Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
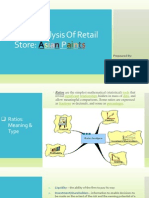
Ratio Analysis: Market Ratios
Transféré par
Kaushik PaulTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ratio Analysis: Market Ratios
Transféré par
Kaushik PaulDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RATIO ANALYSIS
RATIOS Profitability Ratios Gross Profit Ratio Return on Shareholders Fund Return on Shareholders Equity Return on Capital Employed Return on Assets Operating Ratio Operating Profit Net Profit Ratio Expenses Ratio* 75% - 80% 25% - 30% STANDARDS Investors Company
Market Ratios Earning Per Share (EPS) Dividend Yield Payout Ratio Price Earning Ratio ( P/E) Coverage Ratios Fixed Interest Fixed Dividend
Debt service Coverage Turnover Ratios Capital Turnover Ratio Fixed Assets Turnover Working Capital Turnover Ratio Total Assets turnover ratio Inventory Turnover Ratio Debtors Turnover Ratio Creditors Turnover Ratio 45 days/8 times
1. Material Consumed= Material consumed/NetSale 2.Conversion Cost=Labour+Manufacturing exp/Net S
INTERPRETATION
Higher the ratio, Higher is the profitability. helps the shareholders to know the companies position to give them return. helps the equity shareholders know the percentage of Profit they can get. higher the ratio more efficient is capital employed. It measures the profits to the assets to see the profitability of investment Lower operating ratio shows higher operating profit.
Higher the ratio better the Efficiency of company. Lower the ratios better the profitability.
This ratio checks the earning power of the companies and its capacity to pay dividend Shows the rate of return to shareholders in the form of dividends based on the market price of the share. It indicates what portion of the EPS has been used to paying back the dividend and what has been retained. It indicates the market value of every rupee earning in the firm to the industry average. High ratio indicates
It indicates whether the business would earn sufficient profits to pay periodically the interest charges. It helps the preference shareholders know the dividend at fixed rate they would receive in preference to the equity shareholders.
It shows whether the company is in the position to make payment of principal amount on time.
Lower ratio shows the lower profits and higher ratio shows the higher profits. Helps to indicate how the fixed assets are used to generate sales in the business. Low ratio indicates the ineffeciency of fixed assets. Higher the ratio lower the investment in working capital and vice versa Higher ratio indicates overtrading of total assets while low ratio indicates the idle capacity. It measeures how quickly inventory is sold. Its a test of inventory mangement. low collection period and low ratio indicate delayed payment by debtors. Higher ratio indicates that the creditors are not paid in time. A lower ratio indicates that the business is not taking full advantage of the credit period allowed by the
Expense Ratios* 1. Material Consumed= Material consumed/NetSales*100 2.Conversion Cost=Labour+Manufacturing exp/Net Sales*100 3.Administration Expenses=Admin Exp/Net Sales *100 4.Selling &DistributionExp= S&D exp/Net Sales*100
CALCULATION
(GP/Net Sales) *100 (Net PAT & Interest/Shareholders Funds)*100 (Net PAT & Interest/Equity shareholders Fund)*100 (Operating Profit/capital employed)*100 (Net PAT/Total Asset)*100 (C.O.G.S+Expenses/Net Sales)*100 (OperatingProfit/Net Sales)*100 (NP/Net Sales)*100 (Expenses /Net Sales)*100
Net PAT/ Number of Equity DPS/MPS (Dividend Per Share (DPS)/EPS or retained earning/total earning)*100 Market Price Per Share(MPS) /Earning Per share
net profit after tax and Interest/Interest amount net profit after tax and Interest/Preference Dividend
Net profit before Interest and taxes/Interst+principal installment/1-tax rate
Sales / Capital Employed Sales/Net fixed Asset Sales /Net working Capital Sales/Total asset COGS/ Average Inventory at cost Net Credit Sales/Average Debtors+Bills Recievable Net Credit Purchases/Average Creditors+Bills Payable
tSales*100 Net Sales*100
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsD'EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsPas encore d'évaluation
- RATIO ANALYSIS BREAKDOWNDocument7 pagesRATIO ANALYSIS BREAKDOWNvarun325Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio and AnalysisDocument8 pagesRatio and Analysislee organicPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Financial Ratios (R)Document3 pagesList of Financial Ratios (R)Nurfa AhzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis: by S Surya Rajendra KumarDocument11 pagesRatio Analysis: by S Surya Rajendra KumarSurya SivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio analysis reveals Asian Paints' financial performanceDocument14 pagesRatio analysis reveals Asian Paints' financial performanceAshish MahendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Ratios Type Standard Norm For Investors For Company Profitability RATIOS: (Expressed in %)Document12 pagesClassification of Ratios Type Standard Norm For Investors For Company Profitability RATIOS: (Expressed in %)parivesh16Pas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE X XI Profitability and IndicesDocument3 pagesMODULE X XI Profitability and IndicesInah LataganPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyzing The Financial StatementsDocument30 pagesAnalyzing The Financial StatementsIshan Gupta100% (1)
- Ratios FormulasDocument4 pagesRatios FormulasTutii FarutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Working with financial statementsDocument4 pagesWorking with financial statementsLeilaabotiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis: Shiekh Alam Siraj WaseemDocument15 pagesRatio Analysis: Shiekh Alam Siraj WaseemRaja Fahd SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis: Understanding Financial Performance and PositionDocument26 pagesRatio Analysis: Understanding Financial Performance and PositionAnubhav Singhal0% (1)
- Financial Ratio Analysis GuideDocument5 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis GuideSef Getizo CadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental AnalysisDocument6 pagesFundamental AnalysisanandhvvvPas encore d'évaluation
- ROI formula and componentsDocument7 pagesROI formula and componentsVineet AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- ProfitabilityDocument30 pagesProfitabilitySumit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Financial Ratios BreakdownDocument25 pagesKey Financial Ratios Breakdownwinnerme100% (1)
- (ENG) Các Cã NG Thá ©C Tã - NH Chá Sá TCDocument3 pages(ENG) Các Cã NG Thá ©C Tã - NH Chá Sá TCHoài ThuPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesList of Financial RatiosHyacinth ApitPas encore d'évaluation
- AUD Financial RatiosDocument3 pagesAUD Financial RatiosNick HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- Narayana Engineering College Autonomous-Nellore: Prepared by M.Bhargav Charan 20711E0054Document15 pagesNarayana Engineering College Autonomous-Nellore: Prepared by M.Bhargav Charan 20711E0054CH ANIL VARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Ratio Current Assets / Current LiabilitiesDocument6 pagesCurrent Ratio Current Assets / Current LiabilitiesAnkush ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratio Analysis With FormulasDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis With FormulasLalit Bom Malla100% (1)
- Term/Ratio Definition or Use Calculation Target BenchmarkDocument6 pagesTerm/Ratio Definition or Use Calculation Target BenchmarkShufan ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis - A2-Level-Level-Revision, Business-Studies, Accounting-Finance-Marketing, Ratio-Analysis - Revision WorldDocument5 pagesRatio Analysis - A2-Level-Level-Revision, Business-Studies, Accounting-Finance-Marketing, Ratio-Analysis - Revision WorldFarzan SajwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Profitability Ratios ExplainedDocument8 pagesProfitability Ratios ExplainedRakesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratios Guide for Measuring Company PerformanceDocument15 pagesFinancial Ratios Guide for Measuring Company PerformanceHojol100% (1)
- Ratio AnalysisDocument17 pagesRatio AnalysisFrank Agbeko TorhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument14 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisAllona BatonghinogPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Chapter 4Document18 pages10 - Chapter 4DishuPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of ValuationDocument7 pagesGlossary of Valuationveda20100% (1)
- Financial Statement Analysis RatiosDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis RatiosshahbazsiddikiePas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate Financial Analysis NotesDocument19 pagesCorporate Financial Analysis NotesWinston WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis Guide for Financial Statement AnalysisDocument7 pagesRatio Analysis Guide for Financial Statement Analysisramsan1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial AnalysisDocument3 pagesFinancial AnalysisAllan OchiengPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Ratio Analysis Formulas and ExplanationsDocument18 pagesList of Ratio Analysis Formulas and ExplanationsCharish Jane Antonio CarreonPas encore d'évaluation
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28Document3 pagesFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 8 - Reading 28RafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Net Profit Margin:: SignificanceDocument7 pagesNet Profit Margin:: Significanceamisha kbPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis Formulas Guide Under 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesRatio Analysis Formulas Guide Under 40 CharactersSri Royal100% (1)
- RatioDocument21 pagesRatiojmanager777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Value Investor EncyclopediaDocument1 111 pagesValue Investor EncyclopediamanojdavangePas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio AnalysisDocument38 pagesRatio AnalysismdalakotiPas encore d'évaluation
- FSA Chapter 8 NotesDocument9 pagesFSA Chapter 8 NotesNadia ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dividend YieldDocument5 pagesDividend YieldPoojaGuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1Document18 pagesTopic 1Nivaashene SaravananPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis GuideDocument5 pagesRatio Analysis GuideZeshan MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio AnalysisDocument34 pagesRatio AnalysisavdhutshirsatPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Financial RatiosDocument9 pagesList of Financial RatiosPrinces Aliesa BulanadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Return On EquityDocument6 pagesReturn On EquitySharathPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Key Financial RatiosDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Key Financial RatiosMaxhar AbbaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument4 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysisapi-299265916Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratio HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesFinancial Ratio HANDOUTSMichelle GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Calculation Comments Gross Profit Margin: 1.1 Profitability RatiosDocument3 pagesRatio Calculation Comments Gross Profit Margin: 1.1 Profitability RatiosUttara NaktodePas encore d'évaluation
- 10 ProfitabilityDocument15 pages10 ProfitabilityJamaica May SuficienciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analyze Profitability & Activity RatiosDocument38 pagesAnalyze Profitability & Activity RatiosSUDIPTA SHIBPas encore d'évaluation
- Suganthi - Financial Mangement AssignmentDocument3 pagesSuganthi - Financial Mangement AssignmentSylvad LuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratio Analysis ToolDocument6 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis ToolJuan Pascual CosarePas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Formula Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesRatio Formula Cheat Sheet PDFkumarashish2150% (2)
- Shares and Dividends Class X Maths CISCEDocument23 pagesShares and Dividends Class X Maths CISCENatasha SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Dangote Cement's financial charges and tax cut into profit as sales revenue grows slowlyDocument16 pagesDangote Cement's financial charges and tax cut into profit as sales revenue grows slowlygregPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in Accounting - xlsx-3Document59 pagesReviewer in Accounting - xlsx-3Franchesca CortezPas encore d'évaluation
- Statement of Financial Position: Fundamental of Accountancy, Business, and Management 2 ABM12Document53 pagesStatement of Financial Position: Fundamental of Accountancy, Business, and Management 2 ABM12Mercy P. YbanezPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal ReconstructionDocument26 pagesInternal ReconstructionGaurav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Start-Up E-Commerce Financial ModelDocument8 pagesStart-Up E-Commerce Financial ModelManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument45 pagesFMSaumya GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting SolutionsDocument11 pagesAccounting SolutionsKrittima Parn SuwanphorungPas encore d'évaluation
- MS04Document34 pagesMS04Varun MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- Walmart vs Amazon: Long-Term Investment Case for WalmartDocument20 pagesWalmart vs Amazon: Long-Term Investment Case for WalmartEduardo TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Technician Pilot Papers PDFDocument133 pagesTechnician Pilot Papers PDFCasius Mubamba100% (4)
- Corporate Finance Case Study AnalysisDocument7 pagesCorporate Finance Case Study AnalysisFaaiz YousafPas encore d'évaluation
- Greenergy Holdings Incorporated - SEC Form 17-Q - 17 May 2021Document66 pagesGreenergy Holdings Incorporated - SEC Form 17-Q - 17 May 2021John AzellebPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting ReviewerDocument6 pagesAccounting ReviewerFictional PlayerPas encore d'évaluation
- ADVACTDocument4 pagesADVACTMariel Princess100% (2)
- Partnerships PT 2 FormationDocument10 pagesPartnerships PT 2 FormationJohn Ashnaz DemaguilPas encore d'évaluation
- Dysas - Fin Acc - 3rdDocument5 pagesDysas - Fin Acc - 3rdJao FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- 04.recording Process Journal - TB FinalDocument49 pages04.recording Process Journal - TB FinalChowdhury Mobarrat Haider Adnan100% (1)
- Investing and Financing Decisions and The Accounting SystemDocument44 pagesInvesting and Financing Decisions and The Accounting SystemSina RahimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes: Afar G/N/E de Leon 2813-Joint and by Product Costing MAY 2020Document4 pagesLecture Notes: Afar G/N/E de Leon 2813-Joint and by Product Costing MAY 2020May Grethel Joy PerantePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15&16 Problems and AnswersDocument22 pagesChapter 15&16 Problems and AnswersMa-an Maroma100% (10)
- تمرين 1Document4 pagesتمرين 1نجم الدين طه الشرفيPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice of Cost Volume Profit Breakeven AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractice of Cost Volume Profit Breakeven AnalysisHafiz Abdulwahab100% (1)
- PT YANAPRIMA HASTAP E RSADA TB K LAPORAN TAHUNAN 2015Document163 pagesPT YANAPRIMA HASTAP E RSADA TB K LAPORAN TAHUNAN 2015raka rayiPas encore d'évaluation
- LUMS ACCT 100 Financial AccountingDocument7 pagesLUMS ACCT 100 Financial AccountingZulfeqar HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Investmentquestfinal PDFDocument13 pages08 Investmentquestfinal PDFralphalonzo0% (1)
- Financial Analysis of National FoodDocument24 pagesFinancial Analysis of National FoodArslan NawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting and Auditing Responsibilities of Sme'sDocument129 pagesAccounting and Auditing Responsibilities of Sme'stsar_philip2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coles GroupDocument9 pagesColes GroupSubash UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Fu Wang Income Statement 2016 2017 2018 2019Document5 pagesFu Wang Income Statement 2016 2017 2018 2019Md Abil KhanPas encore d'évaluation