Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Storage Protein
Transféré par
princessicyjulietDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Storage Protein
Transféré par
princessicyjulietDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
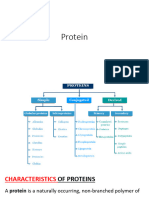
STORAGE PROTEIN .
The human body does store protein, but it doesn't keep the protein structure, it turns it to fat, the body's only storage is adipose tissue (fat cells) the reason why the body doesn't store pure protein is because it can't get energy off it, the body's storage system is designed for energy. The main function of storage proteins is to store metal ions such as iron in your body. Your body needs iron to transport hemoglobin for cell metabolism. The storage protein ferritin also helps regulate any bad effects of too much iron. The amino acids in storage protein aid in embryonic development. Casein and ovalbumin are two storage proteins found in egg whites and breast milk. Perhaps the most thoroughly studied storage protein is ferritin, which stores iron. Iron is a mineral required by all living things; it is a component of heme, which is found in the transport protein hemoglobin, as well as of cytochromes, molecules taking part in cell metabolism (including drug metabolism). Free iron in solution, on the other hand, is able to participate in free radical reactions that damage proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Therefore, within organisms, in addition to serving as an iron reserve, ferritin provides a safeguard against potentially harmful side effects of iron. Ferritin is a complex of 24 polypeptide chains that form a nearly spherical shell around a core of up to 4,500 iron atoms stored as iron oxidehydroxide (ferrihydrite) complexes. Ferritin is able to store and release iron in a controlled fashion.
Proteins are made from amino acids, and many storage proteins serve as reserves of amino acids in embryonic and developing organisms. This is true of both animals and plants. Two well-known storage proteins in animals are casein and ovalbumin. Casein, found in mammalian milk, and oval-bumin, found in egg white, both provide a developing organism with a ready source of amino acids and organic nitrogen. Plant storage proteins are found in high concentrations in seeds, especially in leguminous plants, in which the storage proteins constitute up to 25 percent of the dry weight of the seed. These proteins have no known enzymatic function and often exist within separate vesicles (packets) in the seeds. In addition to their importance to the germinating seed, these plant storage proteins are a valuable source of human nutrition.
Definition of Storage Protein Storage protein is biological reserves of metal ions and amino acids, used by organisms. It serves as reserves of metal ions and amino acids which can be mobilized and utilized for the maintenance and growth of organisms. They are particularly prevalent in plant seeds, egg whites, and milk. Function of Storage Protein Storage protein is use to store metal ions such as iron and amino acids in our body. Our body needs iron to transport hemoglobin for cell metabolism. Example of Storage Protein Ferritin. It stores iron in our body. The storage protein ferritin helps to regulate any bad effects of too much iron. Iron is a mineral required by all living things; it is a component of heme, which is found in the transport protein hemoglobin, as well as of cytochromes, molecules taking part in cell metabolism (including drug metabolism). Free iron in solution, on the other hand, is able to participate in free radical reactions that damage proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Therefore, within organisms, in addition to serving as an iron reserve, ferritin provides a safeguard against potentially harmful side effects of iron. Ferritin is a complex of 24 polypeptide chains that form a nearly spherical shell around a core of up to 4,500 iron atoms stored as iron oxidehydroxide (ferrihydrite) complexes. Ferritin is able to store and release iron in a controlled fashion. Some storage protein stores amino acids such as animals and plants. Proteins are made from amino acids, and many storage proteins serve as reserves of amino acids in embryonic and developing organisms. This is true of both animals and plants. Two well-known storage proteins in animals are casein and ovalbumin. Casein, found in mammalian milk, and oval-bumin, found in egg white, both provide a developing organism with a ready source of amino acids and organic nitrogen. Plant storage proteins are found in high concentrations in seeds, especially in leguminous plants, in which the storage proteins constitute up to 25 percent of the dry weight of the seed. These proteins have no known enzymatic function and often exist within separate vesicles (packets) in the seeds. In addition to their importance to the germinating seed, these plant storage proteins are a valuable source of human nutrition.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pediatric AcupunctureDocument366 pagesPediatric AcupuncturePasc777100% (7)
- Michael Grant Anaesthetics Emergency Medicine Notes PDFDocument70 pagesMichael Grant Anaesthetics Emergency Medicine Notes PDFMimansaDixit100% (1)
- Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo Test BankDocument21 pagesPilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo Test Bankhelgasophie7478k0100% (32)
- Diagnostic HDiagnostic Hemoglobinopathies Secon Edition, Emoglobinopathies Secon Edition, August 21, 2015Document510 pagesDiagnostic HDiagnostic Hemoglobinopathies Secon Edition, Emoglobinopathies Secon Edition, August 21, 2015Fahad100% (1)
- ProteinDocument25 pagesProteinMohaajanan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- PROTEIN AND WATER (Updated)Document17 pagesPROTEIN AND WATER (Updated)abahojomacynthiaPas encore d'évaluation
- BCH 317 ProteinsDocument5 pagesBCH 317 Proteinsmaryjanenzubechukwu901Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparative Study of Protein Content in Eggs and Soy ChunksDocument33 pagesA Comparative Study of Protein Content in Eggs and Soy ChunksNamratha DevadigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pro TiensDocument11 pagesPro TiensBk Anubhav GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science q3 Week 4 v2 RecoveredDocument9 pagesPhysical Science q3 Week 4 v2 Recoveredjensenearl934Pas encore d'évaluation
- NutrientsDocument11 pagesNutrientsChrysellePas encore d'évaluation
- Components of FoodDocument11 pagesComponents of Foodapi-246586162100% (1)
- Animal NutritionDocument111 pagesAnimal NutritionOliver TalipPas encore d'évaluation
- 6-7 ProteinDocument17 pages6-7 Proteinyr44grf94kPas encore d'évaluation
- FST3107-INTRODUCTION TO FOOD CHEMISTRY - ProteinDocument67 pagesFST3107-INTRODUCTION TO FOOD CHEMISTRY - ProteinZHOU TIANLEPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein PDFDocument27 pagesProtein PDFSumaiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Biology Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesIGCSE Biology Digestive SystemDr.CharinPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinDocument33 pagesProteinIhsan Badsha100% (1)
- Protein 1Document17 pagesProtein 1slmen1269Pas encore d'évaluation
- File 1667187373 0008901 ProteinsDocument8 pagesFile 1667187373 0008901 ProteinsSachin Kumar RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinsDocument4 pagesProteinsDave RovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein: Bab 1 PendahuluanDocument18 pagesProtein: Bab 1 PendahuluanvikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins: AcidsDocument5 pagesProteins: AcidsHannahPas encore d'évaluation
- BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesBiomoleculesVicente Cervano ST-1BPas encore d'évaluation
- General Amino Acids Pool and UtilizationDocument61 pagesGeneral Amino Acids Pool and UtilizationBaylon, MarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals and Nutrition, 8Document8 pagesMinerals and Nutrition, 8aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins Classification of ProteinDocument7 pagesProteins Classification of ProteinKrishnanand NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Nutrition Act 1Document1 pageAnimal Nutrition Act 1Princess CudalPas encore d'évaluation
- IJSO Biology Module - 3Document207 pagesIJSO Biology Module - 3Ikhbaat Atiqur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins Are Essential Nutrients For TheDocument9 pagesProteins Are Essential Nutrients For TheapriantokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Report Outline AgamDocument6 pagesBiochem Report Outline AgamKhey AgamPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein ClassificationDocument14 pagesProtein ClassificationMark Wael Karam GergasPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolisme FN, IodDocument10 pagesMetabolisme FN, IodIrfan LawlietPas encore d'évaluation
- SHS-Physical Science (Biological Macromolecules) : I-Introductory ContentDocument13 pagesSHS-Physical Science (Biological Macromolecules) : I-Introductory ContentJane182004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm (Protein, Carbs&Lipids)Document132 pagesMidterm (Protein, Carbs&Lipids)Yo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- PROTEINDocument90 pagesPROTEINYo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Protein ?: Growth and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesWhat Is Protein ?: Growth and DevelopmentUjjawal GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinsDocument3 pagesProteinsstudents athlonePas encore d'évaluation
- Protos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of PrimeDocument16 pagesProtos, Meaning of The First Rank' or of Primepinkish7_preciousPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutritional Problems FinalDocument23 pagesNutritional Problems Finalgrace williamPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 NutritionDocument24 pagesUnit 5 Nutritionyarutewelde5.yaredteweldePas encore d'évaluation
- Food Nutrients and NutritionDocument10 pagesFood Nutrients and NutritionAcePas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins Notes and TestsDocument5 pagesProteins Notes and TestsJanicSmithPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE 4th QUARTER EXAMINATION REVIEWERDocument8 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE 4th QUARTER EXAMINATION REVIEWERsiwestitohahahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramankulangara,: ST - Mary'S Residential Central School KollamDocument44 pagesRamankulangara,: ST - Mary'S Residential Central School KollamRamjith RananPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are BiomoleculesDocument18 pagesWhat Are Biomoleculessusan pajarilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 7Document58 pagesBio 7Prince SanjiPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinDocument31 pagesProteinClarise MoringPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Nutritional FactorsDocument17 pagesAnti Nutritional FactorsMalvika Shah JainPas encore d'évaluation
- BionutrisiDocument21 pagesBionutrisiEnina Eninta SinuhajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oleh: Sri Sumarmi: Pelangi GiziDocument55 pagesOleh: Sri Sumarmi: Pelangi GiziRika AmeiliawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive of RuminantsDocument4 pagesDigestive of RuminantsRosel Gonzalo-AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- LAS Physical Science Week 4Document10 pagesLAS Physical Science Week 4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition 2011 EAMDocument38 pagesNutrition 2011 EAMJayson BasiagPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins and LipidsDocument6 pagesProteins and LipidsRey AlegrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 - Food an-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesUnit 2 - Food an-WPS Officepash blessingsPas encore d'évaluation
- 252-Article Text-1458-2-10-20230225dididikdjejejejdjdjdDocument9 pages252-Article Text-1458-2-10-20230225dididikdjejejejdjdjdJuan SitinjakPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Macronutrients-11: Proteins A N D Fats: Omino OcidsDocument10 pagesThe Macronutrients-11: Proteins A N D Fats: Omino OcidsasndmpPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsDocument11 pagesBio Chemistry Chapter # 3 ProteinsEmo tionsPas encore d'évaluation
- ProteinsDocument13 pagesProteinsMitra RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Technology Notes Year 11Document50 pagesFood Technology Notes Year 11Belinda ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- The Science of Tastes - Introduction to Food Chemistry for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandThe Science of Tastes - Introduction to Food Chemistry for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Exchange & O2 TransportDocument11 pagesGas Exchange & O2 Transportmina mounirPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolisme EritrositDocument50 pagesMetabolisme EritrositRamdhana ZaqifahPas encore d'évaluation
- DirectHemoglobin DrabkinDocument2 pagesDirectHemoglobin DrabkinLee-Ya AchmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Microcirculation Monitoring - LOCAL GhalebDocument46 pagesMicrocirculation Monitoring - LOCAL GhalebGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen-Induced Hypercapnia in COPD PDFDocument4 pagesOxygen-Induced Hypercapnia in COPD PDFsatyagraha84Pas encore d'évaluation
- IBO 2004 Theory Part 1Document59 pagesIBO 2004 Theory Part 1pdbiocomp100% (3)
- Hematology NotesDocument17 pagesHematology NotesEly Sibayan100% (2)
- Cocos Nucifera Water: Therapeutic Benefits and Sickle Cell Anaemia A ReviewDocument7 pagesCocos Nucifera Water: Therapeutic Benefits and Sickle Cell Anaemia A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Tests and Keys PDFDocument43 pages2014 Tests and Keys PDFshaturocks123Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCHD ScreeningDocument3 pagesCCHD ScreeningAhmad ThotuchingPas encore d'évaluation
- DyshemoglobinemiasDocument30 pagesDyshemoglobinemiasowlscowlPas encore d'évaluation
- Tropical Haematology and Blood Transfusion PDFDocument77 pagesTropical Haematology and Blood Transfusion PDFZiauddin AzimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument56 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombePas encore d'évaluation
- Over View of BloodDocument42 pagesOver View of BloodJenadi BinartoPas encore d'évaluation
- MUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingDocument42 pagesMUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingMerhella Amor Suerte MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Study of The Efficacy of Gleptoferron and Iron Dextran in Anemia Prevention in PigletsDocument1 pageComparative Study of The Efficacy of Gleptoferron and Iron Dextran in Anemia Prevention in PigletsVincent Auvigne100% (3)
- Problem No. 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Carrying Capacity of The Blood As Evidenced by Decreased Level of HemoglobinDocument3 pagesProblem No. 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Carrying Capacity of The Blood As Evidenced by Decreased Level of HemoglobinGensen Cu RoxasPas encore d'évaluation
- CPCDocument110 pagesCPCShafaq MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExercise Physiology Lab Reportlaurabruce27Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Artificial BloodDocument5 pages13 Artificial BloodchristelhamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Patricia Isabel Sandoval Martínez - Circ. Syst. ST - ANSWER SHEET 12-26Document4 pagesKami Export - Patricia Isabel Sandoval Martínez - Circ. Syst. ST - ANSWER SHEET 12-26p.sandoval.2027Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9700 s15 QP CompleteDocument264 pages9700 s15 QP CompleteJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Quizzes by Ronnie BaticulonDocument20 pagesBiochemistry Quizzes by Ronnie BaticulonMhartin GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled17 PDFDocument16 pagesUntitled17 PDFElizabeth LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Firecracker QuestionsDocument92 pagesBiochemistry Firecracker QuestionsSatishAdvaniPas encore d'évaluation