equations for that will have no remainder for numbers from 0 to 100 for addition and subtraction and 0 to 100 for multiplication. Instructional Example Have student solve a variety of equations that could be made from situations at home. Example: If there are x cookies in a package when you started eating, you know you at 6 cookies there were 14 left when you finished, how many were there when you started (x - 6 = 14)? Item Specification Category 2: Perform Procedures: 2d. Solve equations, formulas, or routine word problems Assessment Item Example What is the value of x in the equation 32=17+x A. B. C. D. 15 25 39 49
Correct Answer: A
Indicator M.5.2.2.K2
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.2.3.K4 Standard: Algebra Benchmark: Functions Indicator: Uses a function table (input/output machine, T-table) to identify, plot, and label whole number ordered pairs in the first quadrant of a coordinate plane Explanation of Indicator A function table is a table of values that has sets of points that can be graphed on a coordinate grid such as the set below. The sets called ordered pairs for this function table would be (1,5), (2,10), (3,15), (4, 20), and (5,25). 1 5 2 10 3 15 4 20 5 25
The student can graph and label these on a coordinate grid. Instructional Example 1. Have student make a coordinate grid with graph paper and draw a map of there yard using points to represent landmarks such as the swing set, a tree, a flower bed, or other physical identifiers in the yard. 2. Have student make a function table of values for the cost of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 candy bars. Then graph the function table on graph paper. Item Specification Category 1: Memorize Facts/Definitions/ Formulas: 1b. Recite or recall basic mathematics facts Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2c. Follows procedures and/or instructions Assessment Item Example The function table below represents ordered pairs for a graph.
Which is ANOTHER way to correctly show this information? A. B. C. D. (1, 8) (7, 14) (10, 17) (15, 22) (33, 61) (8, 1) (14, 7) (17, 10) (22, 15) (61, 33)
Correct Answer: A
Indicator M.5.2.3.K4
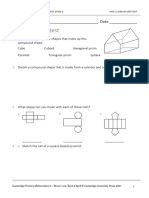
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.3.1.K3 Standard: Geometry Benchmark: Geometric Figures and Their Properties Indicator: Recognizes and describes the solids (cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, cones, spheres, triangular prisms, rectangular pyramids, triangular pyramids) using the terms faces, edges, and vertices (corners) Explanation of Indicator Solids are three dimensional figures such as cube, rectangular prism (cereal box), cylinder (can), sphere (ball), triangular prism (a piece of trim that is a triangle on each end), rectangular prism (pyramids of Egypt), or triangular pyramid (pyramid with the base or bottom on have three sides). The faces are the sides of the figure, the edges are where two faces join, and the vertices are where the edges meet (a corner point). Instructional Example Have student identify a variety of objects around the house according to what type of figure they are, then have them write down how many faces, edges, and vertices each object has. Examples would be boxes that may be cubes or rectangular prisms, cans such as Pringles cans or oatmeal cans, etc. Item Specification Category 1: Memorize Facts/Definitions/ Formulas: 1b. Recite or recall basic mathematics facts Category 3: Demonstrates an Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3b. Use representations to model mathematical ideas Assessment Item Example A sphere is shown below.
How many faces are on a sphere? A. B. C. D. 0 faces 1 face 2 faces 3 faces
Correct Answer: A
Indicator M.5.3.1.K3
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.3.2.K4a Standard: Geometry Benchmark: Measurement and Estimation Indicator: Converts: a) within the customary system: inches and feet, feet and yards, inches and yards, cups and pints, pints and quarts, quarts and gallons, pounds and ounces Explanation of Indicator Converting means to change from one measurement to another such as 2 pounds equals 32 ounces. Convert with a variety of measurements such as inches and feet, feet and yards, inches and yards, cups and pints, pints and quarts, quarts and gallons, and pounds and ounces. Instructional Example Have student write several different measurements taken from around the home and then convert them into another equivalent measurement. For example how many quarts would be in a three gallon fish tank? Item Specification Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2b. Do computational procedures or algorithms Assessment Item Example How many inches are there in 8 feet? A. B. C. D. 72 inches 80 inches 84 inches 96 inches
Correct Answer: D
Indicator M.5.3.2.K4a
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.3.3.K3 Standard: Geometry Benchmark: Transformational Geometry Indicator: Recognizes three-dimensional figures (rectangular prisms, cylinders, cones, spheres, triangular prisms, rectangular pyramids) from various perspectives (top, bottom, side, corners) Explanation of Indicator Identify the three-dimensional figures rectangular prisms (cereal box), cylinder (can), sphere (ball), triangular prism (a piece of trim that is a triangle on each end), and rectangular prism (pyramids of Egypt) from different perspectives such as top, bottom, front, back, side, or corner. Instructional Example 1. Student will use a variety of three-dimensional objects around the home to draw different perspectives looking only from top, bottom, front, back, side, or corner. 2. Give the student a variety of three-dimensional objects with a drawing of several different perspectives of one object and have them identify which object the drawings are from. Item Specification Category 3: Demonstrates an Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3b. Use representations to model mathematical ideas Assessment Item Example Which figure shows the SIDE view of a rectangular pyramid? A. B.
C.
D.
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.3.3.K3
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.4.2.K3a-e Standard: Data Benchmark: Statistics Indicator: Identifies, explains, and calculates or finds these statistical measures of a whole number data set of up to twenty whole number data points from 0 through 1,000: a) minimum and maximum values; b) range c) mode (no-, uni-, bi-); d) median (including answers expressed as a decimal or a fraction without reducing to simplest form); e) mean (including answers expressed as a decimal or a fraction without reducing to simplest form) Explanation of Indicator Find minimum, maximum, mean, median, mode, and range of a whole number set of data. Minimum is smallest value, maximum is the largest value, range is the largest value minus the smallest value, mean is the sum of the values divided by the number of values, median is middle value when all values are ordered, and mode is the value that appears the most. Instructional Example Have your student use a set of data such as the number of pages in a set of 20 books to compute minimum, maximum, range, mean, median, and mode. Item Specification Category 1: Memorize Facts/Definitions/ Formulas: 1b. Recite or recall basic mathematics facts Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2c. Follows procedures and/or instructions Category 3: Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3a. Communicates mathematical ideas or rules and/or explains the process Assessment Item Example A data set is shown below. 11 30 24 20 15 31 32 20 18 29 What is the MEDIAN of the data set? A. B. C. D. 20 21 22 23
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.4.2.K3a-e
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.1.3.A4 Standard: Number and Computation Benchmark: Estimation Indicator: Determines if a real-world problem calls for an exact or approximate answer using whole numbers from 0 through 100,000 and performs the appropriate computation using various computational methods including mental math, paper and pencil, concrete materials, and appropriate technology Explanation of Indicator Look at a variety of situations form real-world situations to determine if the answer should be an estimate of and exact answer by using mental math, paper and pencil, or appropriate technology (calculator, etc.). Instructional Example 1. Have student explain if an estimate or exact answer is needed and compute using appropriate method to see if $10 is enough to purchase a loaf of bread at $1.89, a bag of apples at $2.29, and a half gallon of ice cream at $3.19. 2. Have student explain if an estimate or exact answer is needed and compute using appropriate method to see how much they should receive for working for their neighbor for 6 hours at $6.25 per hour (nothing is deducted from payment). 3. Have student explain if an estimate or exact answer is needed and compute using appropriate method to see how long it will take to drive from Hays, KS to Kansas City, KS or some other traveling distance. Item Specification Category 2: Performs Procedures: 2c. Follows procedures and/or instructions Category 3: Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3a. Communicates mathematical ideas or rules and/or explains the process Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4f. Identify faulty arguments or identify misrepresentations of data Category 5: Solve Non-routine Problems/Make Connections: 5a. Apply and adapt a variety of appropriate strategies to solve non-routine problems Assessment Item Example Barb is filling empty jars with pieces of candy. Each jar will hold 300 pieces of candy. Barb has 5,000 pieces of candy to put in jars. Which steps can Barb take to find the EXACT number of jars she will need to hold all the candy? A. B. C. D. add 5,000 and 300 to find the number of jars needed multiply 5,000 and 300 to find the number of jars needed divide 5,000 by 300 and round up to find the number of jars needed divide 5,000 by 300 and round down to find the number of jars needed
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.1.3.A4
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.1.4.A1a-f N Standard: Number and Computation Benchmark: Computation Indicator: Solves one- and two-step real-world problems using these computational procedures: a) adds and subtracts whole numbers from 0 through 100,000; b) multiplies through a four-digit whole number by a two-digit whole number; c) multiplies monetary amounts up to $1,000 by a one- or twodigit whole number; d) divides whole numbers through a 2-digit divisor and a 4-digit dividend with the remainder as a whole number or a fraction; e) adds and subtracts decimals from thousands place through hundredths place when used as monetary amounts Explanation of Indicator Solve real-world problems by using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with monetary and non-monetary values. Instructional Example Have student solve a variety of real-world problems that require one or two computational procedures using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and/or division from every day situations, with monetary and non-monetary answers. Item Specification Category 2: Perform Procedures: 2d. Solve equations, formulas, or routine word problems Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4f. Identify faulty arguments or identify misrepresentations of data Category 5: Solve Non-routine Problems/Make Connections: 5b. Apply mathematics in contexts outside of mathematics (whenever possible, include diagrams/visuals Assessment Item Example ABC Bedspreads has received an order for 1,650 bedspreads. To make each bedspread, 78 square feet of fabric are needed. How many square feet of fabric should ABC Bedspreads order? A. B. C. D. 128,700 square feet 113,700 square feet 24,750 square feet 12,870 square feet
Correct Answer: A
Indicator M.5.1.4.A1a-f
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.3.1.A1a Standard: Geometry Benchmark: Geometric Figures and Their Properties Indicator: Solves real-world problems by applying the properties of: a) plane figures (circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, ellipses, rhombi, parallelograms, hexagons, pentagons) and the line(s) of symmetry Explanation of Indicator Solve real-world problems that use a line of symmetry in circle, square, rectangle, triangle, ellipse, rhombus, parallelogram, hexagon, and pentagon. A line of symmetry divides a figure into two equal parts that are mirror images of each other. Instructional Example 1. Using only one cut, have student figure the number of ways a cake (variety of shapes) can be cut to create two equal pieces. 2. Find various shapes around the house and identify a line or lines of symmetry for the shape. Item Specification Category 2: Perform Procedures: 2d. Solve equations, formulas, or routine word problems Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4f. Identify faulty arguments or identify misrepresentations of data Category 5: Solve Non-routine Problems/Make Connections: 5b. Apply mathematics in contexts outside of mathematics (whenever possible, include diagrams/visuals Assessment Item Example A class is planning to make a painting using a geometric shape that has EXACTLY 3 lines of symmetry. Which shape could the class use? A.
B.
C.
D.
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.3.1.A1a
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.3.2.A1a,c,f,g,h Standard: Geometry Benchmark: Measurement and Estimation Indicator: Solves real-world problems by applying appropriate measurements and measurement formulas: a) length to the nearest eighth of an inch or to the nearest centimeter; c) weight to the nearest whole unit (pounds, grams, nonstandard units) f) months in a year and minutes in an hour; g) perimeter of squares, rectangles, and triangles; h) area of squares and rectangles Explanation of Indicator Solves real-world problems that deal with measures and formulas that include inches to the nearest 1/8 inch, metric to the nearest centimeter, weight the nearest pound or gram, perimeter of squares, rectangles, and triangles, area of squares and rectangles, and months of the year and minutes and hours. Instructional Example 1. Have student figure are of several rooms in your house in square feet. 2. Have your student figure perimeter of several rooms in your house in feet. 3. If a movie starts at 7:35 and lasts 1 hour and 45 minutes, when will the movie end? 4. Have the student figure the number of months it will take for them reach their 16 birthday form now. Item Specification Category 2: Perform Procedures: 2d. Solve equations, formulas, or routine word problems Category 3: Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3a. Communicates mathematical ideas or rules and/or explains the process Category 5: Solve Non-routine Problems/Make Connections: 5b. Apply mathematics in contexts outside of mathematics (whenever possible, include diagrams/visuals Assessment Item Example The table below shows the weight per box of several types of bolts.
What is the TOTAL weight of 1 box of 10-inch bolts and 2 boxes of 5-inch bolts? A. B. C. D. 35lb 52 lb 69 lb 70 lb
Correct Answer: C
Indicator M.5.3.2.A1a,c,f,g,h
Standard/Benchmark/Indicator M.5.4.2.A1a-f Standard: Data Benchmark: Statistics Indicator: Interprets and uses data to make reasonable inferences, predictions, and decisions, and to develop convincing arguments from these data displays: a) graphs using concrete materials; b) pictographs; c) frequency tables; d) bar and line graphs; e) Venn diagrams and other pictorial displays; f) line plots; g) charts and tables; h) circle graphs Explanation of Indicator Uses graphs, pictographs, frequency tables, bar and line graphs, circle graphs, charts and tables, Venn diagrams, and line plots to make predictions about future events based on the data representations. Instructional Example Have student look through newspapers to identify different data displays to make predictions, and if possible follow up to see if predictions actually happen. Item Specification Category 2: Perform Procedures: 2f. Read or produce graphs and tables Category 3: Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas: 3c. Explain findings and/or results from data analysis strategies or experiments/simulations Category 4: Conjecture/Generalize/Prove: 4a. Determine the truth of a mathematical pattern, a mathematical statement, and/or proposition or make predictions, 4f. Identify faulty arguments or identify misrepresentations of data Category 5: Solve Non-routine Problems/Make Connections: 5c. Analyze data or recognize patterns Assessment Item Example Gerard asked 100 students whether they like math, reading, or both. He displayed the results in the Venn diagram shown below.
How many students like math? A. B. C. D. 39 students 43 students 57 students 61 students
Correct Answer: C Indicator M.5.4.2.A1a-f
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- 5 TH Jci All India Basket Ball Tournament - Tariff CardDocument1 page5 TH Jci All India Basket Ball Tournament - Tariff Cardkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- BVM Safety Manual For SchoolsDocument26 pagesBVM Safety Manual For Schoolskvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sail JyotiDocument1 pageSail Jyotikvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- VSP BrochureDocument14 pagesVSP BrochurePritam KhobragadePas encore d'évaluation
- 5 TH Jci All India Basket Ball Tournament BroshureDocument1 page5 TH Jci All India Basket Ball Tournament Broshurekvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- BVM Safety Manual For FamilyDocument18 pagesBVM Safety Manual For Familykvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ten Common Investment Strategies and Why They May Not Work - Business TodayDocument21 pagesTen Common Investment Strategies and Why They May Not Work - Business Todaykvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Money WiseDocument4 pagesMoney Wisekvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- FTEquityKIM June 2012Document36 pagesFTEquityKIM June 2012kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Talwalkars - BUY - 28 APR 2014 RS 167Document2 pagesTalwalkars - BUY - 28 APR 2014 RS 167kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- PTC India - Buy 28 Apr 2014 Rs 67Document2 pagesPTC India - Buy 28 Apr 2014 Rs 67kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Quest 5 - Class 6 - Equiz-16 NOV 2012 PDFDocument4 pagesScience Quest 5 - Class 6 - Equiz-16 NOV 2012 PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- L&T Finance - Buy 14 Apr 2014 Rs 67Document2 pagesL&T Finance - Buy 14 Apr 2014 Rs 67kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- When in Doubt Dont DiversifyDocument2 pagesWhen in Doubt Dont Diversifykvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Sensex Gone Awry - The Hindu Dated 04 NOV 2013Document2 pagesA Sensex Gone Awry - The Hindu Dated 04 NOV 2013kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aditya Birla Nuvo 07 APR 2014 RS 1065Document1 pageAditya Birla Nuvo 07 APR 2014 RS 1065kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reap Profits When The Going Is GoodDocument2 pagesReap Profits When The Going Is Goodkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Page5Document1 pagePage5kvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- What To Do If Your Car Doesn't Start - Team-BHPDocument9 pagesWhat To Do If Your Car Doesn't Start - Team-BHPkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Prac TestDocument23 pagesMath Prac Testkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- What To Do If Your Car Doesn't Start - Team-BHPDocument9 pagesWhat To Do If Your Car Doesn't Start - Team-BHPkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Legend Bids Adieu - The Hindu PDFDocument1 pageThe Legend Bids Adieu - The Hindu PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- 224 - The Hindu) PDFDocument2 pages224 - The Hindu) PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Olympiad 8Document8 pagesScience Olympiad 8Rajiv KabadPas encore d'évaluation
- Money WiseDocument4 pagesMoney Wisekvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Principles For Living A Happy Life - Times of India PDFDocument2 pages8 Principles For Living A Happy Life - Times of India PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moneycontrol - 10 MID CAP STOCKS PDFDocument4 pagesMoneycontrol - 10 MID CAP STOCKS PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- ) I III PUBJ ( S Chool : NoidaDocument11 pages) I III PUBJ ( S Chool : Noidakvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- High School Chemistry Grade 10-12Document486 pagesHigh School Chemistry Grade 10-12Todd95% (39)
- Corp Bank AR 2013 - Low-Res PDFDocument240 pagesCorp Bank AR 2013 - Low-Res PDFkvinodan73Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 5.7 Rational Exponents PowerpointDocument23 pages5.7 Rational Exponents PowerpointJimmy MandapatPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank 0606Document189 pagesQuestion Bank 0606WeteachPas encore d'évaluation
- Clase 2 Estatica PARTE1Document7 pagesClase 2 Estatica PARTE1Karen KarennPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 1Document6 pages3rd Quarterly Exam in Mathematics 1Jaycer De MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsDocument28 pagesProperties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsAllan AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Functions Last PushDocument14 pagesTrigonometric Functions Last Pushaarkhar0612Pas encore d'évaluation
- Section A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 3 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 Mathematics (Standard) 041Document6 pagesSection A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 3 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 Mathematics (Standard) 041Ashwani PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- Sakurai 1.17Document11 pagesSakurai 1.17uberpawsPas encore d'évaluation
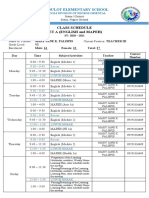
- Class Schedule Set A (English and Mapeh) : Sandulot Elementary SchoolDocument2 pagesClass Schedule Set A (English and Mapeh) : Sandulot Elementary SchoolISAGANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Math - CircleDocument19 pagesGrade 10 Math - CircleRobengie MoneraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 34 Area MethodDocument14 pagesChapter 34 Area Methodthorgod941500% (1)
- X + y - Z, y + Z - X, Z + X - Y: Satyawati Memorial AcademyDocument5 pagesX + y - Z, y + Z - X, Z + X - Y: Satyawati Memorial AcademySarvesh Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equation Problem SheetDocument19 pagesQuadratic Equation Problem SheetGaurav Yadav100% (2)
- Geometry and CombinatoricsDocument32 pagesGeometry and CombinatoricsBHAAJI0001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra 2 & Trig Regent ReviewDocument16 pagesAlgebra 2 & Trig Regent ReviewCassieGrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Y5 Autumn Block 4 WO13 Add Two Mixed Numbers 2022Document2 pagesY5 Autumn Block 4 WO13 Add Two Mixed Numbers 2022Ashish PacharPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Grade 8 Term 3Document277 pagesMaths Grade 8 Term 3Mahati PPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 6th Grade Modul 5 - Teacher MaterialsDocument329 pagesMath 6th Grade Modul 5 - Teacher Materialslelia_panaPas encore d'évaluation
- Huge Edu All Ny SupersDocument16 pagesHuge Edu All Ny SupersJP StorkPas encore d'évaluation
- Prim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit 11 TestDocument3 pagesPrim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit 11 TestKabagambe HamimPas encore d'évaluation
- BUSC2112 Basic Calculus First Quarter Exam - Attempt ReviewDocument17 pagesBUSC2112 Basic Calculus First Quarter Exam - Attempt ReviewChristian TeroPas encore d'évaluation
- CC10 Coplanar Forces in GeneralDocument18 pagesCC10 Coplanar Forces in GeneralSaqlain KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Reilly Core Curriculum Action PlanDocument2 pagesReilly Core Curriculum Action Planapi-300840229Pas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 5 3rd QDocument3 pagesMATH 5 3rd QLoida AbalosPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Calc AB/BC Review SheetDocument2 pagesAP Calc AB/BC Review Sheetmhayolo69100% (1)
- Trigonometry - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Udaan 2024)Document3 pagesTrigonometry - Daily Home Assignment 02 - (Udaan 2024)yash jainPas encore d'évaluation
- Heptagon - From Wolfram MathWorldDocument3 pagesHeptagon - From Wolfram MathWorldmemfilmatPas encore d'évaluation
- A Letter To A FriendDocument3 pagesA Letter To A Friendgiovanni monticoloPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Metrobank-Mtap-Deped Math Challenge Division Finals-Team Oral CompetitionDocument4 pages2017 Metrobank-Mtap-Deped Math Challenge Division Finals-Team Oral CompetitionAndrea CanlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Challenge - Junior - Round 2 - Solutions (2017-18) (Scottish Mathematical Council)Document4 pagesMathematical Challenge - Junior - Round 2 - Solutions (2017-18) (Scottish Mathematical Council)ElevenPlus ParentsPas encore d'évaluation