Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rotationla Motion Answer Book PDF
Transféré par
Vijaykumar Varma0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues3 pagesRotational motion
Titre original
Rotationla Motion answer book.pdf
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRotational motion
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues3 pagesRotationla Motion Answer Book PDF
Transféré par
Vijaykumar VarmaRotational motion
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Answer Key for Rotational Motion XII-Physics (2 July 2012)
Duration:1 Hr 35 weightage
Q.-1 M.I. (2 Marks)
Correct Denition: I = M R2 - (1)
1 Dimension :M L2 - ( 2 )
SI unit: kg.m2 - ( 1 ) 2
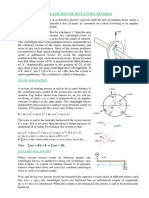
Q.2- Principle of Parallel Axis (4 Marks)
Correct Statement : The moment of inertia about any axis parallel to and a distance D away from this axis is ID = ICM + M D2 - (1) Proof: r = x2 + y 2 => I = (x2 + y 2 )dm - (1) [(x + x)2 + (y + y)2 ]dm - (1) y dm = 0 - (1)
x = x + xCM , y = y + yCM => I = by denition of CM x dm = 0 and
Q.3- Problem (2 Marks)
1 KET otal = 2 M v 2 + 1 I 2 - (1) 2
ISolidSphere = 2 M R2 ( 1 ) 5 2 KET otal = 1 M v 2 + 2
12 2 2 5 M (R) 1 - ( 2 )
Q.4- Problem (3 Marks)
Conservation of Angular Momentum => (I)initial = (I)f inal - (1) => I1 1 + I2 2 = I - (1) Correct Substitution and answer = 200rpm - (1)
Q.5- Derivation of KE (3 Marks)
KE = 1 M v 2 => KE = 2 => KE => I = =1 2 i=1
i=1 2 mi ri 2 i=1
Ki - (1)
- (1)
1 2 mi ri => KE = 2 I 2 - (1)
Q.6- Conservation of Angular Momentum (3 Marks)
Correct Statement: For rotation about a xed axis, and if the external torque is zero, then Lz = I = constant - (1) Correct Explanation:Stretching the arms increases I about the axis of rotation, resulting in decreasing the angular speed . Bringing the arms closer to the body has the opposite eect. - (1) Correct Example: A circus acrobat and a diver take advantage of this principle. Also, skaters and classical, Indian or western, dancers performing a pirouette on the toes of one foot display mastery over this principle. - (1)
Q.7- MI of thin uniform rod (3 Marks)
dm = dx =
M L dx
- (1) r2 dm - (1)
1 2 12 M L
With r = x, => Iy = => Iy = x2 M dx = L
- (1)
Q.8- Radius of Gyration (2 Marks)
Correct Def: Radius of gyration K of rigid body is dened by the expresI sion K 2 = M - (1) Correct Signicance: Radius of gyration K is the distance between an imaginary point mass M and the axis of rotation such that I for the point mass about that axis is the same as that for the rigid body - (1)
Q.9- Problem (2 Marks)
Formulae: K 2 =
I M , EKE
1 2
I 2 - (1)
=> I = K 2 M = 64 102 kg.m2 - (1) EKE =
1 2
I 2 = 8J - (1)
10
Q.10- Problem (3 Marks)
Formula: Conservation of Angular Momentum => I1 1 = I2 2 - (1) I2 = 0.6 I1 ; 1 = 120rpm - (1) 1 = 200rpm - (1) 2
11
Q.11- Problem (3 Marks)
Formulae: (I)initial = (I)f inal - (1) => Idisc i = If f = (mr2 + Idisc )f - (1) Proper substitution and correct answer Idisc = 7.5 103 g.cm2 - (1)
12
Q.12- Problem (3 Marks)
; K2 =
I M
Formulae: I =
- (1)
Substitution and answer => I = Substitution and answer K =
= 20kg.m2 - (1) = 0.707m - (1)
I M
13
Q.12- Problem (2 Marks)
i 2 mi ri = M R2 - (1)
Formulae: I =
2 => I1 = 2 M R1 ; I2 = 2 M (2R1 )2 = 4I1 3 3 => I2 = 4 I1 - (1)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Blue Star Master ManualDocument37 pagesBlue Star Master ManualGration100% (7)
- Banked Curves ReportDocument32 pagesBanked Curves Reportfrancisco bordey viernesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lanzamiento Bola BaseballDocument48 pagesLanzamiento Bola BaseballJhon Freddy Torres GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - Melc 1: (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1)Document7 pagesPre-Calculus Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - Melc 1: (Stem - Pc11T-Iia-1)raymond galagPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano AluminumDocument11 pagesNano AluminumVijaykumar VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Microdrop ControlDocument5 pagesMagnetic Microdrop ControlVijaykumar VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetofluidics SpreadingDocument11 pagesMagnetofluidics SpreadingVijaykumar VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Shield Gas On Thermal Plasma NanomaterialsDocument3 pagesEffect of Shield Gas On Thermal Plasma NanomaterialsVijaykumar VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Install Simply Track For 10mDocument7 pagesHow To Install Simply Track For 10mDimitri KABOREPas encore d'évaluation
- ch4 PDFDocument123 pagesch4 PDFPaula MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Problems-Balancing-Rotating MassesDocument5 pages4-Problems-Balancing-Rotating MassesvrushPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Translation MatricesDocument8 pages03 Translation MatricessolteanPas encore d'évaluation
- Irbp LDocument2 pagesIrbp LMaurício Jorge CostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DDocument1 pageSynopsis Synopsis Synopsis Synopsis: D D D DAishwarya ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Testing of Unbalanced Mass Mechanical Vibration ExciterDocument6 pagesDesign and Testing of Unbalanced Mass Mechanical Vibration ExciteresatjournalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Jet Fire Report Workspace Phast ExampleDocument136 pagesJet Fire Report Workspace Phast ExampleAchraf Ben DhifallahPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Active Notebook Grade 11 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONDocument12 pagesMath Active Notebook Grade 11 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONahmad athallahPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Build A Self Balancing Gyroscopic VehicleDocument48 pagesHow To Build A Self Balancing Gyroscopic VehicleJames Demello0% (1)
- Earth's Rotation and RevolutionDocument48 pagesEarth's Rotation and RevolutionArenas JenPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.1. Weinberg (1963)Document23 pages10.1. Weinberg (1963)jorefe12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Section 6-4: Volumes of Solids of Revolution / Method of CylindersDocument3 pagesSection 6-4: Volumes of Solids of Revolution / Method of Cylindersblack bloodPas encore d'évaluation
- BRIDGE DESIGN Specifications by Practise EngineersDocument152 pagesBRIDGE DESIGN Specifications by Practise Engineersveeru naidu75% (4)
- Cam-Follower: GUI Familiarity Level Required: Lower Estimated Time Required: 25 MinutesDocument25 pagesCam-Follower: GUI Familiarity Level Required: Lower Estimated Time Required: 25 MinutesDrSn PadhiPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYS 2425 Exp 8 ManualDocument7 pagesPHYS 2425 Exp 8 ManualMulangira MulangiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Estimation ManualDocument57 pagesAdvanced Estimation ManualOrestes Gomez GPas encore d'évaluation
- LibreOffice Draw 7Document20 pagesLibreOffice Draw 7Neuer FamilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument53 pagesClass 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functionsmr_agarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure (Part 1 Sentence Completion)Document2 pagesStructure (Part 1 Sentence Completion)Yeni PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 5Document8 pages2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 5Sergio Bernal OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cases and How To Solve The Triangle (Note: Solving The Triangle Means Finding The Measures of Its Angles and Sides)Document7 pagesCases and How To Solve The Triangle (Note: Solving The Triangle Means Finding The Measures of Its Angles and Sides)Robert Kier Tanquerido TomaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Practice Test Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGear Practice Test Answer KeykinikinayyPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric FormulasDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Formulasanshumansingh042006Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSC Solid State Physics Lecture#3Document17 pagesMSC Solid State Physics Lecture#3Shehzad AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- A 181731Document624 pagesA 181731James Clavert100% (1)