Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electrolyte Imbalances
Transféré par
sccctutorCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electrolyte Imbalances
Transféré par
sccctutorDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
E-lyte Hyponatremia Hypernatremia Hypokalemia Hyperkalemia
Imbalance
[< 135 mEq/L] [> 145 mEq/L] [< 3.5 mEq/L] [> 5.1 mEq/L]
Causes • ↑ Na excretion • ↓ Na excretion • Potentially life- • Excessive K+ intake
threatening!
: Excessive diaphoresis : Corticosteroids : Food
: GI losses (vomiting, diarrhea) : Cushing’s syndrome • Total body K+ loss : Meds = potassium chloride
: Diuretics : Hyperaldosteronism : ↑ use of meds (diuretics or or salt substitutes
: Hypoaldosteronism : RF corticosteroids) : Rapid infusion of K+-
• Inadequate Na intake • ↑ Na intake : Hyperaldosteronism / containing IV solutions
: NPO / low-salt diet : ↑ oral sodium ingestion Cushing’s syndrome • ↓ K+ excretion
• Dilution of serum Na • ↓ Water intake : Vomiting, diarrhea : K+-sparing diuretics
: ↑ ingestion of hypotonic : NPO : Prolonged NG suction : RF
fluids • ↑ Water loss : Renal dis imparing : Adrenal insufficiency
: RF : ↑ metabolism reabsorption of K+ (Addision’s dis)
: SIADH (= ↑ ADH activity = : Fever • Inadequate K+ intake • Movement of K+ from the
= water retention & : Infection : NPO ECF to ICF
inappropriate urinary excretion : Diarrhea • Dilution of serum K+ : Tissue damage = trauma,
of Na) : Diabetes insipidus : Water intoxication burns, sepsis etc
: Hyperglycemia • Movement of K+ from : Acidosis
the ECF to ICF : Hyperuricemia
: Alkalosis : Hypercatabolism
: Insulin treatment /
Hyoerinsulinism
Assessment / • CV • CV • CV • CV
Sx
: Sx vary w/ changes in : Sx vary w/ changes in : Thready, weak, irregular : Slow, weak, irregular HR
vascular vol vascular vol pulse : ↓ BP
: Normovolemic = rapid pulse • Resp : Peripheral pulse weak • ECG changes
: Hypovolemic = Thready, : Pulm edema if : Orthostatic hypotension : Tall peaked T waves
weak, rapid pulse, hypervolemia • ECG changes : Flat P waves
hypotension, flat neck vein • Neuromuscular : ST depression : Widens QRS complexes
: Hypervolemic = Rapid, : Early = spontaneous muscle : Shallow, flat or inverted T : Prolonged PR intervals
bouncing pulse twitches, irregular muscle wave • Resp
• Resp contractions : Prominent U wave : SK muscle weakness leading
: Shallow, ineffective resp : Late = sk muscle weakness, • Resp to resp failure
mvmt r/t sk muscle weakness diminished or absent DTR : Shallow, ineffective resp • Neuromuscular
• Neuromuscular • CNS : Diminished breath sounds : Early = muscle twitches,
: Generalized sk muscle : Altered cerebral fxn (the • Neuromuscular cramps, paresthesias in the
weakness most common : Anxiety, lethargy, hands and feet and mouth
: ↓ DTR manifestation) confusion, coma : Late = profound weakness,
• Cerebral fxn : Normo-/hypovolemia = : Sk muscle weakness → ascending flaccid paralysis in
: HA agitation, confusion, flaccid paralysis the arms and legs
: Personality changes seizures : Loss of tactile • GI
: Confusion : Hypervolemia = lethargy, discrimination : ↑ motility
: Seizures → Coma stupor, coma : ↓ DTR : Hyperactive bowel sounds
• GI • Renal • ↑GI : Diarrhea
: ↑ motility & bowel sounds : ↓ urinary specific gravity : ↓motility
: Abd cramping : ↑ UO : Hypoactive bowel sounds
: N&V • Integumentary : N&V, constipation
• Renal : Dry skin : Paralytic ileus
: ↓ urinary specific gravity • Renal
: ↑ UO : ↓ urinary specific gravity
: ↑ UO
Tx • Hypovolemia → IV NS • For inadequate renal • Oral K+ supplement • D/C IV or PO K+
infusion (slowely) excretion of sodium, supplement
administer diuretics to : Not take on an empty
promote sodium loss
* Always • Hypervolemia → Osmotic stomach to ↓ GI effects • K+-restricted diet
monitor CV, diuretic • Restrict sodium and fluid : AEs = abd pain, distention, • K+-excreting diuretics if
resp, neuro, • Water restriction for pt w/ intake N&V, diarrhea, or GI renal fxn is patent
cerebral, normal or excess fluid vol bleeding → d/c supplement • If renal fxn is impaired,
renal, and GI • SIADH → Lithium, : Liquid K+ = take w/ juice administer sodium
status Demeclocycline to mask the bad taste polystyrene sulfonate
(Declomycin) • IV K+ (Kayexalate) [= promote GI
* Hyponatremia potentiates : NEVER given by IV push Na+ absorption and K+
lithium toxicity → monitor : Use infusion pump (5-10 excretion]
lithium level closely mEq/hr) • If severe, dialysis
• ↑ oral sodium intake : Observe sx of phlebitis • IV hypertonic glucose w/
• D/C K+-losing diuretics regular INS to move excess
K+ into the cells
E-lyte Hypocalcemia Hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia Hypermagnesemia
Imbalance
[ < 8.6 mg/dL] [ > 10.0 mg/dL] [< 1.6 mg/dL] [> 2.6 mg/dL]
Causes • ↓ GI Ca absorption • ↑ Ca absorption • Inadequate Mg intake • ↑ Mg intake
: Inadequate oral intake of Ca : Excessive oral intake of Ca : Malnutrition : Mg-containing antacids
: Lactose intolerance : Excessive oral intake of Vit : Vomiting or diarrhea and laxatives
: Malabsorption syndrome D : Malabsorption syndrome : Excessive IV therapy
(Celiac sprue, Crohn’s dis) • ↓ Ca excretion • ↑ Mg secretion • ↓ renal excretion of Mg
: Vit D deficiency : RF : Diuretics : Renal failure
: ESRD : Use of thiazide diuretics : Chronic alcoholism
• ↑ Ca excretion • ↑ bone resorption of Ca • Intracellular mvmt of Mg
: RF, polyuric phase : Hyperparathyroidism : Hyperglycemia
: Diarrhea : Hyperthyroidism : INS administration
: Wound drainage, esp GI : Malignancy (bone : Sepsis
• ↓ the ionized fraction of Ca destruction from metastatic
: Medications (calcium tumors)
chelators or binders) : Immobility
: Acute pancreatitis : Use of glucocorticoids
: Hyperphosphatemia • Hemoconcentration
: Immobility / bed rest : Dehydration
: Removal or destruction of the : Use of lithium
parathyroid glands (= : Adrenal insufficiency
Hypoparathyroidism)
Assessment / Sx • CV • CV • CV • CV
: ↓ HR : Early = ↑ HR : Tachycardia : Bradycardia, dysrhythmias
: Hypotension : Late = bradycardia → : HTN : Hypotension
: ↓ peripheral pulse cardiac arrest • ECG changes • ECG changes
• ECG changes : ↑ BP : Tall T waves : Prolonged PR interval
: Prolonged ST interval • ECG changes : Depressed ST segments : Widened QRS complexes
: Prolonged QT interval : Shortened ST segment • Resp • Resp
• Resp : Widened T wave : Shallow resp : Resp insufficiency
: Not directly affected • Resp • Neuromuscular • Neuromuscular
: Possible resp failure d/t : Ineffective resp mvmt d/t sk : Twitches, paresthesias : Diminished or absent DTR
muscle tetany or seizures muscle weakness : Trousseau’s and Chvostek’s : Sk muscle weakness
• Neuromuscular • Neuromuscular signs • CNS
: Twitches, cramps, tetany, : Profound muscle weakness : Hyperreflexia : Drowsiness and lethargy
seizures : Diminished or absent DTR : Tetany, seizures : Coma
: Paresthesias f/b numbness : Disorientation, lethargy, • CNS
: Trousseau’s and Chvostek’s coma : Irritability
signs • GI : Confusion
: Hyperactive DTR : ↓ motility, hypoactive bowel • GI
: Anxiety, irritability sounds : ↓ motility
• GI : Anorexia, nausea, abd : Anorexia, nausea, abd
: ↑ gastric motility; hyperactive distention, constipation distention, constipation
bowel sounds • Renal
: Abd cramping, diarrhea : ↑ UO → dehydration
: Low back pain from renal
calculi (kidney stones)
Tx • Administer Ca via PO or IV • D/C IV or PO meds • Hypocalcemia freq • Diuretics to ↑ renal
containing Ca or Vit D accompanies excretion of Mg
• IV Ca = warm the solution to hypomagnesemia →
interventions aim to restore
the body temp and monitor • D/C thiazide diuretics → normal serum Ca levels • IV calcium chloride or
* Always for hypercalcemia replace w/ diuretics that ↑ calcium gluconate to
monitor CV, • Medications to ↑ Ca Ca excretion • For severe case, IV reverse the effects of Mg
resp, neuro, absorption • Medications that inhibit Ca magnesium sulfate (No IM on cardiac muscle
cerebral, renal, : Aluminum hydroxide [= ↓ resorption from the bone injection to prevent pain • Restrict dietary intake of
and GI status serum phosphorus levels, : Phosphorus and tissue damage) Mg-containing foods
causing the countereffect of ↑ : Calcitonin (Calcimar) • Initiate seizure precautions
Ca] : Bisphosphonates • Monitor for DTR,
: Vit D to aid Ca GI absorption : Prostaglandin synthesis suggesting
• ↓ env stimuli inhibitors (aspirin, NSAIDs) hypermagnesiemia during
• Initiate seizure precautions • Monitor for fracture the administration of Mg
• Monitor for fracture • Monitor for flank or abd • PO Mg may cause diarrhea
• Keep 10% Ca gluconate pain, and strain the urine to and ↑ Mg loss
available check for the presence of
urinary stones
Phosphorus [2.7 – 4.5 mg/dL]: ↓ serum phosphorus = ↑ serum calcium / ↑ serum phosphorus = ↓ serum calcium
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet For Fluid Balance and ElectrolytesLiel TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Decrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous SystemDocument1 pageDecrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous Systemahmed K.Abd el SaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesPneumonia Cheat Sheet: by ViaGayle MariePas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Serotonin Supplements To Boost Mood Naturally - Be Brain FitDocument11 pages15 Serotonin Supplements To Boost Mood Naturally - Be Brain FitkrishanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Body of A Greek GodDocument51 pagesThe Body of A Greek GodJohn O. Ichie80% (10)
- Cholesterol Lowering Secrets ReportDocument12 pagesCholesterol Lowering Secrets ReportSantoshKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Brainsheet f04Document2 pagesBrainsheet f04mrsfelic08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intravenous Medication Care and ComplicationDocument42 pagesIntravenous Medication Care and Complicationtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Mi 40 X Pro AdvancedDocument49 pagesMi 40 X Pro Advancedkrymis0% (1)
- The Complete Guide to Using the Law of AttractionDocument20 pagesThe Complete Guide to Using the Law of AttractionCoral Tyack100% (2)
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- Admission NotesDocument16 pagesAdmission NotesCaisar Dewi MaulinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal Assessmnt Tool PDFDocument2 pagesNeonatal Assessmnt Tool PDFYestin Reece Corpus ArcegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Overload Student PagesDocument4 pagesFluid Overload Student PagesJess OswaldPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Element Introduction FinalDocument9 pagesFive Element Introduction Finalapi-275824177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical KardexDocument2 pagesClinical KardexJackie Frey100% (2)
- Telemetry Patient Shift ReportDocument2 pagesTelemetry Patient Shift ReportSweta100% (1)
- Fluid Electrolyte - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument62 pagesFluid Electrolyte - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Beats Per Minute. Many DifferentDocument4 pages100 Beats Per Minute. Many Differentjovan teopizPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument9 pagesCardiac Study GuideJane DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiologic Changes of Aging Lecture NotesDocument1 pagePhysiologic Changes of Aging Lecture Notesshenric16100% (1)
- HTMA Mineral RatiosDocument3 pagesHTMA Mineral RatiosluckydexxxPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSESSMENT FORM: Spring 2006 Client's Number: InstructionsDocument6 pagesASSESSMENT FORM: Spring 2006 Client's Number: Instructionsdenisemw88Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5P Handoff SheetDocument1 page5P Handoff SheetBarry SeeboPas encore d'évaluation
- Potato Pastillas: A Healthy Twist on a Filipino FavoriteDocument71 pagesPotato Pastillas: A Healthy Twist on a Filipino FavoriteCJ Caneba100% (3)
- KimberlyMueller JoshHingst Theathletesguidetosportssupplements HumanKinetics2013Document359 pagesKimberlyMueller JoshHingst Theathletesguidetosportssupplements HumanKinetics2013Glke100% (2)
- Stroke Signs, Risks, and Nursing CareDocument1 pageStroke Signs, Risks, and Nursing CareMariel Febreo MerlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Worksheet2023 PDFDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet2023 PDFjj100% (1)
- Mineral MetabolismDocument34 pagesMineral Metabolismalaa haithamPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Oils in Poultry NutritionDocument33 pagesEssential Oils in Poultry NutritionGopi Marappan100% (6)
- Bakeries and ConfectioneriesDocument26 pagesBakeries and ConfectioneriesMihai UngureanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurseslabs Lab Values PDFDocument2 pagesNurseslabs Lab Values PDFJan BularioPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Disease McqsDocument20 pagesRenal Disease McqsShankar Deshmukh100% (1)
- HypotensionDocument7 pagesHypotensionNader Smadi100% (2)
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrineUnclePorkchopPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Profusion Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Peripheral Tissue Profusion Care Planstacie4roher4smithPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Hormone Pill, Patch, Ring Progestin Only Mini Pill, Depo-Provera, IUDDocument1 pageCombined Hormone Pill, Patch, Ring Progestin Only Mini Pill, Depo-Provera, IUDnkuligowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Abbreviations ListDocument6 pagesAbbreviations ListolivedaisychainPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Values and Vital SignsDocument4 pagesLab Values and Vital SignsWole Olaluwoye100% (1)
- An Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 2011-1 PDFDocument6 pagesAn Easy Guide To Head To Toe Assessment Vrtis 2011-1 PDFkatherine dayagPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFDocument1 pagePharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inPas encore d'évaluation
- Municable DiseasesDocument18 pagesMunicable DiseasesEdamarie ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock With Hemodynamic ChangesDocument2 pagesShock With Hemodynamic ChangesBNA_RN100% (1)
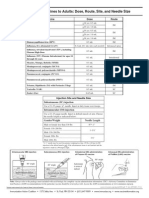
- Administering Vaccines To AdultsDocument1 pageAdministering Vaccines To AdultsPaul Anthony LoricaPas encore d'évaluation
- CARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditDocument2 pagesCARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditFrances Katrina Siruno100% (1)
- Hierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsDocument1 pageHierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsRevPas encore d'évaluation
- SBARQ FormDocument1 pageSBARQ FormTracy100% (5)
- Addison Vs CushingsDocument1 pageAddison Vs CushingsChris ZantiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Downtime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimeDocument5 pagesDowntime Daily Nursing Assessment & Care Plan: 1 of 5 Date: TimerupaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Care SkillsDocument15 pagesPatient Care SkillsIts John100% (1)
- Drug Classificati On Indications Action Route/Dos e Side Effects Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument7 pagesDrug Classificati On Indications Action Route/Dos e Side Effects Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJenny NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- West Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessDocument4 pagesWest Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessPhylum Chordata100% (1)
- Simple Method of Acid Base Balance Interpretation: UsefulnessDocument2 pagesSimple Method of Acid Base Balance Interpretation: UsefulnessPeej ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cesarean Section PrimaryDocument33 pagesCesarean Section PrimaryKazvin Carl PeraltaPas encore d'évaluation
- NLE Poisons and AntidotesDocument2 pagesNLE Poisons and AntidotesGodfrey Franco100% (1)
- H Hemolysis E Elevated L Liver Function L Low P Platelet B Breast U Uterus B Bowel B Bladder L Lochia E Episiotomy H HemorrageDocument7 pagesH Hemolysis E Elevated L Liver Function L Low P Platelet B Breast U Uterus B Bowel B Bladder L Lochia E Episiotomy H HemorrageAlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Bam Slam Drug CardDocument4 pagesBam Slam Drug CardLeticia GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Maldistribution of Blood Flow ShockDocument2 pagesMaldistribution of Blood Flow ShockBNA_RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Nasopharyngeal Airway SuctioningDocument3 pagesNasopharyngeal Airway SuctioningHaitham ZraigatPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartal Fetal Assessment: Developed by D. Ann Currie, R.N.,M.S.NDocument38 pagesAntepartal Fetal Assessment: Developed by D. Ann Currie, R.N.,M.S.NismailalviPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Res Case Presentation: Jo Anne N. Ramos, MDDocument72 pagesPre-Res Case Presentation: Jo Anne N. Ramos, MDKah Mote KyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesDocument14 pagesComprehensive Nursing Assessment For Care Plan: AllergiesBrittany ShrewsburyPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport of Critically Ill Adults 2011Document1 pageTransport of Critically Ill Adults 2011velocity25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing QuestionnairesDocument3 pagesNursing QuestionnairesDianne Marbella AlvaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Low of Blood Flow ShockDocument2 pagesLow of Blood Flow ShockBNA_RNPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids Electrolytes Visual NotesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes Visual NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Lab ValuesDocument4 pagesCommon Lab ValuesRaf LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- VN8 Term 2 Calendar Updated June 2, 2021Document7 pagesVN8 Term 2 Calendar Updated June 2, 2021Janmarie BongcaronPas encore d'évaluation
- Parenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianDocument45 pagesParenting Styles: - Dictatorial or AuthoritarianCourseTree LearningPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of PlanDocument16 pagesNursing Care of PlanDbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Intake and Output (I&O) : Key TerminologyDocument5 pagesIntake and Output (I&O) : Key TerminologyJack KeurigPas encore d'évaluation
- PG PREPARATION - Mnemonics in PharmacologyDocument12 pagesPG PREPARATION - Mnemonics in PharmacologyRaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes MelitusDocument44 pagesDiabetes MelitusDwi Novianti SugihartiPas encore d'évaluation
- UTS 101-Module3 v.2Document13 pagesUTS 101-Module3 v.2angel mintsPas encore d'évaluation
- BeautyCare Module3QIBASICMANICURDocument37 pagesBeautyCare Module3QIBASICMANICURmisimon67% (3)
- FolicDocument3 pagesFolicnavsoni08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Factors That Affect Basal Metabolic Rate (BMRDocument3 pagesFactors That Affect Basal Metabolic Rate (BMRTapas DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Leukemia Case StudyDocument32 pagesLeukemia Case Studydsaitta108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Catalog PDFDocument48 pagesCatalog PDFNikita ZhukPas encore d'évaluation
- Cebu Doctors' University Hospital: Summary of Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageCebu Doctors' University Hospital: Summary of Nursing Care Planbhogz1467% (6)
- Complex Consumption Patterns Impact LifestylesDocument23 pagesComplex Consumption Patterns Impact LifestylesSudhanshu KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Diet, Feeding and Nutritional Care of Captive Tigers, Lions and LeopardsDocument5 pagesDiet, Feeding and Nutritional Care of Captive Tigers, Lions and LeopardsMark HietalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portmafia GroupDocument27 pagesPortmafia Groupalvinlarano11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Programa de Entrenamiento para 42K CarreraDocument2 pagesPrograma de Entrenamiento para 42K CarreraKefer Luis Vasquez AsipaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrient DeficiencyDocument23 pagesNutrient DeficiencygodolfintorentPas encore d'évaluation
- JoggingDocument3 pagesJoggingSyahir_90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pea Seed Protein Concentrate in Tilapia FeedsDocument4 pagesPea Seed Protein Concentrate in Tilapia FeedsInternational Aquafeed magazinePas encore d'évaluation