Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
01 - Normal Newborn and Neurologic Exam
Transféré par
Luis Elijah De CastroCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
01 - Normal Newborn and Neurologic Exam
Transféré par
Luis Elijah De CastroDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
THE NORMAL NEWBORN Fetal growth & development Milestones of Prenatal development Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 25 28 38 Developmental events Fertilization &
implantation, beginning of embryonic period Endoderm & ectoderm appear (bilaminar embryo) First missed menstrual period; mesoderm appears (trilaminar embryo); somites begin to form Neural folds fuse; folding of embryo into human-like shape; arm & leg buds appear; crown-rump length 4-5 mm Lens placodes, primitive mouth, digital rays on hands Primitive nose, philtrum, primary palate, crown-rump length 21-23 mm Eyelids begin Ovaries & testes distinguishable Fetal period begins; crown-rump length 5 cm; weight 9g External genitals distinguishable Usual lower limit of viability; weight 460 grams; length 19 cm Third trimester begins; 900 grams; length 25 cm Eyes open; fetus turns head down; weight 1,300 grams Term
Somatic Development Embryonic Period Implantation begins by 6 days post conceptual age By 2 weeks, implantation is complete & uteroplacental circulation has begun By 3 weeks, appearance of the primitive neural tube & paired blood vessels; paired heart tubes begin to pump By 4-8 weeks, budding of arm & legs, appearance of branchial arches which will form the maxilla, mandible, palate, external ear By the end of week 8, this period closes Fetal period Begins at 9th week By 10th week, the face is recognizably human, counter-clockwise rotation of intestinal contents By 12th week, the gender of external genitalia is established Lung development starts By 20-24 weeks, primitive alveoli, surfactant production have begun 3rd week a neural plate appears on the ectodermal surface Neural tube central nervous system Neural crest peripheral nervous system 5th week forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain Myelinization begins at midgestation & continues until 2 years old Fetal behavioral development 8 weeks: muscle contractions, lateral flexion movements 13-14 weeks: breathing & swallowing motion 17 weeks: grasp reflex appears, well-developed at 27th week 26 weeks: eye opening 3rd trimester: respond to external stimuli with heart rate elevation & body movements
Neonatal History Gestational/ Maternal History Mothers general data: Mothers & fathers name, age, gravidity & parity (G1P0), race, birthplace, present address, religion, educational attainment, nutritional status, state of health, illnesses before & during pregnancy, familial diseases, infections, prenatal checkup, intake of drugs/ alchohol, smoking, roentgen exposure, familial diseases, outcome of previous pregnancy, duration of gestation Perinatal History Hours of labor Start of regular uterine contractions Rupture of bag of water Hours of delivery of the baby & placenta Obstetrical blood loss Fetal heart tone characteristic Manner of delivery Person who assisted the delivery Neonatal History Presenting part upon delivery Spontaneous respiration or required resuscitation APGAR score Presence of cyanosis, pallor, jaundice, convulsions, hemorrhage Abnormal physical examination findings Type of feeding How long did the baby stayed in the nursery/ NICU Any use of antibiotics Hepatitis B vaccine given at birth Newborn/ Hearing screening done Neonatal History should 1. Identify disabling diseases that are amenable to prompt preventive action or treatment (e.g. RDS) 2. Anticipate condition that maybe of late importance (e.g. gonococcal conjunctivitis) 3. Uncovers possible causative factors that may explain pathologic conditions regardless of their immediate future significance (e.g. metabolic diseases) Physical Examination of the Newborn Infant Three periods of examination 1. Immediately after delivery (focus on congenital problems & adaptation to extra uterine life, birth injuries) 2. At 24 hours of life (more detailed examination) 3. Upon discharge (If possible together with the mother) Anthropometric measurements Birth weight (normal: 3.4 kg; boys slightly > girls) Birth length (normal: 50 cm) Head circumference (normal:35 cm) Chest circumference (HC > (1-2 cm) than CC) Abdominal circumference Physical Examination Pulse/ cardiac rate: 120-160 bpm Respiratory rate: 30-60 breaths/ min Blood pressure: Not routinely taken unless the baby is ill or with heart murmur
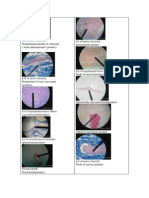
General appearance Posture (Flexion) Physical activity Edema Muscle tone Level of alertness (18-20 hours sleep) Color (cyanotic, acrocyanotic, pallor, plethoric, jaundice) Skin Vasomotor instability; mottling, acrocyanosis (blue discoloration, coldness, sweating of extremities, especially hands), harlequin color change Cyanosis Pallor Plethora beefy red coloration of a newborn; boiled lobster hue of the infants skin caused by an unusually high proportion of erythrocytes per volume of blood Jaundice or icterus Vernix caseosa: Grayish white cheeselike substance, consisting of sebaceous gland secretions, lanugo & desquamated epithelial cells that cover the fetus skin Erythema toxicum (eosinophils): Pink popular rash frequently superimposed with vesicles or pustule; rash appears within 24-48 hours after birth & disappear spontaneously after several days (benign) Pustular melanosis (neutrophils) Milia: Nonpathologic dermatological condition characterized by minute epidermal cysts containing keratinous debris that occur on the face occasionally on the trunk of the newborn Milaria: Miunte vesicles & papules often with surrounding erythema, caused by occlusion of sweat ducts during times of exposure to heat & high humidity Mongolian spots: Benign bluish-black macule, between 2 & 8 cm, occurring over the sacrum & on the buttocks of some newborns. It usually disappears during early childhood Capillary hemangioma: A blood-filled birthmark or benign tumor consisting of closely packed small blood vessels, commonly found during infancy. It first grows, them may spontaneously disappear in early childhood without treatment (vascular tumor) Meconium staining of skin, cord & nails (post-term) Lanugo (preterm) Vellus hair (term) Gelatinous skin Parchment-like skin (post-term) Tuft of hair Amniotic band (secondary to ruptured amniotic membrane/ vascular compromise) Storks bite (benign vascular hematomas) Pigmented nevi Petechiae/ purpura Head/ skull Molding: The natural process by which a babys head is shaped during labor as it is squeezed into & through the birth passage by the forces of labor; the head often becomes elongated & the bones of the skull maybe caused to overlap slightly at the suture lines. Usually resolved during the 1st few days of life
Cephalhematoma (10-20% may have skull fractures) Caput succedaneum: A localized pitting edema in the scalp of a fetus that may overlie sutures of the skull. It is usually formed during labor as a result of the circular pressure of the cervix on the fetal occiput (diffuse swelling of the soft tissue of the skull) Skull defects (anencephaly) Anterior & posterior fontanels (a: 7-18mos, p: 6-8 wks; ecchymosis) Craniosynostosis: Premature ossification of the sutures of the skull often associated with other skeletal defects; the sutures close before or soon after birth without surgical correction, the growth of the skull is inhibited, the head is deformed& the eyes & brain are often damaged Craniotabes: Benign congenital thinness of the top & back of the skull of a newborn. Because the rate of brain growth exceeds the rate of ossification of the skull during the last month of gestation Microcephaly: Congenital anomaly characterized by abnormal smallness of head in relation to the rest of the body & by underdevelopment of the brain resulting in some degree of mental retardation Macrocephaly: Congenital anomaly characterized by abnormally largeness of the head & brain in relation to the rest of the body Hydrocephaly: Pathologic condition characterized by abnormal accumulation of CSF, usually under increased pressure, within the cranial vault & subsequent dilatation of the ventricles Cutis aplasia congenital Bruits Face Dysmorphic features: epicanthal folds, widely spaced eyes, microphthalmia, asymmetry, long philtrum, low set ears Asymmetrical face (7th CN palsy) Moebius syndrome: Hypoplasia of the 7th nerve nucleus) Eyes Dolls eye maneuver: A normal response in newborns to keep the eye stationary as the head is moved to the right or left. Reflex disappears as ocular fixation develops Subconjunctival/ retinal hemorrhages Red orange reflex Leucokoria (white pupillary reflex)(Appearance of a whitish reflex or mass in the papillary area behind the lens): Cataracts, tumors, ROP Chemical irritation White sclerae Blue sclerae (osteogenesis imperfecta) Chorioretinitis: Inflammatory condition of the choroids & retina of the eye, usually d/t parasitic/bacterial infection Ears Anotia (Treacher-Collins syndrome): Congenital absence of one or both ears Microtia Preauricular tags & pits Dull gray tympanic membrane Low set ears Malformed ears
Nose Broad in appearance Choanal atresia: Congenital anomaly in which a bony or membranous occlusion blocks the passageway between the nose & pharynx Flaring of the ala nasi Mouth Natal teeth (lower incisors) (remove if loose to avoid risk of aspiration) Bifid uvula Cleft lip & palate Sucking pads Small tonsils High-arched palate Large tongue Ankyloglossia: A severe restriction of tongue movement as a result of adhesion or fusion of the tongue to the floor of the mouth Retention cysts (ranula): Large mucocele in the floor of the mouth caused by destruction of the ducts of the salivary glands Epsteins pearls: Small white-pearl-like epithelial cysts that occur on both sides of the midline of the hard palate of the newborn Micrognathia (Pierre-Robin syndrome): Underdevelopment of the jaw, especially the mandible Excessive salivation Macrostomia Neck Short neck Hematoma on sternocleidomastoid muscle Cystic hygroma Branchial cleft cysts Thyroglossal duct cyst Webbing: Skinfolds connectinf adjacent structures such as fingers or toes as the neck from the acromion to the mastoid, associated with genetic abnormalities Resistant neck to flexion (meningitis or SAH) Bruits of thyroid gland Congenital torticollis: An abnormal condition in which the head is inclined Clavicular fracture in LGA babies (large for gestational age) Thorax & Lungs Chest Breast hypertrophy with or without milk (Witches milk) Mastitis: Inflammation condition of the breast common in lactation chaaracterized by pain, swelling & redness Supernumerary nipples Inverted nipples Widespread nipples Chest circumference: 2 cm < HC Lungs Breathing is predominantly abdominal Retractions, grunting Asymmetric breathing
Stridor: Abnormal, high-pitched sounds caused by an obstruction in lungs or trachea usually heard during inspiration, may ndicate glottic edema, asthma, diptheria Bronchovesicular breath sounds Apnea Periodic breathing Crackles or rales Cardiovascular system Normal resting heart rate: 90-160 bpm PMI at 4th ICS Characteristic of pulses: Coarctation of aorta Dextrocardia: Location of the heart in the right hemithorax, either as a result of displacement or as a congenital defect Benign/ pathologic murmur Sinus bradycardia Blood pressure: Systolic 40-80 mmHg, Diastolic 20-55 mmHg, mean 25-60 mmHg Abdomen Liver palpable 2 cm BRCM Palpable splenic tip Gas in rectum by 24 hours Umbilical hernia Masses Scaphoid abdomen: diaphragmatic hernia Omphalocoele (Congenital herniation of intraabdominal viscera thru a defect in the abdominal wall around umbilicus), gastroschisis Omphalitis: Inflammation of umbilical stump marked by redness, swelling & purulent exudates in severe cases Umbilical cord: 2 arteries, 1 vein, Whartons jelly Tufts of hair Genitourinary system Penis should at least be 2 cm in length Transitory hydrocoele: Accumulation of fluid in any saclike cavity or duct specifically in the tunica vaginalis testis or along the spermatic cord Hypospadias: Developmental anomaly in male which the urethra opens on the underside of the penis or on perineum Tight prepuce Ambiguous genitalia (CAH) Pseudomenses Erection of the penis Voiding within 24 hours Undescended testes Large labia majora Hymenal tags: Normal redundant hymenal tissue protruding from the floor of the vagina during the first weeks of birth Testicular torsion Anus Passage of meconium within the 1st 12 hours after birth Imperforate anus Fistula in ano Meconium pearls
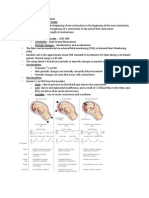
Musculoskeletal system Unequal limbs due to lymphangiomas (A benign yellowish tan tumor on the skin composed of a mass of dialted lymph vessels)/ hemangiomas Syndactyly (Fusion of the fingers/ toes)/ polydactyly (Presence of more than normal number of fingers or toes)/ clinodactyly (Abnormal lateral or medial bending of one or more fingers or toes) Ortolani maneuver: Congenital hip dislocation Talipes equinovarus/ equinovalgus Amelia (Absence of one or more limbs)/ pocomelia Rocker-bottom feet Simian crease: Single crease across the palm produced from the fusion of proximal & distal palmar creases evident in children with Downs syndrome Breech presentation: Intrauterine position of the fetus in which the buttocks or feet present Brachial palsy ** Barlow maneuver, Ortolani maneuver NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF THE INFANT General considerations The following reflect the neurologic status of the baby Posture Sleep state Feeding Breathing Cardiac status The optimal time to do NE is usually immediately prior to feeding awake & responsive Observation of the infant At term the infant remains alert for reasonable periods of time & responds to visual, auditory & tactile stimuli Presence of congenital anomalies neural tube defects Look for neurocutaneous lesions caf au lait spots, nevus Observe respiratory movements Developmental reflexes Primitive reflexes which reflect the integrity of the brainstem & spinal cord Moro reflex Tonic neck reflex Grasp reflex Placing reflex Stepping reflex Parachute reflex These reflexes are present at birth & disappear by 6 months Persistence: maturational lag or impaired CNS function Asymmetry: CNS or PNS dysfunction Motor function Evaluate the posture & tone Gentle manipulation of the infants limb allows for assessment of muscle tone & strength The baby should be supine with the head in midposition while tone is evaluated so that the tonic neck reflex does not augment tone unilaterally
Posture There is hypertonia of the elbow, hip & knee flexors during the 1st three months Flexion The newborn should be gently held in the horizontal position & at vertical suspension to determine if flexor tone is present & symmetric Tone Involves examination of passive & active tone Passive tone is evaluated by determining the degree of resistance to passive movements of the joints The active tone is evaluated by observing the babys response to gentle pulling from supine to the prone position (traction response) Cranial Nerve Examination Cranial Nerve 1 Infrequently tested Pleasant, aromatic substances The newborn manifests arrest of activity & sucking activity Cranial Nerves 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 Assessment of the eyes Bilateral symmetric pupils (response to light by blinking) Ptosis: abnormality of CN 3 Grayish-white optic disc Eyes fix on bright object & face Presence of visual threat Observe conjugate eye movements on Dolls eye maneuver Cranial Nerve 5 Test for the corneal reflex by blowing air towards the eyes Observe for symmetrical closure of the eyelids Cranial Nerve 7 Facial movements are readily observed during crying Observe for symmetry Cranial Nerve 11 Observed by turning the infants head to one side while restraining it at the opposite shoulder Observe contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle Cranial Nerves 9, 10, 12: Assess the quality of sucking & swallowing as well as the quality of the voice during crying Sensory testing Tests for pain & sensation are imprecise in this period, & the gross response of infants to stroking & pinprick with withdrawal, crying & changes in sucking rates maybe the only information possible CHRABI
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Case Study 2Document3 pagesCase Study 2jamesPas encore d'évaluation
- TicklerDocument37 pagesTicklerLuis Elijah De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Edu101 Debate IsteachingaprofessionDocument3 pagesEdu101 Debate Isteachingaprofessionapi-236906829Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHCCCS007 Learner Guide V1.1Document71 pagesCHCCCS007 Learner Guide V1.1rasna kc100% (1)
- NURS 3337 Day1 WorkbookDocument18 pagesNURS 3337 Day1 WorkbookEmerald Holly TagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyDocument5 pagesDrugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyMarjoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk PregnancyDocument2 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyCaren ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of Labor: PassengerDocument6 pagesComplications of Labor: PassengerR-Chian Jose Germanp100% (1)
- Assessment of Fetal WellbeingDocument71 pagesAssessment of Fetal WellbeingDanny Apw100% (2)
- High Risk Newborn Conditions Present at BirthDocument47 pagesHigh Risk Newborn Conditions Present at BirthChinchu ChinchuPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 14 Wardand HInsley Maternity Power PointDocument25 pagesCH 14 Wardand HInsley Maternity Power PointJonalyn ChewacheoPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Problems in NeonatesDocument73 pagesCommon Problems in NeonatesWan FaizuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Growth and Development ToddlersDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Growth and Development ToddlersSimranPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet To Accompany FHR Review Video: Emerald Spangler May 6, 2021Document3 pagesWorksheet To Accompany FHR Review Video: Emerald Spangler May 6, 2021Emerald SpanglerPas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn Assessment ToolDocument5 pagesNewborn Assessment ToolReana AbillarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Premature NewbornDocument17 pagesA Premature NewbornMegatFitriAzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Packet OBDocument7 pagesClinical Packet OBLiza Jean BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Trust Guideline For The Newborn and Infant Physical Examination (NIPE)Document37 pagesTrust Guideline For The Newborn and Infant Physical Examination (NIPE)Clara CarneiroPas encore d'évaluation
- 160 OB Fetal Monitoring Strip Information 4pgsDocument4 pages160 OB Fetal Monitoring Strip Information 4pgshorse4lisa100% (2)
- OB Exam 1 ComboDocument82 pagesOB Exam 1 ComboHope RobersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn AssessmentDocument5 pagesNewborn Assessmentlanilyn aquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Ogans Internal Organs of ReproductionAngela NeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum PeriodDocument3 pagesAntepartum PeriodjisooPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The AsthmaDocument27 pagesAsthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The Asthmasimonedarling100% (1)
- Neonatal PharmacologyDocument61 pagesNeonatal PharmacologyAnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Neonatal ProblemsDocument32 pagesCommon Neonatal ProblemsbrhomzalatPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Risk NewbornDocument28 pagesHigh-Risk Newborncjolou100% (2)
- JaundiceDocument41 pagesJaundicesavina hasbianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal Care: Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument2 pagesAntenatal Care: Physiological Changes in PregnancyAlexander Ennes100% (1)
- Ob Study PacketDocument85 pagesOb Study PacketEagles171100% (2)
- BubbleHe AssessmentDocument1 pageBubbleHe AssessmentVictoriaStoneHarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiologic Changes in PregnancyDocument13 pagesPhysiologic Changes in PregnancyLauren Levy100% (1)
- Name: Mohammad Farez Sayfoo Student Number: 310300440Document21 pagesName: Mohammad Farez Sayfoo Student Number: 310300440mohammadsayfooPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Monitoring Orientation Day-1Document50 pagesFetal Monitoring Orientation Day-1Scott CalfeePas encore d'évaluation
- Kaplan Focus ReviewDocument9 pagesKaplan Focus ReviewSaidel ElizondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of NewornDocument4 pagesCare of NewornArchana SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Which Signs and Symptoms Would The Nurse Expect To Assess in A Newborn WithDocument1 pageWhich Signs and Symptoms Would The Nurse Expect To Assess in A Newborn WithjamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal SubgalealDocument6 pagesNeonatal SubgalealIrenLayPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts in Pregnancy: Prenatal Care and Health TeachingsDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts in Pregnancy: Prenatal Care and Health Teachingswanda100% (2)
- OB Chap 22 - Normal LaborDocument4 pagesOB Chap 22 - Normal LaborChino Paolo SamsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal Jaundice DrkumarDocument44 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Drkumarvasu_5ivePas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Distress Management in NewbornDocument5 pagesRespiratory Distress Management in Newbornagirl_9807100% (1)
- Trial of LabourDocument2 pagesTrial of Labourgeorgeloto12Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 NewbornDocument123 pages2 NewbornANNIE SHINE MAGSACAYPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital AnomaliesDocument22 pagesCongenital Anomaliesjessy100% (1)
- Pediatrics NotesDocument72 pagesPediatrics NotesSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk Newborn and FamilyDocument93 pagesHigh Risk Newborn and FamilyJen IlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Labor and Delivery Assessment2nd SemDocument16 pagesLabor and Delivery Assessment2nd SemCharisse Ann MonsalePas encore d'évaluation
- Intrapartum AssessmentDocument84 pagesIntrapartum AssessmentAnne Carlie Bucoy RoldanPas encore d'évaluation
- New Born Care 1Document12 pagesNew Born Care 1Tsuyoshi BangPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsDocument3 pagesName: Year & Course: Test Type Timing Process ResultsAllyah Anthonette Ferwelo100% (1)
- Complications in PregnancyDocument81 pagesComplications in PregnancyTia TahniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Child NursingDocument16 pagesMaternal Child NursingKUKURO AURANTIUM100% (1)
- Amniotic Band SyndromeDocument47 pagesAmniotic Band SyndromeNazrul Islam JhinukPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Newborn, - 130319150346Document45 pagesClassification of Newborn, - 130319150346Ez Ball100% (1)
- Assessing The Newborn and Infant-NewDocument11 pagesAssessing The Newborn and Infant-NewJan Jamison ZuluetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Postpartum CareDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Postpartum CareZaire DylanPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument7 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhagekman0722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum 1Document3 pagesAntepartum 1Emily DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn Assessment NORMALDocument2 pagesNewborn Assessment NORMALVanessaMUellerPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal Sepsis 1Document18 pagesNeonatal Sepsis 1Fãhâd Õró ÂhmédPas encore d'évaluation
- Fanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandFanconi Anemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandInflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Atp III NcepDocument12 pagesAtp III NcepLuis Elijah De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Apraxia Mood and AffectDocument1 pageApraxia Mood and AffectLuis Elijah De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mikey Neuro 1stshift PracticalDocument8 pagesMikey Neuro 1stshift PracticalLuis Elijah De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Programme Guide Certificate in Community Health (BPCCHN) - CompressedDocument120 pagesProgramme Guide Certificate in Community Health (BPCCHN) - CompressedChakrapani ChaturvediPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogen Peroxide Market Analysis and Segment Forecast To 2028Document103 pagesHydrogen Peroxide Market Analysis and Segment Forecast To 2028Khiết NguyênPas encore d'évaluation
- Arcadia Reptile 2018Document32 pagesArcadia Reptile 2018marianpcbPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiocare 2000 Operation ManualDocument61 pagesCardiocare 2000 Operation ManualDokter MoezPas encore d'évaluation
- Crowding: Let'S Differentiate!Document4 pagesCrowding: Let'S Differentiate!Lorraine BagolPas encore d'évaluation
- MRU-QMS-HSE-Form - JSA - Geotechnical Drilling & Geotechnical Field Investigation - Rev00Document11 pagesMRU-QMS-HSE-Form - JSA - Geotechnical Drilling & Geotechnical Field Investigation - Rev00AditPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Magnesium Sulphate (Mgso4: Group 5Document11 pagesTopic: Magnesium Sulphate (Mgso4: Group 5Wan Ahmad FaizFaizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Attitude and Practice of ContraceptiveDocument5 pagesKnowledge Attitude and Practice of ContraceptiveSam AdePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanDocument9 pagesCardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanjikookPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsDocument8 pages02 Revman Exercise Caffeine Articles JournalsKenneth TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge of The Utility of Toilets and Hazards of Open Air Defecation Practice Among Rural Adults of Muchakandi VillageDocument6 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge of The Utility of Toilets and Hazards of Open Air Defecation Practice Among Rural Adults of Muchakandi VillageInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Forgiveness Leads To Anger ManagementDocument15 pagesForgiveness Leads To Anger Managementjai_tutejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Environmental ManagementDocument9 pagesJournal of Environmental ManagementAndriani SilfianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Theories and FoundationDocument59 pagesNursing Theories and FoundationMaria EdelPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance Manual: SMV 10-65 B / SMV 37-52 B GANTRYDocument136 pagesMaintenance Manual: SMV 10-65 B / SMV 37-52 B GANTRYJesùs AlbertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Controlling Genset NoiseDocument2 pagesControlling Genset NoiseNishant BhavsarPas encore d'évaluation
- Man Against HimselfDocument507 pagesMan Against Himselfalbatros3000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Liver & Biliary DiseaseDocument41 pagesLiver & Biliary Diseasesaump3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shigella, ShigellosisDocument52 pagesShigella, Shigellosistummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Workup For ProteinuriaDocument17 pagesWorkup For ProteinuriaSantiago ChávezPas encore d'évaluation
- FOUR Score Instruction Guide For Application On MISH ICUDocument2 pagesFOUR Score Instruction Guide For Application On MISH ICUMohamed Farouk El-FaresyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lit Review Paper 1Document7 pagesLit Review Paper 1api-679552755Pas encore d'évaluation
- TONSILLITIS AND TONSIL STONE EdittedDocument5 pagesTONSILLITIS AND TONSIL STONE EdittedNineja NinejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Injuries & Their ManagementsDocument78 pagesHand Injuries & Their ManagementsKuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Potings List 2021-22Document1 pageClinical Potings List 2021-22Dani ursPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Philosophy Statement Assignment 2017Document2 pagesPersonal Philosophy Statement Assignment 2017api-538727441Pas encore d'évaluation
- T&C Procedure Grease Interceptors Vida Ok 13sept2020Document115 pagesT&C Procedure Grease Interceptors Vida Ok 13sept2020Gopa KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Hubungsn Stres Dengan Kesehatan Gigi Dan MulutDocument8 pagesJurnal Hubungsn Stres Dengan Kesehatan Gigi Dan MulutTyasNurFauzianaPas encore d'évaluation