Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Visio-SNMP Cheat Sheet V1
Transféré par
Walter ValverdeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Visio-SNMP Cheat Sheet V1
Transféré par
Walter ValverdeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SNMP
Versions SNMPv1Simple Network Management Protocol: a full Internet standard, defined in RFC 1157. (RFC 1157 replaces the earlier versions that were published as RFC 1067 and RFC 1098.) Security is based on community strings. SNMPv2cThe community string-based Administrative Framework for SNMPv2. SNMPv2c (the "c" is for "community") is an experimental Internet protocol defined in RFC 1901, RFC 1905, and RFC 1906. SNMPv2c is an update of the protocol operations and data types of SNMPv2p (SNMPv2 Classic) and uses the community-based security model of SNMPv1. SNMPv3Version 3 of SNMP. SNMPv3 is an interoperable standards-based protocol defined in RFCs 3413 to 3415. SNMPv3 provides secure access to devices by authenticating and encrypting packets over the network. The security features provided in SNMPv3 are as follows: Message integrityEnsuring that a packet has not been tampered with in transit. AuthenticationDetermining that the message is from a valid source. EncryptionScrambling the contents of a packet to prevent it from being learned by an unauthorized source. Terminology Community String MIB
<url here>
Passwords for SNMP access to network devices Management Information Base, collection of variables which is shared between NMS and network device.
SNMP Trap
Message sent by device and sent to NMS
SNMP GET
Message sent by NMS to retrieve MIB data from network device
SNMP SET
Message sent by NMS when it wants to change or configure network device
Troubleshooting show snmp community show snmp host show snmp group show snmp user show snmp view debug snmp packet
Configuration Block
! There is no specific command that you use to enable SNMP. The first snmp-server command that you enter enables the supported versions of SNMP. All other configurations are optional. snmp-server community <text string> [ro | rw] snmp-server host <host-id> version <{1 | 2c | 3 [auth | noauth | priv]} > <community string> !When you configure SNMP version 3 and you want to use the SNMPv3 security mechanism for handling SNMP packets, you must establish SNMP groups and users with passwords. You can assign views to community strings to limit which MIB objects an SNMP manager can access. snmp-server view <view-name> <oid-tree> {included | excluded} snmp-server group <[groupname {v1 | v2c | v3 [auth | noauth | priv]}] [read readview] [write writeview] [notify notifyview] [access access-list]> snmp-server user <username groupname [remote ip-address{v1 | v2c | v3 [auth | noauth | priv]}] [read readview] [write writeview] [notify notifyview] [access access-list]>
Versions SNMP Security Models and Levels
Model Level Authentication Community String Community String Encryption What Happens
v1 v2c v3 v3
noAuthNoPriv noAuthNoPriv noAuthNoPriv authNoPriv
No No No No
Uses a community string match for authentication. Uses a community string match for authentication. Uses a username match for authentication. Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMACSHA algorithms. Provides authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 or HMACSHA algorithms. Provides DES 56-bit encryption in addition to authentication based on the CBC-DES (DES-56) standard.
Username
MD5 or SHA
v3
authPriv
MD5 or SHA
DES
by Garry L. Baker
v1.0
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ATG Commerce - Intercepting PipelineDocument1 pageATG Commerce - Intercepting PipelineAmit Kumar LakraPas encore d'évaluation
- Trading FunctionsDocument21 pagesTrading FunctionspetefaderPas encore d'évaluation
- EtherNet-IP Modbus Getting StartedDocument7 pagesEtherNet-IP Modbus Getting StartedcbalivePas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Secrets To A Great BodyDocument16 pages10 Secrets To A Great BodyimrancenakkPas encore d'évaluation
- Attunity Replicate User Guide PDFDocument831 pagesAttunity Replicate User Guide PDFgudicmPas encore d'évaluation
- SQL Server Detailed ArchitectureDocument15 pagesSQL Server Detailed ArchitectureMadhu ThellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intsol UniFLOW v5 FAQ 081611Document6 pagesIntsol UniFLOW v5 FAQ 081611edgiffordPas encore d'évaluation
- Linux Tuning For ASE and IQDocument61 pagesLinux Tuning For ASE and IQVivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Rac Aix System Stability 131022 PDFDocument32 pagesRac Aix System Stability 131022 PDFtuxfriedPas encore d'évaluation
- Atg IntroDocument35 pagesAtg IntroSahil MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kernel Module ProgrammingDocument25 pagesKernel Module ProgrammingCiluveru Chandana KishoriPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerVC V1.3.2Document308 pagesPowerVC V1.3.2ecorradiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wsorkout Programme Wider FitnessDocument7 pagesWsorkout Programme Wider FitnessNedim100% (1)
- Penny Stocks List For 2019 - All Stocks Traded On NSEDocument21 pagesPenny Stocks List For 2019 - All Stocks Traded On NSEAravind AllamPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Day SplitDocument15 pages4 Day SplitTony GalantePas encore d'évaluation
- Omegamon Db2 ClassicDocument634 pagesOmegamon Db2 Classicvijaymanand1100% (1)
- OCRHindi Using VietOCR and Tesseract PDFDocument7 pagesOCRHindi Using VietOCR and Tesseract PDFJagdesh RebbaPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 3 All ModulesDocument48 pagesCCNA 3 All ModulesFi3ta100% (1)
- Top 30 Linux System Admin Interview Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTop 30 Linux System Admin Interview Questions & AnswersRachit KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- PostgreSQL Administration Essentials Sample ChapterDocument25 pagesPostgreSQL Administration Essentials Sample ChapterPackt PublishingPas encore d'évaluation
- Atg IoDocument4 pagesAtg Ioikehd100% (1)
- Paging Space Management in AixDocument14 pagesPaging Space Management in Aixamshadab-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- MySQL Master-Master ReplicationDocument7 pagesMySQL Master-Master ReplicationStephenEfangePas encore d'évaluation
- FormHander DARGSDocument2 pagesFormHander DARGSI@SydneyPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Create A Fully Automated AI Based TradingDocument20 pagesHow To Create A Fully Automated AI Based TradingmawcomwPas encore d'évaluation
- Srs Event Management System PDF FreeDocument4 pagesSrs Event Management System PDF FreeShubham YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- ModBus Coding Example VBDocument13 pagesModBus Coding Example VBdcapps_7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Packet Analyzer - 15 TCPDUMP Command ExamplesDocument12 pagesPacket Analyzer - 15 TCPDUMP Command ExamplesMARCO FERRANTIPas encore d'évaluation
- AssemblerDocument13 pagesAssemblerHemil Patel100% (1)
- The Running Guru Runner's Training GuideDocument25 pagesThe Running Guru Runner's Training GuideRustyRPas encore d'évaluation
- To Compute and Compare The Execution Time (S) of Des Algorithm Serially, Parallelly Using Rmi With JVMDocument23 pagesTo Compute and Compare The Execution Time (S) of Des Algorithm Serially, Parallelly Using Rmi With JVMkv bharadwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Troubleshooting IBM Campaign Perform Ance: Web Application ServerDocument4 pagesTroubleshooting IBM Campaign Perform Ance: Web Application ServersrimkbPas encore d'évaluation
- Size 8 Workout Plan by Guru MannDocument4 pagesSize 8 Workout Plan by Guru MannThreadrootsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sterling Trader Pro en PDFDocument91 pagesSterling Trader Pro en PDFAyush ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- ATG Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesATG Interview QuestionsPriyanka KakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- © 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument18 pages© 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedaabcdPas encore d'évaluation
- K Means PseudocodeDocument1 pageK Means PseudocodeMusa Milli100% (1)
- Derivatives ChaptersDocument19 pagesDerivatives Chapterslatiful188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comandos 3parDocument6 pagesComandos 3parLucas FreirePas encore d'évaluation
- CL Programming - 1Document87 pagesCL Programming - 1AshPas encore d'évaluation
- PICO CMS How To InstallDocument5 pagesPICO CMS How To InstallrakeshPas encore d'évaluation
- DOCUMENTATION How To Troubleshoot Frozen Media On UNIX and WindowsDocument6 pagesDOCUMENTATION How To Troubleshoot Frozen Media On UNIX and Windowssubhrajitm47Pas encore d'évaluation
- HP UX Common+Unix+CommandsDocument12 pagesHP UX Common+Unix+Commandsnid5649Pas encore d'évaluation
- LinuxDocument72 pagesLinuxMishraa_jiPas encore d'évaluation
- Netbackup - How To Create A Scratch PoolDocument3 pagesNetbackup - How To Create A Scratch PoolamsreekuPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Practise and Profit From InvestingDocument43 pagesLearn Practise and Profit From Investingvipinkala1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Week Workout Program Planner v1fDocument32 pages12 Week Workout Program Planner v1fHeath HopkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- How To+use QuickRefDocument223 pagesHow To+use QuickRefkashifmfPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On Array For Interviews and Competitive Programming (., Tushti Kiao, Ue Chatterjee, Aditya) (Z-Library)Document475 pagesProblems On Array For Interviews and Competitive Programming (., Tushti Kiao, Ue Chatterjee, Aditya) (Z-Library)qmu94562Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mariadb Maxscale HADocument12 pagesMariadb Maxscale HADang Huu AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Eca 1 Project (LAb Report of Automatic Led Light)Document5 pagesEca 1 Project (LAb Report of Automatic Led Light)Äbů BäķäŗPas encore d'évaluation
- Better Optimization in Tradestation, Part 2Document12 pagesBetter Optimization in Tradestation, Part 2jramongvPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexibility and Muscular Strength Muscular Endurance (Handout)Document8 pagesFlexibility and Muscular Strength Muscular Endurance (Handout)Raven WintersPas encore d'évaluation
- Eckmar's Marketplace Script 2.0 - LATEST VERSION - Java Virtual MachineDocument5 pagesEckmar's Marketplace Script 2.0 - LATEST VERSION - Java Virtual MachineEckmarPas encore d'évaluation
- SNMP Cisco PDFDocument30 pagesSNMP Cisco PDFjjdegraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- SNMP Over IPv6Document7 pagesSNMP Over IPv6Ryduano VicentPas encore d'évaluation
- B UCSM GUI System Monitoring Guide 3 2 Chapter 01000Document8 pagesB UCSM GUI System Monitoring Guide 3 2 Chapter 01000yerocic586Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide To Understanding SNMP PDFDocument10 pagesA Guide To Understanding SNMP PDFIammewa IammewaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nx-Os 6x SNMPDocument30 pagesNx-Os 6x SNMPAllan BrandPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP TutorialDocument4 pagesSimple Network Management Protocol SNMP TutorialmaguettePas encore d'évaluation
- Clothhabit Rosy LadyshortsDocument13 pagesClothhabit Rosy LadyshortsWalter Valverde100% (3)
- CCNA3 - Answers Chapter 2 v.4.0: Updated Daily New Updated Mar 01 2009 by Quocvuong EmailDocument6 pagesCCNA3 - Answers Chapter 2 v.4.0: Updated Daily New Updated Mar 01 2009 by Quocvuong EmailWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Router Command Quick ReferenceDocument4 pagesCisco Router Command Quick ReferenceWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- TCP Keep Alive 1Document2 pagesTCP Keep Alive 1Walter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
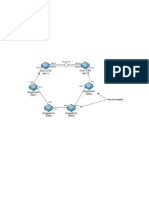
- Lab TopologyDocument2 pagesLab TopologyWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- IOS Zone-Based FirewallDocument1 pageIOS Zone-Based FirewallWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Frame Relay CheatSheetDocument1 pageFrame Relay CheatSheetWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco 3750 (Site 1) Cisco 3750 (Site 2) : Gig1/0/1 Gig2/0/1 Gig1/0/1 Gig2/0/1 EtherchannelDocument1 pageCisco 3750 (Site 1) Cisco 3750 (Site 2) : Gig1/0/1 Gig2/0/1 Gig1/0/1 Gig2/0/1 EtherchannelWalter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
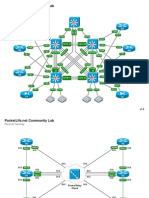
- Lab Topology2Document2 pagesLab Topology2Walter ValverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Nitro2 User Manual v2.24 PDFDocument29 pagesNitro2 User Manual v2.24 PDFReifesxd ProPas encore d'évaluation
- TECDCT-2145 Cisco FabricPathDocument156 pagesTECDCT-2145 Cisco FabricPathWeiboraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Peer For WebRTC - WhitepaperDocument11 pagesOpen Peer For WebRTC - Whitepaperhookflash100% (1)
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDocument4 pages9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructRadu Florin TriponPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Local Area Network VLAN TutorialDocument6 pagesVirtual Local Area Network VLAN TutorialplanifikuesiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit V Handoffs & Dropped CallsDocument25 pagesUnit V Handoffs & Dropped Callsramanaidu1100% (3)
- Configure Nokia E71WiFi SIP Client With The 3300Document14 pagesConfigure Nokia E71WiFi SIP Client With The 3300Angelo IonPas encore d'évaluation
- DD-WRT Network OptimizationDocument2 pagesDD-WRT Network Optimizationsrogers99Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3G Support List (RK2918)Document3 pages3G Support List (RK2918)far117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meraki Datasheet MR12Document4 pagesMeraki Datasheet MR12Chow Kok KeePas encore d'évaluation
- Ping LTEDocument5 pagesPing LTEward_chPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Shortest Path in Packet Switching Network Using Genetic AlgorithmDocument6 pagesImplementation of Shortest Path in Packet Switching Network Using Genetic Algorithmeditor_ijarcssePas encore d'évaluation
- Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview NIC and Switch Embedded Teaming User GuideDocument61 pagesWindows Server 2016 Technical Preview NIC and Switch Embedded Teaming User GuidenetvistaPas encore d'évaluation
- OBN208111 IManager N2000 BMS Introduction ISSUE2.00Document47 pagesOBN208111 IManager N2000 BMS Introduction ISSUE2.00AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab # 12: Access Control List Access Control ListDocument9 pagesLab # 12: Access Control List Access Control ListMudassir ZiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Application Protocol: Unit - 5Document39 pagesWireless Application Protocol: Unit - 5Rajesh RajPas encore d'évaluation
- CN Assignment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesCN Assignment 2 PDFSalman chaudhary0% (1)
- WIN-Wireless Intelligent Network Full ReportDocument37 pagesWIN-Wireless Intelligent Network Full ReportGarvit Shrivastava90% (10)
- Network Security and ManagementDocument4 pagesNetwork Security and Managementrashid1986Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Communication Policy: 1. OverviewDocument3 pagesWireless Communication Policy: 1. OverviewSpit FirePas encore d'évaluation
- Dialaw@Y Ip System SpecificationsDocument15 pagesDialaw@Y Ip System SpecificationsLissy AranaPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 ZTE's Future Oriented Microwave SolutionDocument35 pages04 ZTE's Future Oriented Microwave SolutionZeljko VrankovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Health - Check - S5300-09.05.13 08-00-01Document79 pagesHealth - Check - S5300-09.05.13 08-00-01K.m.khizir AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Service AssuranceDocument143 pagesService AssuranceAlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- VLAN Basics PDFDocument4 pagesVLAN Basics PDFAnuja AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Headends For TV Signal Processing: SAT LNB SAT LNBDocument6 pagesHeadends For TV Signal Processing: SAT LNB SAT LNBVíctor MayaPas encore d'évaluation
- DIR-2150 ManualDocument153 pagesDIR-2150 ManualGuleBamsePas encore d'évaluation
- List of Mobile Number Prefixes - PhilippinesDocument1 pageList of Mobile Number Prefixes - PhilippinessevillaarvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Distance Vector Algorithm: Bellman-Ford Equation (Dynamic Programming)Document36 pagesDistance Vector Algorithm: Bellman-Ford Equation (Dynamic Programming)harish babu aluruPas encore d'évaluation
- Switch Lt. 1 - BDCom S3756M-2ACDocument7 pagesSwitch Lt. 1 - BDCom S3756M-2ACFeby AndyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationD'EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (6)
- Evaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsD'EverandEvaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesD'EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsD'EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeD'EverandSocial Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomePas encore d'évaluation
- Blender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)D'EverandBlender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Art of Social Media: Power Tips for Power UsersD'EverandThe Art of Social Media: Power Tips for Power UsersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (59)
- How to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyD'EverandHow to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (27)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxD'EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (67)
- The YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueD'EverandThe YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (33)
- Branding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsD'EverandBranding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (32)
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationD'EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessD'EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineD'EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachinePas encore d'évaluation
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryD'EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (260)
- App Innovator's Guide: Mobile App Development for Android and iOS: Building Cross-Platform SolutionsD'EverandApp Innovator's Guide: Mobile App Development for Android and iOS: Building Cross-Platform SolutionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Wordpress 2023 A Beginners Guide : Design Your Own Website With WordPress 2023D'EverandWordpress 2023 A Beginners Guide : Design Your Own Website With WordPress 2023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowD'EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (388)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.D'EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Photoshop: A Step by Step Ultimate Beginners’ Guide to Mastering Adobe Photoshop in 1 WeekD'EverandPhotoshop: A Step by Step Ultimate Beginners’ Guide to Mastering Adobe Photoshop in 1 WeekPas encore d'évaluation
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamD'EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)