Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ionic Bonding
Transféré par
wakakkaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ionic Bonding
Transféré par
wakakkaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stable Noble Gas Structure (Group 0)
Noble gases are unreactive (inert) and do not form compounds because they have the duplet (example - helium) or octet configuration (example - neon).
Ion
An ion is a charged particle. In an ion, the number of protons is different from the number of electrons. For example, a sodium ion, Na+, consists of 11 protons and 10 electrons. A chloride ion, CI-, consists of 17 protons and 18 electrons. An atom forms an ion in order to achieve a noble gas structure. Metals form positively charged ions (cations). Example: Na+, Li+, Mg2+ Non-metals usually form negatively charged ions (anions). Example: Cl-, F-, I-
*Ionic bonding Key points
- Metals react with non-metals to form ionic compounds. - Each ion in an ionic compound has the electronic configuration of a noble gas. - An ionic bond is defined as the electrostatic force of attraction between a positive ion and a negative ion. - An ionic bond is formed when electron/s are transferred from a metallic atom to a nonmetallic atom. - In ionic compound, the total positive charge is equal to the total negative charge.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------When metals react with non-metals, an ionic compound is formed. For example, sodium reacts with chlorine to form an ionic compound called sodium chloride.
Step 1. The formation of positive ions
Each sodium atom loses it single valence electron to form a positively charged sodium atom to obtain a stable electronic configuration.
Na Na+ + e(2.8.1) (2.8) Step 2. The formation of negative ions
Each chlorine atom gains an electron from a sodium atom to form a negatively charged chloride ion to obtain a stable electronic configuration.
Cl + e- Cl(2.8.7) (2.8.8) Step 3. The formation of ionic bonds
Positive sodium ions and negative chloride ions are attracted to one another by electrostatic attraction to form sodium chloride.
Na+ + Cl- NaCl
The electrostatic forces of attraction that holds the sodium ions and chloride ions together are called ionic bonds. We use dot and cross diagram to show ionic bonding.
* Na CI Sodium atom (2.8.1) Chlorine atom (2.8.7) Sodium ion (2.8) Na
+
CI Chloride ion (2.8.8)
Structure of Ionic Compound
Ionic compound form giant ionic structures. An example is sodium chloride. The sodium ions and chloride ions are very strongly attracted to one another. They are arranged in a giant lattice structure or crystal lattice.
*Physical Properties of Ionic Compounds 1) Volatility melting and boiling points
The lattice of an ionic compound is held together by strong ionic bonds between the ions. A large amount of energy is needed to overcome these strong bonds and to change an ionic compound fro solid to liquid. As a result, ionic compounds are solids at room temperature and pressure. Ionic compounds are non-volatile substances due to their high melting and boiling points.
2) Solubility
Ionic compounds are usually soluble in water. This is because water molecules can separate the positive ions (cations) from the negative ions (anions), causing them to dissolve. Ionic compounds are insoluble (does not dissolve) in organic solvents. Organic solvents are compounds such as ethanol, petrol and turpentine.
3) Electrical conductivity
Ionic compounds do not conduct in the solid state because the ions are not free to move about. However, when an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water to form an aqueous solution, it can conduct electricity. This is because the ions are free to move in the molten or in aqueous solution.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Vibrational SpectrosDocument82 pagesVibrational SpectrosPedro CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Emily of Emerald Hill AnalysisDocument2 pagesEmily of Emerald Hill AnalysiswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- MeasurementDocument9 pagesMeasurementDaizLee AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- DreamSpark InstallDocument1 pageDreamSpark InstallwakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- GEM2900 ProbabilityDocument2 pagesGEM2900 ProbabilitywakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Intro To OM - HandoutDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To OM - HandoutStephen BaoPas encore d'évaluation
- GP Article 2 NeuroscienceDocument2 pagesGP Article 2 NeurosciencewakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Singapore Factsheet For AQDocument1 pageSingapore Factsheet For AQwakakka67% (3)
- ConceptsDocument7 pagesConceptswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Poem AnalysisDocument1 pagePoem AnalysiswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brainstorming Techniques HandoutDocument3 pagesBrainstorming Techniques HandoutwakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes of Conflict in Sri LankaDocument3 pagesCauses of Conflict in Sri LankawakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Envmt Compiled NotesDocument3 pagesEnvmt Compiled NoteswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- SS Diplomacy, Singapore's InvolvementDocument4 pagesSS Diplomacy, Singapore's InvolvementwakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Map ReadingDocument2 pagesMap ReadingwakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table NotesDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table NoteswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acids and BasesDocument6 pagesAcids and Basescharlene1982Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mole Concept (Stoichiometry) 5 LevelsDocument4 pagesMole Concept (Stoichiometry) 5 LevelswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Limitations of Hdi and GDP EssayDocument1 pageLimitations of Hdi and GDP EssaywakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classes of CompoundsDocument3 pagesClasses of CompoundswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Insights Chapter 7 WSDocument3 pagesChem Insights Chapter 7 WSwakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Acids & Bases April 10Document8 pagesNotes On Acids & Bases April 10wakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure Plastics (Q&A)Document3 pagesPeriodic Table Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure Plastics (Q&A)wakakka100% (1)
- Revision Notes On Chemical Formulae: Name: - Date: - ClassDocument4 pagesRevision Notes On Chemical Formulae: Name: - Date: - ClasswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8.1-8.3Document8 pagesChapter 8.1-8.3wakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Speed of Reaction (Key Points and Q&A)Document8 pagesSpeed of Reaction (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
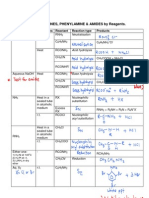
- SUMMARY - Reactions of Amines Phenylamine AmidesDocument1 pageSUMMARY - Reactions of Amines Phenylamine AmideswakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals (Key Points and Q&A)Document7 pagesMetals (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Chemical BondingDocument1 pageSummary of Chemical Bondingchong56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hess's Law (1.5.5) - CIE As Chemistry Revision Notes 2022 - Save My ExamsDocument9 pagesHess's Law (1.5.5) - CIE As Chemistry Revision Notes 2022 - Save My ExamsSahana KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Test3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Document18 pagesTest3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Anas SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Eurecat General Capabilities PresentationDocument54 pagesEurecat General Capabilities PresentationChristianGuerrero0% (1)
- IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1Document11 pagesIB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1Vibha RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Module J: Rubbers As Entropic Springs Example of A Silicone RubberDocument37 pagesModule J: Rubbers As Entropic Springs Example of A Silicone RubberJohn McLovenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidDocument9 pagesLab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidAndrea Satira100% (1)
- Thermal Performance Investigation of Finned Tube Heat Exchanger With PCMDocument24 pagesThermal Performance Investigation of Finned Tube Heat Exchanger With PCMSanjay GehlotPas encore d'évaluation
- StandardizationDocument18 pagesStandardizationCHEA MICH L. ABELLANOPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument34 pagesChapter 11: Reactions of Alkyl HalidesHeena DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 09Document40 pagesChapter 09AC BañaresPas encore d'évaluation
- M.tech. Textile TechnologyDocument26 pagesM.tech. Textile TechnologyNilesh Shingote100% (1)
- Identification of Cations Using Ammonium Hydroxide Exp - No.3Document2 pagesIdentification of Cations Using Ammonium Hydroxide Exp - No.3vishal kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- BASF Alumina Catalysts Broschuere UpdateDocument13 pagesBASF Alumina Catalysts Broschuere Updatevibage2942Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamic Properties Dupont Isceon Mo49 (R-413A)Document20 pagesThermodynamic Properties Dupont Isceon Mo49 (R-413A)Hari SrihariPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base Indicators: Indicators As Weak AcidsDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Indicators: Indicators As Weak AcidsSaurav PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual For Fluid Mechanics 1St Edition by Hibbeler Isbn 0132777622 9780132777629 Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Fluid Mechanics 1St Edition by Hibbeler Isbn 0132777622 9780132777629 Full Chapter PDFscott.fischer352100% (9)
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Document3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings Class 9Pushpa Kumari89% (18)
- Evaporators and The Refrigeration System Unit 21 GroupDocument27 pagesEvaporators and The Refrigeration System Unit 21 Groupnyein chanPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Design A Spectrometer: Alexander ScheelineDocument16 pagesHow To Design A Spectrometer: Alexander ScheelineYongJun ChoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijddt 1st ArticleDocument6 pagesIjddt 1st ArticleShiv SMSPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective 1. To Compare The Reaction of Aliphatic and Aromatic Hydrocarbon 2. To Determine The Identity of Unknown CompoundDocument7 pagesObjective 1. To Compare The Reaction of Aliphatic and Aromatic Hydrocarbon 2. To Determine The Identity of Unknown CompoundAHLA AMANI AHMAD SYAYUTHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Final05 PDFDocument7 pagesFinal05 PDFRam chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo Electron North America LLC Lot 1 Equipment & InstrumentsDocument66 pagesThermo Electron North America LLC Lot 1 Equipment & Instrumentsproyectos serimetcPas encore d'évaluation
- Petrochemical ProcessDocument20 pagesPetrochemical Processsanjeevs01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Multi-Component Polymer Systems: M.SC - Polymer EngineeringDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Multi-Component Polymer Systems: M.SC - Polymer EngineeringItamar PolitzerPas encore d'évaluation
- EN 15265 Calc of Energy Use PDFDocument74 pagesEN 15265 Calc of Energy Use PDFDragos PastravPas encore d'évaluation
- (Isao Ando) Annual Reports On NMR Spectroscopy, Vo (BookFi)Document337 pages(Isao Ando) Annual Reports On NMR Spectroscopy, Vo (BookFi)Rogério SiqueiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ammonia Refrigeration PDFDocument8 pagesAmmonia Refrigeration PDFducky 99100% (1)
- PP ManualDocument50 pagesPP ManualMohammad RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Crystal Imperfection CH 4Document44 pagesCrystal Imperfection CH 4maxxolimousPas encore d'évaluation