Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Triple Science Option
Transféré par
stretfordhighCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Triple Science Option
Transféré par
stretfordhighDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GCSE Biology, GCSE Chemistry and GCSE Physics Pupils work through units of Biology, Chemistry and Physics
developing subject knowledge and using their understanding to link Science to the world around us. Subject Content Biology 1 Keeping healthy Nerves and hormones The use and abuse of drugs Interdependence and adaptation Energy and biomass in food chains Waste materials from plants and animals Genetic variation and its control Evolution Biology 2 Cells and simple cell transport Tissues, organs and organ systems Photosynthesis Organisms and their environment Proteins their functions and uses Aerobic and anaerobic respiration Cell division and inheritance Speciation Biology 3 Movement of molecules in and out of cells Transport systems in plants and animals Homeostasis Humans and their environment Chemistry 1 The fundamental ideas in chemistry Limestone and building materials Metals and their uses Crude oil and fuels Other useful substances from crude oil Plant oils and their uses Atoms, The periodic table, Chemical reactions Calcium carbonate Extracting metals, Alloys, Properties and uses of metals Crude oil, Hydrocarbons, Hydrocarbon fuels Obtaining useful substances from crude oil, Polymers, Ethanol Vegetable oils, Emulsions, Saturated and unsaturated oils Diet and exercise, How our bodies defend themselves against infectious diseases, The nervous system, Control in the human body, Control in plants Drugs Adaptations, Environmental change Energy in biomass Decay processes, The carbon cycle Why organisms are different, Reproduction Evolution
Cells and cell structure, Dissolved substances Animal organs, Plant organs Photosynthesis Distribution of organisms Proteins, Enzymes Aerobic respiration, Anaerobic respiration Cell division, Genetic variation, Genetic disorders Old and new species
Dissolved substances, Gaseous exchange, Exchange systems in plants, The blood system, Transport systems in plants Removal of waste and water control, Temperature control, Sugar control Waste from human activity, Deforestation and the destruction of areas of peat, Biofuels, Food production
Changes in the Earth and its atmosphere Chemistry 2 Structure and bonding How structure influences the properties and uses of substances Atomic structure, analysis and quantitative chemistry Rates of reaction Exothermic and endothermic reactions Acids, bases and salts Electrolysis Chemistry 3 The periodic table Water Calculating and explaining energy change Further analysis and quantitative chemistry The production of ammonia Alcohols, carboxylic acids and esters Physics 1
The Earths crust, The Earths atmosphere
Structure and bonding Molecules, Ionic compounds, Covalent structures, Metals, Polymers, Nanoscience Atomic structure, Analysing substances, Quantitative chemistry Rates of reaction Energy transfer in chemical reactions Making salts, Acids and bases Electrolysis
The early periodic table, The modern periodic table, Trends within the periodic table Hard and soft water, Purifying water Energy from reactions Analysing substances Making ammonia Alcohols, Carboxylic acids, Esters
The transfer of energy by heating Infrared radiation, Kinetic theory, Energy transfer by processes and the factors that affect the heating, Heating and insulating buildings rate at which that energy is transferred Energy and efficiency The usefulness of electrical appliances Methods we use to generate electricity The use of waves for communication and to provide evidence that the universe is expanding Physics 2 Forces and their effects Resultant forces, Forces and motion, Forces and braking, Forces and terminal velocity, Forces and elasticity Forces and energy, Momentum Static electricity, Electrical circuits Household electricity, Current, charge and power Energy transfers and efficiency Transferring electrical energy Generating electricity, The National Grid General properties of waves, Reflection, Sound, Red-shift
The kinetic energy of objects speeding up or slowing down Currents in electrical circuits Using mains electricity safely and the power of electrical appliances What happens when radioactive
Atomic structure, Atoms and radiation
substances decay, and the uses and dangers of their emissions Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion Physics 3 Medical applications of physics Using physics to make things work Keeping things moving
Nuclear fission, Nuclear fusion
X-rays, Ultrasound, Lenses, The eye, Other applications using light Centre of mass, Moments, Hydraulics, Circular motion The motor effect, Transformers
Assessment External Assessment (75%) 3 hour external papers for each science: Biology 25% x 3 = 75% Chemistry 25% x 3 = 75% Physics 25% x 3 = 75%
3 x Centre Controlled Assessment (25%) Practical skills and extended writing questions performed under exam conditions in class. One needed for Biology, Chemistry and Physics Jobs requiring Science a small sample of Jobs that require a qualification in Science Doctor Dentist Nurse Physiotherapists Engineer Forensics scientist Nutritionist Science Teacher Pharmacists Health and Safety Officer Marine Biologist Animal Care Vet Pilot
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Teaching Assistant 1 JD 2013 PDFDocument3 pagesTeaching Assistant 1 JD 2013 PDFstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumental Teacher Oct 2013 PDFDocument2 pagesInstrumental Teacher Oct 2013 PDFstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Equal Opportunities Monitoring May 2013Document2 pagesEqual Opportunities Monitoring May 2013stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance NotesDocument2 pagesGuidance NotesstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
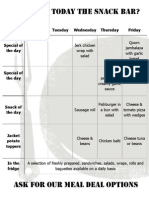
- Snack Bar Weekly Menu 21.10.13Document1 pageSnack Bar Weekly Menu 21.10.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
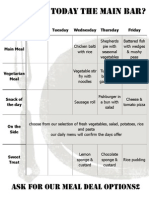
- Main Menu Weekly 14.10.13Document1 pageMain Menu Weekly 14.10.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Snack Bar Weekly Menu 14.10.13Document1 pageSnack Bar Weekly Menu 14.10.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumental Teacher June 2013Document2 pagesInstrumental Teacher June 2013stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Menu Weekly 21.10.13Document1 pageMain Menu Weekly 21.10.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- School Cleaner AdvertDocument1 pageSchool Cleaner AdvertstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- In-Year Application FormDocument2 pagesIn-Year Application FormstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Menu 08.07.13Document1 pageWeekly Menu 08.07.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Menu 05.07.13Document1 pageWeekly Menu 05.07.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Receptionist - Admin June 13Document1 pageReceptionist - Admin June 13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Equal Opportunities Monitoring May 2013Document2 pagesEqual Opportunities Monitoring May 2013stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Stretford High School - Published Inspection Report May 13 FinalDocument9 pagesStretford High School - Published Inspection Report May 13 FinalstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Trafford Non Teaching ApplicationDocument4 pagesTrafford Non Teaching ApplicationstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- School Inspections: Why Does Ofsted Inspect Schools?Document5 pagesSchool Inspections: Why Does Ofsted Inspect Schools?stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- SHS EAL DesignersDocument1 pageSHS EAL DesignersstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Menu 13.05.13.Document1 pageWeekly Menu 13.05.13.stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Stretfordian Spring 2013Document1 pageStretfordian Spring 2013stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- EAL Student DesignersDocument4 pagesEAL Student DesignersstretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Menu 6.05.13Document1 pageWeekly Menu 6.05.13stretfordhighPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Experiment 6Document7 pagesExperiment 6Miguel TeodoroPas encore d'évaluation
- S5 ActivityDocument3 pagesS5 ActivityMaku MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Molten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesDocument68 pagesMolten Sulphur Rail Tank Car Loading and Unloading Operations Final With AppendicesvlabdulazeemPas encore d'évaluation
- AGI Catalogue Industrial Hose and Fittings en Low Res 2016-08-01Document308 pagesAGI Catalogue Industrial Hose and Fittings en Low Res 2016-08-01Анита ВасилеваPas encore d'évaluation
- NEXUS 2104brownsgasDocument8 pagesNEXUS 2104brownsgaswxcvbnnbvcxwPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensor de Oxigeno Mercury MerdicalDocument2 pagesSensor de Oxigeno Mercury MerdicalIrving MontesPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT II ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Important QuestionDocument4 pagesUNIT II ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION Important Questionjowelantonio20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ozone Disinfection: A Technical OverviewDocument4 pagesOzone Disinfection: A Technical OverviewWillian A. Palacio MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Waste ManagementDocument12 pagesLiquid Waste ManagementTidus FarronPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Spill Response GuideDocument7 pagesChemical Spill Response GuideDaniel BobbittPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebosh Idip Unit C: IC1 Workplace Welfare Requirements and Specific Workplace Issues 2017Document18 pagesNebosh Idip Unit C: IC1 Workplace Welfare Requirements and Specific Workplace Issues 2017francisPas encore d'évaluation
- Percentage of Elements PowerPointDocument11 pagesPercentage of Elements PowerPointRomalyn ColomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fertilizer TechnologyDocument127 pagesFertilizer Technologysam0480% (1)
- ODO Measurement in Gas - Technical NoteDocument2 pagesODO Measurement in Gas - Technical Noteigize2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gerson Therapy HandbookDocument149 pagesGerson Therapy HandbookSonya Edwards100% (9)
- Kami Export - Exercise Lab - Mini-2Document3 pagesKami Export - Exercise Lab - Mini-2Ryan FungPas encore d'évaluation
- Economic Incentive For Intermittent Operation of Air Separation Plants With Variable Power CostDocument8 pagesEconomic Incentive For Intermittent Operation of Air Separation Plants With Variable Power CostJose MaximoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wellness Protocol 4.09Document137 pagesWellness Protocol 4.091stoctopPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab: Photosynthesis Lab Gizmo, You Can Monitor The Rate ofDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab: Photosynthesis Lab Gizmo, You Can Monitor The Rate ofAnthony HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- EO User GuidanceDocument96 pagesEO User GuidancesurawutwijarnPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Assignment: ZNCL PBCLDocument7 pagesHome Assignment: ZNCL PBCLmohdriyaz800% (1)
- K/U T/I Comm APPDocument4 pagesK/U T/I Comm APPLewis CarrollPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Science Quarter 1Document3 pagesGrade 9 Science Quarter 1Ford Virtudazo100% (1)
- Perfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ModuleDocument98 pagesPerfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ModuleAhmad RawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Traveller.-.1983.-.SS2 - Exotic AtmospheresDocument13 pagesClassic Traveller.-.1983.-.SS2 - Exotic Atmospherestsothggua100% (2)
- Fuels and CombustionDocument43 pagesFuels and Combustionengineeringchemistry71% (7)
- An Effective Solution For Elemental Sulfur Deposition in Natural Gas SystemsDocument12 pagesAn Effective Solution For Elemental Sulfur Deposition in Natural Gas SystemsDenys PronkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen CompatibiltyDocument2 pagesOxygen CompatibiltymattuiffPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Packaging and Shelf Life: A B A A A ADocument9 pagesFood Packaging and Shelf Life: A B A A A AAnutza PopescuPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Class General Science Full Book Objective Type Questions AnswersDocument7 pages6th Class General Science Full Book Objective Type Questions AnswersNuman KhanPas encore d'évaluation