Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Antenna LP
Transféré par
Sam JaikumarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Antenna LP
Transféré par
Sam JaikumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DEPARTMENT OF : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNIATION ENGINEERING Subject Code & Title Class Regulation Course Prerequisite
ANTENNAS AND WAVE PROPAGATION THIRD YEAR B.E. (ECE) R 2008 I. Electromagnetic fields Semester
L P T MC 3 1 0 100 4 06
II. Transmission lines and waveguides To study radiation from a current element.
To study antenna arrays To study aperture antennas
Objectives
4. To learn special antennas such as frequency independent and broad antennas.
To study radio wave propagation.
band
1. 2.
an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering an ability to design a system, component or process as per needs and specifications an ability to develop skills to use modern engineering tools, software's and equipment to analyze problems an ability to gain broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context
Expected Outcomes
3. 4.
1. To prepare graduates in Electronic and communication Engineering for
successful careers dealing Indian industry with necessary core competency to succeed long-term in engineering/entrepreneurship careers, and who are well
Relationship of course to program objectives
prepared to undertake PG studies and research careers. 2. To prepare the students for competitive and challenging industrial applications in the areas of wireless communications, Biomedical Engineering, Analog and Digital communication, Mobile communication, Microcontrollers and embedded systems, Antennas and Microwave systems. 1. John D-Kraus and Ronalatory Marhefka- "Antennas"- Tata McGraw-Hill Book Company- 2002 2. E-C-Jordan and Balmain- "Electro Magnetic Waves and Radiating Systems"PHI-1968- Reprint 2003-
References
3. R-E-Collins- 'Antennas and Radio Propagation "- McGraw-Hill- 19874. Ballanis "Antenna Theory " - John Wiley & Sons- second edition 2003 5. D.Ganesh rao, B.Somanathan nair, Deepa Reghunath- Antennas and RadioWave Propagation, Sanguine technical publishers, Bangalore- 2007.
Mode of Evaluation Faculty
1. INTERNAL ASSESSMENT (20) 2. EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT(80)
COURSE PLAN
UNIT INTRODUCTION I RADIATION PROPERTIES TOPICS TO BE COVERED AS PER CURRICULUM Introductions and applications of Antennas and Wave Propagation Concept of vector potential- Modification for time varying- retarded caseFields associated with Hertzian dipolePower radiated and radiation resistance of current element Radiation and gain from half-wave dipole and quarterwave monopole antennas and folded dipole REFERENCE R2 : 1-24 T2: 311-317 T2: 317-322 T2: 323-325 T2: 328-332 PERIOD 1 2 2 1 3
Radiation intensity- Directive gain- Directivity- Power gain- Beam Width- Band Width. Reciprocity principle Effective length and Effective area Relation between gain effective length and radiation resistance Expression for electric field from two, three and N element arrays Linear arrays: Broad-side array End-Fire array II ANTENNA ARRAYS Method of pattern multiplication Binomial array Horizontal and Vertical Antennas above the ground plane Phased arrays Frequency-Scanning arrays Adaptive arrays and Smart antennas. Loop Antennas: Radiation from small loop and its radiation resistance- Radiation from a loop with circumference equal to a wavelength Helical antenna: Normal mode and axial mode operation Yagi-uda Antenna Log periodic antenna III ANTENNA TYPES Phased array- rhombic antenna Horn antenna Micro strip Antenna Reflector antennas and their feed systems Selection of antenna based on frequency of operation Antennas for special applications: Antenna for terrestrial mobile communication systems, GPR, Embedded antennas, UWB, Plasma antenna. Ground wave propagation: Attenuation characteristics for ground wave propagation - Calculation of field strength at a distance Space wave propagation: Reflection from ground for vertically and horizontally polarized waves Reflection characteristics of
R2: 40-70 T1: 439-441 R2: 87-92 R2: 92-94 T2 : 359-363 T2 :364-365 T2 :364-365 T2 :365-369 T2 :372-374 R2 :184-208 T1 :572-581 T1 :582-584 T1: 197-210
2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 3
R2 : 566-573 R2 : 577-597 R2 : 629-637 T1 : 587-590 R2 : 739-802 R2 : 811-852 R2 : 883-937 R3 : 227-235
1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2
IV WAVE PROPAGATION
T2 : 644-649
T2 : 629-631 T2 : 631-635
1 1
earth- Resultant of direct and reflected ray at the receiver Duct propagation Sky wave propagation: Structure of the ionosphereEffective dielectric constant of ionized region Mechanism of refraction- Refractive index- Critical frequency Skip distance and Maximum Usable frequency Effect of earths magnetic field Attenuation factor for ionospheric propagation Fading and Diversity reception Antenna Measurements: measurements V ANTENNA AND IONOSPHERIC MEASUREMENTS Reciprocity in Antenna T2 : 662-663 T2 : 668-671 T2 : 671-675 T2 : 676-677 T2 : 687-689 T2 : 681-682 T2 : 680-681, 664 T1 : 829-830 R2 : 1003-1021 R2 : 1021-1045 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 4
Near-field and Far field Measurements ranges Measurement of different Directional pattern, Gain, Impedance, Efficiency. Antenna Phase, parameters: Polarization,
Ionosphere Measurements: Measurement of vertical Incidence- Group Velocity and Group Delay- Relation between oblique and vertical Incidence transmission.
T2 : 694-698
STAFF INCHARGE
HOD
PRINCIPAL
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Line Coding Schemes: Line Coding Is The Process of Converting Binary Data, ADocument19 pagesLine Coding Schemes: Line Coding Is The Process of Converting Binary Data, ASam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- LineCoding ADCSDocument39 pagesLineCoding ADCSNano GomeshPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Lic Viva Test 2013Document6 pagesLic Viva Test 2013Sam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- LP Es NewDocument6 pagesLP Es NewSam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- TLW Rejinpaul Impques 2014Document2 pagesTLW Rejinpaul Impques 2014Sam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Microwave New LPDocument4 pagesMicrowave New LPSam JaikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Electric and Electronic CircuitsDocument23 pagesElectric and Electronic CircuitsAnand GnanasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On The Resonant Properties of The Koch Fractal and Other Wire Monopole AntennasDocument3 pagesOn The Resonant Properties of The Koch Fractal and Other Wire Monopole AntennasShesha PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Antennas: - Radiated Power - Radiation PatternDocument24 pagesAntennas: - Radiated Power - Radiation PatternMad ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
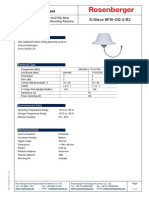
- BXA-80040/6CF - : Mechanical SpecificationsDocument1 pageBXA-80040/6CF - : Mechanical SpecificationsJuan Pablo Calderon VarelaPas encore d'évaluation
- VPol Ceiling Antenna Data SheetDocument2 pagesVPol Ceiling Antenna Data SheetsuongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- 67 ANT-AQU4518R61v06 DatasheetDocument2 pages67 ANT-AQU4518R61v06 DatasheetCarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Horns For CommunicationDocument30 pagesHorns For CommunicationJose Ricardo DescardeciPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- AWP Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesAWP Lesson PlansrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Ttb-709016-172718-172718de-65f (MTS46) PDFDocument1 pageTtb-709016-172718-172718de-65f (MTS46) PDFyevobimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Design of Dual-Band Microstrip Antenna For WiMax and X Band ApplicationsDocument5 pagesDesign of Dual-Band Microstrip Antenna For WiMax and X Band ApplicationsloganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- ODV 065R17B17K17K For - Russia - DS - 0 0 1Document1 pageODV 065R17B17K17K For - Russia - DS - 0 0 1carlosconstructor1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: DBXNH DBXNH - 6565A 6565A - VTM VTMDocument3 pagesProduct Specifications Product Specifications: DBXNH DBXNH - 6565A 6565A - VTM VTMShakeel AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 142 SpecDocument114 pages142 Specmarce572Pas encore d'évaluation
- Excel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth5Document7 pagesExcel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth5Santos ArnelPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 6 Receiving AntennasDocument18 pagesTopic 6 Receiving AntennasAhmed Freidoon FadhilPas encore d'évaluation
- Coaxial Length Calculator: Thanks To Ted G6ODA, Prem G0DCP & Rob M0HVC For Their Valuable InputDocument1 pageCoaxial Length Calculator: Thanks To Ted G6ODA, Prem G0DCP & Rob M0HVC For Their Valuable InputRey Rustan YbeightisiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Antenna Theory Analysis and Design - (Chapter 2 Fundamental Parameters and Figures-Of-Merit of Antennas)Document102 pagesAntenna Theory Analysis and Design - (Chapter 2 Fundamental Parameters and Figures-Of-Merit of Antennas)andy fiuturPas encore d'évaluation
- Array AntennaDocument6 pagesArray AntennasalusivasankaranPas encore d'évaluation
- VHLP3 7W 4WH - ADocument5 pagesVHLP3 7W 4WH - Azz2nktPas encore d'évaluation
- APXVBB20B_43-C-I20 Product DatasheetDocument4 pagesAPXVBB20B_43-C-I20 Product Datasheetjbermeo10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antenna SummaryDocument5 pagesAntenna Summarynmtien1985Pas encore d'évaluation
- TDJ 609015 - 172717deh 65FT2Document1 pageTDJ 609015 - 172717deh 65FT2glukkerPas encore d'évaluation
- HP12 71WDocument5 pagesHP12 71WCulzPas encore d'évaluation
- UNNPX206R3 Product SpecificationsDocument4 pagesUNNPX206R3 Product Specificationsmegamaster0987654321Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- A Compact Printed Spiral FM AntennaDocument3 pagesA Compact Printed Spiral FM AntennaPrabhat NarangPas encore d'évaluation
- AN4190 Application Note: Antenna Selection GuidelinesDocument29 pagesAN4190 Application Note: Antenna Selection Guidelinespasquale_dottoratoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ckt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1Document2 pagesCkt-Odv065r14b17k-B DS 0-0-1АлександрPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Specification - AirHarmony LSBA 2 3-2 4GHz Basta9 v2 (Antenna Model No - LSBA-2300-Airspan-001)Document2 pagesProduct Specification - AirHarmony LSBA 2 3-2 4GHz Basta9 v2 (Antenna Model No - LSBA-2300-Airspan-001)Ikie BariePas encore d'évaluation
- (VF) Commscope RYVV-65B-R4Document4 pages(VF) Commscope RYVV-65B-R4Madalina JariiPas encore d'évaluation
- Amwe MCQ (RMK)Document57 pagesAmwe MCQ (RMK)Santhosh PaPas encore d'évaluation
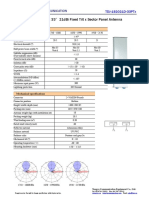
- Xpol 1710 2170Mhz 33°21dbi Fixed Tilt X Sector Panel AntennaDocument1 pageXpol 1710 2170Mhz 33°21dbi Fixed Tilt X Sector Panel AntennaIkap DarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)