Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Calibration of Venturimeter Final
Transféré par
animeshkumarvermaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Calibration of Venturimeter Final
Transféré par
animeshkumarvermaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
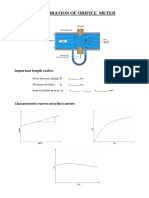
CALIBRATION OF VENTURIMETER
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
Exp no:
Date:
CALIBRATION OF VENTURIMETER
Aim :
To determine the coefficient of discharge and calibration equation for the given Venturimeter.
Specifications :
Diameter of pipe - 25 mm
Diameter of throat - 15 mm
Collecting tank size - 500 x 500 mm
Apparatus :
Venturimeter fitted across a pipeline leading to a collecting tank, Stop Watch, U-Tube manometer
connected across entry and throat sections etc.
Theory :
Venturimeter is a device consisting of a short length of gradual convergence and a long length of
gradual divergence. Pressure tapping is provided at the location before the convergence commences and
another pressure tapping is provided at the throat section of a Venturimeter. The Difference in pressure head
between the two tapping is measured by means of a U-tube manometer. On applying the continuity equation &
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
Bernoullis equation between the two sections, the following relationship is obtained in terms of governing
variables.
Theoretical discharge through Venturimeter,
) a (a
h g 2 .a a
Q
2
2
2
1
2 1
th
= cm
3
/s
Where:
a
1
=
Cross section area of Venturimeter at entry section in cm
2
.
a
2
=
Cross section area of Venturimeter at throat section in cm
2
.
h = Pressure head difference in terms of fluid flowing through pipeline.
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
1
H
w
m
cm of water
H = Mercuric level difference in manometer in cm.
Actual discharge through Venturimeter,
t
h A.
t
V
Q
act
= = cm
3
/s
Where,
V = (A. h), volume of water collected in collecting tank in cm
3
.
A = Cross section area of collecting tank in cm
2
.
h = Height of water collected in collecting tank in cm.
t = Time required to collect the water up to a height h in the collecting tank.
Hence,
Coefficient of discharge of the Venturimeter, C
d
=
th
a
Q
Q
In order to take real flow effect into account, coefficient of discharge (C
d
) must be introduced in equation of
Theoretical discharge. Then,
) a (a
h g 2 .a a
Q
2
2
2
1
2 1
a
=
d
C cm
3
/s
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
ie,
) a (a
1
H g 2 .a a
C Q
2
2
2
1
w
m
2 1
d a
|
|
.
|
\
|
= cm
3
/s
Where, H - manometric difference in cm.
m
= Density of mercury
w
= Density of water
The above equation can be expressed as,
H K Q
n
a
= cm
3
/s .............(1)
Where, K - a constant
n - exponent
Calibration of venturimeter is to find out the numerical values of K and n.
The graph of equation (1) can make linear by taking logarithms on both side.
ie, log Q = log K + n log H
The graph of the above equation is linear and the values of K and n can find from the graph. While
plotting the graph by taking log Q
a
on Y axis and log H on X axis, the slope of the line will give the value of n
and Y-intercept will give the value of log K.
Ref: Fluid mechanics F.M.White, Section. 6.10
Procedure :
- Note the pipe diameter (d
1
) and throat diameter (d
2
) of Venturimeter.
- Note the density of manometric liquid i.e. mercury (
m
) and that of fluid flowing through pipeline ie,
water (
w
).
- Start the pump and adjust the control valve in pipeline for maximum discharge.
- Measure the pressure difference (H) across the Venturimeter by using U tube manometer.
- Measure flow rate ie, actual discharge (Q
act
) through Venturimeter by means of collecting tank.
- Calculate the theoretical discharge (Q
th
) through Venturimeter by using the formula.
- Decrease the flow rate by adjusting the control valve and repeat the process for at least five times.
- Determine the coefficient of discharge (C
d
) for each flow rate and find the mean value of coefficient of
discharge (C
d
).
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
- Tabulate the readings and find the values of log Q
a
and log H.
- Plot the graph log Q
a
Vs log H.
- Determine the value of constant K and n from the graph.
Observation Table :
l
o
g
H
-
-
l
o
g
Q
a
-
-
C
o
e
f
f
i
c
i
e
n
t
o
f
d
i
s
c
h
a
r
g
e
C
d
-
T
h
e
o
r
e
t
i
c
a
l
D
i
s
c
h
a
r
g
e
Q
t
h
c
m
3
/
s
A
c
t
u
a
l
i
s
c
h
a
r
g
e
Q
a
c
m
3
/
s
T
i
m
e
f
o
r
5
c
m
r
i
s
e
i
n
c
o
l
l
e
c
t
i
n
g
t
a
n
k
(
t
)
m
e
a
n
t
s
2
s
1
s
M
a
n
o
m
e
t
e
r
R
e
a
d
i
n
g
D
i
f
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
H
=
h
2
-
h
1
c
m
o
f
H
g
R
i
g
h
t
l
i
m
b
h
2
c
m
L
e
f
t
l
i
m
b
h
1
c
m
S
l
.
N
o
:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
Graph :
Sample Calculations: Set No _____
Aerospace Engineering Department, IIST
Result :
Coefficient of discharge of Venturimeter, C
d
=
The value of K =
The value of n =
The Calibration equation is, Q
a
=
Inference :
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Calibration of Orifice Meter FinalDocument7 pagesCalibration of Orifice Meter FinalHartono PrayitnoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1a - ORIFICE METER - 13jan2015 PDFDocument6 pages1a - ORIFICE METER - 13jan2015 PDFPartha SurvePas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of VenturimeterDocument5 pagesCalibration of VenturimeterRahul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument9 pagesCalibration of Venturi Meterseminarproject40% (5)
- Fluid Mechanics - I Experiments Index Expt. No. Name of The ExperimentDocument37 pagesFluid Mechanics - I Experiments Index Expt. No. Name of The ExperimentAnand DattPas encore d'évaluation
- Determine Coefficient of Discharge Using Orifice MeterDocument62 pagesDetermine Coefficient of Discharge Using Orifice MeterPandiya RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- VenturiMeter PDFDocument5 pagesVenturiMeter PDFLalalalalalalaalalalPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Lab PDFDocument29 pagesFM Lab PDFamitPas encore d'évaluation
- VENTURIMETERDocument4 pagesVENTURIMETERKailash RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Orifice MeterDocument7 pages1 Orifice MeterFlorin EnePas encore d'évaluation
- UTM Flow Measurement Lab Report AnalysisDocument20 pagesUTM Flow Measurement Lab Report AnalysisKhairil IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids Lab Orifice MeterDocument3 pagesFluids Lab Orifice Meterharun_4uPas encore d'évaluation
- Me2134 2Document22 pagesMe2134 2Thomas TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibrate Venturi and Orifice Flow MetersDocument12 pagesCalibrate Venturi and Orifice Flow MetersAaron Fraka Riches100% (1)
- To Determine Coefficient of DischargeDocument7 pagesTo Determine Coefficient of DischargeUmair NawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Flow Coefficients with Orifice & V-Notch MetersDocument7 pagesMeasuring Flow Coefficients with Orifice & V-Notch MetersManoj guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Measurement Using Venturi Meter ExperimentDocument6 pagesFlow Measurement Using Venturi Meter ExperimentCece SesPas encore d'évaluation
- V NotchDocument2 pagesV NotchUstaziyatul AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- TITLE: Venturimeter AIM: To Determine Coefficient of Discharge of Venturimeter. ApparatusDocument8 pagesTITLE: Venturimeter AIM: To Determine Coefficient of Discharge of Venturimeter. Apparatussasha dsilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 8 - The Venturi Meter, The Determination of Discharge From A PipeDocument8 pagesExperiment 8 - The Venturi Meter, The Determination of Discharge From A Pipebkewill6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Measurement through Venturi and Orifice MetersDocument5 pagesFlow Measurement through Venturi and Orifice MetersRaghavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesCalibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterMUTHUKURU VENKATA GOWTHAM REDDYPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Centre of Pressure On A Plane SurfaceDocument19 pagesExperiment 1 Centre of Pressure On A Plane SurfacePatrick Camerino DimabuyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerodynamics Lab ManualDocument42 pagesAerodynamics Lab ManualSathya Narayanan100% (2)
- Fluid Lab ManualDocument27 pagesFluid Lab ManualvenkiteshksPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid 1 LabDocument18 pagesFluid 1 LabHassan MehrizPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibrate Venturimeter Flow MeterDocument4 pagesCalibrate Venturimeter Flow Meterabhishekpatil21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practical flow experimentsDocument14 pagesPractical flow experimentsEngr Muhammad Asif JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of Flow MetersDocument65 pagesCalibration of Flow MetersAyyanrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Venturimeter CoefficientsDocument5 pagesDetermining Venturimeter CoefficientsManish UikePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047Pas encore d'évaluation
- Me2134 2Document18 pagesMe2134 2FlancPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1Document19 pagesLab 1Nisha FareenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 OrificesDocument7 pages3 OrificesPraful N KPas encore d'évaluation
- Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of TechnologyDocument35 pagesChennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of Technology Chennai Institute of TechnologyEdifice Placement SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice Plate Long ReportDocument16 pagesOrifice Plate Long ReportLuqman HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination Coefficient of Velocity From Jet TrjectoryDocument13 pagesDetermination Coefficient of Velocity From Jet TrjectoryMohd Syafiq Akmal81% (31)
- Objective of Experiment. Equipment Set-Up. Theory of Experiment. Procedure. Results & Calculations. Discussion of The Results. ConclusionDocument11 pagesObjective of Experiment. Equipment Set-Up. Theory of Experiment. Procedure. Results & Calculations. Discussion of The Results. ConclusionAmmar Al-AghbariPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturi Flume Critical Flow ExperimentDocument3 pagesVenturi Flume Critical Flow ExperimentMatumbi Naito77% (13)
- Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesVenturi MeterJorah MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- Fallsem2021-22 Che1005 Ela Vl2021220101507 Reference Material I 11-Aug-2021 1.flow Through VenturimeterDocument4 pagesFallsem2021-22 Che1005 Ela Vl2021220101507 Reference Material I 11-Aug-2021 1.flow Through Venturimeterkeerthana satheeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesOrifice MeterJorah MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry Final ReportsDocument13 pagesPhysical Chemistry Final ReportsRheannePas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Through an Orifice - Calculating Discharge, Velocity & Contraction CoefficientsDocument6 pagesFlow Through an Orifice - Calculating Discharge, Velocity & Contraction Coefficientshozipek559950% (2)
- Calibration of Triangular NotchDocument8 pagesCalibration of Triangular Notchseminarproject50% (4)
- (Instrumentation) Measurement of Flow of FluidsDocument40 pages(Instrumentation) Measurement of Flow of FluidsLWYenPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibrate V-Notch Weir for Fluid Mechanics LabDocument2 pagesCalibrate V-Notch Weir for Fluid Mechanics LabRahul Kumar0% (1)
- Experiment No 3 HM LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3 HM Labprajwalwanjari5524Pas encore d'évaluation
- Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDocument8 pagesEstimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusAyman N YassinPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Lab Manual PDFDocument55 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Lab Manual PDFjyothiPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibrating a Venturi MeterDocument10 pagesCalibrating a Venturi MeterAgyeman EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Document9 pagesVenturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Somya MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- CE6461 - Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory PDFDocument65 pagesCE6461 - Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory PDFjeroldscdPas encore d'évaluation
- Flight Test Instrumentation: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium 1964D'EverandFlight Test Instrumentation: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium 1964M. A. PerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume ID'EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IPas encore d'évaluation
- A Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityD'EverandA Treatise on Meteorological Instruments: Explanatory of Their Scientific Principles, Method of Construction, and Practical UtilityPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992D'EverandComputational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992S. MurakamiPas encore d'évaluation
- HomeWork 1Document1 pageHomeWork 1animeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Latest Trends in MachiningDocument209 pagesLatest Trends in Machiningalexkr16661Pas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Useful Open Source Web Based File ManagersDocument1 page10 Useful Open Source Web Based File ManagersanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- ES490 Lecture - Notes 04Document55 pagesES490 Lecture - Notes 04animeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Use The Hungarian AlgorithmDocument2 pagesHow To Use The Hungarian AlgorithmanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Structures Course OverviewDocument42 pagesAircraft Structures Course OverviewShwetha BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Crack PropagationDocument5 pagesConcrete Crack PropagationanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- MTech Aerospace Structures Curriculum Syllabus 20130918Document6 pagesMTech Aerospace Structures Curriculum Syllabus 20130918Muralikrishnan GMPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Structures DefinitionsDocument8 pagesAircraft Structures DefinitionsJerin CyriacPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS Recommendation Letter FormatDocument2 pagesIAS Recommendation Letter FormatAshwin RamanujamPas encore d'évaluation
- B.tech TimeTableDocument7 pagesB.tech TimeTableanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- What is a prototypeDocument5 pagesWhat is a prototypeanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- IIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATDocument8 pagesIIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATLee SweeneyPas encore d'évaluation
- AE BTech Syllabus 2011Document58 pagesAE BTech Syllabus 2011animeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- S Sukeshkumar@vssc - Gov.inDocument1 pageS Sukeshkumar@vssc - Gov.inanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop PDFDocument3 pagesWorkshop PDFanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- AE 331 Lab Manual PDFDocument22 pagesAE 331 Lab Manual PDFanimeshkumarverma0% (1)
- AE312 Assignment 1 PDFDocument1 pageAE312 Assignment 1 PDFanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- LC49-List of BooksDocument29 pagesLC49-List of BooksanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sixth Semester Classes ScheduleDocument1 pageSixth Semester Classes ScheduleanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- AE BTech Syllabus 2011Document58 pagesAE BTech Syllabus 2011animeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Our Wastewater Systems Overview - SA Water PDFDocument1 pageOur Wastewater Systems Overview - SA Water PDFanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Jet CutterDocument7 pagesWater Jet Cutteranimeshkumarverma100% (1)
- Springs PDFDocument7 pagesSprings PDFanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Value EnggDocument6 pagesValue EngganimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Semester Internship Evaluation CriteriaDocument1 page6 Semester Internship Evaluation CriteriaanimeshkumarvermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage REgulationDocument8 pagesVoltage REgulationJacob CarterPas encore d'évaluation
- IIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATDocument8 pagesIIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATLee SweeneyPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and EnvironmentDocument18 pagesInternational Journal of Mining, Reclamation and EnvironmentRiza SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet-5-Logs (Practice Test) (With WS)Document6 pagesWorksheet-5-Logs (Practice Test) (With WS)Moloy GoraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Adv Loreto Kirribilli Prelim Yearly Paper 64d1f34da1e07Document65 pagesMaths Adv Loreto Kirribilli Prelim Yearly Paper 64d1f34da1e07kody.patel18Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14 - Laws of LogarithmsDocument8 pages14 - Laws of LogarithmsDevita OctaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Folding Endurance Tester CalibrationDocument14 pagesFolding Endurance Tester Calibrationmazahir razaPas encore d'évaluation
- Logs Express 5packDocument10 pagesLogs Express 5packKevinRick B MalicdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloth Stiffness and Hysteresis in BendingDocument16 pagesCloth Stiffness and Hysteresis in BendingAtieh YousefiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reddy 1972Document16 pagesReddy 1972FlorinPas encore d'évaluation
- AIME QuestionsDocument86 pagesAIME QuestionsAnkitPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Physics MeasurementDocument12 pagesIB Physics MeasurementCaleb LPas encore d'évaluation
- (Pender Et Al, 2019) Cambridge Mathematics Advanced Year 11Document586 pages(Pender Et Al, 2019) Cambridge Mathematics Advanced Year 11Nihara A74% (23)
- Full Scientific Calculator: Brief User GuideDocument18 pagesFull Scientific Calculator: Brief User Guidejitendra jhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahuja Et Al, 2007Document18 pagesAhuja Et Al, 2007JonasPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1 Notes - 6.9 Notes - Logs With Other Bases-KeyedDocument2 pagesDay 1 Notes - 6.9 Notes - Logs With Other Bases-Keyedmika piusPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Utility Theory - JohnNorstadDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Utility Theory - JohnNorstadwagndavePas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra 2 End of Course Test Preparation WorkbookDocument7 pagesAlgebra 2 End of Course Test Preparation Workbookafiwjkfpc100% (2)
- Chemical Gauging Method (Dilution MethodDocument38 pagesChemical Gauging Method (Dilution MethodAsjad UllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 (Logarithms)Document8 pagesChapter 8 (Logarithms)bggvrgunrhbrPas encore d'évaluation
- Groundwater Hydrology Course NotesDocument52 pagesGroundwater Hydrology Course NotesshambelPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Course Notes GuideDocument270 pagesCalculus Course Notes GuideAriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lab Manual RevisedDocument72 pagesPhysics Lab Manual Revisedjayant lanjewarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lelm 2nd PUCDocument81 pagesLelm 2nd PUCAarav MantripragadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ml0101En-Reg-Nonelinearregression-Py-V1: 1 Non Linear Regression AnalysisDocument12 pagesMl0101En-Reg-Nonelinearregression-Py-V1: 1 Non Linear Regression AnalysisRajat SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- My Revision Notes Edexcel A Level Maths (Pure)Document467 pagesMy Revision Notes Edexcel A Level Maths (Pure)Prince Yug83% (6)
- Determination of Precision and Bias Data For Use in Test Methods For Petroleum Products and LubricantsDocument27 pagesDetermination of Precision and Bias Data For Use in Test Methods For Petroleum Products and LubricantsImran AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Superposition (Repaired)Document77 pages5 Superposition (Repaired)Leng Chai100% (1)
- Graduate Macro Theory II Notes Log-Linear ApproximationDocument5 pagesGraduate Macro Theory II Notes Log-Linear ApproximationDynamix SolverPas encore d'évaluation
- Saxelby A Course in Practical Mathematics (1913)Document492 pagesSaxelby A Course in Practical Mathematics (1913)Marcelo Silvano de Camargo0% (1)
- Workbook Log ByMCSirDocument19 pagesWorkbook Log ByMCSirSanjay YadavPas encore d'évaluation