Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Huawei BSC6900 Troubleshooting Guide For Access
Transféré par
Umar Abbas BabarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Huawei BSC6900 Troubleshooting Guide For Access
Transféré par
Umar Abbas BabarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GSM CS Signal Flow After a CS call is established in the GSM Network, the MS and the network communicate with
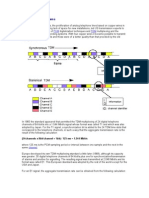
each other through the CS signal flow. The method of processing the GSM CS signal flow varies according to the transmission mode adopted on the Abis and A interfaces and the configuration mode of the BSC6900 subracks. Abis over TDM and A over TDM The figure below shows the CS signal flow in Abis over TDM, Ater over TDM, A over TDM, and BM/TC separated mode. Note: The Abis, Ater, and A interface boards can be the EIUa/OIUa/POUc board. the INT in the figure stands for the interference board. You can use different interface boards as required.
interface board, and then to the MSS over the A interface The DL flow is the reverse of the UL flow. The figure below shows the CS signal flow in Abis over TDM, Ater over IP, A over TDM, and BM/TC separated mode.
The CS signal flow on the UL is as follows 1- The UL CS signals are sent from the BTS to the Abis interface board in the MPS/EPS 2- The CS signals are demultiplexed in the Abis interface board. each CS signal uses a 64Kbit/s timeslot. The CS signals are transmitted to the TNUa board and then to the DPUc board. 3- The CS signals are converted from TRAU frames to PTRAU frames in the DPUc board. 4- The CS signals are transmitted to the SCUa board and then to the Ater interface board. 5- The CS signals are multiplexed in the Ater interface board. each full rate CS signal uses a 16Kbit/s sub-timeslot, and each half-rate CS signal uses an 8Kbit/s sub timeslot. The CS signals are then transmitted to the Ater interface board in the TCS over the Ater interface 6- The CS signals are demultiplexed in the Ater interface board of the TCS. Each CS signal uses a 64Kbit/s timeslot and is transmitted to the SCUa board and then to the DPUc board. 7- The DPUc board adjusts the order of PTRAU frames, eliminates jitter, and performs speech codec and rate adaptation on CS signals, which are converted to 64Kbit/s PCM frames. The 64Kbit/s PCM frames are transmitted to the TNUa board, to the A interface board, and then to the MSS over the A interface.
1- The UL CS signals are sent from the BTS to the Abis interface board in the MPS/EPS 2- The CS signals are demultiplexed in the Abis interface board. Each CS signal uses a 64Kbit/s timeslot and is transmitted to the TNUa board and then to the Ater interface board. 3- The CS signals are multiplexed in the Ater interface board. Each full-rate CS signal uses a 16Kbit/s sub-timeslot, and each half-rate CS signal uses an 8Kbit/s sub-timeslot. The CS signals are then transmitted to the Ater interface board in the TCS over the Ater interface. 4- The CS signals are demultiplexed in the Ater interface board of the TCS. Each CS signal uses a 64Kbit/s timeslot and is transmitted to the TNUa board and then to the DPUc board. 5- The DPUc board performs speech codec and rate adaptation on the CS signals, which are converted to 64Kbit/s PCM frames. The 64Kbit/s PCM frames are transmitted to the TNUa board, to the A
The DL flow is the reverse of the UL flow. In case of BM/TC combined mode, the Ater interface does not exist. The figure shows like CS signal flow in Abis over TDM and A over TDM mode.
The CS signal flow on the UL is as follows: 1- The uplink CS signals are sent from the BTS to the Abis interface board in the MPS/EPS. 2- The CS signals are demultiplexed in the Abis interface board. Each CS signal uses a 64Kbit/s timeslot and is transmitted to the TNUa board and then to the DPUc board. 3- The DPUc board performs speech codec and rate adaptation on the CS signals, which are converted to 64Kbit/s PCM frames. The 64Kbit/s PCM frames are transmitted to the TNUa board, to the A interface board, and then to the MSS over the A interface. The DL flow is the reverse of the UL flow.
Huawei BSC6900 Troubleshooting Guide for Access Faults
Page 1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BSC6900 GSM Signal FlowDocument18 pagesBSC6900 GSM Signal FlowPhuong TranPas encore d'évaluation
- BSS Interface - Presentation TranscriptDocument7 pagesBSS Interface - Presentation TranscriptFahmida AfrinPas encore d'évaluation
- TC & BSC OverviewDocument36 pagesTC & BSC OverviewVarun VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- BSS Interface (A, A-ter&A-bis) With Time Slots DetailDocument37 pagesBSS Interface (A, A-ter&A-bis) With Time Slots Detailvinaygautamgautam100% (1)
- BSC Signaling FlowsDocument26 pagesBSC Signaling FlowsSidy Elbechir Drame100% (1)
- TC General and TCIFDocument27 pagesTC General and TCIFDeepayan ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Report On OperationsDocument16 pagesTechnical Report On OperationsSamSameleviPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcatel BSC HardwareDocument25 pagesAlcatel BSC HardwareHakim KassimiPas encore d'évaluation
- CN Prob. (Ingilizce) 3Document18 pagesCN Prob. (Ingilizce) 3gin220Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Frame Structure-Finalwith GraphsDocument28 pagesGSM Frame Structure-Finalwith GraphsMohammed Fabin100% (1)
- Understanding the T1/E1 Interface: A Tutorial on TDM TechnologiesDocument16 pagesUnderstanding the T1/E1 Interface: A Tutorial on TDM Technologiesমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর50% (2)
- Presentation On Six Months Industrial Training Undertaken atDocument67 pagesPresentation On Six Months Industrial Training Undertaken atbsgnsPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Unit 2nd PartDocument32 pages4th Unit 2nd PartyuvasreePas encore d'évaluation
- BSS EssentialDocument38 pagesBSS EssentialJeetu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- TranscoderDocument15 pagesTranscoderanand_k_singhPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM BSS OverviewDocument20 pagesGSM BSS OverviewchadidiabPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communication RecordDocument46 pagesDigital Communication Recordathavan12tc08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Broadcast Service in Ericsson RAN P7Document36 pagesCell Broadcast Service in Ericsson RAN P7Saky KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Frame StructureDocument25 pagesGSM Frame StructureVarun SoodPas encore d'évaluation
- T1 and E1 PCM systems explainedDocument10 pagesT1 and E1 PCM systems explainedPrafull BPas encore d'évaluation
- Evdo 2Document29 pagesEvdo 2Win LinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Channels in CdmaDocument17 pagesChannels in CdmaDeepesh KanungoPas encore d'évaluation
- Switch CdotDocument8 pagesSwitch CdotbikkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcatel BSC HardwareDocument25 pagesAlcatel BSC HardwarefarhancobraPas encore d'évaluation
- Upstream Channel BondingDocument13 pagesUpstream Channel BondingppPas encore d'évaluation
- CAN Bus DescriptionDocument6 pagesCAN Bus DescriptionLuis Manuel GodoyPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM PresentacionDocument81 pagesGSM PresentacionRoberto RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Bsc6900 GSM and UmtsDocument83 pagesBsc6900 GSM and Umtsdramous1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2G Radio CapacityDocument29 pages2G Radio CapacityDithchai TangtrongjittawornPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Document34 pages3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Brian Edward HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Tranciever AppsDocument7 pagesFM Tranciever Appsinsomnium86Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2.3.3 GSM: Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98 1Document14 pagesCH 2.3.3 GSM: Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98 1zultharPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless M-BUS Solutions and MoreDocument33 pagesWireless M-BUS Solutions and MoreARCC2030100% (1)
- 05 SkyEdge II Inbound Overview v6.1Document44 pages05 SkyEdge II Inbound Overview v6.1Nelo QuispeAduviriPas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For Mobile Communication: 2000 SASKEN All Rights ReservedDocument53 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication: 2000 SASKEN All Rights ReservedKausik RaychaudhuriPas encore d'évaluation
- OVERVIEWDocument79 pagesOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- Introduction to CDMA Air Interface Standard IS-95ADocument23 pagesIntroduction to CDMA Air Interface Standard IS-95AGaurav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication System Lecture 3-2Document9 pagesCommunication System Lecture 3-2miro jasimPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To CDMA Air Interface: TIA/EIA/IS-95ADocument71 pagesAn Introduction To CDMA Air Interface: TIA/EIA/IS-95AgoosecoolPas encore d'évaluation
- CANBus: (1) How It Works, (2) Case Applications For Nissan Leaf & Volvo S80Document33 pagesCANBus: (1) How It Works, (2) Case Applications For Nissan Leaf & Volvo S80yogapost100% (3)
- Um Layers: Physical Layer (L1)Document13 pagesUm Layers: Physical Layer (L1)naeem05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microcontroller Basics and ProgrammingDocument92 pagesMicrocontroller Basics and ProgrammingVishal Gudla NagrajPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC6900 Introduction - Documento HuaweiDocument9 pagesBSC6900 Introduction - Documento HuaweiMiguel Angel LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- CAN BusDocument9 pagesCAN Buspablodanielrigo100% (2)
- CDMA Course Outlines: Key Technologies and Air InterfaceDocument42 pagesCDMA Course Outlines: Key Technologies and Air InterfaceAhmed GamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communication Systems Formats and Multiplexing MethodsDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Systems Formats and Multiplexing MethodsMIsh GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Payload 4 02Document232 pagesPayload 4 02rahul_mhatre_26Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To CDMA Air InterfaceDocument71 pagesAn Introduction To CDMA Air InterfacetycoonaPas encore d'évaluation
- ATM & BISDNDocument56 pagesATM & BISDNPratik AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- RF Arris PDFDocument42 pagesRF Arris PDFproyectostelemicPas encore d'évaluation
- GSMDocument38 pagesGSMapi-370641475% (8)
- CDOTDocument52 pagesCDOTMahesh Kumar NigamPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission: N No of LevelsDocument14 pagesTransmission: N No of LevelsAshwani BhallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondD'EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessD'EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandD'EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandPas encore d'évaluation
- Copyright Enforcement Police HandbookDocument28 pagesCopyright Enforcement Police HandbookUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- 27361pay Revision RulesDocument136 pages27361pay Revision Rulesguddu_bhai100% (1)
- PIDE Working Paper 2006 - 4 - PDFDocument29 pagesPIDE Working Paper 2006 - 4 - PDFUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Local and Special LawsDocument26 pagesLocal and Special LawsUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- USAID Project Management Specialist VacancyDocument3 pagesUSAID Project Management Specialist VacancyUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Deduction of Salary in Case of Absenteesium 16-12-2014Document1 pageDeduction of Salary in Case of Absenteesium 16-12-2014Umar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Harassment in PAkistanDocument16 pagesSexual Harassment in PAkistanUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- General Financial RulesDocument105 pagesGeneral Financial RulesShayan Ahmad QureshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Guide PDFDocument86 pagesField Guide PDFUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Guide PDFDocument86 pagesField Guide PDFUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of PayDocument7 pagesTypes of PayUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Policing Plan For District Haripur by Essa and UmarDocument40 pagesAnnual Policing Plan For District Haripur by Essa and UmarUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Abis For GSM TelecommunicationsDocument2 pagesAbis For GSM TelecommunicationsUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- NOA EDS Presentation FileDocument31 pagesNOA EDS Presentation FileUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- SC Judgement On Cantonments ElectionsDocument17 pagesSC Judgement On Cantonments ElectionsUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pakistans Energy Crisis PDFDocument32 pagesPakistans Energy Crisis PDFFahadPas encore d'évaluation
- Operator Swap AnalysisDocument12 pagesOperator Swap AnalysisUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Press Release: Federal Public Service CommissionDocument8 pagesPress Release: Federal Public Service CommissionUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Countering Extremism in PakistanDocument3 pagesCountering Extremism in PakistanUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Codecs Employed in GSM NetworksDocument1 pageCodecs Employed in GSM NetworksUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- PFC Feature AlcatelDocument1 pagePFC Feature AlcatelUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE O LEVEL SYLLABUS Physics 5054Document40 pagesCIE O LEVEL SYLLABUS Physics 5054Sakib Ex-rccPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Civil Society in Creating Religious TolerationDocument3 pagesRole of Civil Society in Creating Religious TolerationUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Police Act 1861Document19 pagesPolice Act 1861Umar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- PW88 Understanding Pakistan's Water Security NexusDocument40 pagesPW88 Understanding Pakistan's Water Security NexusUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- ATM in B10 AlcatelDocument8 pagesATM in B10 AlcatelUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel at USIP Considers Counterterrorism in Pakistani Tribal AreasDocument3 pagesPanel at USIP Considers Counterterrorism in Pakistani Tribal AreasUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Class9 - GPRS ExplainedDocument17 pagesClass9 - GPRS ExplainedUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Trade Relations Between Pakistan and IndiaDocument0 pageTrade Relations Between Pakistan and IndiaUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- SGSN ExplainedDocument8 pagesSGSN ExplainedUmar Abbas BabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts Abt Roman NumeralsDocument3 pagesFacts Abt Roman NumeralsnavneetPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study of 802.11 Bitrate Selection in Linux: Robert CopelandDocument8 pagesA Study of 802.11 Bitrate Selection in Linux: Robert CopelandFavour AdenugbaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH3 TaDocument17 pagesCH3 TasanjaykashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Exchange Methods: Diffie-Hellman and RSADocument13 pagesKey Exchange Methods: Diffie-Hellman and RSAmarioPas encore d'évaluation
- GSA Chipset Report November 2018Document14 pagesGSA Chipset Report November 2018Muhammad Jamil AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Siglab ManualDocument58 pagesSiglab ManualOmar CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser LinkDocument2 pagesLaser LinkRaziel VelazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel F-Shaped Quad-Band Printed Slot AnDocument4 pagesNovel F-Shaped Quad-Band Printed Slot AnSnehal VarbhePas encore d'évaluation
- CrossWave Propagation Model OverviewDocument23 pagesCrossWave Propagation Model OverviewhectorPas encore d'évaluation
- Subline 2017Document4 pagesSubline 2017Mauricio Yañez PolloniPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei IRAT HandoverDocument54 pagesHuawei IRAT HandoverДимитрий КоноваловPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring Two Wireless Routers With One SSID (Network Name) at Home For Free Roaming - Scott HanselmanDocument3 pagesConfiguring Two Wireless Routers With One SSID (Network Name) at Home For Free Roaming - Scott HanselmanCui Lan ZengPas encore d'évaluation
- InvlDocument3 pagesInvlambroserfPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 373FE-09012017 - SolutionsDocument7 pagesECE 373FE-09012017 - Solutionsİsmail ŞahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6: Data Link Layer: Instructor MaterialsDocument27 pagesModule 6: Data Link Layer: Instructor MaterialsDiego LarramendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Phase Lead and Lag CompensatorsDocument8 pagesDesign Phase Lead and Lag CompensatorsNuradeen MagajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Wireless Communications 3rd Edition Olenewa Test BankDocument8 pagesGuide To Wireless Communications 3rd Edition Olenewa Test BankJohnDeckerfrgam100% (16)
- Curriculum Vitae: Ezeh Solomon OnyekachiDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Ezeh Solomon OnyekachiOnyekachi JackPas encore d'évaluation
- HomePlug Green PHY Whitepaper 100614Document17 pagesHomePlug Green PHY Whitepaper 100614Setyo Wahyu TomoPas encore d'évaluation
- DSP Lab Manual (Sksjti)Document102 pagesDSP Lab Manual (Sksjti)shrishaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE705 Project ReportDocument11 pagesEE705 Project ReportAayush ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal & Systems WINTER-2022Document2 pagesSignal & Systems WINTER-2022Mitul YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- ATR4517R1Document2 pagesATR4517R1ivanaru404Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2G Kpi IntroductionDocument3 pages2G Kpi IntroductionImtiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- An-42007 AN42007 Safety, EMI and RFI ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesAn-42007 AN42007 Safety, EMI and RFI ConsiderationsSunu PradanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Baluns - Choosing The Correct Balun by Tom, W8JI ... - DX Engineering - 2Document22 pagesBaluns - Choosing The Correct Balun by Tom, W8JI ... - DX Engineering - 2Bảo BìnhPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Electronic and Communications EngineeringDocument30 pagesSchool of Electronic and Communications EngineeringKamran RaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Difusor BeymaDocument2 pagesDifusor BeymaMarcus VinicyusPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 1 Report: Digital Signal Processing LabDocument13 pagesTutorial 1 Report: Digital Signal Processing LabTuấnMinhNguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
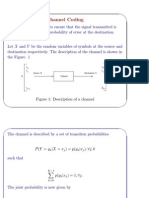
- Channel Coding: X X y yDocument13 pagesChannel Coding: X X y yHarshaPas encore d'évaluation