Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
03 - Carpentry
Transféré par
mazharimechDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
03 - Carpentry
Transféré par
mazharimechDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Unit 03 Carpentry
Introduction Carpentry is the processing of wood to obtain desired shapes and size by Cutting, Planing, Sawing, etc. Carpentry is used for making patterns
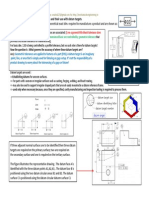
COMMON TOOLS USED IN CARPENTARY SHOP
Commonly used tools to shape wood for various types of joints by driving in and driving out nail involve cutting and smoothening of wood surfaces. A broad classification of tools used in he wood working or carpentry shop are measuring and marking tools, supporting and holding tools, cutting tools, striking tools and miscellaneous tools.
Measuring Tools
(a) Steel Rule Steel rule is used for measuring line of different dimensions. It is specified by its length. It is available in different lengths from 150mm to 600mm.
(b) Wooden Folding Rule The most commonly used wooden folding rule is four fold rule. It is used for marking and measuring length up to 600mm. It is made of four folds pieces of each 150mm length.
(c) Steel Tape The steel tape is used for measuring longer dimensions. They are available in different sizes ranging from 0.6 to 2.5m.
Marking Tools Marking tools are used for marking the workpiece before the working process. The following tools are majorly used in as marking tools: Straight Edge Try Square Marking Knife (a)Straight Edge It is used for checking trueness, flatness of surface and straightness of edge. It is used for drawing straight lines on job surface.
(b)Try Square It is used for marking and smoothness, trueness of the surface of the job work.
(c) Marking Guage The marking guage is the commonly used when absolute accuracy is required. It has a stem with a sharp pin at one edge. It is used to cut line along the grains and parallel to an edge. This can achieve by thumb screw.
(d)Divider It consists of two pointed legs. The points are hardened and tempered to prevent wear. It is used for transferring the sizes and scribing curves or circles.
(e)Marking Knife All dimension lines marked with pencil are cut with marking knife. It is made of steel and generally used with try square.
(f) Mitre Square Mitre Square is used for marking and testing 450. It consists of steel blade fitted in a wooden or metal stock at an inclination of 45 0 with horizontal.
(g)Bevel Edge It is used for marking and testing of any angle between 0 to 180 0. It has a slotted blade and stock. The blade can be fixed at any position by means of screw.
(h)Trammel It is used for drawing very large circles and arcs which are beyond the scope of compass. It consists of a wooden beam on which the two pins are located. The distance between these points can be adjusted by means of thumb screw.
(i) Wing Compass Wing compass is made of steel and consists of two pointed legs. The legs secured in position by means of a set screw and quadrant. It is used for marking equal divisions, and also for scribing circles arcs on work surface.
(j) Calipers Calipers are used for measuring the sizes of component. The size taken by the calipers is read on the steel rule. They are made either with firm joint or spring calipers. The various types of calipers are generally used outside and inside calipers. a. Outside Calipers It has two legs bent inwards. It is used for measuring dimensions of cylindrical shapes and the thickness of workpiece.
Spring Caliper
Firm Joint Caliper
b. Inside Calipers It is used for measuring the diameter of holes, width of key ways or recesses. Its legs are bent outwards.
Spring Caliper
Firm Joint Caliper
(k) Spirit Level The Spirit Level is an instrument used for testing the horizontal levels and also for setting surfaces parallel to the marking off table.
Holding Tools
(a)Work Bench Every carpenter generally needs a good solid bench of rigid construction of hard wood on which he can perform or carry out the carpentry operations. Work bench should be equipped with a vice for holding the work and with slots and holes for keeping the common hand tools. (b)Vice Carpenter vice is very important tool in wood working shops for holding wooden jobs. There are several varieties of vices, each possessing its own particular merit.
(c) Clamps Clamps are commonly used in pairs in gluing up operations at the final assembly of wood joinery work. These clamps can provide pressure required to hold joints together until they are secured due to the setting of glues. Clamps are of two types namely plain rectangular bar type and T-bar type. The former is made of mild
steel and is usually rectangular in section. There are other types of such clamps named as sash clamp, rack clamp, screw clamps, light duty parallel clamp, adjustable bar clamp, G or C-clamp and double bar clamp which are useful for holding different sizes and shapes of wooden jobs.
Cutting Tools Various kinds of cutting tools namely various kinds of saws, planes, chisels, scraper, files, and rasp adze and axe and boring tools such as brace and bits, bradawl, auger, gimlet are used in the carpentry shop. Few important types of cutting tools are described as under. (a)Saws Saws are wood cutting tools having handle and a thin steel blade with small sharp teeth along the edge. They are utilized to cut wood to different sizes and shapes used for making the wooden joints that hold parts together. They can be further classified into three major types namely hand Saws (Rip, Cross-cut, Panel, Keyhole and, Pad saw), Snuff Saws (Tenon and Dovetail) and Frame Saws (Coping, Bow and ret).
(1) Rip Saw The rip saw is used for cutting timber along the grains. The teeth of rip saw are chisel-shaped and are set alternately to the right and left. A 24" long point saw is a good for sawing work.
(2) Cross-Cut Saw Cross cut saw is primarily designed for cutting across the grains of wood. The teeth are knife shaped and bent alternately to the right and left for making the saw to cut wider than the blade.
(3) Keyhole Saw It is generally employed for fine internal and intricate work where the compass saw would be too big and clumsy for the carpentry job. (4) Turning Saw The turning saw is designed for cutting curves, scrolls and rounding on wooden jobs. It is used chiefly on heavier work where long fast stroke and less accuracy of cutting are required. The thin blade of the turning saw is removable. This saw can be pivoted between the handles. The saw generally cuts in the pulling stroke. (5) Dovetail Saw Dovetail saw is little in size. It is lighter and however possesses a thinner blade and finer teeth. The handle is round, to provide a delicate grip for fine cutting. This saw is used where absolutely finer and delicate cutting is required in wood work.
(6) Compass Saw Compass saw carries a tapered blade which is long, thin, narrow and flexible. It is commonly used for making cutouts on the inside surface of a piece of work. A hole is first bored inside the portion which is to be cut out and the pointed compass saw is pushed into the hole to start the sawing operation. Its blade contains about 12 teeth per cm length.
(7) Hacksaw Hacksaw consists of steel frame and a hacksaw blade. While essentially designed for cutting metal, this tool comes in for a variety of uses in the wood working shop. The frame of hacksaw is designed in different ways, some with pistol grips, and others with handles similar to those used on a conventional saw and others with turned handles. Blades of hacksaw are detachable and can be obtained with teeth of varying coarseness.
(b) Planes A plane is a special tool with a cutting blade for smoothing and removing wood as shavings. It is just like a chisel fixed in a wooden or steel body. They can also be classified as jack plane, smooth plane, jointer plane, trying plane, rabbit plane and circular plane and fore plane.
(1)
Jack Plane Jack plane is most commonly used plane. It comprises of its body about 40 cm long, blade 5-6 cm wide and handle. It is good for rough surfaces that require a heavier chip. It is ideal for obtaining a smooth and flat surface. The main working parts are the cutting blade or plane iron. The adjusting nut is operated to raise or lower the blade and the adjusting lever which regulates the blade so as to make possible an even or slanted cut. The cutting blade of the jack plane is guarded with a metal cap which is adjusted on top of the blade. The metal cap of the jack plane eases the cutting action by curling and breaking off the wood shavings evenly, thus preventing splitting or splintering of the wooden part.
(2)
Jointer Plane When a fairly long board is to be planed absolutely straight and square along the edge, it is easier to obtain a straight and level surface with the jointer plane in comparison to any other type of plane. This plane is made up in various sizes but the most popular type of jointer plane is 24 inches in teeth. Smoothing Plane
(3)
Smoothing plane is somewhat smaller than the jack plane, measuring between 6 and 10 inches in length. It is a fine utility tool, especially useful for planning end grain, chamfering, and other edge shaping of wooden part. This plane is also used for cleaning up after gluing and assembly, but owing to its short length should not be used for producing very true surfaces.
(4)
Trying Plane The wooden trying plane is similar in construction to the jack plane except that its blade is wider and much longer than jack plane. Its mouth is also narrower than that of the jack plane.
(5)
Rabbet Plane Rabbet plane is used for sinking one surface below another and shouldering one piece into another. If the edge of a piece of wooden board is to be rebated, this plane is being generally used. The side guide and the cutting blade of the rabbit plane may be adjusted so as to cut rabbets of varying widths and depths. The plane is useful for various types of edge shaping. Rebate or rabbet means a recess or step cut into the edge or end of a wooden board.
(6)
Circular Plane The shape of circular plane adapts it for planning either convex or concave surfaces and for shaping round edges. This plane may be adjusted so that the flexible bed will conform to circles of various sizes. Fore Plane
(7)
This plane may be said as a junior jointer plane. It is slightly shorter than the conventional jointer plane. It is mainly used for planning edges of medium length. (d)Chisels A Chisel is a strong sharp edge cutting tool with a sharp bevel edge at one end. Its construction is composed of handle, tang, ferrule, shoulder, and blade. Chisels are generally made up of high carbon steel. They are used to shape and fit parts as required in joint making. A gouge is a curved chisel. It may be outside or inside ground. Outside ground gouges are called firmer gouges and inside ground gouges are called scribing gouges.
(1)Firmer Chisel Firmer chisel possesses a blade of rectangular section. It consists of the following parts blade made of cast tool steel and it is used for general bench work.
(2)Bevel Edge Firmer Chisel Beveled edge firmer chisel is identical to the firmer chisel except that the edges of the back of the blade are beveled. This enables the chisel to be used for cutting right into the corner of acuteangled wood work such as the base of a dovetail.
(3)Paring Chisel
Paring chisel has a longer and usually slightly thinner blade than firmer chisel. It may be obtained with a blade of rectangular or beveled edge section and is used in pattern making and where long accurate paring is required. The paring chisel should not be struck with a mallet.
(4)Mortise Chisel Mortise chisel is designed for heavy work. A mortise chisel has a blade which is very nearly square in section and so may be used as a lever for removing chips and will withstand heavy blows from a mallet. Various types of handles are fitted to mortise chisel depending upon use.
(e)Scrapers Scraper is used after planning to obtain a smooth surface before final glass papering. Where the grain in wood is particularly twisty so that even a finely set plane tends to tear it, a sharp scraper will be found most useful to tackle this problem. It is also used for cleaning up veneered work as its curved edges are used for cleaning up large molding of concave section and other similar work. The scraper is held as the thumbs being positioned low down and pushed forward to curve the blade so that the center of the edge rather than the outer corners comes into contact with the surface of the wood. A sharp scraper will produce fine shavings on wooden surfaces.
(f) File and Rasps Files and Rasps are used for maintaining other wood working tools and equipment. They are made of hardened tool steel which is tempered and they should never be dropped as they are very brittle to break. They are of various types depending upon their size, shape, cuts and degree of their coarseness.
(g)Adze An adze is used for rough cutting, squaring, to chop inside curves and to produce concave surfaces. Its outer face is convex, inner face concave and edge is beveled to form a cutting edge. It is made of carbon steel.
(h)Axe An axe is used for splitting the logs and for removing bark from the wood. It is made of carbon steel and both sides are beveled to form a cutting edge. Its one side is plane and the other is beveled to form a cutting edge. It is used to make the surface roughly plane.
Boring Tools Boring is cutting a hole in wood with a tool called a bit. Holes of 6 mm size or larger are bored. Holes of 6 mm size or smaller are drilled. Boring is the first step in making any kind of shaped opening or making holes. The commonly used boring tools bits are discussed as under. (a)The Centre Bit The center bits are available in sizes ranging .from 4 mm to 50 mm and are useful for boring holes through thin wood. They are not recommended for deep boring as it has a tendency to wander or drift as a result of varying grain texture and direction in wood.
(b)Shell Bit Shell bit is used for boring holes where the accuracy and finish is not important. It can make holes of diameter upto 12mm.
(c) Twist Bit They are the most commonly used holes making tools used in wooden wood. These bits are more costly than center bits. They can produce holes easily and accurately from 5mm to 35 mm in diameter in wooden jobs.
Shell Bit
(d)Countersink Bit Countersink bit is used for countersinking the predrilled holes to placement of heads of screws.
(e)Spoon Bit Spoon bits are the traditional kinds of bit which are now superseded by the carpenters twist drills or bits. (f) Expanding Bit These are commonly used forms of screw center bit which are adjustable for cutting holes of from 15 mm to 75 mm in diameter. The two combined cutter-spurs are provided in each case to cover the range of hole sizes. (g)Forstner Bit These are used for boring clean sided stopped holes of flat bottom kind.
Forstner Bit (h)Snail Bit The snail bits have only one cutter which gives a clean cutting action. (i) Rose Bits The rose bit tends to scrape rather than cut. It is generally used on soft metals in addition to wood. (j) Bradawl
Bradawl is used for making fine holes, especially nail holes in soft woods. Bradawl (k) Auger It is used for making long and deep hole of diameter ranging from 6 to 40mm. It is a steel bar with an eye at the top which is fitted with a handle.
(l) Gimlet It is used for making small holes. It has a spiral flutes with screw like paint. Gimlet
(m) Wheel Brace It is mainly used for making small holes with drills. It has a chuck with self-centering jaws which holds the round and parallel shank drill.
Wheel Brace (n) Ratchet Brace It is used for making large holes. It has a wooden head and a handle which is filled with bearings to turn easily. At bottom it is provided with a chuck.
Ratchet Brace Striking Tools Mallets and various types of hammers are generally used as striking tools in carpentry shop. A hammer delivers a sharp blow, its steel face being likely to damage the chisel handle whereas the softer striking surface such as mallet will give better result. (a)Mallet A mallet is a short handled wooden hammer with a large head. It is used to strike a chisel for heavy cutting waste wood, from joints such as mortises and halving joints and also for removing unwanted, wood on shaped work etc. Mallet is frequently also used to tap parts of a project together during the assembly process.
(b)Warrington Hammer Warrington hammer is used for knocking in nails, assembling joints and setting wooden plane blades. The head is forged from tool steel and is obtainable in various weights. The face of hammer is hardened, tempered and ground slightly convex. The handle is made of wood and is oval in cross-section to have a comfortable grip.
(c) Peen Hammer The peen hammer is used for striking nails where the use of the face is impracticable. The peen hammer is very light and is used for driving the panel pins and fine nails.
(d)Claw Hammer
The claw hammer is shown in. One of its ends possesses curved claw which is used for extracting nails in order to provide the extra strength needed for this levering action. The other end is used for light striking work. A strong handle on claw hammer is always necessary for carrying out the task.
Miscellaneous Tools Other some miscellaneous carpentry hand tools that are also used in carpentry shop include screw driver, pincer and fasteners. (a)Screw Driver Screw Drivers are used for driving in screws or unscrewing them in wood. There are many sizes and several types of screw drivers. The size is always specific by the length of the blade.
(b)Pincer Pincer is used for pulling out nails and is more efficient than claw hammer.
(c) Glass Paper Glass paper is a sheet of paper which consists of small glass particles. The sharp edge of glass particles cut the wood. It is used to remove minute imperfections in wood surface. (d)Oil Stone An Oil Stone is used for sharpening chisels and plane irons. Modern oil stones are mainly synthetic which are manufactured from silicon carbide or aluminium oxide. These are available in fine, medium and coarse grade. (e)Oil Stone Slip It is a stone for sharpening the gouges.
Oil Stone Slip Carpentry Processes
a. Marking The marking is the operation of setting out dimensions of a product on the surface. It is most important operation of wood work. b. Sawing It is the process of cutting wood by using saw. While sawing, the work should be gripped perfectly in a holding tool. To start a saw cut hold the saw nearly horizontal. Support the blade with the left thumb and draw the blade backward and push forward until it has started a cut. It is important that the whole length of the saw should be used and there should not be any excessive pressure. c. Planing Planing is the process of smoothing the surface of wood by using planes. The work for planing is supported by the bench stop or held in the vice. The pressure is applied in the forward stroke and relieved in the backward stroke. It is important to move plane in a straight line. d. Chiseling Chiseling is the process of cutting excess wood with chisel to obtain desired shape and required of joint. In chiseling hand pressure is applied to remove thin layers. For quick chiseling the chisel can be struck by the mallets. e. Boring It is the process of making holes in wood. The work is secured firmly in a vice and the hole position is marked with punch. The hole is produced by turning and feeding the bit into work. f. Rebating It is the process of cutting a recess along the edge of wood by a rebate plane. While rebating, the plane must be kept press into the side of the wood. g. Grooving & Tongueing These processes are involves in joining of wood. Grooving is the process of cutting a channel in a wooden piece. Tongueing is the process of making a projection corresponding to a groove in which it has to fit. h. Moulding It is the process of making curved surface along the length of wood. This operation is performed with moulding plane. i. Polishing It is the process of producing a smooth reflecting surface with only the minimum removal of material. To obtain such a finish it is necessary to incorporate suitable abrasive within the polishing composition. Carpentry Joints All wooden objects whether doors, windows, furniture, pattern, core boxes, handicrafts, toys, cots, etc., are all assembled with joints. The various common used wood working joints are given through figures given below.
Carpentry Machines Wood working machines are employed for large production work. These possess the following advantages over the hand tools. 1. The carpentry machines help to reduce fatigue of carpenter. 2. The carpentry machines are used for production work. 3. The carpentry machines save time and are used for accuracy work. 4. They are used for variable job variety and more designs are possible. a. Wood Working Lathe A general wood working lathe resembles roughly to an engine lathe. It consists of a cast iron bed, a headstock, tailstock, tool rest, live and dead centers and drawing mechanisms. The long wooden cylindrical jobs are held and rotated between the two centers. The tool is then fed against the job and the round symmetrical shape on the jobs is produced. Scrapping tool and turning gauge are generally used as a turning tool on a woodworking lathe.
b. Circular Saw A circular saw is used to perform various operations such as grooving, rebating, chamfering etc. It consists of a cast iron table, a circular cutting blade, cut off guides, main motor, saw guide, elevating hand wheel, tilting hand wheel etc. The work is held on the table and moved against the circular saw to perform the quick and automatic sawing operation and other operation on wood as said above. The principal parts include the frame, arbor, table, blade, guides for taking cuts, guards and fencing.
c. Band Saw Band saw is used to cut the heavy logs to required lengths, cutting fine straight line and curved work. It consists of a heavy cast bed, which acts as a support for the whole machine, a column, two wheel pulleys, one at the top and other at the bottom, an endless saw blade band, a smooth steel table and guide assembly. It is manufactured in many sizes ranging from little bench saw to a larger band saw mill.
- The End
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Handbook On Building Fire CodesDocument287 pagesHandbook On Building Fire Codesmz1234567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic dimensions and datum targets in mechanical engineeringDocument1 pageBasic dimensions and datum targets in mechanical engineeringmazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- (Ebook) Catia Tutorial PDFDocument38 pages(Ebook) Catia Tutorial PDFmahesh89% (57)
- Design Basis Offshore 2005 Tcm158-160860Document11 pagesDesign Basis Offshore 2005 Tcm158-160860mazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Hammer: Design CriteriaDocument3 pagesWater Hammer: Design CriteriamazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- 28 Design FormulaeDocument31 pages28 Design FormulaemazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- PDC Power PointDocument22 pagesPDC Power PointAshutosh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Design Guideline Storage Tank Rev 2Document8 pagesEngineering Design Guideline Storage Tank Rev 2CaptainToniesPas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Anf Return GrillDocument1 pageSupply Anf Return GrillmazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- Distance CalculaterDocument21 pagesDistance CalculatermazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- DrierDocument64 pagesDriermazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- Air-Cooled Rotary Screw ChillersDocument84 pagesAir-Cooled Rotary Screw Chillersmazharimech100% (1)
- 28 Design FormulaeDocument31 pages28 Design FormulaemazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - CarpentryDocument19 pages03 - Carpentrymazharimech100% (1)
- Sanitary SORsDocument51 pagesSanitary SORskokuei100% (1)
- 28 Design FormulaeDocument31 pages28 Design FormulaemazharimechPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Welding of Stainless SteelDocument103 pagesWelding of Stainless SteelJaime Iván Vera Melgar100% (4)
- BASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING: Types and Properties of Carbon SteelsDocument8 pagesBASIC MECHANICAL ENGINEERING: Types and Properties of Carbon SteelsMohil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Filter Element OverviewDocument6 pagesFilter Element Overviewmona zhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Universalis: Rutile ElectrodeDocument2 pagesUniversalis: Rutile ElectrodeBeshoy RedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Potential Failure Mode & Effects AnalysisDocument12 pagesProcess Potential Failure Mode & Effects Analysisankit kumar100% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Press Wood Pallet TDS (English) - 091014 - 인쇄압축Document63 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Press Wood Pallet TDS (English) - 091014 - 인쇄압축Anjum ParkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cylinder LinerDocument4 pagesCylinder LinerhamidPas encore d'évaluation
- A FEDS Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesA FEDS Structural BoltsCrimsonPoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Machining Surface Finish ChartDocument4 pagesMachining Surface Finish ChartsunilPas encore d'évaluation
- Harris Brazing MaterialsDocument3 pagesHarris Brazing MaterialsfontyflockPas encore d'évaluation
- Pih0101-20240220 (PT PLN Nusantara Power)Document1 pagePih0101-20240220 (PT PLN Nusantara Power)fandyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gpg136 SolderDocument43 pagesGpg136 SolderJuan PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.piping SeminarDocument85 pages5.piping Seminarvg100% (2)
- Introduction To Plastic ProcessingDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Plastic ProcessingShubham ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Welding SymbolsDocument43 pages8 Welding Symbolsjamilhse7759Pas encore d'évaluation
- Balinit Tisaflex Machining Difficult-To-Cut Materials at The Highest LevelDocument4 pagesBalinit Tisaflex Machining Difficult-To-Cut Materials at The Highest Levelnhirpara1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tooling Pricelist BOSCHERT CU 03-2023Document36 pagesTooling Pricelist BOSCHERT CU 03-2023RodrigoPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Lathe From Beginning of Machine Tool InventionDocument4 pagesHistory of Lathe From Beginning of Machine Tool Inventionകൂട്ടുകാരിയെ സ്നേഹിച്ച കൂട്ടുകാരൻPas encore d'évaluation
- The Secret To Longer Machine Life: KOBELCO Genuine Parts Keep Your Machine at Its BestDocument1 pageThe Secret To Longer Machine Life: KOBELCO Genuine Parts Keep Your Machine at Its BestAvaa AmgaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preheat Calculation 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPreheat Calculation 1 PDFravi00098Pas encore d'évaluation
- McqsDocument33 pagesMcqsFaisal100% (2)
- SUS420F Datasheet: Chemical, Physical & Mechanical PropertiesDocument2 pagesSUS420F Datasheet: Chemical, Physical & Mechanical PropertiesarnettoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4 Reactive System Material BalanceDocument36 pages4.4 Reactive System Material Balancemulugeta damisuPas encore d'évaluation
- Itrne: Chemical Kinetics - ProblemsDocument3 pagesItrne: Chemical Kinetics - ProblemsdiveshPas encore d'évaluation
- Amendment No. 2 April 2017 TO Is 16098 (Part 2) : 2013 Structured-Wall Plastics Piping Systems For Non-Pressure Drainage and Sewerage - SpecificationDocument1 pageAmendment No. 2 April 2017 TO Is 16098 (Part 2) : 2013 Structured-Wall Plastics Piping Systems For Non-Pressure Drainage and Sewerage - SpecificationTesting CIPET GuwahatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Full CatalogDocument96 pagesFull Catalogolaff_lozoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Metal Machining: ProblemsDocument44 pagesTheory of Metal Machining: ProblemsAna Maria Trujillo100% (1)
- BS 4825-5 - 2009 - Stainless Steel Tubes and Fittings For The Food Industry - Recessed Ring JointsDocument24 pagesBS 4825-5 - 2009 - Stainless Steel Tubes and Fittings For The Food Industry - Recessed Ring JointsroburtrPas encore d'évaluation
- Spray Paint CatalogueDocument8 pagesSpray Paint CatalogueSamraj Polytex100% (1)
- Tyre Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesTyre Manufacturing ProcessAmit100% (1)