Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
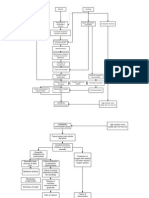
Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn Nogra
Transféré par
Rhealyn NograTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn Nogra
Transféré par
Rhealyn NograDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
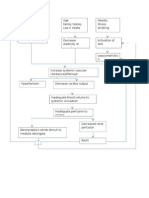
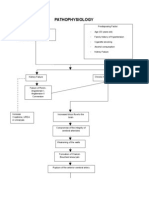
Blood extravates into subarachnoid space
Develops defects in the muscular layer (tunica muscularis) of arteries
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Acute Pain
Blood spreads out and coats other vessels and the brain structure
Alterations in the internal elastic membrane (lamina elastic interna) of cerebral arteries
Subarachnoid blood may produce meningeal signs
Weakening of the vessel wall
Nimotop
Intracranial hypertension occurs
Dilatation of the wall of the cerebral artery
Citicoline
Progressive decrease in cerebral blood flow from a massive increase in ICP or from transient acute vasospasm
Blood flow exerts pressure against a congenitally weak arterial wall
Impaired level of consciousness
Rupture of the arterial wall Decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure
Acute hydrocephalus occurs due to blocked CSF outflow or increase CSF viscosity
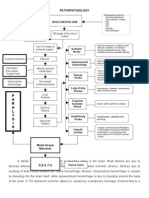
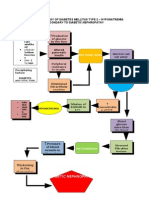
SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
Signs & Symptoms Loss of consciousness Headache MRI Celecoxib
Hyponatremia: 136mmol/L
CT Scan
Seizure Dilantin
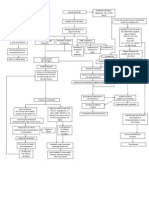
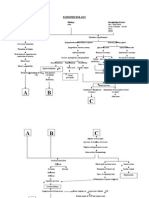
Increase fat deposit on the walls of the blood vessels
Decreased Cardiac Output
Increase workload of the heart Narrowing of blood vessels (Coronary Artery)
Atherosclerosis
Pressure on the wall of blood vessels
Increase blood pressure
Increase peripheral vascular pressure Some fragments joins in the circulation
HCVD
Chest Ap
Goes to small vessels and clog (Deep penetrating arteries)
Signs & Symptoms: Shortness of breath Weakness Fatigue Diaphoresis Dizziness Chest pain
Obstruction/ interruption of oxygen supply to the organs because of poor circulation ECG
Modifiable Factors: Excess alcohol intake Smoking Stress High salt intake Low potassium intake Lifestyle High cholesterol intake
Non- Modifiable Factors: Age Gender Family History Obesity Hypertension Polycystic kidney disease
Changes in arteriolar bed Increase systemic vascular resistance
Increase afterload
Decrease blood flow to the organs specifically in the kidneys
Conversion of angiotensin to angiotensin I
Converted angiotensin II by ACE in the lungs
Angiotensin II constricts arteries
Stimulates to increase aldosterone
HYPERTENSION
Amlodipine
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryGenel Joseph Jacildo Peñaflor100% (2)
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramJessica Peñamora100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 pagesPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Case Study Heart Attack PDFDocument30 pagesCase Study Heart Attack PDFtkgoon634950% (2)
- Case Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke (Subarachnoid Hemorrhage)Document69 pagesCase Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke (Subarachnoid Hemorrhage)verna88% (24)
- Pathophysiology Diagram - StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram - Strokemisstheatricality130100% (1)
- Case Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument69 pagesCase Presentation of Hemorrhagic Stroke Subarachnoid HemorrhageShin FerranculloPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMaureen Balagtas89% (9)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Heart FailureGeevine Cansino100% (2)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Hemorrhagic StrokeMerlash MerlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument16 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageErika NaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyPas encore d'évaluation
- CvaDocument170 pagesCvaApril Jumawan ManzanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument60 pagesGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.6Document19 pagesAneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.6Aldy Setiawan PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCPas encore d'évaluation
- SUBarachnoid HemorrhageDocument4 pagesSUBarachnoid Hemorrhagekhadzx100% (2)
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument12 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageStephanie SarjonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument30 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeAstrina SupandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument2 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Signs and SymptomsDocument8 pagesSubarachnoid Hemorrhage: Signs and SymptomsFatima LacsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Case-Study Hemorrhagic-Stroke FinalDocument102 pagesCase-Study Hemorrhagic-Stroke FinalAngela QuiñonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument8 pagesCerebrovascular Accidentplethoraldork100% (10)
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Document8 pagesCerebral Concussion (Mini Case Study)Airalyn Chavez AlaroPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctDocument38 pagesA Case Presentation of Cerebrovascular Accident InfarctKaycee Toling100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Anatomy Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesAnatomy Myocardial InfarctionLyka Milo AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyKarla Karina Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseNursesLabs.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Document10 pagesPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Myocardial InfarctionYhr YhPas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Case On Intracranial HemorrhageDocument17 pagesCase On Intracranial HemorrhageLorebell100% (2)
- CVA PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular Accident I. General Medical Background A. DefinitionDocument11 pagesCerebrovascular Accident I. General Medical Background A. Definitionner100% (1)
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument3 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageTristan Cunanan0% (1)
- Biologic Crisis:: Prepared By: Recitas, Anna Lou G. BSN-4 Sn-DoscstDocument64 pagesBiologic Crisis:: Prepared By: Recitas, Anna Lou G. BSN-4 Sn-DoscstDonna Solamo TalabocPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesPathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionronvhadzPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulation: Ms. Jonalyn P. SantosDocument18 pagesCirculation: Ms. Jonalyn P. SantosHoward John M. RamiterrePas encore d'évaluation
- CHFSP 2005Document36 pagesCHFSP 2005Andy F MonroePas encore d'évaluation
- Heart FailureDocument10 pagesHeart Failureurmila prajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument38 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSalman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock PresentationDocument21 pagesShock Presentationapi-283170120Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asinas Shairabsn3aDocument28 pagesAsinas Shairabsn3aJoshua ApolonioPas encore d'évaluation