Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Please Read The Paragraph Carefully and Answer The Following Questions With Proper Explanations
Transféré par
bhartiyaanujTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Please Read The Paragraph Carefully and Answer The Following Questions With Proper Explanations
Transféré par
bhartiyaanujDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Please read the paragraph carefully and answer the following questions with proper explanations.
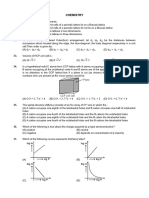
A student was investigating the speed of reaction between limestone granules and different concentrations of hydrochloric acid. However after doing a whole series of experiments at different acid concentrations, there was no time to do the last planned experiment. The volume of carbon dioxide collected after 5 minutes in a 100 cm3 gas syringe was used to determine the rate of reaction. All the experiments were done in one lesson at a temperature of 22 C except for the last one. This was done in the next lesson, giving a carbon dioxide volume of 47.0 cm3 after 5 minutes, but at a higher temperature of 27 C (when in Kelvin call this T1, and the other temperature T2). To make the data analysis fair, all the gas volumes should be ideally measured at the same temperature, but a correction can be made for the last experiment. 1.The Volume the of 47.0 cm3 of gas at 27 C, would occupy at 22 C. (a) 45.6 cm3 (b) 46.5 cm3 (c) 46.2 cm3 (d) 42.6 cm3 2.If the temperature was ignored, what is the % error in the rate of reaction measurement? (a) +1.7% (b) -1.7% (c) +17% (d) - 17% 3.Would you need to do any correction for the volume of acid added to the limestone? (a) No correction needed for this at all. (b) Yes correction need for this at all. (c) Cant be predicted . (d) None of the above
4. A blown up balloon has a volume of 500ml at 278 K.The balloon is distended to its maximum stretching capacity.Determine the min temp above which it will brust.
5) In the arrhenius eqn which of the following statement is assumed (A) The fraction of efeective collisions having activation energy is equal to the fraction of total collisions having activation energy (B) The fraction of efeective collisions having activation energy is less thanl the fraction of total collisions having activation energy (C) The fraction of efeective collisions having activation energy is more than the fraction of total collisions having activation energy (D) The no of effective collisions are those collisions which lead to the formation of the product
6) Liquid ammonia ionizes to a little extent At -500 C , Its ionic product is KNH3 = [NH4+][NH2-] = 10-30
The no of amide ions present in 1 mm3 of pure liquid NH3 would be A) 10-15 ions/mm3 B) 600 ions/mm3
7) What is the pH of a solution prepared by mixing 0.0100 mol HA (with Ka = 1.00*10 -2) and 0.0100 mol of A- and diluting with water to 1.00 L?
HA
= 0.01
H+
A0.01 0.01(1+x)
t=teq. 0.01(1-x) 0.01x Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
=> 10-2 = 0.01x*0.01(1+x)/0.01(1-x) => 10-2 = 10-2 (x+x2)/(1-x) => 1-x = x+x2 => x2+2x-1=0 => x = 2 -1 So pH = -log(0.01x) = 2 - log(x) = 2 - log(0.414) = 2-(-0.38) = 2.38 8) If a cube is made such that small spheres are at the corners and large sphere is at the body centre of the cube, then what is the packing fraction of this system? 1. 0.68 2. 0.74 3. 0.52 4. 0.002
Packing fraction depends on the volume (solid volume).. So contribution of hollow sphere to the PF is negligible So total volume of smaller spheres in the cube = 8*1/8 (corner atoms so contribution of each to one
unit cell = 1/8)*Vsph = Vsph Now as it can be treated as BCC, a3 = 2(R+r) So u can get volume of cube as a3 PF = total volume of smaller spheres in the cube/volume of cube putting the values and taking R=10r we get PF = 0.002
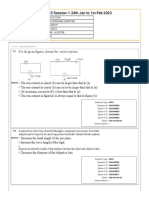
9) Consider a large hollow sphere of radius 'R' in which small solid sphere of radius 'r' has to be placed in closest pascking. ( assume r=R/10) 10) Maximum no. of small spheres that can be filled into the large hollow sphere are : a)1000 b)500 c)250 d)740
11) If small spheres are to be placed in a square of edge R , then how many spheres ( whose centres will lie on or inside the square 0 are possible. ( assume the packing to be 2D square packing ) a) (R+10)2/100 b) R2/100 c) ( R+11)2 / 100 d) 99R2/100
12) If a cube is made such that small spheres are at the corners and large sphere is at the body centre of the cube , then whats the packing fraction of the system ? a)0.68 b) 0.74 c)0.52 d)o.002
13) Equivalent conductance== C of a C normal solution, so am I right in presuming that =C is the equivalent CONDUCTIVITY? If so , we have to plot vs C of a strong electrolyte I tried to proceed as follows : =0- bC, b= Kohlrausch's constant... thus, =C0- bC3/2 and so we have a cubic in C..
Now , I have assumed that =C is the equivalent conductivity of a C normal solution..is it right, if not..what is precisely equivalent conductivity(note: not equivalent conductance)? Besides if it were right, whats the equivalent conductivity at infinite dilution..is it o=C0=0x0=0? I seem to have been mistaken.... BTW, this is my first post at Target IIT, hurray...
Q14. peptization is a) evaporation of dispersed med b)precipiation of dispered phase c)disintegration of dipersed phase d)combined effect of dispersion medium on dispersed phase Actually, peptization is the dispersion of the precipitated material into colloidal solution. So, it involves first adsorption of the suitable ions and electrically charged particles then split frm precipitate as colloidal particles. thus , its c) disintegration of the dispersed phase.
Q15. Colloidal particles of water are coagulated effectively using a)NaCl b)(NH4)2SO4 c)alum d)gold chloride
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GR XI Term 2 CHEMISTRY Ans KeyDocument10 pagesGR XI Term 2 CHEMISTRY Ans Keyrohan fernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dec Exam AnswersDocument17 pagesDec Exam Answersvivivihohoho1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes Abd17Document97 pagesChemistry Notes Abd17parth PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- UniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Document9 pagesUniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Dominador RomuloPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Jee Test Paper MCQ PDFDocument13 pagesIit Jee Test Paper MCQ PDFLuis AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- KampungNangka Term1 Okt 2014Document16 pagesKampungNangka Term1 Okt 2014Febian HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 QuestionsDocument56 pagesChapter 14 QuestionsCaitlene Lee Uy100% (1)
- PHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIDocument5 pagesPHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIlyndsey_erin_aguiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem112 Tutorial Questions-1Document13 pagesChem112 Tutorial Questions-1Gloria BrodaPas encore d'évaluation
- Probset 1bDocument12 pagesProbset 1bRegina Marie MaximoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocument9 pagesChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry TestDocument12 pagesChemistry TestKimmy KuoPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Example: Answer: A. This Is Because in This Reaction, Cu Goes From 2+ in Cuo To 0 in Cu (S) - SoDocument9 pagesFinal Example: Answer: A. This Is Because in This Reaction, Cu Goes From 2+ in Cuo To 0 in Cu (S) - SoAlison JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Problem Set 1Document4 pagesThermodynamics Problem Set 1fadum099Pas encore d'évaluation
- University of LondonDocument6 pagesUniversity of LondonShootingStarPhotonsPas encore d'évaluation
- CY2301Document11 pagesCY2301Prarabdha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM102 051 Old-Exam First-Major UnsolvedDocument5 pagesCHEM102 051 Old-Exam First-Major UnsolvedAbdullah AltwirqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - AnsDocument5 pagesTest 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - Ansmarc jacobs davisPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 341 Physical Chemistry Final Exam: Do Not Open This Exam Until Told To Do SoDocument10 pagesCHEM 341 Physical Chemistry Final Exam: Do Not Open This Exam Until Told To Do SoOmarPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRY-17-09-11th (PQRS) SpaceDocument24 pagesCHEMISTRY-17-09-11th (PQRS) SpaceRaju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: PlaneDocument3 pagesChemistry: PlanegamerwizcastPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry Competency ExamDocument2 pagesPhysical Chemistry Competency ExamRaymond YabutPas encore d'évaluation
- C - 2 (Assignment-1) FINALDocument8 pagesC - 2 (Assignment-1) FINALSachin DedhiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fashion. Some Students Are Allowed To Continue To Work On The ExamDocument11 pagesFashion. Some Students Are Allowed To Continue To Work On The ExamasertvePas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Comprehensive ExamDocument15 pages1st Comprehensive ExamLoala SMDPas encore d'évaluation
- UP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Document6 pagesUP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)kennethleo69100% (1)
- Multiphase Tutorial 7Document7 pagesMultiphase Tutorial 7Anders Rojas Coa.Pas encore d'évaluation
- AS Level Topic 5 TestDocument10 pagesAS Level Topic 5 TestMorvan BarnesPas encore d'évaluation
- CLASS XI TEXTBOOK SOLUTION CHEMISTRY Chapter 6 - EquilibriumDocument84 pagesCLASS XI TEXTBOOK SOLUTION CHEMISTRY Chapter 6 - EquilibriumAyushi ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic C PDFDocument8 pagesTopic C PDFBrian Zachariah DuPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics (Assignment)Document10 pagesThermodynamics (Assignment)Mudit KPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Document20 pagesChemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Alina Syedd32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4 Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas LawDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 Kinetic Theory Ideal Gas Lawhuijing966Pas encore d'évaluation
- TestDocument10 pagesTestJanePas encore d'évaluation
- Question PART 2 (2023)Document6 pagesQuestion PART 2 (2023)01khanh26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eee L-1, T-2 (2016-2017) PDFDocument26 pagesEee L-1, T-2 (2016-2017) PDFআশিক পালোয়ানPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Document8 pagesGen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Nikka LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Chemistry23 24sp 01Document13 pages11 Chemistry23 24sp 01AbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem SetsDocument12 pagesProblem SetsZAKARIA SUNBOLPas encore d'évaluation
- 2022-May CH-322 223Document2 pages2022-May CH-322 223Akhil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Useful InformationDocument11 pagesUseful InformationAhmadAlabadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFJojie-Ann Alabarca100% (1)
- Sample QuestionsDocument20 pagesSample QuestionsginizyPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryArya VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Part 2 (2023)Document9 pagesSolution Part 2 (2023)01khanh26Pas encore d'évaluation
- 73 1st Long Problem SetDocument11 pages73 1st Long Problem SetLemuelClementCastroPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsDocument24 pagesENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsKingstanIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Selection Examination For The 2004 Australian Chemistry Olympiad TeamDocument6 pagesFinal Selection Examination For The 2004 Australian Chemistry Olympiad Teamrajeswar royPas encore d'évaluation
- Class-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir SirDocument2 pagesClass-Xii (Chemistry) Sumit Sir Sirmanyag1605Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2017Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2017parv dhanotePas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 211 KeyDocument16 pagesExam 211 KeyHafidz RafiqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate 2003 PDFDocument20 pagesGate 2003 PDFVammsy Manikanta SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Document10 pagesChem 1120 - Chapter 14: Chemical Equilibrium Practice Quiz 1Danielle Lois AbagPas encore d'évaluation
- QP 3 Xi Chem Paper 3Document5 pagesQP 3 Xi Chem Paper 3technical SitePas encore d'évaluation
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)Document9 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeePas encore d'évaluation
- 1127 Practice FinalDocument8 pages1127 Practice FinalRyan GrijalvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Thermodynamics HomeworkDocument6 pagesExtra Thermodynamics HomeworkSelenaYeliPas encore d'évaluation
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsD'EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Special GTM 27-02-2020Document12 pagesSpecial GTM 27-02-2020bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Bill FormatDocument1 pageFuel Bill Formatbhartiyaanuj100% (2)
- 29-01-2023 Shift 2 PaperDocument38 pages29-01-2023 Shift 2 PaperbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- (Adv) - Jr-Iit-Star-Super Chaina-60 S.No Adm No NameDocument6 pages(Adv) - Jr-Iit-Star-Super Chaina-60 S.No Adm No NamebhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- CuuumDocument2 pagesCuuumbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadratic Equations Quadratic Equations Prac Ctice Sheet 1Document11 pagesQuadratic Equations Quadratic Equations Prac Ctice Sheet 1bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- CuuuuuuummmmmDocument10 pagesCuuuuuuummmmmbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Document PDF 275Document8 pagesDocument PDF 275bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Science Mixed Test 01Document2 pages09 Science Mixed Test 01bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- (Mains) Sr. Iit Co-Spark Iz Internal Grand Test-6 Results On 12-05-2019Document8 pages(Mains) Sr. Iit Co-Spark Iz Internal Grand Test-6 Results On 12-05-2019bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Pi200930 PDFDocument1 pagePi200930 PDFbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- (Adv) JR Iit Spark Super Chaina 604 13052019 Cummulative Iit Comman Cut 2 (2013 p2 60b 180m)Document1 page(Adv) JR Iit Spark Super Chaina 604 13052019 Cummulative Iit Comman Cut 2 (2013 p2 60b 180m)bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 05 04 - JR - IIT N120 - WAT 39 - ANALYSISDocument562 pages19 05 04 - JR - IIT N120 - WAT 39 - ANALYSISbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Number SystermDocument22 pagesNumber SystermbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced High-School - David B. SurowskiDocument435 pagesAdvanced High-School - David B. SurowskiSanotestPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture PlannerDocument1 pageLecture PlannerbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Time Table Goa, Mad,&VascoDocument1 pageMedical Time Table Goa, Mad,&VascobhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Class - X Social Science: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80Document6 pagesClass - X Social Science: Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter14Document6 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter14Nabh AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch15 Food Resources p204 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch15 Food Resources p204 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 7 Civics Practice Worksheet (7) FinalDocument1 pageCBSE Class 7 Civics Practice Worksheet (7) FinalbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- JNV 3Document2 pagesJNV 3bhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch15 Food Resources p204 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch15 Food Resources p204 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch11 Work and Energy p149 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch11 Work and Energy p149 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch08 Motion p100 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch08 Motion p100 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch14 Natural Resources p193 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch14 Natural Resources p193 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch14 Natural Resources p193 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch14 Natural Resources p193 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill p180 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch13 Why Do We Fall Ill p180 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Sol 09 Science Ch12 Sound p162 163 QDocument1 pageNcert Sol 09 Science Ch12 Sound p162 163 QbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- Class-Ix Diversity in Living Organisms (Page No. 80) QuestionsDocument1 pageClass-Ix Diversity in Living Organisms (Page No. 80) QuestionsbhartiyaanujPas encore d'évaluation
- EEC 319 Engineer in The Society DocumentDocument3 pagesEEC 319 Engineer in The Society Documentgodspower odior100% (1)
- Training CoursesDocument16 pagesTraining CoursesFeroz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Amadeus Web ServicesDocument2 pagesAmadeus Web ServicesBoris ChoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-7 Set-1 Chapter-27Document32 pagesSumanta Chowdhury - CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Phy Study-Package-7 Set-1 Chapter-27Rohit Raj0% (1)
- lm230wf1 Tla6Document32 pageslm230wf1 Tla6Charlie SierraPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Payment System On E-Commerce in India: Karamjeet Kaur, Dr. Ashutosh PathakDocument9 pagesE-Payment System On E-Commerce in India: Karamjeet Kaur, Dr. Ashutosh Pathakdharshinee1961Pas encore d'évaluation
- Riso Rp310 Panel MessagesDocument44 pagesRiso Rp310 Panel MessagesKhin Zaw50% (2)
- Chapter 14 - Storm and Sanitary Analysis PDFDocument41 pagesChapter 14 - Storm and Sanitary Analysis PDFdobridorinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyroelectric Array CameraDocument7 pagesPyroelectric Array Cameraziggie_lenzPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument107 pagesUntitledniko_seppanenPas encore d'évaluation
- Hexadecimal To DecimalDocument7 pagesHexadecimal To DecimalMushfik ArafatPas encore d'évaluation
- Elevated Intz Tank 279Document23 pagesElevated Intz Tank 279Navasivayam Sankar100% (2)
- Plastic Coatings: Advanced Polymer Technologies ForDocument13 pagesPlastic Coatings: Advanced Polymer Technologies ForFazlul HoquePas encore d'évaluation
- D91 PDFDocument3 pagesD91 PDFJuan Diego ArizabalPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Processing - Quality Management Is Vital in Heat-TreatingDocument1 pageThermal Processing - Quality Management Is Vital in Heat-TreatingJader PitangueiraPas encore d'évaluation
- C#.Net Interview Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesC#.Net Interview Questions and AnswersManoj ManuPas encore d'évaluation
- Babies of 2010Document16 pagesBabies of 2010Sierra Nevada Media GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Mooring SystemsDocument6 pagesMooring SystemsVinicius PessottiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vol Damper (Smacna)Document9 pagesVol Damper (Smacna)MohamedOmar83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water and Environmental Sanitation Strategic Plan BihacDocument53 pagesWater and Environmental Sanitation Strategic Plan BihacEddiemtongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rossler Chaotic Circuit and It's Application For Communication SecureDocument10 pagesRossler Chaotic Circuit and It's Application For Communication SecureMada Sanjaya WsPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Controlled Car For Disabled Using Artificial IntelligenceDocument17 pagesBrain Controlled Car For Disabled Using Artificial IntelligenceMdkhanzPas encore d'évaluation
- ICE Annex A Methodologies For RecyclingDocument17 pagesICE Annex A Methodologies For RecyclingChai Lin NyokPas encore d'évaluation
- NEOCLASSICAL CITY PlanningDocument10 pagesNEOCLASSICAL CITY PlanningAfrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 (ME 03) - Hoa Phat GroupDocument42 pagesGroup 2 (ME 03) - Hoa Phat GroupLê Thành DanhPas encore d'évaluation
- SampleDocument2 pagesSamplesaurabhverma08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Explosion WeldingDocument22 pagesExplosion WeldingLesther Alexander CorreaPas encore d'évaluation
- 496 - SSP481 - Audi A7 Onboard Power Supply and Networking PDFDocument40 pages496 - SSP481 - Audi A7 Onboard Power Supply and Networking PDFbenjaminhuku100% (5)
- The PA Bible Addn 03 Microphones PDFDocument4 pagesThe PA Bible Addn 03 Microphones PDFjosiasns5257100% (1)
- Business Plan On Plastic Recycling & ManufacturingDocument19 pagesBusiness Plan On Plastic Recycling & ManufacturingSah Sanjiv KumarPas encore d'évaluation