Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Aspirin Drug Summ
Transféré par
Warren0%(1)0% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
2K vues2 pagesDrug summary in full details with info.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDrug summary in full details with info.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0%(1)0% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
2K vues2 pagesAspirin Drug Summ
Transféré par
WarrenDrug summary in full details with info.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Score: _________ Grade: _____________
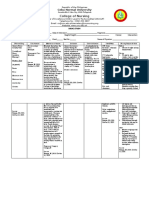
DRUG SUMMARY
Name of Drug Date Classification Dose Mechanism Specific Side Effects Nursing Implications
Generic Ordered Frequenc of Action Indication
(Brand) y
Route
Aspirin Antipyretics, 80 mg tab Produce Prophylaxis EENT: hearing loss, BEFORE:
Non-opioid od analgesia and of transient tinnitus. >Patients who have asthma,
(acetylsalicylic GI: GI BLEEDING,
analgesics PO reduce ischemic allergies, and nasal polyps or
acid) dyspepsia, epigastric who are allergic to tartrazine are
inflammation and attacks and distress, heartburn, at an increased risk for
fever by inhibiting MI. nausea, abdominal developing hypersensitivity
the production of pain, anorexia, reactions.
prostaglandins hepatotoxicity,
vomiting. DURING:
Hemat: aspirin— >Do not crush or chew enteric-
Decreases anemia, hemolysis, coated tablets.
platelet increased bleeding >Administer after meals or with
aggregation. time. food or an antacid to minimize
Misc: allergic reactions gastric irritation. Food slows but
including does not alter the total amount
ANAPHYLAXIS and absorbed.
LARYNGEAL EDEMA, AFTER:
noncardiogenic >Assess pain and limitation of
pulmonary edema. movement; note type, location,
and intensity before and at the
peak after administration.
>Caution patient to avoid
concurrent use of alcohol with
this medication to minimize
possible gastric irritation;
Reference: DAVIS DRUG GUIDE FOR NURSES 8th EDITION___
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management Planrojon pharmacy84% (37)
- NIcardipine Drug SummDocument1 pageNIcardipine Drug SummWarren50% (2)
- NCP Pain HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP Pain HypertensionEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Ranitidine Drug SummDocument1 pageRanitidine Drug SummWarren100% (3)
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors - Past, Present and Future - S. Stanford (Landes, 1999) WWDocument237 pagesSelective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors - Past, Present and Future - S. Stanford (Landes, 1999) WWKitty CristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Books PDFDocument29 pagesList of Books PDFDevansh Agarwal75% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityShiva TorinsPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Mandibular)Document5 pagesNCP Mandibular)yellarfPas encore d'évaluation
- CarvedilolDocument2 pagesCarvedilolKarl Lourenz DeysolongPas encore d'évaluation
- JM CarbocisteineDocument1 pageJM CarbocisteineKatrina MagtalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGrace CadawasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study RopivacaineDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarPas encore d'évaluation
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaPas encore d'évaluation
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaPas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81Pas encore d'évaluation
- IrbesartanDocument3 pagesIrbesartanapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAspirin Drug StudyIRISH CACAYANPas encore d'évaluation
- DS (Fenofibrate)Document5 pagesDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- HydrocortisoneDocument4 pagesHydrocortisoneiammaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study #2Document3 pagesDrug Study #2mharjoe pulmanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHPas encore d'évaluation
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)Document3 pagesDrug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)amitPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY Allopurinol (Purinase)DennMarkTaponPas encore d'évaluation
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug CarbocisteineDocument1 pageDrug CarbocisteineDhan LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanPas encore d'évaluation
- Insuget Drug StudyDocument1 pageInsuget Drug StudydollythesheepPas encore d'évaluation
- Therabloc DrugDocument2 pagesTherabloc DrugMsOrangePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanDocument1 pageDrug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanVoid LessPas encore d'évaluation
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 pagesNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCeftriaxone Drug StudyRose EchevarriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY CLOBETASOL CREAMrevisedswitchlers annePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRej Gallien PontalbaPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY AtorvastatinKyla BeconiaPas encore d'évaluation
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Document5 pagesF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioPas encore d'évaluation
- AlgesiaDocument1 pageAlgesiaSaf DicamPas encore d'évaluation
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidPas encore d'évaluation
- FenofibrateDocument4 pagesFenofibrateGwyn RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyGerome ManantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Apr. 8-11 Grp3 Sched For ScribdDocument1 pageApr. 8-11 Grp3 Sched For ScribdWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Tentative Sched For Apr 28-30 & May 1Document1 pageTentative Sched For Apr 28-30 & May 1WarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mar. 19-22 Grp3 Sched For ScribdDocument1 pageMar. 19-22 Grp3 Sched For ScribdWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 3 Nurse Volunteer Schedule Feb 7 - 10 & Feb 27 - Mar 2Document3 pagesGroup 3 Nurse Volunteer Schedule Feb 7 - 10 & Feb 27 - Mar 2WarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Vit.B Complex Drug SummDocument1 pageVit.B Complex Drug SummWarren100% (5)
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gentamicin Drug SummDocument1 pageGentamicin Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Clarithromycin Drug SummDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug SummWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummDocument1 pageAcetaminophen Paracetamol Drug SummWarren100% (1)
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Alzheimer Disease Case StudyDocument6 pagesAlzheimer Disease Case StudyWarren67% (3)
- Control Banding B NaumannDocument11 pagesControl Banding B NaumannipliprensPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Clinical TrialsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Trialsmuhammad murtazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory ManualDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory Manuallalag yanPas encore d'évaluation
- NABH Standard Document Matrix D125Document18 pagesNABH Standard Document Matrix D125senthilPas encore d'évaluation
- Halar 300DADocument2 pagesHalar 300DAJayvee FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- TC 218661-Vrbg-Gelose EN 110909Document2 pagesTC 218661-Vrbg-Gelose EN 110909dijana9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Duphalac Bristol PediaFlyerDocument2 pagesDuphalac Bristol PediaFlyerNikola StojsicPas encore d'évaluation
- GMP ManualDocument26 pagesGMP ManualBobec TungolPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Benefits Enrollment Expert in Chicago IL Resume Paulette BarrettDocument2 pagesEmployee Benefits Enrollment Expert in Chicago IL Resume Paulette BarrettPauletteBarrettPas encore d'évaluation
- Hakim Muhammad Said Was Born in New DelhiDocument2 pagesHakim Muhammad Said Was Born in New DelhiMuhammad BilalPas encore d'évaluation
- 903Document8 pages903getjenPas encore d'évaluation
- Schedule J - WikipediaDocument9 pagesSchedule J - WikipediaArabic ArabicPas encore d'évaluation
- The Medication Order Unit 11Document10 pagesThe Medication Order Unit 11novie100% (2)
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaMarya Fanta C LupuPas encore d'évaluation
- Insitu GelDocument96 pagesInsitu Gelvinsijuvin555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Registration in ASEAN CountriesDocument35 pagesDrug Registration in ASEAN CountriesAvish JollyPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology Industry DatabaseDocument150 pagesBiotechnology Industry Databasebrindatamma100% (2)
- 〈711〉 DissolutionDocument12 pages〈711〉 DissolutionArifin Rh92Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 2 Bioaivers ExperienceDocument80 pages2 2 Bioaivers Experienceblashyrkh_79Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14.natural GumsDocument10 pages14.natural Gumsparuldutt1996Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dysthymia More Than "Minor" DepressionDocument5 pagesDysthymia More Than "Minor" DepressionNathaly BerríoPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of General AnesthesiaDocument60 pagesPrinciples of General Anesthesiaمحمد عبد حسين100% (5)
- Questions in Our MindDocument21 pagesQuestions in Our MindpundalikPas encore d'évaluation
- The Green Chemistry Approach To Pharma ManufacturingDocument4 pagesThe Green Chemistry Approach To Pharma ManufacturingSiti ChotimahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3 Dealing With MedicationDocument12 pagesLesson 3 Dealing With Medicationkim chi 04Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Government of Pakistan Ministry of Health and Social WelfareDocument3 pagesThe Government of Pakistan Ministry of Health and Social Welfarefysi mackPas encore d'évaluation
- Rule: Animal Drugs, Feeds, and Related Products: Pimobendan Oral Dosage FormDocument1 pageRule: Animal Drugs, Feeds, and Related Products: Pimobendan Oral Dosage FormJustia.comPas encore d'évaluation