Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Various Types of Generators: Form 3 Chapter 8
Transféré par
Linda ChanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Various Types of Generators: Form 3 Chapter 8
Transféré par
Linda ChanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Form 3 Chapter 8
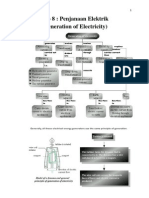
Various Types of Generators 1. A generator consists of copper coils surrounded by magnets as shown in Figure beside. Turbines are usually connected to the copper coils of the generator by a shaft. When the turbines are turned, the spinning shaft will cause the copper coils to spin and electrical energy is produced. 2. Thermal power station Fossil fuels such as petroleum, coal and natural fuel are used to heat water in boiler to produce steam under high pressure. The steam is used to turn turbines of a thermal generator. The steam then cools in a condenser and becomes water again. The water is channelled back to the boiler.
3. 3.
Gas turbine power station
In the station, natural gas or petroleum is burned in a high-pressure combustion chamber. The hot gases produced are used to turn turbines of a gas turbine generator. The turbines also spin a compressor to provide high-pressure air to the combustion chamber to enable efficient burning of fuel. 4. Hydroelectric power station In the station, water flowing in high speed and pressure from the dam forces the turbines to rotate the generator to produce electrical energy. 5. Nuclear power station
Radioactive substances such as uranium and plutonium are used to produce heat by nuclear reactions in a reactor. The heat is used to heat water to produce steam. The steam is then used to turn the turbines of a nuclear generator. 6. Diesel power station uses a
1
Form 3 Chapter 8
diesel motor to turn the copper coils of the generator. Diesel generators are usually used to produce small supplies of electrical energy to small villages.
7.
Biomass power station
The composition of the remains and wastes of living things by bacteria produces methane. Methane can be used as a fuel and it can be burnt to provide energy to turn turbines and produce electrical energy. 8. Solar power station a. There are two ways to tap solar energy to produce electrical energy. b. Use of solar cells to convert energy from the sun into electrical energy. c. Use of solar energy to heat up water to produce steam. The steam is then used to turn turbines and generate electrical energy.
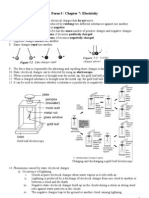
Transformer 1. 2. A transformer is a device used for raising or lowering the voltage of alternating current. A simple transformer consists of a soft iron core with two coils of wire on each side of the core.
A transformer 3. 4. 5. 6. that is connected to the output is called the secondary coil.
Symbol of a transformer
The first coil that is connected to a power supply or the input is called the primary coil. The second coil In a transformer, when an alternating current passes through the primary coil (input), the iron core As the direction of the alternating current keeps changing, the magnetic field created also keeps changing. This changing magnetic field induce an alternating current and an alternating voltage in the secondary
becomes an electromagnet.
coil (output). 7. a The output voltage produced in the secondary coil depends on: the input voltage, and
2
Form 3 Chapter 8
b 8.
the number of turns at the primary coil and the secondary coil on the soft iron core. The relationship between the voltage across the primary coil and the secondary coil:
9.
There are two types of transformers, step-up transformer and step-down transformer.
10. The table shows the differences between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer. Step-up transformer Step-down transformer
Symbol:
Symbol:
The number of turns on the secondary coil is more than the number of turns on the primary coil The output voltage is more than the input voltage The output current is less than the input current
The number of turns on the primary coil is more than the number of turns on the secondary coil The output voltage is less than input voltage The output current is more than the input current
Electricity Transmission and Distribution System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The generators at the power station produce alternating current with a voltage of 11 kV or 25 kV. When the alternating current enters the step-up transformer station, the voltage is increased to 132 kV or The increase in voltage through aluminium or copper cables is to reduce energy loss in the form of heat The Malaysian National Grid Network consists of a network of transmission cables which interconnects This is to ensure a continuous supply of electrical energy to all parts of the country in case of blackouts in At the end of the grid, the alternating current flows through the switch zone which controls the input of Then, the alternating current flows through a series of step-down transformers and switch zones thus
275 kV or 500 kV. when the electrical energy is transmitted over a long distance through the National Grid Network. main power stations in Peninsular Malaysia. certain areas. energy into the National Grid Network. lowering the voltage gradually as shown in the figure.
Form 3 Chapter 8
Electrical energy transmission and distribution system
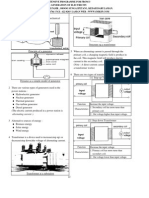
Electrical Supply and Wiring System At Home 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Electricity supply to homes consists of alternating current at 240 V by the mains wire and distributed Single-phase wiring is used in most homes where the consumption of electricity is not high, with a The single-phase wiring consists of a live wire, a neutral wire and an earth wire. The other type of wiring, known as three-phase wiring, consists of three wires carrying the current into Three-phase wiring is used in hospitals, shopping complexes and larger homes where many electrical The main components of the electrical wiring system in homes are shown in the figure. throughout the home by a wiring network known as the wiring system in the home. voltage of 240 V.
the home and one wire taking it away, with a voltage of 415 V. appliances like air conditioners and water heaters are used.
Electrical wiring system in home
4
Form 3 Chapter 8
7.
The table below shows the components and their functions. Function Controls the amount of current to be supplied to the electrical appliances in homes. It will break the circuit if there is excessive current flowing into the house Measures the electrical energy used in the house Controls the electric current that flows through all the electrical appliances Breaks off the flow of electric current when there is a short circuit, leakage of current or thunder and lightning Contains fuses that protects individual circuits throughout the house by breaking oft the electric current when there is a short circuit
Main component Main fuse
Electric meter (joule meter / kilowatt-hour meter) Main switch Earth leakage circuit breaker and miniature circuit breaker Fuse box
8. 9.
The 3-pin plug contains three wires and a fuse. Each wire has a certain colour based on the international colour code.
3-pin plug
The Cost of Electrical Energy Usage 1. 2. 3. 4. Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is converted to other forms of energy. The S.I. unit for electrical power is watt (W) or joule per second (J/s). Electrical power can be measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW). The amount of electrical energy used by an electrical appliance depends on:
the electrical power of the appliance; how long the appliance is in use (time taken for using the appliance).
5.
The relationship between power, voltage and current can be represented by the following formula:
5
Form 3 Chapter 8
6.
To calculate the cost of using an electrical appliance, the following formula is used:
The Functions of Fuse and Earth Wire 1. 2. 3. A fuse is a safety device used to protect an electric circuit against excessive current. It consists of a wire The wire of the fuse which is made from an alloy of tin and lead has a low melting point and will Short circuit (a lower-resistance path that allows current to flow through without passing through the that will melt at a certain temperature. therefore melt when excess current flows through it. load) When a short circuit occurs, there is low resistance and a large amount of current flowing in the circuit. This may cause a fire and damage to electrical appliances. To prevent this, fuses are used. The large current that flows during a short circuit will cause the wire of the fuse to heat up and melt. The circuit then becomes incomplete and current stops flowing in the circuit. After the circuit problem has been fixed and the fuse replaced, the circuit can then operate normally again. In electrical appliances that have complex circuits, such as televisions, radios and air-conditioners, a broken wire may touch another wire resulting in a short circuit. A short circuit also occurs when bare wires touch each other. 4. In the home electrical wiring system, there are two main types of fuses. In a replaceable wire fuse, a length of wire is attached to the terminals. The wire can be replaced when it breaks due to excessive current. Replaceable wire fuse used in main fuse box where the fuse wire can be replaced if it is blown'. The other type of fuse, called the cartridge fuse, consists of a wire enclosed in a cylindrical tube made of an insulating material. Cartridge fuse used in 3-pin plugs where the fuse wire cannot be replaced if it has melted.
A replaceable wire fuse 5. 6. 7. ratings are needed to protect the electrical appliances.
A cartridge fuse
Different electrical appliances require different amounts of current to function. Therefore, different fuse The rating of a fuse is the maximum amount of current that can flow through the fuse without the wire of The most suitable fuse has a rating slightly higher than the maximum current that can flow through an
6
the fuse melting. The rating of a fuse is always indicated on the fuse. electrical appliance.
Form 3 Chapter 8
8. 9.
The common ratings of fuses used are 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 10A and 13A. A suitable rating of a fuse can be determined by using the following formula:
10. The earth wire found in a 3-pin plug is another safety device which protects a person from receiving electric shocks or from being electrocuted. 11. The earth wire connects the metal casings of electrical appliances such as televisions and electric kettles directly to the ground. 12. When a 3-pin plug of an electrical appliance is plugged into an electrical socket, the metal casing of the electrical appliance brings excess current or any leakage of current to the ground safely.
The Importance of Safety Pre Cautions in the Use of Electricity Improper use of electrical appliances can cause electrical accidents and endanger the life of a person using them. Electrical accidents are usually caused by human negligence, overloading and short circuit. Main causes of electrical accidents Connecting more than two electrical appliances at the same socket and causing overloading Touching electrical appliances or sockets with wet hands Frayed / worn and exposed wire cables Poor or loose connection between the 3-pin plug and the socket Repairing electrical appliances that are connected to the mains supply Replacing a fuse with a copper wire Safety and precautionary measures Carbon dioxide fire extinguishers are used to put out fires caused by electric current. Fit homes with safety features such as miniature circuit breaker (MCB) and the earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) which breaks off the circuit when there is excess current flowing it. Cover electrical sockets so that children cannot reach them. Get a qualified electrician to repair electrical appliances or wiring systems at home. Switch off the mains supply in case of a short circuit. In case of electric shocks or electrocution: immediately switch off the mains supply; move the victim away from the source of electrical appliance or wires by using an insulator such as a dry wooden stick; try to resuscitate the victim by performing artificial respiration if the victim is not breathing; call for an ambulance or seek medical help as soon as possible.
The Importance of Conserving Electricity
7
Form 3 Chapter 8
We should try to conserve electrical energy to reduce wastage. Some ways of using electrical energy efficiently and reducing wastage Use electrical appliances only when required and switch off any appliance when not in use. Use air conditioners sparingly. When buying electrical appliances, choose wisely by studying and comparing the energy labels on the appliances. Avoid opening and closing the refrigerator door frequently. If there is a shortage of electricity supply, many of our activities will be disrupted, such as: factories that depend on electricity cannot function. computers in homes and offices cannot be used.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- F3 Chapter 8 - Generation of ElectricityDocument5 pagesF3 Chapter 8 - Generation of Electricitylccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 3Document63 pagesScience Form 3qq23583% (6)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 8 - Generation of Electricity PDFDocument7 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 8 - Generation of Electricity PDFFarah Sofea Razali50% (8)
- Bab 8-Sains Form 3Document19 pagesBab 8-Sains Form 3Mohamad TarmiziPas encore d'évaluation
- Submission 27 - David Roy PackhamDocument16 pagesSubmission 27 - David Roy Packhamaussienewsviews5302Pas encore d'évaluation
- Old Testament and Anti-Usurial LawsDocument0 pageOld Testament and Anti-Usurial LawsRyan HayesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hegel Branch, Ethel L. Chandler and Donald Chandler v. James S. Steph, Trustee, Chickasaw Lumber Company of Duncan, Oklahoma, Inc., 389 F.2d 233, 10th Cir. (1968)Document4 pagesHegel Branch, Ethel L. Chandler and Donald Chandler v. James S. Steph, Trustee, Chickasaw Lumber Company of Duncan, Oklahoma, Inc., 389 F.2d 233, 10th Cir. (1968)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Titan AR 2002-03Document10 pagesTitan AR 2002-03bondamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity AssignmentDocument11 pagesEquity AssignmentFarahSuhailaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1100-1200 History of The Catholic ChurchDocument74 pages1100-1200 History of The Catholic ChurchShawn ArevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Space Weather PresentationDocument13 pagesChapter 9 Space Weather PresentationnaomiPas encore d'évaluation
- O'Sullivan V Management Agency & Music LTDDocument4 pagesO'Sullivan V Management Agency & Music LTDJoey WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Growth Rings - Tree Knowledge - Booklet - Forest Academy - DomtarDocument6 pagesAnnual Growth Rings - Tree Knowledge - Booklet - Forest Academy - DomtarGek CagatanPas encore d'évaluation
- Supreme Court of The State of New York County of New York: Defendal TsDocument28 pagesSupreme Court of The State of New York County of New York: Defendal TscorruptioncurrentsPas encore d'évaluation
- Taeusch C.-History of UsuryDocument29 pagesTaeusch C.-History of UsuryRaicea Ionut GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity FactsDocument16 pagesElectricity Factsapi-313455759Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Chapter 1) Organisation of Plant Tissue and GrowthDocument31 pages(Chapter 1) Organisation of Plant Tissue and Growthjolene ang min huiPas encore d'évaluation
- Void Judgment Info Great StuffDocument5 pagesVoid Judgment Info Great StuffTony HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Energi 1 PDFDocument7 pagesFree Energi 1 PDFFatekhunFarisPas encore d'évaluation
- 1849 1862 Statutes at Large 780-974Document200 pages1849 1862 Statutes at Large 780-974ncwazzyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Best and Greenest Composting of Your Household Waste EVER!!!!Document1 pageThe Best and Greenest Composting of Your Household Waste EVER!!!!shawnleegabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Pocket Allen-Bradley Heater Sizing ChartDocument1 pagePocket Allen-Bradley Heater Sizing ChartshawnleegabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Man Windmill - 8x1M 1° JULDocument8 pagesIron Man Windmill - 8x1M 1° JULcristobal_tl2277Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Space Exploration: ThemeDocument13 pagesEarth and Space Exploration: ThemeMritheya RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Spectrum & Relationship Between Energy, FrequencyDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum & Relationship Between Energy, Frequencyapi-285612479100% (2)
- Introduction To Biochemistry USPDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry USPSyifaAnandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 1003: TA-in-charge: SONG Bo (Email: Bsong@connect - Ust.hk)Document33 pagesPhysics 1003: TA-in-charge: SONG Bo (Email: Bsong@connect - Ust.hk)Ho Lan AuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Practical Guide To Free Energy' Devices: What Is An Electrolyser?Document47 pagesA Practical Guide To Free Energy' Devices: What Is An Electrolyser?lucas123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water More Precious Than Gold Cloze Passage 1Document5 pagesWater More Precious Than Gold Cloze Passage 1api-287416221100% (1)
- The New DealDocument18 pagesThe New Dealapi-271172081Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Biological AgricultureDocument5 pagesWhat Is Biological AgricultureFelicianna Ashwinie StanleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Complaint & Jury Demand Filed 1-26-21Document22 pagesComplaint & Jury Demand Filed 1-26-21WXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitPas encore d'évaluation
- High Frequency Dynamo and Tesla CoilDocument4 pagesHigh Frequency Dynamo and Tesla CoilAlejandro MagninPas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Aspects of International OrganizationsDocument14 pagesLegal Aspects of International OrganizationsAbhimanyu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Erlandson v. Northglenn Municipal Court, 528 F.3d 785, 10th Cir. (2008)Document10 pagesErlandson v. Northglenn Municipal Court, 528 F.3d 785, 10th Cir. (2008)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Banks and Fiduciary RelationshipsDocument19 pagesBanks and Fiduciary RelationshipsElisabeth ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro CultureDocument65 pagesElectro CultureJake WattsPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is An Earthship?Document2 pagesWhat Is An Earthship?Ana SakvarelidzePas encore d'évaluation
- D14 Updated 24 Dec 2007 PDFDocument14 pagesD14 Updated 24 Dec 2007 PDFVinayak SanghaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Clogging The Equity of Redemption: An Outmoded Concept?: L W B DDocument18 pagesClogging The Equity of Redemption: An Outmoded Concept?: L W B Dadvopreethi100% (1)
- A Tuned Rectifier For RF Energy Harvesting From Ambient RadiationsDocument6 pagesA Tuned Rectifier For RF Energy Harvesting From Ambient RadiationsAppu ManiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cook County Sheriff Tom Dart Sued - Minor Child RapedDocument15 pagesCook County Sheriff Tom Dart Sued - Minor Child RapedTrue News-usaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Wheel EngineeringDocument10 pagesWater Wheel EngineeringgkrstinPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Hydrogen Generator PDFDocument0 pageAtomic Hydrogen Generator PDFmanos306Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3A Contractual Estoppel TFDocument17 pages3A Contractual Estoppel TFMutahar SahtoPas encore d'évaluation
- Policies: Attendance - ID & Uniform - Quizzes - Grading System - 40% Quizzes - 30% Manual - 10% Exam - 60%Document67 pagesPolicies: Attendance - ID & Uniform - Quizzes - Grading System - 40% Quizzes - 30% Manual - 10% Exam - 60%kamiya008100% (1)
- Magna Carta Translated From LatinDocument9 pagesMagna Carta Translated From LatinAldivam SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lightning Arresters Definition and How It WorksDocument61 pagesLightning Arresters Definition and How It WorkslgaungPas encore d'évaluation
- RE BANSC-2012-187 TD Bank N.A. V, Twila A. Wolf Case With Exhibits 09-18 and 22 2012 SubmissionsDocument110 pagesRE BANSC-2012-187 TD Bank N.A. V, Twila A. Wolf Case With Exhibits 09-18 and 22 2012 SubmissionsCharlton ButlerPas encore d'évaluation
- ATF Form 4473Document6 pagesATF Form 4473Bob PricePas encore d'évaluation
- Classification PDFDocument34 pagesClassification PDFFaiaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant HormonesDocument40 pagesPlant HormonesSakina26100% (1)
- Any GASOLINE Car CAN Run ON WATER ONLY!!!this IS SCIENTIFIC PROOF!!!Document7 pagesAny GASOLINE Car CAN Run ON WATER ONLY!!!this IS SCIENTIFIC PROOF!!!kremenePas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 3-Generation of ElectricityDocument15 pagesScience Form 3-Generation of Electricitymohamedsehat100% (7)
- 1.1 Electrical InstallationDocument44 pages1.1 Electrical InstallationVimal MathivananPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Electricity Supply System 070323Document17 pagesChapter 1 Electricity Supply System 070323Kan Fock-KuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Final AssignmentDocument6 pagesDistribution Final AssignmentGabrielGrecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document9 pagesChapter 8Rozita JamaludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Electricity Supply SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Electricity Supply SystemKan Fock-KuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical ElectricityDocument10 pagesPractical Electricityanwar9602020Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of Feeling WordsDocument4 pagesList of Feeling WordsLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Poem Form 1Document14 pagesPoem Form 1vino7850% (2)
- Chapter 7Document9 pagesChapter 7Linda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Feeling WordsDocument4 pagesList of Feeling WordsLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Teenagers NowadaysDocument9 pagesTeenagers NowadaysLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Teenagers NowadaysDocument9 pagesTeenagers NowadaysLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Teenagers Nowadays Public SpeakingDocument1 pageTeenagers Nowadays Public SpeakingLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Easy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet & Sticking To ItDocument5 pagesEasy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet & Sticking To ItLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Easy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet & Sticking To ItDocument5 pagesEasy Tips For Planning A Healthy Diet & Sticking To ItLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- The ControllersDocument10 pagesThe ControllersLinda ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Capital Goods - HSBC Jan 2011Document298 pagesIndian Capital Goods - HSBC Jan 2011didwaniasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Book-2Document37 pagesChapter 4 Book-2sufiiiiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2036 2 MarksDocument19 pagesEE2036 2 MarksSaravanan RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission PricingDocument57 pagesTransmission PricingMuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Pumped Hydro Energy StorageDocument19 pagesA Review of Pumped Hydro Energy StorageAdi PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Line Protection: Mahendra S Hada PowergridDocument48 pagesLine Protection: Mahendra S Hada PowergridshashankaumPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 - 25 KV Traction Power Supply System - RailElectricaDocument4 pages05 - 25 KV Traction Power Supply System - RailElectricarajimuruganPas encore d'évaluation
- PDC - Distribution ManagementDocument13 pagesPDC - Distribution ManagementMirzi Ann Sayson RegaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Line Carrier CommunicationDocument4 pagesPower Line Carrier Communications_123_rana3519100% (1)
- Training Syllabus Electrical DesigningDocument8 pagesTraining Syllabus Electrical Designingzaheer2931Pas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Training ReportDocument21 pagesIndustrial Training ReportAsim iqbal438Pas encore d'évaluation
- Xiao Kai, HU Qingchun, XIE Wenping, WEN Jiaqi, LUO Xiaoyu, LIN ZhishengDocument8 pagesXiao Kai, HU Qingchun, XIE Wenping, WEN Jiaqi, LUO Xiaoyu, LIN ZhishengEmir JusićPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Community - First Indicative List of ProjectsDocument38 pagesEnergy Community - First Indicative List of ProjectsFaruk AtalarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tariff Order 2010-11Document187 pagesTariff Order 2010-11Nannapaneni P. ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Trends in Power SystemDocument43 pagesRecent Trends in Power SystemSayonsom Chanda100% (1)
- ME 403 Power Plant Engineering: Maj Najmus Saquib Sifat Military Institute of Science & TechnologyDocument21 pagesME 403 Power Plant Engineering: Maj Najmus Saquib Sifat Military Institute of Science & TechnologysaquibPas encore d'évaluation
- TWS FL-8-edit Presentation-Panca-1Document52 pagesTWS FL-8-edit Presentation-Panca-1Proteksitrans1 p3bsPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigned People Vs EstellaDocument10 pagesAssigned People Vs EstellaJustin Andre SiguanPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Lines P1Document6 pagesTransmission Lines P1Janmarc CorpuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Agricultural ElectrificationDocument335 pagesAgricultural ElectrificationAbas S. AcmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On The Method of Calculating Temperature Rise of TransformerDocument5 pagesStudy On The Method of Calculating Temperature Rise of Transformersametb_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final TNUoS Tariffs 201415Document35 pagesFinal TNUoS Tariffs 201415Cecy JonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual On Transmission Line TowersDocument79 pagesManual On Transmission Line TowerselsayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Xenturic Engineering ProfileDocument47 pagesXenturic Engineering ProfileOsiPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE305 Part02Document67 pagesEEE305 Part02qwertPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Power Transmission TechnologyDocument10 pagesDC Power Transmission TechnologyDrVikas Singh BhadoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEEE-PES PSRC Report On Design and Testing of Selected System Integrity Protection SchemesDocument5 pagesIEEE-PES PSRC Report On Design and Testing of Selected System Integrity Protection Schemesdes1982Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power and Distribution TransformerDocument7 pagesPower and Distribution TransformerlegasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Board of Assessment Appeals v. Meralco 10 SCRA 63Document4 pagesBoard of Assessment Appeals v. Meralco 10 SCRA 63Lexa L. DotyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation Method To Estimate Electrostatic and Electromagnetic Induction in The Design of Telecommunication FacilitiesDocument4 pagesCalculation Method To Estimate Electrostatic and Electromagnetic Induction in The Design of Telecommunication FacilitiesReza AfarandPas encore d'évaluation