Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Enlargement Gingival
Transféré par
Muhammad WachidDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Enlargement Gingival
Transféré par
Muhammad WachidDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
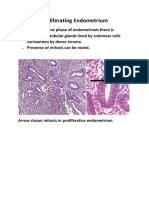
INFLAMMATORY ENLARGEMENT Chronic Inflammatory Enlargement Histopathology Chronic inflammatory gingival enlargements show the exudative and proliferative
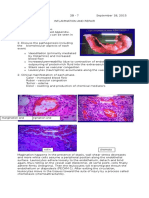
features of chronic inflammation (Figure 9-3). Lesions that are clinically deep red or bluish red are soft and friable with a smooth, shiny surface, and they bleed easily. They also have a preponderance of inflammatory cells and fluid, with vascular engorgement, new capillary formation, and associated degenerative changes. Lesions that are relatively firm, resilient, and pink have a greater fibrotic component with an abundance of fibroblasts and collagen fibers Acute Inflammatory Enlargement Histopathology The gingival abscess consists of a purulent focus in the connective tissue, surrounded by a diffuse infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), edematous tissue, and vascular engorgement. The surface epithelium has varying degrees of intracellular and extracellular edema, invasion by leukocytes, and sometimes ulceration. DRUG-INDUCED GINGIVAL ENLARGEMENT Histopathology Drug-induced gingival enlargement consists of a pronounced hyperplasia of the connective tissue and epithelium (Figure 9-9). There is acanthosis of the epithelium, and elongated rete pegs extend deep into the connective tissue, which exhibits densely arranged collagen bundles with an increase in the number of fibroblasts and new blood vessels.90 An abundance of amorphous ground substance has also been reported.68 Structural changes in the outer epithelial cell surface have been reported in cyclosporine-induced enlargements.3 The enlargement begins as a hyperplasia of the connective tissue core of the marginal gingiva and increases by its proliferation and expansion beyond the crest of the gingival margin. An inflammatory infiltrate may be found at the bottom of the sulcus, or pocket. Cyclosporine enlargements usually have a more highly vascularized connective tissue with foci of chronic inflammatory cells, particularly plasma cells.75 The mature phenytoin enlargement has a fibroblast/collagen ratio equal to that of normal gingiva from normal individuals, suggesting that at some point in the development of the lesion, fibroblastic proliferation must have been abnormally high.43 Recurring phenytoin enlargements appear as granulation tissue composed of numerous young capillaries and fibroblasts and irregularly arranged collagen fibrils with occasional lymphocytes. IDIOPATHIC GINGIVAL ENLARGEMENT Histopathology Idiopathic gingival enlargement shows a bulbous increase in the amount of connective tissue that is relatively avascular and consists of densely arranged collagen bundles and numerous fibroblasts. The surface epithelium is thickened and acanthotic with elongated rete pegs. ENLARGEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH SYSTEMIC DISEASES Conditioned Enlargements Enlargement in Pregnancy. Histopathology
Gingival enlargement in pregnancy is called angiogranuloma. Both marginal and tumorlike enlargements consist of a central mass of connective tissue, with numerous diffusely arranged, newly formed, and engorged capillaries lined by cuboid endothelial cells (Figure 9-14), as well as a moderately fibrous stroma with varying degrees of edema and chronic inflammatory infiltrate. The stratified squamous epithelium is thickened, with prominent rete pegs and some degree ofintracellular and extracellular edema, prominent intercellular bridges, and leukocytic infiltration. Enlargement in Puberty. Histopathology The microscopic appearance of gingival enlargement in puberty is chronic inflammation with prominent edema and associated degenerative changes. Enlargement in Vitamin C Deficiency. Histopathology In vitamin C deficiency the gingiva has a chronic inflammatory cellular infiltration with a superficial acute response. There are scattered areas of hemorrhage, with engorged capillaries. Marked diffuse edema, collagen degeneration, and scarcity of collagen fibrils or fibroblasts are striking findings. Plasma Cell Gingivitis. Histopathology In plasma cell gingivitis the oral epithelium shows spongiosis and infiltration with inflammatory cells; ultrastructurally, there are signs of damage in the lower spinous layers and the basal layers. The underlying connective tissue contains a dense infiltrate of plasma cells that also extends to the oral epithelium, inducing a dissecting type of injury.76 Systemic Diseases That Cause Gingival Enlargement Leukemia. Histopathology Gingival enlargements in leukemic patients show various degrees of chronic inflammation. Mature leukocytes and areas of connective tissue are infiltrated with a dense mass of immature and proliferating leukocytes, the specific nature of which varies with the type of leukemia. Engorged capillaries, edematous and degenerated connective tissue, and epithelium with various degrees of leukocytic infiltration and edema are found. Isolated surface areas of acute necrotizing inflammation with a pseudomembranous meshwork of fibrin, necrotic epithelial cells, PMNs, and bacteria are often seen. Granulomatous Diseases Wegeners Granulomatosis Histopathology Chronic inflammation occurs, with scattered giant cells and foci of acute inflammation and microabscesses covered by a thin, acanthotic epithelium. Vascular changes have not been described with gingival enlargement in Wegeners granulomatosis, probably because of the small size of the gingival blood vessels.51 Sarcoidosis. Histopathology Sarcoid granulomas consist of discrete, noncaseating whorls of epithelioid cells and multinucleated, foreign bodytype giant cells with peripheral mononuclear cells.88
NEOPLASTIC ENLARGEMENT (GINGIVAL TUMORS) Benign Tumors of the Gingiva Fibroma. Histopathology Fibromas are composed of bundles of wellformed collagen fibers with a scattering of fibrocytes and a variable vascularity Papilloma. Histopathology The papilloma lesion consists of fingerlike projections of stratified squamous epithelium, often hyperkeratotic, with a central core of fibrovascular connective tissue. Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma. Histopathology The giant cell granuloma has numerous foci of multinuclear giant cells and hemosiderin particles in a connective tissue stroma (see Figure 9-22). Areas of chronic inflammation are scattered throughout the lesion, with acute involvement occurring at the surface. The overlying epithelium is usually hyperplastic, with ulceration at the base. Bone formation occasionally occurs within the lesion (Figure 9-23). Central Giant Cell Granuloma Leukoplakia. Histopathology Leukoplakia exhibits hyperkeratosis and acanthosis. Premalignant and malignant cases have a variable degree of atypical epithelial changes that may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of involvement of the epithelial layers. When dysplastic changes involve all layers, it is diagnosed as a carcinoma in situ, and this may become invasive carcinoma when the basement membrane is breached.31 Inflammatory involvement of the underlying connective tissue is a common associated finding. Gingival Cyst. Histopathology A gingival cyst cavity is lined by a thin, flattened epithelium with or without localized areas of thickening. Less frequently, the following types of epithelium can be found: unkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, and parakeratinized epithelium with palisading basal cells.16
INFLAMASI PEMBESARAN Pembesaran inflamasi kronis Histopatologi Pembesaran gingiva inflamasi kronis menunjukkan ciri eksudatif dan proliferatif peradangan kronis. Lesi yang secara klinis merah tua atau merah kebiruan lembut dan mudah pecah dengan permukaan halus, mengkilat, dan mereka mudah berdarah. Mereka juga memiliki kelebihan dari sel-sel inflamasi dan cairan, dengan pembengkakan pembuluh darah, pembentukan kapiler yang baru dan terkait dengan perubahan degeneratif. Lesi yang relatif kuat, tangguh, dan merah muda memiliki komponen fibrotic yang lebih besar dengan fibroblas dan serat kolagen yang berlimpah Pembesaran inflamasi akut Histopatologi Abses gingiva terdiri dari inti bernanah di jaringan ikat, dikelilingi oleh infiltrasi polimorfonuklear (PMNs) yang menyebar, edematous jaringan dan pembengkakan pembuluh darah. Epitel permukaan memiliki berbagai derajat intraseluler dan ekstraseluler edema, invasi oleh leukosit meningkat, dan kadang-kadang terdapat ulserasi. OBAT-INDUCED PEMBESARAN GINGIVA Histopatologi Obat-induced pembesaran gingiva terdiri dari hiperplasia yang jelas pada jaringan ikat dan epitel. Ada acanthosis dari epitel, dan rete pegs memanjang jauh ke dalam jaringan ikat, yang memadat diatur kumpulan kolagen dengan peningkatan jumlah fibroblas dan pembuluh darah baru. Juga terdapat kelimpahan amorf dari substansi dasar. Perubahan struktur di permukaan sel epitel luar telah dilaporkan di perluasan yang diinduksi siklosporin. Pembesaran dimulai sebagai hiperplasia inti jaringan ikat dari marginal gingiva dan meningkatkan oleh proliferasi dan meluas ke luar puncak margin gingiva. Inflamasi infiltrasi dapat ditemukan di bagian bawah sulkus, atau pocket. Perluasan siklosporin biasanya memiliki jaringan ikat yang bervaskularisasi lebih tinggi dengan inti dari sel-sel inflamasi kronis, khususnya sel plasma. Pembesaran fenitoin "dewasa" memiliki rasio fibroblast kolagen yang setara dengan gingiva normal dari individu normal, menunjukkan bahwa di beberapa titik dalam perkembangan lesi, fibroblast proliferasi pasti terjadi abnormalitas yang tinggi. Perluasan fenitoin yang berulang muncul sebagai jaringan granulasi yang terdiri dari banyak kapiler muda dan fibroblas dan kolagen fibril yang tersusun tidak teratur dengan jarang terdapat limfosit. IDIOPATIK PEMBESARAN GINGIVA Histopatologi Pembesaran gingiva idiopatik menunjukkan peningkatan jumlah bulbous pada jaringan ikat yang relatif avascular dan terdiri dari kumpulan kolagen padat yang teratur dan banyak fibroblast. Epitel permukaan menebal dan acanthotic dengan rete pegs memanjang. PERLUASAN YANG TERKAIT DENGAN PENYAKIT SISTEMIK
Perluasan berPembesaran pada kehamilan. Histopatologi Pembesaran gingiva pada kehamilan disebut angiogranuloma. Perluasan marginal dan tumorlike terdiri dari massa jaringan ikat, dengan banyak kapiler tersusun menyebar, baru terbentuk dan membesar yang dilapisi oleh sel-sel endotel yang berbentuk kubus, serta stroma cukup berserat dengan berbagai tingkat edema dan infiltrasi inflamasi kronis. Epitel skuamosa berlapis menebal, dengan rete pegs menonjol dan beberapa derajat edema intraselular dan ekstraseluler, jembatan interselular tampak dan ada infiltrasi leukocytic. Pembesaran pada masa pubertas. Histopatologi Munculnya mikroskopis pembesaran gingiva masa pubertas adalah peradangan kronis dengan adanya edema dan terkait perubahan degeneratif. Pembesaran pada kekurangan Vitamin C. Histopatologi Kekurangan vitamin C gingiva terdapat infiltrasi inflamasi kronis selular dengan respons akut yang superfisial. Yang tersebar di daerah perdarahan, dengan kapiler membesar. Ditandai edema menyebar, degenerasi kolagen dan kelangkaan kolagen fibril atau fibroblas merupakan temuan yang mencolok. Gingivitis sel plasma. Histopatologi Dalam sel plasma gingivitis, epitel oral menunjukkan spongiosis dan infiltrasi dengan sel-sel inflamasi; ultrastructurally, ada tanda-tanda kerusakan di lapisan spinous dan lapisan basal yang lebih rendah. Jaringan ikat yang mendasari berisi infiltrasi padat dari sel-sel plasma yang juga meluas ke oral ephitelium, mempengaruhi cedera karena bedah. Penyakit sistemik yang menyebabkan pembesaran gingiva
Leukemia. Histopatologi Pembesaran gingiva pada pasien leukemia menunjukkan berbagai derajat peradangan kronis. Leukosit dewasa meningkat dan area jaringan ikat diisi dengan massa padat leukosit yang belum matang dan masih berkembang, sifatnya bervariasi dengan tipe leukemia tertentu. Terdapat kapiler membesar, edematous dan degenerasi jaringan ikat dan epitel dengan berbagai tingkat infiltrasi leukocytic dan edema. Daerah permukaan yang terisolasi peradangan necrotic akut dengan meshwork pseudomembranous dari fibrin, sel-sel epitel nekrotik, PMNs, dan bakteri sering terlihat. Granulomatous penyakit Wegener Granulomatosis Histopatologi Terjadi peradangan kronis, dengan sel-sel raksasa yang tersebar dan inti peradangan akut dan microabscesses tertutup oleh epitel acanthotic tipis,. Perubahan vaskular tidak dijelaskan dengan pembesaran gingiva di Wegener granulomatosis, mungkin karena kecilnya ukuran pembuluh darah gingiva. Sarkoidosis.
Histopatologi Granuloma sarcoid terdiri dari diskrit, ulir dari sel epitel dan berinti banyak, sel raksasa tipe asing dengan sel berinti satu di tepinya. NEOPLASTIC PEMBESARAN (GINGIVA TUMOR) Tumor jinak gingiva Fibroma. Histopatologi Fibromas terdiri dari kumpulan serat kolagen dengan fibrocytes yang berserakan dan variabel vaskularisasi. Papiloma. Histopatologi Lesi papiloma terdiri dari proyeksi fingerlike dari epitel skuamosa berlapis, sering hyperkeratotic, dengan inti pusat dari jaringan ikat fibrovascular. Granuloma perifer sel raksasa. Histopatologi Sel raksasa granuloma memiliki banyak inti dari sel-sel raksasa multinuclear dan partikel hemosiderin dalam stroma jaringan ikat. Daerah peradangan kronis tersebar di seluruh lesi, dengan keterlibatan akut yang terjadi pada permukaan. Epitel atasnya biasanya hyperplastic, dengan ulserasi di dasar. Pembentukan tulang kadangkadang terjadi dalam lesi. Pusat sel raksasa Granuloma Leukoplakia. Histopatologi Leukoplakia tampak hyperkeratosis dan acanthosis. Kasus semi ganas dan ganas memiliki derajat variabel perubahan atipikal epitel yang mungkin ringan, sedang, atau berat, tergantung pada tingkat keterlibatan lapisan epitel. Ketika perubahan dysplastic melibatkan semua lapisan, itu didiagnosis sebagai carcinoma in situ, dan ini mungkin menjadi karsinoma invasif ketika membran basement dilanggar. Keterlibatan inflamasi jaringan ikat yang mendasari adalah temuan umum yang terkait. Gingiva kista. Histopatologi Rongga gingiva kista dilapisi oleh epitel tipis, pipih dengan atau tanpa wilayah lokal dari penebalan. Kurang sering, jenis epitel berikut dapat ditemukan: epitel skuamosa berlapis tidak berkeratin, epitel skuamosa berlapis berkeratin dan epitel parakeratin dengan palisading sel-sel basal.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rifts - The Complete Skills BookDocument104 pagesRifts - The Complete Skills BookSgt. Mushroom100% (2)
- DisabilityDocument450 pagesDisabilityTony Kelbrat100% (1)
- Brief Evaluation of Executive DysfunctionDocument2 pagesBrief Evaluation of Executive DysfunctionIon Arrieta ValeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Roman AchievmentsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Roman Achievmentsapi-253749086100% (1)
- MSK CasesDocument331 pagesMSK CasesRadio Resident100% (6)
- Olive Leaf ExtractDocument9 pagesOlive Leaf ExtractCristina100% (1)
- Idiopathic Non Neoplastic Salivary Gland DiseasesDocument33 pagesIdiopathic Non Neoplastic Salivary Gland Diseasesgud4nothingPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Acquired PneumoniaDocument48 pagesHospital Acquired PneumoniaKartika RezkyPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN MidtermDocument119 pagesCHN MidtermAbellon Maria PaulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gingival InflammationDocument12 pagesGingival InflammationdeenmPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervicofacial LymphangiomasDocument11 pagesCervicofacial LymphangiomasCharmila Sari100% (1)
- Connective Tissue LesionsDocument285 pagesConnective Tissue LesionsRwskhans KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Necrotizing SialometaplasiaDocument33 pagesNecrotizing SialometaplasiaJessica GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Periodontal DiseasesDocument18 pagesClassification of Periodontal DiseasesDock AcePas encore d'évaluation
- Ug Practical SlideDocument18 pagesUg Practical SlideKPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodontal Pathogenesis SalinanDocument66 pagesPeriodontal Pathogenesis SalinanEka RahayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Margination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionDocument3 pagesMargination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionKat JolejolePas encore d'évaluation
- BDS10012 Oral HyperplasiaDocument50 pagesBDS10012 Oral Hyperplasiahabibahafez282Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amyloid, Chronic Cholecystitis, Acute AppendicitisDocument29 pagesAmyloid, Chronic Cholecystitis, Acute AppendicitisDivya GauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Microscopy - Practical Exam (English Programme)Document16 pagesMicroscopy - Practical Exam (English Programme)Salsa Salaa HPas encore d'évaluation
- Gambar Makros Mikros RadangDocument41 pagesGambar Makros Mikros RadangBevi Ayu Kumala WardaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Glomerular Diseases: Ass - Prof. Rihab Al-Mudhaffer Kufa University Department of Pathology and Forensic MedicineDocument37 pagesGlomerular Diseases: Ass - Prof. Rihab Al-Mudhaffer Kufa University Department of Pathology and Forensic MedicineAli HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- PA IMODocument31 pagesPA IMOAulia RahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Small Intestine and Colon Account For The Majority of GIDocument13 pagesThe Small Intestine and Colon Account For The Majority of GIMohammed Yousif AbdualjabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Intestinal Tuberculosis and AppendixDocument45 pagesIntestinal Tuberculosis and AppendixrashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fascia PathologyDocument37 pagesFascia PathologytheintrovPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019 Dr. Sahilah Kelainan KonjungtivaDocument15 pages2019 Dr. Sahilah Kelainan KonjungtivaYoggaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Appendicitis: InflammationDocument3 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Inflammationshahidkhan 654321654321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Patho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Document34 pagesPatho FEU PGI BCA Exit Exam May 2020Sheryl Layne LaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vascular Tumors: Pgi Pauline BaluisDocument114 pagesVascular Tumors: Pgi Pauline BaluisPahw BaluisPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Diseases That Cause Gingival Enlargement: LeukemiaDocument7 pagesSystemic Diseases That Cause Gingival Enlargement: LeukemiaCristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOLOGYJasellePantePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Document26 pagesPathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Lin AdutPas encore d'évaluation
- Gingival EnlargementDocument56 pagesGingival EnlargementVikas ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulcerative Colitis: Pathogenesis & PathologyDocument12 pagesUlcerative Colitis: Pathogenesis & PathologyironPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodontal Pathology: by Dr. Marcel HallareDocument24 pagesPeriodontal Pathology: by Dr. Marcel Hallareceudmd3d100% (1)
- Wound Healing: Schwartz'S Principles of Surgery 10 EdDocument95 pagesWound Healing: Schwartz'S Principles of Surgery 10 EdPatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument28 pagesChronic Pyelonephritisarun j.rPas encore d'évaluation
- 200 Important Points of Special Pathology - DR NotesDocument17 pages200 Important Points of Special Pathology - DR NotesDr NotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Conjunctivitis: by PGMI Jasleen MonrealDocument77 pagesConjunctivitis: by PGMI Jasleen MonrealJade MonrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical No 29 - Gastrointestinal TractDocument7 pagesPractical No 29 - Gastrointestinal Tractkartik.patil151106Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tumors of Oral CavityDocument57 pagesTumors of Oral CavityRobins DhakalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mutia Skenario B Blok 19Document8 pagesMutia Skenario B Blok 19Mutia AgustriaPas encore d'évaluation
- GP Male Genital Tract TransDocument13 pagesGP Male Genital Tract TransKathlene EmbodoPas encore d'évaluation
- Which May Be Bloody If Inflammation Is Severe) : (I.e. Full Thickness of Bowel Wall)Document4 pagesWhich May Be Bloody If Inflammation Is Severe) : (I.e. Full Thickness of Bowel Wall)abdullah albayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Lab PA RPS 17-18Document42 pagesIntroduction Lab PA RPS 17-18Lismi Awliya RahmahPas encore d'évaluation
- OMCDocument37 pagesOMCyurie_ameliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Giant Cell Fibroma of The Gingiva: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesGiant Cell Fibroma of The Gingiva: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureAgiePas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesDisorders of Urinary Systemakkineni ruchithaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Anatomy) Histology SlidesDocument31 pages(Anatomy) Histology SlidesMa. Althea Gabrielle LoretoPas encore d'évaluation
- Enteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverDocument2 pagesEnteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverAlaa BahjatPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Histology of Breast Tissue Consists of The LobulesDocument10 pagesNormal Histology of Breast Tissue Consists of The LobulesFaizalherliansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of GingivitisDocument42 pagesStages of Gingivitislia wardinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodontal PocketDocument48 pagesPeriodontal PocketMaha JabeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology ReviewDocument20 pagesPathology ReviewPoornima JayasekaraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 Gosche Vick SemPedSurgeryDocument8 pages2006 Gosche Vick SemPedSurgeryResya I. NoerPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in The Treatment of DiabeticDocument28 pagesHyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in The Treatment of Diabeticnadya shabirah zahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical CancerDocument6 pagesCervical Cancershashi mittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 Male ReproDocument34 pagesChapter 21 Male ReproIsfahan MasulotPas encore d'évaluation
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Lab Guidebook 2019 CH 17 Hepatobiliary SystemDocument11 pagesPathology Lab Guidebook 2019 CH 17 Hepatobiliary System6460801016Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Pathology: Non-Epithelialized Primary Bone CystDocument4 pagesOral Pathology: Non-Epithelialized Primary Bone Cystعلي صادق جعفرPas encore d'évaluation
- Carranza Edisi 11 Hal 84-87Document11 pagesCarranza Edisi 11 Hal 84-87erninurhayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Death: Apoptotic Bodies Which Are Phagocytised by Neighbouring Phagocytes. Apoptosis Is Not AssociatedDocument5 pagesCell Death: Apoptotic Bodies Which Are Phagocytised by Neighbouring Phagocytes. Apoptosis Is Not AssociatedIsak ShatikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fissural CystsDocument17 pagesFissural CystssailalithaPas encore d'évaluation
- G9 Gingival InflammationDocument59 pagesG9 Gingival Inflammationsamys2ndemailPas encore d'évaluation
- Periapical PeriodontitisDocument7 pagesPeriapical Periodontitisعلي صادق جعفرPas encore d'évaluation
- AsdsDocument5 pagesAsdsGerald MasagandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonataljaundice 140128015601 Phpapp02Document39 pagesNeonataljaundice 140128015601 Phpapp02Tina TalmadgePas encore d'évaluation
- The Prevalence of Sleep Disorders in College StudentsDocument8 pagesThe Prevalence of Sleep Disorders in College StudentsAmirah OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- JuRnal 6 PDFDocument8 pagesJuRnal 6 PDFNurhajar AzzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Javma-Javma 21 04 0213Document5 pagesJavma-Javma 21 04 0213Black manPas encore d'évaluation
- ACOG On CA EndometriumDocument14 pagesACOG On CA EndometriumzoviPas encore d'évaluation
- ASPAK Alkes IGDDocument2 pagesASPAK Alkes IGDAdra AdePas encore d'évaluation
- Under Supervision of Dr. Ommia AliDocument15 pagesUnder Supervision of Dr. Ommia AliAbdelrhman AboodaPas encore d'évaluation
- 366-Article Text-1782-1-10-20230930Document6 pages366-Article Text-1782-1-10-20230930Elang kurniati Elang kurniatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lingering InjuriesDocument12 pagesLingering Injuriessunrei musicPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Respiratory TractDocument39 pages2 Respiratory TractnanxtoyahPas encore d'évaluation
- About Clinical Performance of Nursing Students by Adah ChungDocument3 pagesAbout Clinical Performance of Nursing Students by Adah ChungNel Joshua MicayabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Liu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityDocument17 pagesLiu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityMas NuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Region X: January 1, 2021 Advanced Life Support Standard Operating ProceduresDocument126 pagesRegion X: January 1, 2021 Advanced Life Support Standard Operating ProceduresC ScribPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Picture: 73 Year Female 49320502554Document1 pageComplete Blood Picture: 73 Year Female 49320502554ahmed khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Theory FlorenceDocument19 pagesNursing Theory FlorencesrinivasanaPas encore d'évaluation
- IGNOU Block 3 Unit 4 Communicable Diseases 3 - Zoonotic DiseasesDocument17 pagesIGNOU Block 3 Unit 4 Communicable Diseases 3 - Zoonotic Diseaseserice.researchPas encore d'évaluation
- Poort Et Al. - 2020 - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or Graded Exercise THDocument8 pagesPoort Et Al. - 2020 - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or Graded Exercise THIván DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- HYGIENCE and SANITATIONDocument4 pagesHYGIENCE and SANITATIONZefren BotillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaastu and CancerDocument2 pagesVaastu and CancervivekpatelbiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mandatory RT-PCR Test For PNP Personnel and Other Guests Attending Command Activities in Camp Bgen Rafael T CrameDocument10 pagesMandatory RT-PCR Test For PNP Personnel and Other Guests Attending Command Activities in Camp Bgen Rafael T CrameDaffodil BuslonPas encore d'évaluation
- Association Between Work-Related Stress and Coronary Heart Disease: A Review of Prospective Studies Through The Job Strain, Effort-Reward Balance, and Organizational Justice ModelsDocument15 pagesAssociation Between Work-Related Stress and Coronary Heart Disease: A Review of Prospective Studies Through The Job Strain, Effort-Reward Balance, and Organizational Justice ModelsthomasPas encore d'évaluation