Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Problems Statics
Transféré par
Wageeh El-AskaryDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sample Problems Statics
Transféré par
Wageeh El-AskaryDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Engineering Fluid Mechanics I Example Problems: Fluid Statics
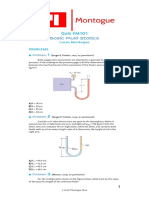
Problem 1. Pressure Difference in a Manometer a) Write an expression for the water difference between points A and B, pA-pB, in terms of w , the specific gravity of the oil, SGoil, the levels of the fluids zs at A, B, C, D and E. b) Determine the pressure difference between locations A and B in the figure below. The water has a w = 9800 N/m3 and the oil specific gravity, SGoil = 0.85.
Water Water A
0.15 m B
0.2 m
0.15 m
D 0.1 m
Oil, SG = 0.85
Oil
Solution: p A pB = ( p A pC ) + ( pC pD ) + ( pD pE ) + ( pE pB )
= w ( z A zC ) oil ( zC z D ) w ( z D z E ) oil ( z E z B ) = w ( z A zC ) + SGoil ( zC z D ) + ( z D z E ) + SGoil ( z E z B ) = 9800 N/m3 0.15 m + 0.85 ( 0.10 m ) + ( 0.20 m ) + 0.85 ( 0.15 m ) = 73.5 Pa = p A pB
Problem 2. In the figure below, the tank contains water and immiscible oil at 20oC. What is h in cm if the density of the oil is 898 kg/m3?
Solution: We identify the level of the top surface of the oil as 1, the interface between the oil and the water as 2 and the level of the top surface of water as 3. We choose the zero level to be the bottom of the tank; therefore:
z1 = h + 12 cm + 8 cm = h + 20 cm = h + 0.2 m, z2 = 8 cm = 0.08 m, z3 = 6 cm+12 cm + 8 cm = 0.26 m. The density of oil is, oil = 898 kg/m3; therefore, its specific weight, oil = oil g = 898 9.8 = 8800.4 N/m3 . The specific weight is:
water = 9,800 N/m3 . Now, we integrate
dp = between 1 and 3: dz
p3 z3 z2 z3 dp = dp = dz p3 p1 = oil dz water dz p1 z1 z1 z2 dz
= oil ( z2 z1 ) water ( z3 z2 ) = oil ( z1 z2 ) water ( z3 z2 ) = 0 .
We set the difference between p1 and p3 to be zero, because both of them are equal to the atmospheric pressure (both ends are open to the atmosphere). Substituting the values of the specific weights and the levels, we get:
oil ( z1 z2 ) water ( z3 z2 ) = 0 8,800.4 ( h + 0.2 0.08 ) 9,800 ( 0.26 0.08 ) = 0.
this h= expression, the only unknown is 9,800 ( 0.26 0.08 ) 0.12 = 0.08 m = 8 cm = h . 8,800.4
In h:
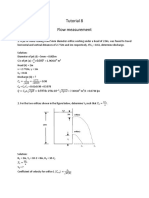
Problem 3. Gate AB is 1.2 m long and 0.8 m into the paper. Neglecting atmospheric pressure effects, compute the force F on the gate and its center of pressure position X from point A (see Figure).
Solution: First, to find the resultant force, we use the following expression: F = oil hc Agate (neglect atmospheric pressure, pa ) . The specific weight of oil may be
expressed as: oil = SGoil w = 0.82 9.8 kN/m3 . The height, hc, corresponds to the vertical distance from the oil surface to the centroid of the gate. This centroid, given that the gate is rectangular, sits in the middle of the gate at 1.2/2 or 0.6 m from A along the gate. hc may then be expressed as: hc = 4 m + (1+0.6) m sin 40= 5.028 m = hc
You have to be careful here to use the right units for the angle. Here, we use degrees; but, sometimes, the default is to use radians; explicitly state that the angle is in degrees when computing the sine. The area of the gate is expressed as the length times its width:
Agate = 1.2 m 0.8 m = 0.96 m 2 = Agate
The center of pressure sits below the centroid by the followind distance along the plate incline (note that along the width into the paper, xCP = 0, i.e. no shift for the center of pressure relative to the centroid in the x-direction): I sin yCP xc hc Agate By using the following figure:
1 3 1 3 ba = ( 0.8 m )(1.2 m ) = 0.1152 m 4 =I xc . Note, here that we used 12 12 the coordinate system, as shown in the figure above, to determine that a corresponds to the length and b corresponds to the depth into the paper. The value for yCP is: I sin ( 0.1152 ) sin 40 = = 0.0153 m = yCP yCP xc hc Agate ( 5.028)( 0.96 ) Note that if yCP is positive, then the position of the center of pressure is below the centroid. Now, we evaluate the distance X from A to the center of pressure as: X = 0.6 + yCP = 0.615 m = X
Therefore, I xc =
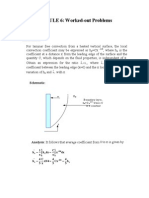
Problem 4. The tank shown below is 2 m wide into the paper. Neglecting atmospheric pressure, find the resultant hydrostatic force on panel BC.
Solution: The resultant force acting normal to panel BC may be expressed as: F = w hc A (neglect atmospheric pressure, pa ). The centroid depth is determined as follows:
hc = 3 + 3 / 2 = 4.5 m = hc . The
A=
area
of
the
gate
is
determined
as
follows:
(3 m ) + ( 4 m )
2 panel length
( 2 m ) = 10 m 2 =A
panel width
Therefore, the resultant force is: F = w hc A = 9.8 kN/m3 ( 4.5 m ) 10 m 2 = 441 kN = F
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Capitulo 12 StoeckerDocument11 pagesCapitulo 12 StoeckerPaulo Azañero75% (4)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsD'EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Zadky RiosPas encore d'évaluation
- TPDocument8 pagesTPSteel BeingPas encore d'évaluation
- HW Set 1Document6 pagesHW Set 1GsusKrystPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set For HydroDocument9 pagesProblem Set For HydroogulPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid MechanicsDocument64 pagesFluid MechanicsCiutac Ionut CristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Bell Delaware Math Cad ExampleDocument8 pagesBell Delaware Math Cad ExampleMohammed A IsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mech - 1.70Document2 pagesFluid Mech - 1.70شيماء الهاشميPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 2200 Test 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesCE 2200 Test 1 SolutionsGrantPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PDFDocument9 pages1 PDFalihasan12Pas encore d'évaluation
- School of Civil Engineering: DR Matthew Scase H22 HG2Document4 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering: DR Matthew Scase H22 HG2Kunal RamnatsingPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 2016 Fluid MechanicsDocument26 pagesCE 2016 Fluid MechanicsKyaw Zin HeinPas encore d'évaluation
- Example (1) :: SolutionDocument12 pagesExample (1) :: Solutionياسر فاضلPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiDocument8 pagesSolutions Manual Fluid Mechanics 5th EdiАпцгдк Ьфш БгднчллPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid ReferenceDocument19 pagesFluid ReferencemarkalvinbonPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics HW2 SolnDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics HW2 Solncollegedude89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cive1400 200203Document7 pagesCive1400 200203naefmubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedures To Design A Sieve Tray TowerDocument14 pagesProcedures To Design A Sieve Tray TowerSaidPas encore d'évaluation
- PS9Soln 2014Document13 pagesPS9Soln 2014Eddz Del Rosario RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics D203 Sae Solutions Tutorial 2 - Applications of Bernoulli Self Assessment Exercise 3Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics D203 Sae Solutions Tutorial 2 - Applications of Bernoulli Self Assessment Exercise 3nanduslns07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Fluid Statics Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesBasic Fluid Statics Solved ProblemsSamuel Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part8Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part8Jose EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hge Refresher Exam 9 SolutionDocument12 pagesHge Refresher Exam 9 SolutionaceeeceeePas encore d'évaluation
- Exam FDocument20 pagesExam FJohn Wafula wekesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1. A solid cylindrical needle of diameter d, length L, and density ρn may "float" on a liquidDocument5 pagesQ1. A solid cylindrical needle of diameter d, length L, and density ρn may "float" on a liquid엄기웅Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 2 - Justine T. SaldivarDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 2 - Justine T. SaldivarJustine Tizon SaldivarPas encore d'évaluation
- R A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis SDocument945 pagesR A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis STommyc102477% (13)
- ch03 Fox Fluid MechanicsDocument167 pagesch03 Fox Fluid MechanicsLoanFagetPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU Method: Sections 11.4 Through 11.7Document15 pagesHeat Exchangers: The Effectiveness - NTU Method: Sections 11.4 Through 11.7Joli SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Example, Chap. 1&2Document46 pagesExample, Chap. 1&2Solomon AlemuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part7Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part7Jose EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- MUCLecture 2023 1114885Document13 pagesMUCLecture 2023 1114885Shaiwin JiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutionmanual7!8!150303094025 Conversion Gate01Document12 pagesSolutionmanual7!8!150303094025 Conversion Gate01Omar BahgatPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Ch8Document15 pagesSolution Ch8Anonymous ou6LhnW6qv100% (2)
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Transferencia de CalorDocument10 pagesEjercicios Resueltos de Transferencia de CalordeibissotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 10 Fluids SolutionsDocument8 pagesHomework 10 Fluids SolutionsHa ViPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems of Chapter FiveDocument11 pagesProblems of Chapter FiveCesar HVPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Center of PressureDocument12 pagesExperiment 1 Center of PressureOsama RashaydaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument14 pages02 Stoichiometric CalculationsDhavanLalPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Flow Measurement Tutorial SolutionDocument22 pages8 Flow Measurement Tutorial SolutionJohn MalonePas encore d'évaluation
- Exchap 02 AnsDocument11 pagesExchap 02 AnsMewnEProwtPas encore d'évaluation
- ME3122 Tutorial 1 - Conduction-SolutionsDocument9 pagesME3122 Tutorial 1 - Conduction-SolutionsUnknown uploaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document9 pagesChapter 5abdel83Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 045 FDSDocument8 pages02 045 FDSJaveria NaseemPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesDocument6 pagesECE 309 Tutorial # 4 First Law of Thermodynamics: Control VolumesSaran JiPas encore d'évaluation
- P2Document55 pagesP2Abdulla BaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part5Document5 pagesFluid Mechanics White 7th SOL Part1 Part5Jose EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportD'EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportPas encore d'évaluation
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsD'EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationD'EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationPas encore d'évaluation