Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Group 17 Elements
Transféré par
Amirah AmanDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Group 17 Elements
Transféré par
Amirah AmanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
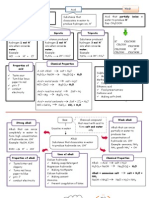
GROUP 17 ELEMENTS - Also known as halogens.
- Elements: fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine - Exist as diatomic covalent molecule (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, and At2) PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 1. Atomic size increases when going down group 17 because the number of F2 shells occupied with electrons increases. Cl2 2. All halogens have low melting and boiling points because halogen attracted to each other by Br2 weak Van der Waals forces. Little heat energy required to overcome it. However, going down the group, the melting points and boiling points I2 increases due to increases in molecular size 3. All halogens have low densities. Going down the group, density increases At2 because increase in atomic mass is bigger than increase in atomic radius. 4. The colour of halogens become darker when going down Group 17. 5. Do not conduct electricity 6. Weak conductors of heat. 7. High electronegativity ( ability to accept electron). Going down the group, electronegativity decreases. This is because, size become bigger, outermost occupied shell further away from nucleus, strength of nucleus to attract electron become weaker. Halogens Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine CHEMICAL PROPERTIES -All group 17 elements have 7 valence electrons, they exhibit similar chemical properties. - Differ in reactivity - Reactivity decreases when going down Group 17 i. Atomic size increases ii. Outermost electrons become further away from nucleus iii. Attraction weaker when going down the group iv. ability to receive one more electron decreases. v. Reactivity decreases. A) Reactivity of halogens with water All halogens react with water to produce acidic solution. X2 + H2O HX + HXO Cl2 + H 2O HCl + HClO (hypochlorus acid) Br2 + H 2O HBr + HBrO (hypobromus acid) I2 + H 2O HI + HIO F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 At2 Physical state Gas Gas Liquid Solid Colour Pale yellow Greenish-yellow Red Purplish black
* Chlorine water and Bromine water are bleaching agents due to presence of hypochlorus acid and hypobromus acid B) Reactivity of halogens with iron All halogens reacts with iron to produce iron(III) halides (brown salt) 2 Fe + 3Cl2 2FeCl3 (iron (III) chloride) 2 Fe + 3Br2 2FeBr3 (iron (III) bromide) 2 Fe + 3I2 2FeI3 (iron (III) iodide) C) Reactivity of halogens with sodium hydroxide solution All halogens react with sodium hydroxide solution to produce two types of sodium salt and water. Cl2 + 2NaOH NaCl + NaOCl + H 2O (sodium chlorate (I)) Br2 + 2NaOH NaBr + NaOBr+ H 2O (sodium bromate (I)) I2 + 2NaOH NaI + NaOI + H 2O (sodium iodate (I)) Safety precautions in handling Group 17 elements - Handle halogens in the fume chamber - Wear safety goggles - Wear gloves ELEMENTS IN PERIOD 3 a) Atomic radius (atomic size) decreases when going across period from left to right. -Going across Period 3, number of electrons increases -The attraction by the nucleus on the electrons becomes stronger -Positive charge also increases b) Electronegativity -Ability of an atom to attract electrons towards its nucleus -Electronegativity increase when going across period from left to right -Due to increasing the ability of nucleus to attract electrons increases c) Physical state - Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S: solid -Cl, Ar: Gas d) Electrical conductivity - Na, Mg Al (metal) : Good conductors of electricity - Si (semi-metal) : Weak conductor of electricity -P, S, Cl (non-metal): Cannot conduct electricity PROPERTIES OF OXIDES OF ELEMENTS IN PERIOD 3 a) Na, Mg : form oxides with basic properties
b) Al : form oxides with amphoteric properties: both basic and acidic properties c) Si, P, S, Cl : form oxides with acidic properties USES OF SEMI-METALS (METALLOIDS) IN INDUSTRY -Silicon : Making diodes, transistors and other electronic components. Also to make microchips. -Microchips are used in the manufacture of computers, calculators, cellphones video cameras, televisions, and others. -Germanium: used in microelectronic industry TRANSITION ELEMENTS -Located in Group 3 to group 12 -Physical properties: Solids with shiny surfaces Ductile and malleable high tensile strength High melting and boiling points High densities Good conductors of electricity and heat -Special characteristics: Form coloured ions/ compounds o e.g: Cobalt (II) ion: pink, copper (II) ion: blue, iron (II) ion: pale green Different oxidation numbers o iron: +2, +3;nickel: +2, +3 ; copper:+1, +2 Form complex ion o e.g: Hexaamine chromium (III) ion, [Cr(NH3)6] Act as catalyst o Nickel: catalyst in hydrogenation of alkene to form alkane o iron: catalyst in Harber process o Platinum: catalyst in Ostwald process o Vanadium (v) oxide: catalyst in Contact process
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Periodic TableDocument33 pagesThe Periodic TableIra MunirahPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Group 17 Elements UpdatedDocument8 pages4 Group 17 Elements Updatedkarim100% (1)
- Manufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongDocument73 pagesManufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongSanthiya MadhavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Patterns in Period 3 ElementsDocument18 pagesPatterns in Period 3 ElementsDania Dobbs100% (2)
- Chapter Polymerisation MethodDocument56 pagesChapter Polymerisation MethodwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements in Period 3Document13 pagesElements in Period 3FAthiyah Abdul RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- About Group 18 ElementsDocument2 pagesAbout Group 18 ElementsHoi YanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDocument16 pagesChapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionKavitha ThayagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrolysisDocument31 pagesElectrolysisteddaboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufactured Substances in Industry2Document20 pagesManufactured Substances in Industry2Sam ZeePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1.3 Exercise 1 - Water of CrystallisationDocument1 page1.1.3 Exercise 1 - Water of CrystallisationFakhar LateefPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsRoty005100% (4)
- 10-Reactivity of Metals and Displacement ReactionsDocument3 pages10-Reactivity of Metals and Displacement ReactionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenlePas encore d'évaluation
- C18 PolymersDocument31 pagesC18 PolymersKris DookharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021Document41 pagesTopic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021HotTornado XDPas encore d'évaluation
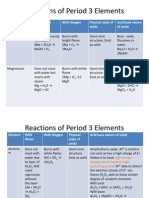
- Reactions of Period 3 ElementsDocument4 pagesReactions of Period 3 Elementsciliyap100% (1)
- Applications of EsterificationDocument13 pagesApplications of EsterificationZia Ur Rehman HashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Water As A Polar MoleculeDocument13 pagesWater As A Polar MoleculeAyaan Asim KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals and Their Properties - Physical and ChemicalDocument5 pagesMetals and Their Properties - Physical and Chemicalcourtz911Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionDocument9 pages6 Displacement of Halogen From Its Halide SolutionJedidah JongPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Chapter 8Document60 pagesForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Natural RubberDocument15 pagesNatural RubberHazilah AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of Reaction NotesDocument27 pagesRate of Reaction NotesYong SiewkuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsDocument5 pagesTopic 9 Manufactured Substances in Industry: 9.6 Composite MaterialsPutri MalayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 AlloyDocument58 pagesChapter 8 AlloyChe NorasiykinPas encore d'évaluation
- CeramicsDocument39 pagesCeramicsraja keshavPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal and ExtractionDocument57 pagesMetal and ExtractionMirawati EfendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form 5 (Soaps)Document7 pagesChemistry Form 5 (Soaps)emir906Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap4 - Reactivity of MineralDocument124 pagesChap4 - Reactivity of MineralYeLynTanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument41 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsPawan GoswamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 8elinePas encore d'évaluation
- SaltsDocument34 pagesSaltscar_yii100% (1)
- Chemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 SchemeDocument41 pagesChemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 Schemespm_victim2010100% (5)
- A CidDocument3 pagesA CidJerry Pui Chaw MinPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Unique Nature of CarbonDocument17 pages15 Unique Nature of CarbonlairinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Document2 pagesChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- Transition Elements PDFDocument18 pagesTransition Elements PDFArslanAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18Document126 pagesChemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18nalla casuga100% (1)
- Group 1 ElementsDocument5 pagesGroup 1 ElementsLeong Kit WaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Flame TestDocument9 pagesFlame TestChristopher YepmoPas encore d'évaluation
- HalogenDocument37 pagesHalogenPutri Dierla Dela100% (1)
- The Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsDocument14 pagesThe Reactivity Series of Metals and Its ApplicationsSaadiah MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrolysisDocument48 pagesElectrolysisGina100% (4)
- EJSK SK025 Physical PropertiesDocument30 pagesEJSK SK025 Physical PropertieschiaPas encore d'évaluation
- EstersDocument2 pagesEstersafoo1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- WS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESDocument4 pagesWS2 IG I Chemistry (1) SEPERATING MIXTURESRaj MalkanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 8 Part 2Document3 pagesChap 8 Part 2Naguib ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation
- REDOXDocument67 pagesREDOXLeo PietroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Document23 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Ng Wan LinPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction RatesDocument52 pagesReaction Ratestausman100% (1)
- Voltaic and Electrolytic Cell ComparisonDocument32 pagesVoltaic and Electrolytic Cell Comparisonmamta2111Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Oxidation and ReductionDocument25 pages3 Oxidation and ReductiondonutPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document27 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- CH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMDocument87 pagesCH 1.4 Electrolytic Cell Chemistry F5 KSSMleong cheng liyPas encore d'évaluation
- The S-Block ElementsDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elementswealthy58771% (7)
- Chapter 11 - Group IIDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Group IINabindra RuwaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 - The S-Block ElementssahilDocument13 pagesChapter 10 - The S-Block ElementssahilSk SahilPas encore d'évaluation
- Extractive Metallurgy 1: Basic Thermodynamics and KineticsD'EverandExtractive Metallurgy 1: Basic Thermodynamics and KineticsPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolysis of Molten CompoundDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Molten CompoundAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacture of Sulphuric AcidDocument8 pagesManufacture of Sulphuric AcidAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkanes: H H C H HDocument6 pagesAlkanes: H H C H HAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Relation Betwee N HCDocument1 pageRelation Betwee N HCAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Steps To Name Branched AlkenesDocument1 pageSteps To Name Branched AlkenesAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesDocument3 pagesComparing Alkanes and AlkenesAmirah Aman100% (1)
- 1 Soap and DetergentDocument9 pages1 Soap and DetergentKhairul Abadi PutehPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Chemical For ComsumersDocument29 pages14 Chemical For ComsumersAmirah AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat Dcs Sis ControllerDocument2 pagesCat Dcs Sis ControllerToth Zoltán100% (2)
- Adina CFD FsiDocument481 pagesAdina CFD FsiDaniel GasparinPas encore d'évaluation
- Desigo SystemDocument9 pagesDesigo Systemcindy .(00000050761)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Testing BrochureDocument12 pagesFlow Testing BrochureImadPas encore d'évaluation
- Dh3 Generation Lototo Plan Phase 2 RGC 08sep2023Document8 pagesDh3 Generation Lototo Plan Phase 2 RGC 08sep2023Borislav VulicPas encore d'évaluation
- Off Grid PV Systems Design GuidelinesDocument24 pagesOff Grid PV Systems Design Guidelinestantiba100% (1)
- Physics NotesDocument13 pagesPhysics Noteswaheedlakho100% (2)
- VLT2800 Quick Guide PDFDocument2 pagesVLT2800 Quick Guide PDFlieldPas encore d'évaluation
- E20 Heat Load Calculation SheetDocument1 pageE20 Heat Load Calculation SheetȘtefan C. Petre50% (2)
- CBC-DH For Wheisman-2022.11-DH2209-05Document1 pageCBC-DH For Wheisman-2022.11-DH2209-05Martín OsorioPas encore d'évaluation
- CIAT Podplafonski MJLINEDocument30 pagesCIAT Podplafonski MJLINEIgor SpasovicPas encore d'évaluation
- RCR Products BrochureDocument10 pagesRCR Products BrochureBOPas encore d'évaluation
- A Proactive 2-Stage Indoor CO2-based Demand-Controlled Ventilation Method Considering CoDocument18 pagesA Proactive 2-Stage Indoor CO2-based Demand-Controlled Ventilation Method Considering CoMariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Based Grass CutterDocument6 pagesSolar Based Grass CutterTTPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Hydro Forming: Indian Institute of Technology, BhuDocument10 pagesElectro Hydro Forming: Indian Institute of Technology, BhuSourabh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Project EvsDocument8 pagesProject Evsnaveenkmr04550% (2)
- Hse Ems Enviornmental PolicyDocument7 pagesHse Ems Enviornmental Policyshaquan josephsPas encore d'évaluation
- A GCE Physics B 2865 01 January 2006 Question PaperDocument24 pagesA GCE Physics B 2865 01 January 2006 Question PaperMitul KaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Motion Controls FC1010Document7 pagesAdvanced Motion Controls FC1010Servo2GoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Essential Engineer PDFDocument5 pagesThe Essential Engineer PDFDharmaraj MartynPas encore d'évaluation
- Yamaha Outboard Carburetor KitsDocument4 pagesYamaha Outboard Carburetor KitsMarine Parts ChinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: Carl T. A. JohnkDocument5 pagesEngineering Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: Carl T. A. JohnkMarce MatosPas encore d'évaluation
- ME8512 - TE - AU Practical Students Individual QuestionDocument4 pagesME8512 - TE - AU Practical Students Individual Questionsikkandar faizPas encore d'évaluation
- 0-2103471 Introduction To Engine DesignDocument85 pages0-2103471 Introduction To Engine DesignJulian DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Besic Electrical Engineering Lab: Experiment - 8Document9 pagesBesic Electrical Engineering Lab: Experiment - 8Rajesh RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress of PV Cell TechnologyDocument17 pagesProgress of PV Cell TechnologysriPas encore d'évaluation
- CombineDocument56 pagesCombineRajagopal GanapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Som Intelligent Densities Vertical CommunitiesDocument50 pagesSom Intelligent Densities Vertical CommunitiesRizwan Yousaf CheemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ReporttDocument5 pagesLab ReporttAngela BalanjianPas encore d'évaluation
- Megasan-Catalog CompressedDocument16 pagesMegasan-Catalog CompressedCasamed ServicePas encore d'évaluation