Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Study Guide For Financial Economics Test 1-3
Transféré par
Henry LatourTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Study Guide For Financial Economics Test 1-3
Transféré par
Henry LatourDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Obi Nwaigwe Study guide for test 1 Chap1 Portfolio is a combination of assets designed to serve as a store of value The
e factors that affect the construction of a portfolio ; goals of the investor, the risk involved, the taxes that will be imposed on any gain , and the knowledge of investment alternatives. They set a general framework for the asset allocation of the portfolio among various types of investments Security analysis considers the merits of the individual asset Portfolio management determines the impact that the specific asset has on the portfolio Preliminary Definitions The term investment can have more than one meaning, it refers to the purchase of a physical asset and its result of a productive asset. Investments occur with the notation of receiving a higher return and storing value An investment is made because the investor anticipates a return. The total return on an investment earns, income (dividends and interest) Capital gains or appreciation if the asserts price rises The seller trades the security for cash, and the buyer trades the cash for the security. This transaction occurs in the secondary market When the security are initially first issued and sold in the primary market Return is frequently expressed in percentages, such as the rate of return, which is the annualized return that is earned by the investment relative to its cost The investor anticipates that the return will be greater than that other assets with similar risk
If the rate of inflation exceeds the rate on interest rates that is earned on these accounts, the investor suffers a loss of purchasing power
Diversification and Asset Allocation Asset allocation refers to acquiring a wide spectrum of assets. Individuals use infinite resources to acquire various assets that include stocks and bonds Diversification is important because it reduces risk exposure. Asset allocation is important because it reduces you risk exposure. Asset allocation is important because it has a major impact on the return of your portfolio earns. Efficient and Competitive Markets Financial markets tend to be efficient. Securities prices depend on future cash flows, such as interest or dividend payments. If new information suggests that these flows will be altered, the market rapidly adjusts the assets prices. An efficient financial market implies that a security current price embodies all the known information concerning the potential return and risk associated with in that particular asset. If an asset is undervalued an Offered at an excessive return, investors would seek to buy it , which you drive the price up and reduce the return that subsequent investors will earn If an asset is was overvalued and offered an inferior return, investor would seek to sell it , which would drive down the prices and increase the return to subsequent investors
Efficient markets imply that investors on average cannot expect to beat the market consistently. Basically investors would choose securities that earn large returns Returns
Risk is the uncertainty that the anticipated return will be received
Chap2 Secondary markets and the role or markets makers
Although securities are issued in the primary market, all subsequent transactions are in the secondary market The transfer may occur on an organized exchange located in New York called the New York Stock Exchange(NYSE) or the BIG Board or the American Stock exchange (AMEX) curb A company must apply to have its securities accepted for trading. If the company meets the conditions set by the exchange market , the securities are listed and may be bought and sold through the exchange Securities of public companies with shares that are not listed on the exchange are traded over the counter (OTC). The most important OTC market is the NASDAQ stock market. National Associations of securities dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ), which is the system of communication for over the counter price quotations. Dealers in the OTC markets are referred to as Market makers and dealers in listed securities on the NYSE or AMEX are referred to as specialist . All these dealers offer to buy securities from any seller on the NYSE or sell securities to any purchaser The securities and exchange act of 1934 defines a dealer as anyone who engages in the business of buying and selling from his own account. Securities dealers quote prices on a bid and ask basis; they buy at one price (bid) and sell it at the other price (the ask) The difference between the bid and ask is the spread The spread like brokerage commission , is part of the cost of investing The spread is one source of commission of maintaining a market in the security The brokers commission is the compensation for executing your purchase if sells and orders
The Mechanics of investing in securities Individuals sectors usually purchase stock and bonds through brokers, who buy and sell securities for their customers accounts To be permitted to buy and sell securities , brokers must pass a proficiency exam . Once the individual passes the test, he or she is a registered representative and can buy and sell securities for customer accounts The Long and Short Positions If an investor expects a security to rise, the security is purchased. The investor takes s a long position in the security in anticipation of a price increase. The investor is bullish because he or she believes that the prices will rise. The long position earns profits for the investor if the price rises above the security has been purchased Short Position, Bearish, in which the investor anticipates that the security will fall. The investor sells the security and holds cash or places it in interest bearing short term securities. Some investors who are particularly bearish or are willing to speculate on the decline of prices may even sell short , which is a sell for future delivery
Type of orders After an investor decides to purchase a security, a buy order is placed with the broker. The investor may ask the broker to buy the security at the best price currently available, such a request is called a Market order The investor may enter a limit order and specify a price below the current asking price and wait till the price declines to the specified level. Such an order may be placed for one day, day order, or the order may remain in affect indefinitely, a good till canceled order. Such an order is remained on the book s of the broker until it is either executed or canceled. If the price of the security does not decline to the specified level, the purchase is not made. After purchasing a security an investor may place a stop order to sell, which may be at a higher or lower price. Once the stock reaches that price, the stop order becomes a market order. An investor who desires to limit a potential loss may place a stop loss order which specifies
Market Makers also make their income through dividends and interest from the securities they own Another source of profit is through the increase in security prices, for the value of the dealers portfolios rises
the price below the cost of the security at which the broker is authorized to sell An inventor may also place a stop loss on an order above the purchase price.
In order to protect the broker from investors default, a second margin requirement is established. Maintenance margin sets the minimum equity the investor must have in the position. If the stock price declines sufficiently, the investor receives a margin call and must advance additional funds or the broker will sell the stock and close the position
Cash and Margin Accounts The investor must pay for the security as they are purchased. This can be done with either cash or with a combination of cash and borrowed funds, Margin When an investor uses margin , purchases the security partially with credit supplied by the broker , he or she makes an initial payment To open a margin account, the investor signs an agreement with the broker that gives the use of the securities and some control over the account to the broker. The security serves as a collateral for the loan . Should the collateral on the amount fall below a specified level, the broker can require that the investor put more assets in the account, margin call. If an investor fails to meet a margin call, the broker will sell some, of the securities in the account to raise the cash needed to protect the loan o Pstock - $owed/Pstock0. Regulation
The purpose of these laws is to protect the investor by ensuring honest and fair practices. These laws require that the investor be provided with information upon which to base their decision of. These acts are frequently referred to as Full disclosure laws, publically owned companies must inform the public of certain facts relating to their firms to prevent fraud and manipulation of stock prices
Margin requirement is the minimum percentage of total price that the investor must pay and is set by the Federal Reserve board The minimum payment required of the investor is the value of the security times the margin requirement Investors use margins to increase the potential return on the investment
Blue Sky laws - security firms and brokers be licensed, financial information concerning issues of new securities be filed by the state regulatory bodies, new securities meet specific standards before they are sold, regulatory bodies be established to enforce laws The Federal securities law The first modern federal legislation governing the securities industry was the securities act of 1933, which was primarily concerning the issues of new securities. It required that new securities should be registered under the Securities exchange commission (SEC) The Securities exchange act of 1934 the act forbids market manipulation, deception and misrepresentation of facts and fraudulent practices Under the Securites exchange act of 1934, publically held companies are required to keep current information on file with the SEC. 10-K, a firms annual report to the SEC, giver detailed statements of a firms financial statement 10-Q-the firms quarterly report for the SEC
Maintenance Margin The margin requirement establishes the minimum amount the investor must deposit when purchasing a security If the price of the stock subsequently rises , the investors position improves because the amount borrowed as a proportion of the total value of the stock declines If however, the value of the stocks falls, the investor position deteriorates and the amount owed becomes a larger proportion of the value of stock
8-k provides information and must be filed within 15 days after an event that may affect the value of the stock 13-D a stockholder that who acquires 5 percent of a publically held corporations stock must submit. This document requires crucial information , such as the intentions of the stock holder acquiring a large stake
Investment bankers is an underwriter, a firm that sells new issues of securities to the general public An investor serves as a middle man to channel money from investors to firms that need money
Initial public offerings (IPO) is the sale of new securities or common stock to the public Firms sell securities when the internally generated funds are sufficient to finance the desired level of investment and when the firms believed it be to advantageous to obtain outside funding from the general public
Initial Public Offerings Two methods exist to facilitate a transfer. First is the direct investment that occurs when an individual stars their own business and invest their savings in the operations A direct transfer occurs when securities are initially sold to investors in the primary market through investment bankers
The mechanics of underwriting If s firm needs funds for external source, it can approach an investment banker, to discuss underwriting , the process of selling new securities. In an underwriting firm that is selling a security, and not the firm that is issuing the shares, bears the risk associated with the sale.
The alternative to the direct transfer of savings is an indirect transfer called financial intermediaries , such as a bank. Financial intermediaries stand between the user and the user of the funds, and it facilitates the flow of money and the credit between the suppliers and the users. The direct sale of an entire issue if bonds or stock to an investor or to a financial institution is called a private placement . The primary advantages of a private placement to issuing firm are the elimination of the cost of selling securities to the general public and ready availability of large amounts of cash Private placements are especially important for small, emerging firms . the size of these firms or the risk associated with them often precludes their raising funds from traditional sources Firms who do not have private placements of securities issued by emerging firms are called venture capitalist . Venture capitalist is a major source of finance for small firms or firms developing new technology
An underwriter starts with a particular firm that manages the underwriting, originating house, it is when several firms can jointly underwrite and sell the securities to the general public The originate does not usually sell all the securities by itself but instead forms a syndicate, is a group of brokerage houses that join together to underwrite a specific sale of securities. A member of a syndicate may bring in additional brokerage firms to help distribute securities The use of syndicates has many advantages , they are able to access more potential buyers for securities ,the number of each security that each brokerage firm must sell is reduced , and reduces the risk when trading large offerings
Investment Bankers
Types of Agreements
the investment banker may make the best efforts agreement , in which they agree to make their best effort to sell securities but no to guarantee that a specified amount of money will be raised the alternative is a firm commitment, which is an underwriting in which the investment bankers purchase the entire securities at a specified price and subsequently sells them to the general pubic Instead of supporting the price underwriters might let the security fall. The inventory of unsold securities can then be sold off and the underwriter will not tie up capital or have to borrow money from their sources of credit There is also an incentive to underprice new securities. If the issue is underpriced all the securities will be readily sold and their prices will rise because demand will exceed supply. It will generate immediate profit for the initial buyer Lock up period To avoid price volatility the insiders may be forbidden by an agreement with the underwriter to sell their holdings for a period of time , Shelf registration Many publicly held firms construct a prospectus describing a proposed issue of new securities and file it with the SEC. After the shelf registration has been accepted by the SEC, the firm may sell the securities whenever the need for funds arises Short Sale An investor make makes money in securities by buying low and selling high Short sale is the sale of borrowed securities in anticipation of a price decline, a contract for a future delivery This type of investment do not own the security that are being sold short
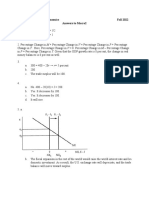
Present value annuity is always worth more than an ordinary annuity because you can invest the money EXAMPLES>.. Chap4 Taxes(bases) Imports ,wealth, consumption( sales tax), Income (tax on money ) Personal income tax a tax where the marginal tax rate (MTR) increases and income increases We dont have o Proportional tax rate MTR stays the same o Regressive MTR decreases and income increases
Tax rate for single tax payers 0-9000 = 10% 179-388=33% 9000-35 =15% 388 and above = 35% 35-86=25% 86-176=28% Tax shelter Is an asset where the income earned on that asset is such that taxes are eliminated or they are reduced or deferred to the future Interest on home mortgages are deducted from income Favorable treatment on long term capital gain Short term capital again hold something for less than one year Long term capital gain o If you have first two income brackets (10%,15%) you pay 0% o In higher brackets, the long term capital gain rate is 15% o Promote long term investments
Chap 3 Time value of money Payment each year is at the beginning of each year, annuity due Payment at the end of the year, ordinary annuity
Wash sale is a transaction where an investor sells a losing security to claim a capital loss, only to repurchase it again for a bargain Favorable treatments of government bonds State, local ,and local agencies bonds pay zero federal tax
On U.S. treasury bonds You pay federal tax but not state tax
Capital Asset Pricing Model RP= RF + (RM + RF)( p/ )
In NY you pay a FED tax, NYS Tax, City TAX Local bonds ( village ,towns, counties) you pay no federal tax or state tax Chapter 5 Retirement accounts Qualified plans 401K tax deferred retirement plan , private sector ( for profit), work for a private firm 403B public sector ( non-profit) tax deferred retirement plan
Rf = risk free tax Rm = expected market return STDVP=price they offered you STDVM= portfolio risk
Dark pools The book expands on The Quants to show how the rise algorithmic trading, artificial intelligence bots, and high frequency trading have rigged the current stock market. Patterson also discusses how governmental agencies, like the SEC, cannot keep up with the rapid evolution of technology. Everyone wanted to build the fastest and best code put in order to receive the most profit Large traders used dark pools to hide from algorithms programmed and it was unregulated. They were able to detect rapid changes in the market in order to make money. they used these programmers to trade at prices that its competitors thought werent profitable enough and detect the volatility of trades Fast traders most made their money by picking up pennies and nickels on thousands of trades a day. Because they move in and out of positions so rapidly . The trading community was becoming increasingly electronic, driven by powerful algo computers that could execute trades in less than seconds. Human dealers such as specialist and market makers were getting pushed aside by computer networks, electronic experts such as Josh Levine who developed an idea for investors to bypass the middleman and match buyers and sellers when prices matched. He believed that the faster the trading the better People who were building these programmers because they believed that computers could do a better job far quicker, and mistake free. It allowed investors to seek for information freely and allowed investors to trade without the interference of middle men Negotiate on better terms with buyers and sellers, lower fees, quicker data feeds
Regular IRAs , every person who works of wages is to establish a IRA, maximum you can put in is 6,000 Roth IRA you pay taxes on the amount you put in (not tax deferred) , you do not have to pay interest or tax Tax deferred plan ask government to offer retirement plan to employees Employees stock option Stock purchase plan - A company-run program in which participating employees can purchase company shares at a discounted price Incentive stock option - A type of employee stock option with a tax benefit, when you exercise, of not having to pay ordinary income tax. Instead, the options are taxed at a capital gains rate. Death tax Federal Estate tax - tax levied on an heir's inherited portion of an estate if the value of the estate exceeds an exclusion limit set by law State inheritance tax - Taxes imposed by the federal and/or state government on someone's estate upon their death
People were worries that computer trading threatened the stability of the financial system on a global scale. Senator Kaufman believed that the crash occurred because there was less and less human market specialist and market transaction that were floor based.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Fall of The Berlin WallDocument4 pagesFall of The Berlin WallHenry LatourPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Economic Development Essay On PopulationDocument7 pagesEconomic Development Essay On PopulationHenry LatourPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- St. Lawrence UniversityDocument21 pagesSt. Lawrence UniversityHenry LatourPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Internet As A Liberating ForceDocument11 pagesInternet As A Liberating ForceHenry LatourPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- General Principles of Contracts & Transactions in Islamic PDFDocument19 pagesGeneral Principles of Contracts & Transactions in Islamic PDFMuhammad Ammar100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Juice Palm: A Cold-Press Juice CompanyDocument17 pagesJuice Palm: A Cold-Press Juice CompanyIan PalenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Pelatihan Awareness Integrated Management System Qhse: Based OnDocument77 pagesPelatihan Awareness Integrated Management System Qhse: Based OnAchmad FiqriPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- WeTransfer On Companies and CommunitiesDocument51 pagesWeTransfer On Companies and CommunitiescgoulartPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 MKTG - 104 Product Management-Brand ValuationDocument14 pages11 MKTG - 104 Product Management-Brand ValuationMaynard RolloPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Inventory Optimization EbookDocument18 pagesInventory Optimization EbookDiego Cortez GranadosPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Introduction and Roadmap of Ind As For 1st 2nd August Pune Branch Programme CA. Zaware SirDocument51 pagesIntroduction and Roadmap of Ind As For 1st 2nd August Pune Branch Programme CA. Zaware SirPratik100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Verma EnterprisesDocument2 pagesVerma EnterpriseskapilazarchitectsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Finding The Right International MixDocument3 pagesFinding The Right International MixКсения БорисоваPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Introduction To The Andy Elliott Trainingw22Document5 pagesIntroduction To The Andy Elliott Trainingw22Carlos Parra RavenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Designing An Information Management System For OLA A Information System Management Presentation Report by Aditya KhandelwalDocument19 pagesDesigning An Information Management System For OLA A Information System Management Presentation Report by Aditya KhandelwalAditya Khandelwal100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- RFI FormDocument1 pageRFI FormNoel MadesPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracking, Track Parcels, Packages, Shipments - DHL Express TrackingDocument2 pagesTracking, Track Parcels, Packages, Shipments - DHL Express TrackingmmemonPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 2 - MergedDocument43 pagesProblem Set 2 - MergedSamantha Marie RebolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- IIC - Schemes & ImplementationDocument17 pagesIIC - Schemes & Implementationelangoprt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Order Appealed Against 2Document27 pagesOrder Appealed Against 2Jyoti MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Roll No 34 & 35 AssigmentDocument3 pagesRoll No 34 & 35 AssigmentRitikaPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- 31 (2) Sbi and IciciDocument6 pages31 (2) Sbi and IciciShyla PascalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lean Production TaskDocument3 pagesLean Production Taskfabiosurace05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Entrepreneurs: The Driving Force Behind Small BusinessDocument33 pagesEntrepreneurs: The Driving Force Behind Small BusinessBibhu R. TuladharPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic of Sap MMDocument12 pagesBasic of Sap MMRooplata NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- IPD Export: Indonesia Export Shipment RatesDocument6 pagesIPD Export: Indonesia Export Shipment RatesVia Anggi TastietranPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- SHRM - Training & DevelopmentDocument49 pagesSHRM - Training & DevelopmentFidan HajiyevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared By: Jilly Boy G. Bruno Jr. and Jerome Marquez (Set A) - 1Document8 pagesPrepared By: Jilly Boy G. Bruno Jr. and Jerome Marquez (Set A) - 1BSIT 1A Yancy CaliganPas encore d'évaluation
- PM January 2021 Lecture 4 Worked Examples Questions (Drury (2012), P. 451, 17.17)Document6 pagesPM January 2021 Lecture 4 Worked Examples Questions (Drury (2012), P. 451, 17.17)KAY PHINE NGPas encore d'évaluation
- Understand Arrangement OverviewDocument5 pagesUnderstand Arrangement OverviewNandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation By:: 1. Aakanksha Sakpal 2. Darpan Patil 3. Yash Gandhi 4. Madhuja Hagde 5. Nikita KanojiaDocument10 pagesPresentation By:: 1. Aakanksha Sakpal 2. Darpan Patil 3. Yash Gandhi 4. Madhuja Hagde 5. Nikita KanojiarahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Valuation and Negotiation of Technology Step 2 - Create Value From Technologic InnovationDocument10 pagesValuation and Negotiation of Technology Step 2 - Create Value From Technologic InnovationPaola HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Aud339 Group Report: Article ReviewDocument8 pagesAud339 Group Report: Article ReviewAhmad Danish Mohammad ZairinPas encore d'évaluation
- MXN MLMDocument11 pagesMXN MLMKC CarreonPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)