Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Corona: Visual
Transféré par
KARAM ZAKARIATitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Corona: Visual
Transféré par
KARAM ZAKARIADroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
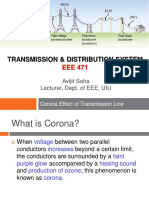
CORONA
If the alternating voltage on a line conductor is gradually raised, it will reach a value known as the visual critical voltage. Vv, at which a faint violet glow known as CORONA appears, together with a slight hissing and smell of ozone (O3). Let Vo to be the voltage level just before. Vv, when the corona occurs, an additional power loss at that level begins to occur in the system, and is given by the following empirical formula for corona power loss: Po = K (VL Vo)2 neutral OR
Po = 242
{ K as constant for given conductor arrangements VL is the rms operating voltage line to
( f + 25)
r (VL Vo ) 2 . 10 5 kW / km / Ph Dm
is air density factor, at the system frequency is conductor radius
Dm is the GMD
Thus CORONA can be defined as a partial discharge or incomplete failure of the air dielectric.
Corona occurs when the local electric field near the conductor surface is sufficiently high to give enough energy to free electrons. Thus more electrons and positive ions appear which in turn are accelerated by the electric field and cause further ionizing collisions. For long uniform round wire of radius r and charge Q c/m, the electric field at its surface is
Er =
Q 2 Eo r
V /m
For a very large diameter smooth conductors in air at normal temperature and pressure, corona power loss begins at the critical disruptive stress when: Eo = 30 kV peak/cm OR Eo = 3000 kV peak/m Eo is also called the peak voltage gradient If the conductor is placed at long d distance from another conductor such that the effect from the another conductor is negligible. If V is the p.d. between the two conductors.
V=
Q d ln Eo r
d r
d 2r
OR
V = 2r Er ln
since Q =2 Eo r Er
&
Vo 2 r ln
d r
In three phase line with r.m.s phase voltage VL, then from the transmission line formulas:
VL =
or
D Q ln m 2 Eo r
VL = r Er ln
30 2
Dm r
Dm r KVrms
Vo =
r M ln
And the visual critical voltage is given by
Vv =
30 0. 3 D r M [1 + ] ln m r 2 r
KVrms
Where Dm r is the GMD is the conductor radius is the air density factor where
3 . 86 p 273 + t
Where {P is an mm mercury & t in oC
M is the roughness factor or irregularity factor M = 1 for smooth, polished cylindrical conductor M = 0.93 - .98 for weathered cylindrical conductor M = 0.87 weathered cond. Having more than 7 strands The above equation says that the air around the conductor will be ionized at a distance = 1 & M = 1 the distance = r+0.3 1. rain, 2. mist, 3. fog,
r M [1 +
r
0 .3
] or for r
The Factors that reduce the break down strength of air are
4. humidity 5. temperature 6. pressure 7. pollution and, 8. thunder storms which may reduce it to about 80%, 9. conductor dimensions and conditions.
The disruptive critical voltage Vo of the phase voltage is given by:
H.W#3 Design a conductor which has no coron
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CoronaDocument6 pagesCoronaIslam MasoudPas encore d'évaluation
- A Full Guide About Corona Effect / Corona Discharge in Transmission LinesDocument13 pagesA Full Guide About Corona Effect / Corona Discharge in Transmission LinesShishir AcharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona, Sag and Conductor Vibration: Batch IXDocument15 pagesCorona, Sag and Conductor Vibration: Batch IXShyamala Chettiraj100% (1)
- Experiment No. 6: MATLAB R2015aDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 6: MATLAB R2015aAvinash RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee302 - Corona & InsulatorsDocument48 pagesEe302 - Corona & Insulatorsreddystar3161Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corona DischargeDocument6 pagesCorona Dischargemustafaayman6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corona Loss in Transmission LinesDocument18 pagesCorona Loss in Transmission LinesGaurav OrganPas encore d'évaluation
- PEE17 M Lecture Series 2Document22 pagesPEE17 M Lecture Series 2Christian 07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corona EffectDocument13 pagesCorona Effectketan adhwan100% (1)
- Electric Field Calculation For Corona DischargeDocument2 pagesElectric Field Calculation For Corona DischargeRintuMathunniPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Last Class: What Is Corona? Why It Is Important To Know Factors Affecting Corona Partial DischargeDocument22 pagesReview of Last Class: What Is Corona? Why It Is Important To Know Factors Affecting Corona Partial DischargennvpratapPas encore d'évaluation
- EPTD W8-L2 Corona in Transmission Lines MAZSDocument17 pagesEPTD W8-L2 Corona in Transmission Lines MAZSBoŋɗʜoŋ SʌʀĸɘʀPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Six Corona)Document29 pagesChapter Six Corona)Magarsaa Qana'iiPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar ReportDocument10 pagesSeminar ReportGaurav Organ100% (1)
- Corona DischargeDocument6 pagesCorona DischargeIslam MasoudPas encore d'évaluation
- CORONADocument14 pagesCORONABiswajeet RoutPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona and Insulators Lecture IVDocument16 pagesCorona and Insulators Lecture IVview sasaPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Corona: 7.1. Effect of Corona On Transmission LineDocument5 pages7 Corona: 7.1. Effect of Corona On Transmission LineParimal PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona 3 PDFDocument6 pagesCorona 3 PDFlimkokchiang809Pas encore d'évaluation
- Specialtopics 10Document43 pagesSpecialtopics 10boopelectraPas encore d'évaluation
- Power 1 Chapter-6 PDFDocument29 pagesPower 1 Chapter-6 PDFEnyewPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona: Electrical Power Transmission and Distribution Eee/Git/GitamuniversityDocument10 pagesCorona: Electrical Power Transmission and Distribution Eee/Git/GitamuniversityRohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System PPT On CORONADocument17 pagesPower System PPT On CORONAShadab Khan80% (10)
- Sag in Transmission Line and Corona EffectDocument34 pagesSag in Transmission Line and Corona EffectWaqar Uddin75% (4)
- What Is Corona Effect or Corona LossDocument5 pagesWhat Is Corona Effect or Corona LossDjidi Egrey SougoumiPas encore d'évaluation
- PS - II - GTU - Study - Material - GTU-Paper-Analysis - Unit-7 - 04072020090542AMDocument5 pagesPS - II - GTU - Study - Material - GTU-Paper-Analysis - Unit-7 - 04072020090542AMParimal PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona LectureDocument22 pagesCorona LectureSangeen PanezaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Drop and Short CircuitDocument39 pagesVoltage Drop and Short CircuitMinerva Abanto100% (1)
- BLOCK II: Reasons of EMI: Division For Electricity and Lightning Research Uppsala UniversityDocument34 pagesBLOCK II: Reasons of EMI: Division For Electricity and Lightning Research Uppsala UniversityArnulfo SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- CORONADocument25 pagesCORONAMohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System PPT On CORONADocument13 pagesPower System PPT On CORONAg4ubhPas encore d'évaluation
- EPTD - W8-L2 - Corona in Transmission LinesDocument16 pagesEPTD - W8-L2 - Corona in Transmission LinesJunied TazrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Last Class: Potential Distribution Over An Insulator StringDocument24 pagesReview of Last Class: Potential Distribution Over An Insulator StringnnvpratapPas encore d'évaluation
- Paschen Curve For MEMS - ESDDocument5 pagesPaschen Curve For MEMS - ESDdinhnv9533Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Design CalcDocument38 pagesTransmission Line Design CalcparmenderPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line,: ASCR (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) Are Used in This Type of Transmission LineDocument5 pagesTransmission Line,: ASCR (Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced) Are Used in This Type of Transmission Linemana danaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 DN 87 Oc 8 EaDocument55 pages4 DN 87 Oc 8 EaAhmed SeddikPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona Effects On Ehv Ac Transmission LinesDocument5 pagesCorona Effects On Ehv Ac Transmission LinesjayanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission & Distribution System: Avijit Saha Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, UIUDocument18 pagesTransmission & Distribution System: Avijit Saha Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, UIUBelal IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- CORONA - A Self-Sustained External Partial DischargeDocument16 pagesCORONA - A Self-Sustained External Partial DischargevirenpandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Coron A EffectDocument15 pagesCoron A EffectGunjan VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis: Development of Transmission Line Models Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickDocument29 pagesPower System Analysis: Development of Transmission Line Models Tom Overbye and Ross BaldickEarly JobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 4.1.I2R Loss and Corona Loss: Fig.4.1 Corona Current WaveformDocument13 pagesUnit 4 4.1.I2R Loss and Corona Loss: Fig.4.1 Corona Current WaveformAjay Kumar RelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Underground Cable 2Document39 pagesUnderground Cable 2Ranajoy BhattacharjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3Document17 pagesWeek 320bee107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corona Characteristics: Instructed By: Mr. M. K. C. D. ChinthakaDocument6 pagesCorona Characteristics: Instructed By: Mr. M. K. C. D. ChinthakaIsuru KodikaraPas encore d'évaluation
- TIS (Travel Information System) : These System Is Used To Data Communication System in Medium Frequency (MF)Document20 pagesTIS (Travel Information System) : These System Is Used To Data Communication System in Medium Frequency (MF)Basuki Rahmat HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-6 - Power Systems 3rd YearDocument4 pagesLecture-6 - Power Systems 3rd YearIraqi for infoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage I: Breakdown in Non-Uinform Fields and Corona DischargesDocument35 pagesHigh Voltage I: Breakdown in Non-Uinform Fields and Corona DischargesPoi LkjPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (3) PNP JunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 2 (3) PNP JunctionJoel WatsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona Losses Dependence From The Conductor Diameter: October 2011Document7 pagesCorona Losses Dependence From The Conductor Diameter: October 2011tusarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Problem Sheet No 3C - CoronaDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Problem Sheet No 3C - CoronaDeepak Srinivas YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1D'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyD'EverandModern Devices: The Simple Physics of Sophisticated TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignD'EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendalePas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesD'EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Electrical Work Practices - PreviewDocument14 pagesElectrical Work Practices - PreviewKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line ArrestersDocument13 pagesTransmission Line ArrestersKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving MV Network Efficiency With Feeder AutomationDocument12 pagesImproving MV Network Efficiency With Feeder AutomationKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjustable Speed Drives TutorialDocument13 pagesAdjustable Speed Drives Tutorialapi-3765150100% (2)
- Electrical Work Practices - PreviewDocument14 pagesElectrical Work Practices - PreviewKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Factor Correction ActualDocument34 pagesPower Factor Correction ActualKARAM ZAKARIA86% (7)
- Electrical Relay Diagram and PID SymbolsDocument5 pagesElectrical Relay Diagram and PID SymbolsKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Experience Using Power Quality Data To Improve Power Distribution ReliabilityDocument11 pagesReal Experience Using Power Quality Data To Improve Power Distribution ReliabilityKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- What Will MV Switchgear Look Like in The FutureDocument16 pagesWhat Will MV Switchgear Look Like in The FutureKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lichtwissen12 Lighting Quality PDFDocument32 pagesLichtwissen12 Lighting Quality PDFAntunPas encore d'évaluation
- نظم التأريضDocument23 pagesنظم التأريضriyadh zakiPas encore d'évaluation
- White Paper Machine SafetyDocument14 pagesWhite Paper Machine SafetyTien Dung TranPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing A Metering System For Small and Medium Sized BuildingsDocument60 pagesDesigning A Metering System For Small and Medium Sized BuildingsKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Purpose of A BallastDocument14 pagesPurpose of A BallastKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Cable Fault LocatingDocument41 pagesElectrical Cable Fault LocatingKARAM ZAKARIA100% (1)
- Improving MV Network Efficiency With Feeder AutomationDocument12 pagesImproving MV Network Efficiency With Feeder AutomationKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Focus On Outdoor LightingDocument4 pagesFocus On Outdoor LightingKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy - Efficient LightingDocument8 pagesEnergy - Efficient LightingKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Safety in Battery Maintenance and Testing PDFDocument7 pagesElectrical Safety in Battery Maintenance and Testing PDFpranab_473664367Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lighting in The WorkplaceDocument7 pagesLighting in The WorkplaceKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Lighting Design GuideDocument11 pagesEmergency Lighting Design GuideKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Tray ManualDocument60 pagesCable Tray ManualKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- XLPE Cable Systems Users Guide-ABBDocument32 pagesXLPE Cable Systems Users Guide-ABBsujithmohandasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lead Acid Battery Formation TechniquesDocument31 pagesLead Acid Battery Formation TechniquesKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Electrical Measurements - 2004Document10 pagesElementary Electrical Measurements - 2004KARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical-Guide Load CalculationDocument19 pagesElectrical-Guide Load CalculationMohiuddin Ahmed Ranju100% (1)
- Battery Technology Life Verification Test ManualDocument133 pagesBattery Technology Life Verification Test ManualKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Nickel Cadmium BatteriesDocument11 pagesNickel Cadmium BatteriesKARAM ZAKARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical-Guide Load CalculationDocument19 pagesElectrical-Guide Load CalculationMohiuddin Ahmed Ranju100% (1)
- MPD 810HDocument5 pagesMPD 810Hdan22yPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterprise ExtensionDocument15 pagesEnterprise ExtensionDanielle De Leon50% (2)
- SW Driver User Manual For Marvell Serial ATA Host AdaptersDocument116 pagesSW Driver User Manual For Marvell Serial ATA Host Adapterstosser12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stepper Principle Prezentare Power PointDocument15 pagesStepper Principle Prezentare Power PointPetrovai AlexandruPas encore d'évaluation
- ECP 4083935 - O&m - EcpgDocument100 pagesECP 4083935 - O&m - Ecpgsam_stranger200589% (9)
- Basic PLC VDEE 2Document70 pagesBasic PLC VDEE 2Lawrence DataPas encore d'évaluation
- GV-N98TZL-512H GV-N98TZL-1GH: Sales KitDocument8 pagesGV-N98TZL-512H GV-N98TZL-1GH: Sales Kitchristophe_GIGABYTEPas encore d'évaluation
- LNCTGroup Data Login IDs - For DisplayDocument18 pagesLNCTGroup Data Login IDs - For DisplaySiddharth NagayachPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Ic Applications SyllabusDocument2 pagesDigital Ic Applications SyllabusSuyog ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Owner's Manual: The Tone Hammer Preamp/DiDocument4 pagesOwner's Manual: The Tone Hammer Preamp/DiflexlopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesa Boogie Mark II-BDocument10 pagesMesa Boogie Mark II-BscheisshandyPas encore d'évaluation
- DCCDocument35 pagesDCCkhushbu patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Cmos Check Sum ErrorDocument3 pagesCmos Check Sum Erroryogeshdhuri22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1 1. Determination of Catchment Area Using Topographic MapDocument43 pagesLab 1 1. Determination of Catchment Area Using Topographic MapAashutosh KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- Canafusion - CA-2000 Specification - 1Document1 pageCanafusion - CA-2000 Specification - 1Anggaran RSUD.M.Natsir SolokPas encore d'évaluation
- ARFCN GSM SpecsDocument7 pagesARFCN GSM SpecsEyotrePas encore d'évaluation
- At Command ManualDocument38 pagesAt Command ManualOpulens KeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ad 9833Document21 pagesAd 9833cristianiacobPas encore d'évaluation
- MuramasaDocument4 pagesMuramasaThomson AffendyPas encore d'évaluation
- MV PFC - Metal Enclosed - EatonDocument24 pagesMV PFC - Metal Enclosed - EatonlassasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Markemimaje Smartdate 5Document198 pagesMarkemimaje Smartdate 5alfredo campos bartoloPas encore d'évaluation
- IEEE Device NumbersDocument12 pagesIEEE Device NumbersKuwat Riyanto100% (1)
- 2009 SAJC Prelims H2 P2 QuestionsDocument18 pages2009 SAJC Prelims H2 P2 QuestionsJasonPas encore d'évaluation
- SM Me411 21 en 01Document97 pagesSM Me411 21 en 01Sulay Avila Llanos100% (1)
- Motorola's STARLINE Cable Simulator Are Used in Place of Fixed Forward Equalizer in Systems Where The Amplifiers Are Located Close TogetherDocument2 pagesMotorola's STARLINE Cable Simulator Are Used in Place of Fixed Forward Equalizer in Systems Where The Amplifiers Are Located Close TogetherRodrigo AlonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Liebert Intellislot Modbus Rtu Reference Guide SL 28170 - 001 435 456Document40 pagesLiebert Intellislot Modbus Rtu Reference Guide SL 28170 - 001 435 456Ivan OlveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdfs Standardgainhorn CMIWR8SeriesDocument0 pagePdfs Standardgainhorn CMIWR8SeriesMahendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Instructions: KX-T7420 KX-T7425 KX-T7431 KX-T7433 KX-T7436Document34 pagesOperating Instructions: KX-T7420 KX-T7425 KX-T7431 KX-T7433 KX-T7436Marina BoljanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectralert® Series: Horns, Strobes, and Horn/StrobesDocument4 pagesSpectralert® Series: Horns, Strobes, and Horn/Strobesmechengineer3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 623 2320 1 PBDocument4 pages623 2320 1 PBbatuhanPas encore d'évaluation