Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Basics of Electricity & Magnetism: What's An Electron?
Transféré par
kiranphdDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Basics of Electricity & Magnetism: What's An Electron?
Transféré par
kiranphdDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Basics of Electricity & Magnetism
Rachael Lancor Wonders of Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison APS-DPP Teachers Day November 13, 2007
Whats an electron?
Helium
Model of the atom
Cartoon is deceptive.
This is a better image of electrons.
Static Electricity
Electric Fields
Whats electric charge?
Wheres the field?
Scotch tape activity
Induced Charge vs. Charge Transfer Demos
The field indicates a force that can push on a charged particle.
Van de Graaff generator
Balloons Fur, wool, plastic, & glass
Electric Potential
Current Electricity
Equipotential Lines
Always perpendicular to lines of force No work to move charges along lines Takes work (energy) to cross lines
Circuit game - Whats it like to be an electron?
Series Circuits
Parallel Circuits
What happens when a light burns out?
The problem with the Christmas lights
What happens here?
Act it out if you arent sure
Current vs. Voltage vs. Power
How do you jump start a car?
Current = # of electrons per second Voltage = energy per electron
Series or parallel?
Also called Electrical potential or Potential difference
Power = energy (of all electrons) per second
High voltage wont kill, but high current will!
Whats going on here?
AC vs. DC
Tesla Coil & Fluorescent Light bulb Plasma Ball Lab
Direct Current
Batteries Current is constant Wall socket Current oscillates AC travels better over long distances P=I2R, smaller current = less lost power
Alternating Current
Why the difference?
Generating AC current
Generating Electricity
Identify the energy transformations:
Hand-held generator Windmill Hydroelectric Power Nuclear Power Coal Power (steam generator)
Magnetic Fields
Types of Magnets
What do the fields look like?
Map using iron filings
The refrigerator vs. the fridge magnet Magnetic Domains
The presence of a field means theres a force!
Examples
Electromagnetism
Ring Magnets
What forces are acting here? Why do they balance? The earth has a magnetic field, is this how it stays in orbit?
Floating Globe
Whats the relationship? Use the compass and current-carrying wire to find out.
A current carrying wire produces a magnetic field. This is Amperes Law.
Electromagnetism (in reverse)
Examples - Eddy Currents
Can a magnet create a current?
Yes, a moving magnetic field creates a current in a wire. This is Faradays Law.
Battery free flashlight Eddy currents Ring launcher Can Crusher (at Plasma Expo)
Motors
Can you make a motor from this?
A force is created by the current in the magnetic field. It makes the wire loop spin.
Mini Motor
Generator
A motor in reverse. Turning the loop creates a current in the wire.
Generating AC current
Maxwells Equations
Gauss Law
Faradays Law Amperes Law
Electromagnetic Radiation
What is a light wave?
Maxwells Equations predict the speed of light
c= 1 0"0
Electromagentic Waves
So light must be an electromagnetic wave
!
How do we make EM waves?
-----
The EM Spectrum
r E r B
e-
! !
1. Start with an antenna with an AC current 2. Build up of electrons creates a net charge 3. Therefore, an E-field 4. As e-s move, E-field oscillates 5. E-field makes a B-field we get an em wave
Measuring the speed of light in the microwave
Recall standing waves
Microwave frequency = 2450 MHz
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Riemann Hypothesis PDFDocument19 pagesRiemann Hypothesis PDFFlyLove100% (1)
- Lesson 7: Electricity and Magnetism Learning ObjectivesDocument58 pagesLesson 7: Electricity and Magnetism Learning ObjectivesAdriel MarasiganPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksD'EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Faraday ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Faraday ProjectAlviya Rizwan100% (1)
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument64 pagesElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismFe DPas encore d'évaluation
- Motors PhysicsDocument25 pagesMotors PhysicsBilly100% (1)
- Induced EMFDocument21 pagesInduced EMFJaica Mangurali TumulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Dielectricity and Capacitance by Eric DollardDocument8 pagesDielectricity and Capacitance by Eric DollardSteve Young100% (1)
- Classical Mechanics by Dr. M. O. Aku PDFDocument62 pagesClassical Mechanics by Dr. M. O. Aku PDFLOUI_GR100% (1)
- Building Utilities (Electrical)Document18 pagesBuilding Utilities (Electrical)damsaishPas encore d'évaluation
- CentroidDocument46 pagesCentroidkiranphd100% (2)
- How To Make A Lifting Electromagnet - Ehow PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Make A Lifting Electromagnet - Ehow PDFNaga RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetism & ElectromagnetismDocument38 pagesMagnetism & ElectromagnetismganapathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesLaws of ElectromagnetismSukalyan GhoshalPas encore d'évaluation
- 12V Battery Powered Marx GeneratorDocument14 pages12V Battery Powered Marx Generatorpakde jongko100% (1)
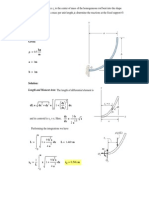
- Influence LineDocument43 pagesInfluence Lineolomu80% (5)
- Electron TheoryDocument13 pagesElectron TheoryAilene Tsui Alferez PaciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Multiphase Flow Science and Technology (Guan Heng Yeoh (Eds.) )Document444 pagesHandbook of Multiphase Flow Science and Technology (Guan Heng Yeoh (Eds.) )thulyyPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project: ON EMP JammerDocument17 pagesPhysics Project: ON EMP JammerAnonymous q9FjgwT5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mag ElectromagDocument38 pagesMag ElectromagJames Paul Micael GargantaPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectromagnetismDocument5 pagesElectromagnetismsusan pajarilloPas encore d'évaluation
- PhyDocument13 pagesPhyasirirastgeleemailPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity And: MagnetismDocument37 pagesElectricity And: MagnetismdrexelPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectromagnetisDocument5 pagesElectromagnetisAachal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam in ElectricityDocument7 pagesFinal Exam in ElectricityNiko Igie Albino PujedaPas encore d'évaluation
- InductionDocument12 pagesInductionAhmad Ibsais100% (1)
- Barrera, Jasper Owen Albeso - Chapters 4-6Document13 pagesBarrera, Jasper Owen Albeso - Chapters 4-6Jade BaliolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxwell's Equations麦克斯韦方程组Document9 pagesMaxwell's Equations麦克斯韦方程组楚梦塬Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSS Physics 2 NotesDocument35 pagesCSS Physics 2 NotesM Faadi Malik50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Electricity and MagnetismDocument126 pagesChapter 4 Electricity and MagnetismCziara JustinePas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10-Lesson 10Document34 pagesScience 10-Lesson 10afloresPas encore d'évaluation
- GenPhy2 Module 5 Electromagnetic InductionDocument50 pagesGenPhy2 Module 5 Electromagnetic InductionTAMAYO, Joelyn 12-STEM-BPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity BasicsDocument8 pagesElectricity BasicsMauritzPas encore d'évaluation
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument16 pagesFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionPawan TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity Unit Test Review AnswersDocument12 pagesElectricity Unit Test Review AnswersRon ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument51 pagesElectromagnetic InductionDantePas encore d'évaluation
- Text Video Youtube FisDasDocument11 pagesText Video Youtube FisDasAprianto YoberdPas encore d'évaluation
- EMEC 1 5th Aug 2013Document25 pagesEMEC 1 5th Aug 2013Harsha DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Date: Fri, Jul 14, 2023 Word Count: 798: Exclude Url: No Rocords Found 3Document3 pagesDate: Fri, Jul 14, 2023 Word Count: 798: Exclude Url: No Rocords Found 3uzairarshad479Pas encore d'évaluation
- How An Electric Generator WorksDocument2 pagesHow An Electric Generator WorksVikram RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism: M C MC MCDocument3 pagesElectromagnetism: M C MC MCsushil4056Pas encore d'évaluation
- AntennaDocument4 pagesAntennavisakcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ge2151 Beee NotesDocument143 pagesGe2151 Beee NotesNanda Subramanian100% (1)
- Electricuty and MagneDocument51 pagesElectricuty and MagneVandana SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 Part 2 ElectromagnetismDocument12 pagesUnit 7 Part 2 Electromagnetism123yousss2222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 18 - Chapter 29 Part 1Document20 pagesLecture 18 - Chapter 29 Part 1Mircea PanteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spintronics: The Spinning Future of Hardware Devices: Submitted By: Ravinder Dahiya 108080Document16 pagesSpintronics: The Spinning Future of Hardware Devices: Submitted By: Ravinder Dahiya 108080Manish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Faraday's LawDocument4 pagesSummary Faraday's LawReg TbPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of ElectromagnetismDocument4 pagesLaws of ElectromagnetismElmer GatchalianPas encore d'évaluation
- 60a0344bf3b25f7260ce0a15 - AP Physics C EM ElectromagnetismDocument13 pages60a0344bf3b25f7260ce0a15 - AP Physics C EM ElectromagnetismNeil MotianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism 3Document61 pagesElectromagnetism 3JohnmerPas encore d'évaluation
- ALCANTARA, JESSIE - Assignment #3 (Finals)Document3 pagesALCANTARA, JESSIE - Assignment #3 (Finals)sweet wobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Spintronics: The Spinning Future of Hardware DevicesDocument16 pagesSpintronics: The Spinning Future of Hardware DevicesRavinder DahiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kha ChanDocument6 pagesKha ChanSherif AdelPas encore d'évaluation
- Faraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetDocument1 pageFaraday's Experiment: Objective: Induce Current in A Wire With A MagnetAnahita SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Theory of Electric Potential by DonSmithDocument1 pageThe Theory of Electric Potential by DonSmithyaiba1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Powerpoint ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPowerpoint Electronicsjanine jabonetePas encore d'évaluation
- ديداكتيك الكهرومغناطسيةDocument2 pagesديداكتيك الكهرومغناطسيةHadil YoubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: ConceptsDocument21 pagesLesson Plan: Electricity and Magnetism: Conceptspauljkt1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On SolarDocument6 pagesNotes On SolarrameshmadhiriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Electricity and Magnetism ConnectionDocument12 pagesThe Electricity and Magnetism ConnectionMikhail YudhiantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- SSS 10 Cha Pter 4 - Sample Lesson - Mirana - 572014Document7 pagesSSS 10 Cha Pter 4 - Sample Lesson - Mirana - 572014Genesis NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Why - Do - Antennas - RadiateDocument4 pagesWhy - Do - Antennas - RadiatePar VeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principle of ElectricityDocument5 pagesBasic Principle of ElectricityFavour OgbonnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramskiranphdPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On AgesDocument1 pageProblems On AgeskiranphdPas encore d'évaluation
- Force Lecture NotesDocument53 pagesForce Lecture NoteskiranphdPas encore d'évaluation
- Free-Body Diagram NotesDocument5 pagesFree-Body Diagram NoteskiranphdPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Measurement 2020Document32 pages01 Measurement 2020fillyana01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Helicons-The Early Years: Rod W. Boswell and Francis F. ChenDocument16 pagesHelicons-The Early Years: Rod W. Boswell and Francis F. ChenNicolas LuhankoPas encore d'évaluation
- .Polarized Circular Ports FiberDocument24 pages.Polarized Circular Ports FiberDr-Mandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- AntennaDocument8 pagesAntennaKimberly Joy FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Relativity: Relativity Deals With Measurement of Events: Where and When They Happen, andDocument23 pagesRelativity: Relativity Deals With Measurement of Events: Where and When They Happen, andAngelica LlamasPas encore d'évaluation
- Hadron - WikipediaDocument5 pagesHadron - WikipediaSmart ArenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Materials: Maximum Torque N I S BDocument15 pagesMagnetic Materials: Maximum Torque N I S BAdriana PetriePas encore d'évaluation
- LabDocument177 pagesLabHiba AbdallahPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - H. M. Hsiao & I. M. Daniel - Effect of Fiber Waviness On Stiffness and Strength Reduction of Uniderectional Composites Under Compressive LoadingDocument13 pages3 - H. M. Hsiao & I. M. Daniel - Effect of Fiber Waviness On Stiffness and Strength Reduction of Uniderectional Composites Under Compressive LoadingImad Al-din KhattabPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic Geometry in Three DimensionsDocument40 pagesAnalytic Geometry in Three DimensionsPapadakis ChristosPas encore d'évaluation
- FG29 fm1Document12 pagesFG29 fm1yassinebouazziPas encore d'évaluation
- V V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsDocument3 pagesV V V VV VV VV VV VV VV VVV: Class 11 - JEE Main Test - 05 / (Dt. 04-09-2021) PhysicsManvi MakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises Section6Document21 pagesExercises Section6hhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Further Mathematics 9231/31Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Further Mathematics 9231/31Trần Sỹ Minh TiếnPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 07 Current and ResistanceDocument11 pagesPhysics 121 Practice Problem Solutions 07 Current and ResistancefragilewindowsPas encore d'évaluation
- G014-E87 Measurement DensityDocument34 pagesG014-E87 Measurement DensityDiego TobrPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedures For The Analysis of Explosives EvidenceDocument15 pagesProcedures For The Analysis of Explosives EvidenceGerman CarlePas encore d'évaluation
- EDX Analysis: How X-Ray Detection WorksDocument2 pagesEDX Analysis: How X-Ray Detection WorksAbhijnan GogoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electrical Circuits DR Nagendra Krishnapura Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 02Document4 pagesBasic Electrical Circuits DR Nagendra Krishnapura Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 02Deeban BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling Fluid IntroductionDocument11 pagesDrilling Fluid IntroductiongasmigasmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Materials Cost and MechanicalDocument8 pagesOptimizing Materials Cost and MechanicalKaleem UllahPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 - Maths Lab ManualDocument25 pages12 - Maths Lab ManualellipticaldonutPas encore d'évaluation
- Asign1 MomDocument4 pagesAsign1 MomAmru AwangPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Analysis Guide PDFDocument14 pagesDynamic Analysis Guide PDFasifPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument45 pagesSolutions and SolubilityAishah JamalPas encore d'évaluation