Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Relationship Between Job and Life Satisfaction in
Transféré par
Askin KeserTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Relationship Between Job and Life Satisfaction in
Transféré par
Askin KeserDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN JOB AND LIFE SATISFACTION IN
AUTOMOBILE SECTOR EMPLOYEES
IN BURSA -TURKEY
Aþkýn KESER
PhD, Uludag University, Economy and Administrative Science Faculty,
Department of Labour Economics and Industrial Relations
email: askin@isguc.org
Introduction
The relationship between job satisfaction and life satisfaction has been heavily researched over the It is interesting that, “the job satisfaction result is higher than life satisfaction” degree. It can be
years. The relationship between job satisfaction and life satisfaction has a substantial research tradition explained with two factor. One of them is mostly blue collar workers participate to the research and the
in Industrial/Organizational Psychology, with a published study as early as 1952. Specially, in the last 30 wages of blue collar workers are high at automobile sector because of trade union factor. And also the
years, job satisfaction and life satisfaction, has been the subject of a considerable amount of empirical blue collar workers main motivational factor depends on economic topics(wage). So they may be
research and as well as several qualitative reviews. (Rice, Near, Hunt, 1979; Near, Smith, Rice and Hunt, satisfied with their job with the hand of economic welfare.
1980, 1984; Near, Rice, Hunt, 1987; London, Crandall, Seals, 1977; Kabanoff, O'Brein 1980) This The second factor can be, the workers may answer the questions on life satisfaction honestly, but
relationship appears to be of interest to a wide variety of scholars, as shown by the fact that studies they may not be that honest with the answers on job satisfaction baring in mind the consequences of
relating job and life satisfaction have been reported in journals devoted to psychology, sociology, the answers on their employment status. So they may intend to give good rates about job satisfaction,
counseling, management, leisure and other disciplines. on the other hand life satisfaction answers do not effect management of organization.
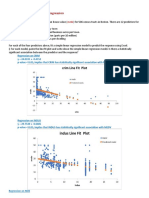
In order to find the relation between job and life satisfaction, “correlational and regression analysis”
Job Satisfaction and Life Satisfaction
has made.
Correlation Analysis of Job/Life Satisfaction:
Relationship Table 3. Correlation Analysis of Descriptive Job/Life Satisfaction
The relation was firstly searched by Wilensky at 1960's. (Dolan and Gosselin, 2000; Smulders, 1983,
Variables N Mean Std. Deviation
285) Researchers, in attemping to explain the linkage between job and life satisfaction, have proposed Life Satisfaction 562 2,7777 0,81034
mainly 6 theoritical model. These comprise the spill over, compensation, segmentation, instrumentally,
conflict and disaggregation perspectives. Some of these relations have negative influence, some of them Job Satisfaction 562 3,8458 0,71468
have positive influence also some of them have no influence. There is also conflict on all of these
models that which is mostly correct result. Table 4. Correlation Analysis of Descriptive Job/Life Satisfaction
In order to give an idea it will be beter to give brief information about these perspectives; (Loscocco
and Roschelle, 1991; Elizur, 1991, 313; Iverson and Maguire, 2000; O'Driscoll, 1996, 281; Greenhaus and Job Satisfaction
Beutell 1985, 76-88) The spill over model, suggests that satisfaction in one domain of individual's life
extends into other areas. The compensatory model, in contrasts to the spill over model, contends a Life Satisfaction 0,3477087
negative relationship between job and life satisfaction, specially, employees experiencing dissatisfaction
Sig. 0,000*
at work are more likely to compensate by engaging in satisfying non-work activities. The segmentation
model, posits no linkage between job and life satisfaction. The instrumentally model, individuals one *(p=2,049E17)
domain help him/her in his/her other domain, so the experiencies of individual will used in other
domain. The conflict model, according to this model there is a conflict between two domains. An As it has seen from Table 4 there is a significant relation between job and life satisfaction (p<0,05)
individual may be experiencing a conflict of roles. For example, as a parent, he/she may think his/her From this result we can understand that there is positive relation between job and life satisfaction, if
working life has got a negative effect on the dialogue with his/her children. So he/she may feel guilty job satisfaction increases, also life satisfaction increases.
because of this conflict. The disaggregation model, this model explains that there may be many Regression Analysis of Job/Life Satisfaction:
relation between these domains. According to this theory, the relation will change with the importance In order to understand the effects of job satisfaction to life satisfaction, in other words, -in which
of work in individual's life. An individual giving more importance to his/her working life will be affected percent does job satisfaction explains life satisfaction-, regression analysis had used.
much more than the one who does less.
Method
Table 5. Regression Analysis of Descriptive Job/Life Satisfaction
Model R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the
Sample Estimate
The sample is chosen from the employees of eleven automobile firms from Bursa, which can be
identified as the capital city of automobile sector in Turkey. The sample consisted of 562 employees, 1 0,348 0,121 0,119 0,76046
included white and blue collar. The question form sent to 660 workers, 562 were returned. So the a Predictors: (Constant), JOB SATISFACTION
representing rate was nearly %85.
Instruments “Job satisfaction” explains %12 (R square= 0.121) of life satisfaction. According to understand if
In this research, two instruments were used to understand the relation between job satisfaction and there is an linear relation between job and life satisfaction we had made variance analysis. (ANOVA)
life satisfaction: Job Satisfaction Scale and Life Satisfaction Scale.
Job Satisfaction Scale, developed by Brayfield ve Rothe's. It consists of 5 items, also used in many
Table 6. ANOVA Results of Regression Analysis of Descriptive Job/Life Satisfaction
researches. (Howard and Frink, 1996, 278) Scale ranges from 1 (not all satisfied) to 4 (very satisfied).
But in order to analysis the two scale the author transform the scale to 5 ranges. Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
Life Satisfaction Scale, developed by Deiner, Emmons, Larsen and Griffin.(Deiner, et.al., 1985, 71-
75) This scale has also 5 items, rated on a 7 point Liker scale, but the author had transform this 7 to 5 in
his question form, in order to be use similar range with job satisfaction scale. Regression 44,538 1 44,538 77,016 0
Residual 323,846 560 0,578
In our study the scales reliability scores are defined below; Total 368,384 561
a Predictors: (Constant), JOB SATISFACTION, b Dependent Variable: LIFE SATISFACTION
Table 1. Reliability coefficients
Reliability Coefficients N of Cases N of Items Cronbach Alpha The ANOVA results show that regression model is also significant. (,000)
Job Satisfaction 555 5 ,75
Life Satisfaction: 555 5 ,78 Table 7. Coefficients
Analysis
Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized Coefficients t Sig.
B Std. Error Beta
(Constant) 1,261 0,176 7,179 0
Descriptive Statistics: JOB SATIS. 0,394 0,045 0,348 8,776 0
A Dependent Variable: LIFE SATISFACTION
Identity of Worker Sex Age In this analyse F value is less than 0.05, we can say that there is an linear relation between job and
45–54 16–24
Woman
19% 35–44
4% 13% life satisfaction. Acording to analyse result, the coefficient of job satisfaction affects to life satisfaction
Blue Collar
48%
26%
had found 0,348 (Beta=0,348) This result is statistically significant. (F= 77,016 P= ,000)
The result of our research, (“Job satisfaction” explains %12 (R square= 0.121) of life satisfaction is
Whit e Collar
52% similiar with the recent researches. Most of the researchs shows that job satisfaction explains %510 of
life satisfaction. (Rice, Near, Hunt, 1979; Near, Smith, Hunt, 1978, 1980,1984; Near, Rice, Hunt, 1986;
Man
81%
25–34
57%
London, Crandall, Seals, 1977)
Conclusion
More than 20 year
5%
Less than 2 year
16–20
Mast er Element ary 15%
8%
6% 11%
11–15 This study set out to address the “job satisfaction” and “life satisfaction” relation. As it has been
Facult y
28%
16%
known, job satisfaction is, pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one's
job or job experince. Life satisfaction is, overall degree to individual likes his/her life. Many researchers
2–5
had found significant relation between these two satisfaction domain.
College High School
28% In this study author made an research at automobile sector in Bursa, at 11 firms. (562 of blue and
6% 49%
6–10 white collar workers.) The question form includes job and life satisfaction scales. It is interesting that,
28%
“the job satisfaction result is higher than life satisfaction” degree. There is a significant relation
Educatioal Level Job Tenure (Year) between job and life satisfaction (p<0, 05) It has been found that the job satisfaction explain %12 of life
satisfaction. The regression results were similiar with the recent researches.
The limitation of our research is; the research had made only at automobile sector maybe it can be
Figure 1. Social Demographic Indicators used in various sectors, and also it may be interesting to do this research to the new form of workers
described as golden collar workers.
Job Satisfaction and Life Satisfaction Results: References
Deiner, E., Emmons, R.A, Larsen, R.J., Griffin, S.; (1985), “The satisfaction with life scale”, Personality Near, J.P.; Rice, R.W.; Hunt, R.G,; (1980), “The relationship between work and nonwork domains: A review of
Assessment, Vol:45 emprical research”, Academy of Management Review, Vol:5
Deiner, E., Napa Scollon C.K., Oishi, S., Dzokoto, V., Suh, E.M.; (2000) “Positivity and construction of life Near, J.P.; Rice, R.W.; Hunt, R.G,; (1987), “Job satisfaction and life satisfaction: A profile analysis”, Social
satisfaction judgements:Global happiness is not the sum of its parts”, Journal of Happiness Studies, Vol:1 Indicators Research, Vol: 19
Dolan, Shimon L., Gosselin, Eric, (2000) “Job satisfaction and life satisfaction:Analysis of a reciprocal model with Near, J.P.; Rice, R.W.; Hunt, R.G.; Smith, A; (1983) “Job satisfaction and nonwork satisfaction as components of life
Table 2. Descriptive Job/Life Satisfaction Statistics social demographic moderators”, Journal of Economics Literature Classification, D23, J20, J28
Dormann, Christian and Zapf, Dieter; (2001), “Job satisfaction:A meta analysis of stabilities”, Journal of
satisfaction”, Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol:13
Near, J.P.; Rice, R.W.; Hunt, R.G.; Smith, A; (1984), “A comparison of work and nonwork predictors of life
Organizational Behavior, Vol:22 satisfaction”, Academy of Management Journal, Vol:27 (1)
Don, Elizur; (1991) “Work and Nonwork Relations: The conical structure of work and human life relationship”, O'drýscoll, Micheal P.,(1996) “The interface between job and off-job roles: Enhancement and conflict”,
Results N Mean Std. Deviation Journal of Organizational Behavior, Vol:12
Greenhaus, J.H./Beutell N. J.; (1985) “Sources of conflict between work and family roles”, Academy of
International Review Of Industrial And Organizational Psychology, Vol:11
Price, J.L. and Mueller, C.W., (1981) Professionals turnover: The case of nurses. New York:SP Medical and Scientific.
Management Review, Vol:10 Rice, R.W.; Near, J.P.; Hunt, R.G.; (1979), “Unique variance in job and life satisfaction associated with work
Job Satisfaction 562 3,8458 0,71468 Howard, Jack, L. And Frink, Dwight, D.; (1996), “The effects of organizational restructure on employee
satisfaction”, Group and Organization Management, Vol:21, Issue,3
Iverson, Roderick D., (2000) “The relationship between job and life satisfaction: Evidence from a remote mining
related and extra work related variables”, Human Relations, Vol: 32
Rode, J.; (2004), “Job satisfaction and life satisfaction revisited: A longitudinal test of an integrated model”,
Human Relations, Vol: 57 (9)
community”, Human Relations, June, 2000 [http://www.findarticles.com] Smith, P.C., Kendall, L.M., Hulin,C.L., (1969) The measure of satisfaction in work and retirement, Rand McNally,
Life Satisfaction 554 2,777 0,8103 Kabanoff, B., O'Brein, G.E., (1980) “Work and leisure:A task analysis”, Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol:65
Locke, E.A., (1976) “The nature and causes of job satisfaction”, In the Handbook of Industrial and Organizational
Psychology, Dunnette, MD., (ed.) Rand McNally:Chicago
Chicago.
Smulders, Peter G.W.; (1983) “Personal, nonwork and work characteristics in male and female absance behavior”,
Journal of Occupational Behaviour, Vol:4
Loscocco, K.A., Roschelle, A.R., (1991) “Influences on the quality of work and nonwork life: Two decades in Steiner, Dirk D. and Truxillo, Donald M.; (1987) “Another look at the job satisfaction-life satisfaction relationship:A
review”, Journal Of Vocational Behavior, Vol: 39 test of the disaggregation hypothesis”, Journal of Occupational Behaviour, Vol:8
Muchinsky, Paul M.,(2000) “Emotions in the workplace:The neglect of organizational behavior”, Journal of Tait, M., Padgett, M.Y. and Baldwin, T.T.; (1989), “Job and life satisfaction: A re-examination of the strengths of the
Organizational Behavior, Vol:21 relationship and gender as a function of the date of the study”, Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol: 74 (3)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Do Dan Wala 2021Document14 pagesDo Dan Wala 2021Natalia KobaPas encore d'évaluation
- IJERT Critical Factors Influencing WorkDocument3 pagesIJERT Critical Factors Influencing WorkAngelica MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Barber_Conlin_Santuzzi_2019_Stress and Health_Workplace telepressure and work–life balance outcomesDocument13 pagesBarber_Conlin_Santuzzi_2019_Stress and Health_Workplace telepressure and work–life balance outcomesLarisa BărnuțPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Life BalanceDocument16 pagesWork Life BalanceEmily XuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Evolution of WorkDocument13 pagesThe Evolution of Workkriisdayanti01Pas encore d'évaluation
- WLBWorkand Life BalanceDocument20 pagesWLBWorkand Life Balancefridolin awaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ifbm 0207650202 PDFDocument12 pagesIfbm 0207650202 PDFAmal Paul MadathumpadyPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Ijhrmrfeb20196Document16 pages06 Ijhrmrfeb20196TJPRC PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Reserach Burnout DocumentDocument9 pagesReserach Burnout DocumentKarthika SundharamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cazan Et Al., 2019Document8 pagesCazan Et Al., 2019Andreia Loredana GînjuPas encore d'évaluation
- Final SynopsisDocument37 pagesFinal SynopsisDr. POONAM KAUSHALPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 V14i5069Document9 pages2023 V14i5069samusichubPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Work-Family Conflict and Community Embeddedness On Employee Satisfaction: The Role of Leader-Member ExchangeDocument10 pagesThe Effects of Work-Family Conflict and Community Embeddedness On Employee Satisfaction: The Role of Leader-Member ExchangeayuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Work Life Balance With Special Reference To BPO SectorDocument6 pagesA Study On Work Life Balance With Special Reference To BPO SectorPreety ToppoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Impact of Individual, Social and Organizational Factors On Work-LifeDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Individual, Social and Organizational Factors On Work-LifePR REBPas encore d'évaluation
- Work-Life BalanceDocument12 pagesWork-Life BalanceShahid NaseemPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Satisfaction: A Literature Review: Aziri BDocument16 pagesJob Satisfaction: A Literature Review: Aziri Brija ravindranPas encore d'évaluation
- Personality Traits, Workers' Age, and Job Satisfaction: The Moderated Effect of ConscientiousnessDocument14 pagesPersonality Traits, Workers' Age, and Job Satisfaction: The Moderated Effect of ConscientiousnesspukePas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological Acceptance and Workplace Well-Being As A Predictor of Work-Life IntegrationDocument14 pagesPsychological Acceptance and Workplace Well-Being As A Predictor of Work-Life IntegrationIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Work Life Balance Among BPO Employees - With Reference To BPO'S inDocument9 pagesA Study On Work Life Balance Among BPO Employees - With Reference To BPO'S inomkarPas encore d'évaluation
- AziriDocument10 pagesAziriKonsultan ETIsPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Life Balance A Literature Review PDFDocument8 pagesWork Life Balance A Literature Review PDFjudyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anchal Kumar - A Study On Work Life Balance in Hospitality IndustryDocument40 pagesAnchal Kumar - A Study On Work Life Balance in Hospitality Industryvipul guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Artikel 3Document14 pagesArtikel 3NOOR AFIDA BINTI AMIRDINPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Chapter 2Document86 pages11 Chapter 2Jaya BhasinPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Eka Suhartini ¿ÜDocument11 pages10 - Eka Suhartini ¿ÜAubin DiffoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pursuit of Happiness When Work Makes The DifferenceDocument30 pagesThe Pursuit of Happiness When Work Makes The DifferenceAhmedShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Work-life+balance+pada+karyawan+generasi+Z Mahardika,+Ingarianti,+ZulfianaDocument16 pagesWork-life+balance+pada+karyawan+generasi+Z Mahardika,+Ingarianti,+ZulfianaNadiah WahyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Job SatisfactionDocument13 pagesJob SatisfactionPrita LestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Bem Estar Proprio e Engajamento No TrabalhoDocument12 pagesBem Estar Proprio e Engajamento No TrabalhoAdrianePas encore d'évaluation
- JS ESM JAP20publishedDocument15 pagesJS ESM JAP20publishedMariana KolynosPas encore d'évaluation
- A Qualitative Study On Work Life Balance of Employees Working in Private SectorDocument8 pagesA Qualitative Study On Work Life Balance of Employees Working in Private SectorFarzana Bano100% (1)
- Report On Relationship Between Job SatisDocument6 pagesReport On Relationship Between Job SatisSamuel Embiza TadessePas encore d'évaluation
- Paths The Job Satisfaction of Bank Employees: Uma SekaranDocument13 pagesPaths The Job Satisfaction of Bank Employees: Uma SekaranwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The Effect Work From Home and Work - Life Balance On Job Satisfaction With The Moderation Role of The Work EnvironmentDocument9 pagesAnalysis of The Effect Work From Home and Work - Life Balance On Job Satisfaction With The Moderation Role of The Work EnvironmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- IJISRT23JUN1741Document9 pagesIJISRT23JUN1741International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Happy-Productive Worker Thesis RevisitedDocument17 pagesThe Happy-Productive Worker Thesis RevisitedNata ShavelashviliPas encore d'évaluation
- Work-Life Balance and Burnout Predict Job SatisfactionDocument7 pagesWork-Life Balance and Burnout Predict Job SatisfactionInna RamadaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 A Meta Analytic Examination of The Relationship Between Job Satisfaction and Subjective Well BeingDocument20 pages4 A Meta Analytic Examination of The Relationship Between Job Satisfaction and Subjective Well BeingVio NeaguPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality of Work CycleDocument2 pagesQuality of Work CycleSeenu Chary MaheshwaramPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0191886923000326 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0191886923000326 MainFatimah ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0024.Document7 pagesWa0024.Rohit SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining The Relationship Between Motivational Factors and Job Satisfaction An Empirical StudyDocument13 pagesExamining The Relationship Between Motivational Factors and Job Satisfaction An Empirical Studyarcherselevators100% (1)
- The Impact of Work-Family Conflict On Job and Life Satisfaction For Female Executive MBA StudentsDocument14 pagesThe Impact of Work-Family Conflict On Job and Life Satisfaction For Female Executive MBA StudentsDiwya Bharathi V I MBAPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Job Satisfaction and Adjustment at Workplace Among Retired Army and Civil Employees Working in A Civilian SettingDocument17 pages3 Job Satisfaction and Adjustment at Workplace Among Retired Army and Civil Employees Working in A Civilian SettingApplied Psychology Review (APR)Pas encore d'évaluation
- PENTRU vBIBLIO Job Satisfaction and Life SatisfactionDocument26 pagesPENTRU vBIBLIO Job Satisfaction and Life SatisfactionRuxandra GorbaciovPas encore d'évaluation
- Kalli A TH Brough 2008 J Mo PaperDocument7 pagesKalli A TH Brough 2008 J Mo PaperBrigitta Pradnya ParamithaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Survey of Bahamian and Jamaican Teachers' Level of Motivation and Job SatisfactionDocument21 pagesA Survey of Bahamian and Jamaican Teachers' Level of Motivation and Job SatisfactionSofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0277953618305100 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0277953618305100 MainrobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Work-Life Balance: An Overview: January 2018Document7 pagesWork-Life Balance: An Overview: January 2018Sowndarya PalanisamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Environment - MotivationDocument5 pagesWork Environment - Motivationحمزة رجبPas encore d'évaluation
- Ersoy Kart WorkBATDocument10 pagesErsoy Kart WorkBATVictoria DereckPas encore d'évaluation
- JoE 2016 PDFDocument27 pagesJoE 2016 PDFmiamoure360Pas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing Act: A Comprehensive Study of Work-Life Balance and Its Impact On Employee Performance and Job SatisfactionDocument11 pagesBalancing Act: A Comprehensive Study of Work-Life Balance and Its Impact On Employee Performance and Job Satisfactionmohitjuyal50645Pas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of WorkFamily Conflict On Intention To QuitDocument28 pagesEffects of WorkFamily Conflict On Intention To QuitNoshairwaan KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- HRM Project ProposalDocument4 pagesHRM Project ProposalSuraj TripathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Work-Family Conflict and Job Satisfaction - The Mediating Role ofDocument11 pagesWork-Family Conflict and Job Satisfaction - The Mediating Role oftiarafitrizqaPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocument14 pagesEmployee Attitudes and Job SatisfactionBobby DPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-2 Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter-2 Literature ReviewshoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- SOCIAL WORK ISSUES: STRESS, THE TEA PARTY ROE VERSUS WADE AND EMPOWERMENTD'EverandSOCIAL WORK ISSUES: STRESS, THE TEA PARTY ROE VERSUS WADE AND EMPOWERMENTPas encore d'évaluation
- Adolescent's Perception of His Influence On Purchase Decision of Mobile Phone For His Own Use: A Consumer Socialization PerspectiveDocument18 pagesAdolescent's Perception of His Influence On Purchase Decision of Mobile Phone For His Own Use: A Consumer Socialization PerspectiveThe IjbmtPas encore d'évaluation
- Martin Bland - An Introduction To Medical Statistics-OUP Oxford (2015) PDFDocument447 pagesMartin Bland - An Introduction To Medical Statistics-OUP Oxford (2015) PDFNitesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Researcharticle Open Access: Steven Chifundo AziziDocument12 pagesResearcharticle Open Access: Steven Chifundo AzizichiradzuluPas encore d'évaluation
- AI and IoT Based Monitoring System For Increasing The Yield in Crop ProductionDocument5 pagesAI and IoT Based Monitoring System For Increasing The Yield in Crop ProductionMadhusudhan N MPas encore d'évaluation
- Identifying Feature Stock Price by Considering Most Influential Parameters Using Prediction Methods in Indian Stock ExchangeDocument4 pagesIdentifying Feature Stock Price by Considering Most Influential Parameters Using Prediction Methods in Indian Stock ExchangeDarth FrootLoopsPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced StatisticsDocument125 pagesAdvanced StatisticsJose GallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Akshaya Patra Impact Assessment ReportDocument32 pagesAkshaya Patra Impact Assessment ReportNitish SanchetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Batc602 Business Simulation All QuestionsDocument29 pagesBatc602 Business Simulation All QuestionsNageshwar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Seat Design Recommendations for Improved ComfortDocument80 pagesAuto Seat Design Recommendations for Improved ComfortFX CristiyantoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1111@tpj 14799Document33 pages10 1111@tpj 14799enesb.yongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Interval Estimation in The Classical Normal Linear Regression ModelDocument16 pagesInterval Estimation in The Classical Normal Linear Regression ModelAmissa AsthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of highways on rural households' socioeconomic well-beingDocument62 pagesImpact of highways on rural households' socioeconomic well-beingtein93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Regression Exercise 4Document3 pagesRegression Exercise 4Boy MicroPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Data Mining and Modelling Based On Machine LearningDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Data Mining and Modelling Based On Machine Learningmouka ayiwouoPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Performance AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial Performance AnalysisJanus GalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 1 - Simple Linear Regression - Neal PaniaDocument4 pagesHomework 1 - Simple Linear Regression - Neal PaniaJohn SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics IIDocument101 pagesEconometrics IIDENEKEW LESEMI100% (1)
- HSC6055 Survival Analysis of PBC DataDocument28 pagesHSC6055 Survival Analysis of PBC DataAndrés García ArcePas encore d'évaluation
- Demand Analysis of CassavaDocument22 pagesDemand Analysis of CassavaJulius Mark Cerrudo100% (1)
- Jurnal Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesJurnal Bahasa InggrisAgrifina HelgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ntabathia - Service Quality and Student SatisfactionDocument58 pagesNtabathia - Service Quality and Student SatisfactionJessa Fernandez PaggaoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Key Performance Indicators of Allen Solly Retail StoreDocument61 pagesA Study On Key Performance Indicators of Allen Solly Retail StoreKomal AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- 8-Simple Regression AnalysisDocument9 pages8-Simple Regression AnalysisSharlize Veyen RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Datamining Lecture6Document41 pagesDatamining Lecture6Vi LePas encore d'évaluation
- Forecasting in Onion PricesDocument26 pagesForecasting in Onion PricesSangitaPas encore d'évaluation
- PM - ExtendedProject - Business ReportDocument35 pagesPM - ExtendedProject - Business ReportROHINI ROKDE100% (2)
- Man Econ (Repaired)Document17 pagesMan Econ (Repaired)addisPas encore d'évaluation
- New Corrosion Growth Model Based On Pipeline Intelligent Pigging Data - Correlating Corrosion Defects Numbers With Their DepthDocument11 pagesNew Corrosion Growth Model Based On Pipeline Intelligent Pigging Data - Correlating Corrosion Defects Numbers With Their DepthIvan PilaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Pavement Roughness Prediction Systems A Bump Integrator ApproachDocument4 pagesPavement Roughness Prediction Systems A Bump Integrator ApproachArun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- REGRESSION AND CORRELATION Assignment RecoveredDocument18 pagesREGRESSION AND CORRELATION Assignment RecoveredCourei-FxAlcazarPas encore d'évaluation