Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Amebiasis (Ant Hroponosis) (20) Forms: E. Histolytica
Transféré par
Deepankar Srigyan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
123 vues7 pagesE. Histolytica, Biological forms are-cyst, trophozoite. Vegetative forms are-tissue form, lumen form EPIDEMIOLOGYSOURCE(S) of TRANSMISSIN(RT),SEN SITIVE PATIENT,VECTORS Enter the organism of a healthy person withvegetables, water,food. Excreted into the external environment from the organism of infected persons in - the feces.
Description originale:
Titre original
Protozoal Infection
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentE. Histolytica, Biological forms are-cyst, trophozoite. Vegetative forms are-tissue form, lumen form EPIDEMIOLOGYSOURCE(S) of TRANSMISSIN(RT),SEN SITIVE PATIENT,VECTORS Enter the organism of a healthy person withvegetables, water,food. Excreted into the external environment from the organism of infected persons in - the feces.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
123 vues7 pagesAmebiasis (Ant Hroponosis) (20) Forms: E. Histolytica
Transféré par
Deepankar SrigyanE. Histolytica, Biological forms are-cyst, trophozoite. Vegetative forms are-tissue form, lumen form EPIDEMIOLOGYSOURCE(S) of TRANSMISSIN(RT),SEN SITIVE PATIENT,VECTORS Enter the organism of a healthy person withvegetables, water,food. Excreted into the external environment from the organism of infected persons in - the feces.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
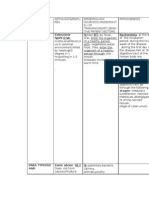
NAME OF AETIOLOGY&FEAT EPIDEMIOLOGY- PATHOGENESIS CLIN
DISEASE URES SOURCE(S),MODE(RO INC
UTE,) OF
TRANSMISSIN(RT),SEN
SITIVE
PATIENT,VECTORS
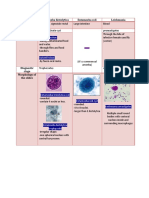
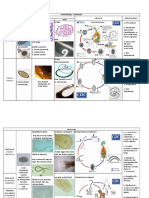
Amebiasis(ant E. histolytica, Enter the organism of Pathogen(s) of Seld
hroponosis)(20 Biological forms a healthy person with- Amebiasis: dev
) are-cyst, vegetables, protozoa. In the hist
trophozoite. water,food. Excreted human body the form
Vegetative forms into the external vegetative form cuta
are-tissue environment from the of E.histolytica unc
form(important organism of infected abd
usually
role ) , lumen persons in - the feces. indi
form
parasitizes-large
Cysts of Flat
intestine. In the
E.histolytica remain abd
large intestine-the
alive in the external digestive tract of in t
environment- the human body of i
several months.S- are the major low
man. R.T-fecal_oral. pathologic mild
Way(s) of (anatomic,morphol &d
transmission- ogical) changes in
alimentary. Factor(s) amebiasis localized.
of transmission in E. hystolitica may
Amebiasis—food, parasitize in- the
water, tissues of the colon
vegetable,fruits, wall,liver,lungs,brai
household utensis n,kidneys,pancreas.
Part(s) of the
gastrointestinal
tract may be
affected in
amebiasis-the
terminal ileum,the
cecum,the
ppendix,ascending
colon, terminal
ileum,
cecum,transverse
colon, descending
colon,
rectum. More
frequently-cecum,
ascending colon.
Morphological
changes in case
of amebiasi-
abscesses in
different
organs,ulcerative
process in the colon
wall, local necrosis
in the colon
wall.There is
hematogenous
dissemination occur
in amebiasis. The
pathological
process in
cutaneous
amebiasis develop
mainly-perianal
region, buttock
region,perineum(ge
nitalia). Relapses of
amebiasis occur-
frequently. Chronic
amebiasis may
persist for- many
months & years.
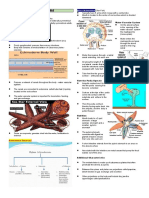
Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasma S-wild Reproductive Mai
(zoonosis)(21) gondii. Biological animals,domestic phases- con
form(s) of animals, human,cat. sexual,asexual. acu
T.gondii- Intermediate host- Sexual 1_5
bradyzoites, human, reproductionin &oc
sporozoites, cattle,domestic the organism of –fev
cyst&- animals, cat. Asexual hea
bradyzoites(respo wild animals,birds, reproduction-in men
nsible forchronic rodents. Definitive the human vom
infection), host-cat.R.T- organism.In the seq
oocysts, vertical,alimentary cattle organism. Con
tachyzoites, transplacental. organ(s) of the toxo
sporozoites.Tissue Factor(s) of body T. gondii may Tox
form(s)- transmission-fruits, infect-limph cho
bradyzoites. meat,, nodes,Liver, atro
Epidemiological pork,water,veal, Brain, lung, eye, infe
form(s)- acquired, mutton,-poultry reproductive preg
congenital products, organs, heart preg
vegetables. T.gondii muscles,skeletal toxo
inside of tissue cyst muscles, smooth the
muscles, eye, from
may remain viable
pancreas, sub
for many years gastrointestinal limp
tract,Kidney,bone min
morrow toxo
mot
trim
trim
chr
mild
hep
,Lym
reac
into
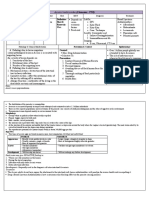
Malarial 4 species- Reservoir of Infective agents of I.P i
plasmodium(2 Vivax(widest infection in malaria malarial parasites in v
2) distributionthroug is-man. in the human body 15
Ronald Ross- hout the world S&Definitive host of mosquitoes are Typ
discovered the is),malariae – man. When concentrated in- be
most (most chronic gametocytes are salivary glands. The stag
important malaria), formed malarial following species of stag
means of ovale(least patient becomes as a malarial parasites ma
transmission incidence), source of infection. have a slee
of malaria . falciparum(sever Malaria may be tissue(exerythrociti unc
est malaria). In transmitted by c) phase of skin
India most of Mosquitos. Forms of development- low
P.malariae- malarial parasites P.vivax, P.ovale, resp
Karnataka. Not are infective to P.falciparum, arry
persistent tissue man- sporozoites. P.malaria. rem
phase in malaria infective Erythrocitic reflx
caused by- to mosquito- phase of pup
gametocyte development in the
P.falciparum
P.vivax, twit
P.malariae P.ovale,P.falciparum feca
,P.malaria.In the inco
female anopheles
mosquitoAll species
of malarial
plasmodia have a
sexual cycle of
development.
Asexual cycle -
human. True
regarding malaria
parasites- P.vivax
develops most
easily in the
youngest
erythrocytes,
P.falciparum affects
all stages of the red
cells,P.malaria
develops most
easily in older
erythrocytes.Durat
ion of
erythrocytic cycle
is 48 hours in
malaria,caused
by-P.vivax,P.ovale,
P.falciparum, 72
hours in malaria
caused by-
P.malariae. Kind of
immunity- repeated
infection may
occur, nonsterile
immunity,does not
produce long
immunity, repeated
infection may
occur.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument2 pagesBacterial InfectionsDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amoeba paraDocument9 pagesAmoeba paraHANNA CASANDRA GARCIAPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Document25 pagesTOPNOTCH Parasitology-Supertable-by-Yns-Pereyra-Cocoy-Calderon-Troy-Soberano-UPDATED-NOVEMBER-2017Waiwit KritayakiranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Micropara (Lab) - Protozoa and Nematodes - Quimno, Ivy N.Document24 pagesMicropara (Lab) - Protozoa and Nematodes - Quimno, Ivy N.ivyPas encore d'évaluation
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtPas encore d'évaluation
- Endoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsDocument5 pagesEndoparasites: (Edit) Protozoan OrganismsimarzenPas encore d'évaluation
- Amoeba Notes 2015Document6 pagesAmoeba Notes 2015Ivy FlorentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 9 HelminthiasisDocument16 pagesCase 9 HelminthiasisNicole NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Helminth Identification and Treatment GuideDocument3 pagesHelminth Identification and Treatment GuideOmphile DansonPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (1)
- INTERMEDIATE HOSTS AND TRANSMISSION MODES IN PARASITIC INFECTIONSDocument3 pagesINTERMEDIATE HOSTS AND TRANSMISSION MODES IN PARASITIC INFECTIONSJoanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasite Morphology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument18 pagesParasite Morphology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and TreatmentManuel RendonPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimPas encore d'évaluation
- AMOEBIASISDocument11 pagesAMOEBIASISsrini9047Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Kingdom Classification and CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom Classification and CharacteristicsAnusree M.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Causing OrganismsDocument4 pagesDisease Causing OrganismsANKITA GAYENPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianPas encore d'évaluation
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases TableKavya SrinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Echinodermata: General CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesPhylum Echinodermata: General CharacteristicsRhod JamandrePas encore d'évaluation
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamPas encore d'évaluation
- ProtozoansDocument3 pagesProtozoansJansen SalgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Wall SurgeryDocument8 pagesAbdominal Wall SurgeryRae Marie AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806Pas encore d'évaluation
- MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesMicrobiologyAnimesh GiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology Guru GuideDocument30 pagesParasitology Guru GuideChristopher Rey BurcePas encore d'évaluation
- TrematodesDocument2 pagesTrematodesIan Josef R. VibarPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Key Features of Protozoan ParasitesDocument3 pagesComparing Key Features of Protozoan ParasitesLembemPas encore d'évaluation
- PARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Document9 pagesPARASITOLOGY (Quizlet)Allyssa AniPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary TrematodesDocument3 pagesSummary TrematodesJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pointers For Medically Important BacteriaDocument2 pagesPointers For Medically Important BacteriamerryPas encore d'évaluation
- AmebaDocument53 pagesAmebaapi-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Report of An Epidermal Papilloma in Mustelus CanisDocument6 pagesA Case Report of An Epidermal Papilloma in Mustelus CanisMichael A. GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes SummaryDocument6 pagesTrematodes SummaryabigailPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes and RicktesiosisDocument2 pagesTrematodes and RicktesiosisDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalDocument21 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalPatricia CabisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesDocument3 pagesTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro ParasitesDocument4 pagesMicro ParasitesKrisha Marie BadilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Top Parasites and DiseasesDocument47 pagesTop Parasites and DiseasesDIVINE GRACE FLORITA PEPITOPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Notes (2nd Sem) 1Document133 pagesAnatomy Notes (2nd Sem) 1Abegail DanasenPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes: Intestinal SpeciesDocument7 pagesTrematodes: Intestinal SpeciesMica BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Factor Normal Cancer CytoplasmDocument2 pagesFactor Normal Cancer CytoplasmYuji TanakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemKirsten CruzadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal NutritionDocument51 pagesAnimal NutritionknlsinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- DIAGNOSIS OF INGUINAL HERNIA AND VARICOCELEDocument3 pagesDIAGNOSIS OF INGUINAL HERNIA AND VARICOCELEdianPas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes LECDocument2 pagesTrematodes LECAki SuzumePas encore d'évaluation
- Super Parasitology TableDocument11 pagesSuper Parasitology Tablesleepyhead archerPas encore d'évaluation
- Small intestinal surgery principlesDocument12 pagesSmall intestinal surgery principlesSara ConnorPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAanchal Pandey100% (2)
- Medical Prefixes and SuffixesDocument12 pagesMedical Prefixes and SuffixesKrishnanunni KLPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitic infections of the gastrointestinal tract and bloodDocument4 pagesParasitic infections of the gastrointestinal tract and bloodAdel AlomarPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspects: Fasciola Hepatica Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument7 pagesAspects: Fasciola Hepatica Fasciolopsis BuskiAnand_Ram_7113Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: Erratic MigrationDocument16 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: Erratic MigrationSiti NurainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Medfools Parasites Chart for USMLE IDocument7 pagesMedfools Parasites Chart for USMLE IJane SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- D Colorectal (blue keyword pyq)Document4 pagesD Colorectal (blue keyword pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqPas encore d'évaluation
- E. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesDocument11 pagesE. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesCorinne MandrezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncma121 Final ReviewerDocument48 pagesNcma121 Final Reviewerchloepaxton030Pas encore d'évaluation
- PorphyriaDocument10 pagesPorphyriaDeepankar Srigyan0% (1)
- Acute Abdomen and Peptic UlcerDocument69 pagesAcute Abdomen and Peptic UlcerDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hodgkin's LymphomaDocument10 pagesHodgkin's LymphomaDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccinations Are Offered To All Children ToDocument1 pageVaccinations Are Offered To All Children ToDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytoestrogens and Breast CancerDocument6 pagesPhytoestrogens and Breast CancerDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease Incubation PeriodDocument1 pageDisease Incubation PeriodDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs in PregnancyDocument2 pagesDrugs in PregnancyDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytoestrogens: Phytoestrogens, Sometimes Called "Dietary Estrogens", Are A Diverse Group of Naturally OccurringDocument5 pagesPhytoestrogens: Phytoestrogens, Sometimes Called "Dietary Estrogens", Are A Diverse Group of Naturally OccurringDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytoestrogens: - by Deepankar SrigyanDocument13 pagesPhytoestrogens: - by Deepankar SrigyanDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Evidence Based MedicinesDocument9 pagesEvidence Based MedicinesDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemolytic AnemiasDocument25 pagesHemolytic AnemiasDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Macrocytic AnemiasDocument28 pagesMacrocytic AnemiasDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancient India's Contribution To Medical ScienceDocument14 pagesAncient India's Contribution To Medical ScienceDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Stable and Light Sensitive Vitamin KDocument2 pagesHeat Stable and Light Sensitive Vitamin KDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Birth InjuriesDocument104 pagesFetal Birth InjuriesDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- AttitudeDocument9 pagesAttitudewhereisthebody100% (13)
- Prostate CancerDocument14 pagesProstate CancerDeepankar Srigyan100% (1)
- Blood DiseasesDocument42 pagesBlood DiseasesDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Say I Love You in 100 LanguagesDocument4 pagesHow To Say I Love You in 100 LanguagesRosca MariusPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast CancerDocument7 pagesBreast CancerDeepankar Srigyan100% (1)
- HepatitisDocument10 pagesHepatitisDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Patient Case History 2009Document11 pagesPediatric Patient Case History 2009Deepankar Srigyan100% (1)
- Three EnemiesDocument1 pageThree EnemiesDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG LectureDocument97 pagesECG LectureDeepankar Srigyan100% (4)
- ImmunityDocument2 pagesImmunityDeepankar Srigyan100% (1)
- Trematodes and RicktesiosisDocument2 pagesTrematodes and RicktesiosisDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- NewYear PpsDocument1 pageNewYear PpsDeepankar SrigyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Health Project of India 2008Document143 pagesPublic Health Project of India 2008Deepankar Srigyan80% (5)
- 2-1-2021 Response To LandlordDocument2 pages2-1-2021 Response To LandlordJessica SwarnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ar-Afff 3 MSDS LCFDocument5 pagesAr-Afff 3 MSDS LCFMark YePas encore d'évaluation
- Warehouse Center Checklist 2Document5 pagesWarehouse Center Checklist 2Sankar ChinnathambiPas encore d'évaluation
- Changes in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidDocument3 pagesChanges in Demand and Supply of Face Masks Under CovidHanh HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Diass Prelim ExamDocument9 pagesDiass Prelim ExamLea Luayon Garcia100% (1)
- Respiratory MechanicsDocument27 pagesRespiratory MechanicsKarla Hernandez100% (1)
- IlpDocument13 pagesIlpapi-253729868Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointDocument3 pagesTypes and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- THHV- 18 G10 ĐỀ NÂNG CAO TỔNG HỢP SỐ 2Document12 pagesTHHV- 18 G10 ĐỀ NÂNG CAO TỔNG HỢP SỐ 2hCby 28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aiapget 2020 QPDocument29 pagesAiapget 2020 QPGanesh RadhakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Marijuana Fact SheetDocument1 pageMarijuana Fact Sheetapi-355176759Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brosur SucofindoDocument14 pagesBrosur SucofindoJay Van BuurninkPas encore d'évaluation
- Vanessa Tarot BookletDocument36 pagesVanessa Tarot BookletClassic Bobby100% (2)
- Principles of Health AdminDocument42 pagesPrinciples of Health AdminAnne BattulayanPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsDocument3 pages16 Potential Key Performance Indicators For HospitalsSyed Murtuza BakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nike Vietnam Factory Empowerment Through Information CampaignsDocument8 pagesNike Vietnam Factory Empowerment Through Information Campaignsvaibhav262Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 2 Internal OrgansDocument1 page02 2 Internal OrgansgabrielaPas encore d'évaluation
- Single/ Exam Zone Centre DetailsDocument5 pagesSingle/ Exam Zone Centre DetailsHarsh AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Exposition Text Corona Should Be Against Surround UsDocument2 pagesAnalytical Exposition Text Corona Should Be Against Surround UsRifkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Trainer TextDocument97 pagesPersonal Trainer Textwuddafren100% (1)
- Postnatal Assessment FormatDocument16 pagesPostnatal Assessment FormatValarmathi92% (13)
- Child Development A Cultural Approach 2nd Edition Arnett Solutions Manual DownloadDocument37 pagesChild Development A Cultural Approach 2nd Edition Arnett Solutions Manual DownloadMichael Pontius100% (24)
- Managing Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDocument2 pagesManaging Mental Health and Stress Online CourseDakota624Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideDocument26 pagesFibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideMuhammad HafizuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- "Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemDocument12 pages"Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemdrnikhilbobadePas encore d'évaluation
- Nutraceutical Products in India Market ReportDocument7 pagesNutraceutical Products in India Market ReportMadan Mohan Sharan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ultimate Guide To Anxiety DisordersDocument66 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Anxiety Disordersnajaxx100% (2)
- Details of Positive Cases in Kurnool DistrictDocument60 pagesDetails of Positive Cases in Kurnool DistrictSohail MullaPas encore d'évaluation
- SASO 1431 (GS 1355) SorbitolDocument5 pagesSASO 1431 (GS 1355) SorbitolakPas encore d'évaluation
- SWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanDocument1 pageSWP-23 Maintenance Machinery Regime DaimanHassan AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation