Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ds67 Evolution Quiz Sol Review
Transféré par
api-110789702Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ds67 Evolution Quiz Sol Review
Transféré par
api-110789702Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
UNIT 8: Evolution
DAYSHEET 67: Evolution Quiz & SOL Review Name: _______________________________
Biology I
Date:
____________________________
Catalyst/Bellringer: Use you daysheets from last class to help you answer the evolution quiz practice questions below.
Cladograms:
Study
the
cladogram
(phylogenic
tree)
below
to
answer
questions
#1-3
1. List
the
traits
that
are
found
in
prosimians:
Which
pair
of
organisms
is
most
closely
related:
Fish
&
Humans
or
Insects
&
Amphibians
or
2.
Birds and Amphibians Prosimians and Humans
3. Study
the
list
of
organisms
below.
Which
organism
was
the
last
to
evolve
according
to
the
cladogram?
a.
Fish
b.
Prosimians
c.
Birds
d.
Humans
4. Study
the
image
of
the
embryos
below.
Which
pair
of
organisms
are
the
most
closely
related?
a. b. c. d.
Organisms I and IV Organisms II and III Organisms III and IV Organisms II and IV
I II
III
IV
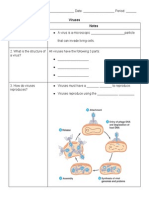
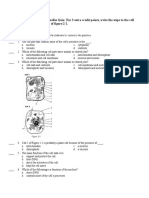
Directions: Match the terms on the left with their definition on the right
a. structures that an organism has, but does not use/need b. structures that are appear similar in different organisms at first glance, but on closer inspection are structurally different. The structures are similar because the organisms live in similar environments and face similar environmental pressures. c. structures that are very similar in different organisms, even though they have been modified for different purposes. The structures are similar because the organisms have a common ancestor.
1. Homologous structures 2. Vestigial structures 3. Analogous structures
Directions: Label the following pictures as homologous structures (HS), vestigial structures (VS) or analogous structures (AS).
A.
B.
C.
7. Study
the
cross-section
of
Earths
sediments
below.
Draw
a
star
next
to
the
oldest
fossils.
Draw
a
tree
next
to
the
youngest
fossils.
Activity 1: Evolution Quiz
Activity 2: Introduction to the Kingdoms of Life
Directions: Type in the following link into your web browser:
http://tinyurl.com/chco5zv
Use the information found on this site to answer the following questions about organisms in the six kingdoms of life. 1. List the six kingdoms of life: 2. What criteria are used to place organisms into their appropriate kingdom of life? 3. List three characteristics of all organism that are placed in Kingdom Plantae: 4. What is an autotroph? Give one example of an autotroph. 5. List 2 characteristics of all organisms that are placed in Kingdom Animalia: 6. What are heterotrophs? Give one example of a heterotroph. 7. What are the two kingdoms that prokaryotes can be placed in? 8. Where are archaebacteria found? 11. How do plants and fungi differ from one another? 12. List 2 characteristics of the Kingdom Protista. Give two examples of a protist. 13. What do plants and protists have in common? 14. What do fungi and animals have in common? 9. Which kingdom of bacteria causes sickness in humans? 10. List 2 characteristics of the Kingdom Fungi:
Activity 3: SOL Review
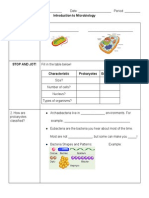
Topic 1: Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Find the section titled Cells: An Overview in your Biology SOL Review Packet. Carefully read (using your reading strategies) this section to fill in the comparison chart below: Comparing Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes Only Eukaryotes Both Eukaryotes and Only Prokaryotes Prokaryotes Cell Organelle Structure Function Prokaryotes? Plants? Animals?
Ribosome
Chloroplast
Mitochondrion
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Body/ Apparatus
4
Topic 2: Transport Find the section titled Transport in your Biology SOL Review Packet. Carefully read (using your reading strategies) this section to help you complete the activities below.
Fill: Place a CHECK in the box that fits with each of the following types of transport
Transports substances into the cell Uses proteins Uses energy Transports substances from a HIGHER to LOWER concentration Transports substances from a LOWER to HIGHER concentration Transports water
Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport
Identify: Given the following example, underlie key words and then identify the type of transport that occurs. A word bank has been provided for you. Some words will be used more than once.
Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport
(A) _______________________ No energy or help from proteins is required to move small molecules in this kind of transport. (B) _______________________ Proteins must help large molecules such as sugar and fat pass through the membrane, but no energy is needed (C) _____________________ There is a higher concentration of salt outside the cell than inside. Salt comes into the cell without help from proteins. (D) _____________________ Energy is needed to help move substances into the cell
(E) _______________________ Water moves into the cell through this process. (F) _______________________ There is a higher concentration of a substance inside the cell than outside, but the cell continues to bring it inside anyways.
Topic 3: Macromolecules Find the section titled Macromolecules in your Biology SOL Review Packet. Carefully read (using your reading strategies) this section to help you complete the activities below.
SOL Practice Questions:
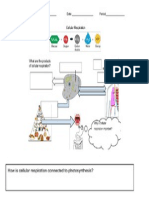
Topic 4: Cellular Respiration & Photosynthesis Find the section titled Metabolism in your Biology SOL Review Packet. Carefully read (using your reading strategies) this section to help you complete the activities below.
Directions: Put a check under photosynthesis, cellular respiration, or both Characteristic Produces food Produces usable energy (ATP) Occurs in the chloroplast Occurs in the mitochondria Occurs in plants Occurs in animals Uses sugar / carbohydrates Produces sugar / carbohydrates Uses oxygen (O2) Produces oxygen (O2) Uses water (H20) Produces water (H20) Uses carbon dioxide (CO2) Produces carbon dioxide (CO2) Uses sunlight Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration
Directions: An arrow going into a diagram represents a reactant. An arrow leaving a diagram represents a product. Fill in the diagram below using the words below: CO2 ATP Glucose Water Oxygen Sunlight Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration
HW67: SOL Review
Biology I Date: __________________
Name: _________________________________________
Directions:
For
each
of
the
words
below,
write
the
everyday
definition
of
the
word
in
the
1. A student is looking at a cell through a microscope and trying to decide whether the cell is a prokaryote or a eukaryote. What are some structures that would be present in a eukaryote, but not a prokaryote? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 2. A student is looking at a cell through a microscope and trying to decide whether a cell is from an animal or a plant. What are some structures that would be absent in an animal cell, but present in a plant cell? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 3. A student is looking at a cell in a microscope and is able to observe the following structures: a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. What type of cell is it? A. It could be any type of cell B. It is definitely a prokaryote C. It is definitely a eukaryote 4. A student is looking at a cell in a microscope and is able to observe the following structures: a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. What type of cell is it? A. It could be any type of cell B. It is definitely a prokaryote C. It is definitely a eukaryote 5. A student is looking at a cell in a microscope and is able to observe the following structures: a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and a nucleus. What type of cell is it? A. It is definitely a prokaryote B. It is definitely a plant cell C. It is definitely an animal cell 6. A student is looking at a cell in a microscope and is able to observe the following structures: a cell a cell membrane, ribosomes, and a region of free-floating DNA. What type of cell is it? A. It is definitely a prokaryote B. It is definitely a plant cell C. It is definitely an animal cell 7. A student is looking at a cell in a microscope and is able to observe the following structures: a cell membrane, ribosomes, a nucleus, a Gogli apparatus, and an rough ER. What type of cell is it? A. It is definitely a prokaryote B. It is definitely a eukaryote, but it could be a plant or an animal cell C. It is definitely an animal cell D. It is definitely a plant cell
8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- MmiummealDocument1 pageMmiummealapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- FossilstationsDocument3 pagesFossilstationsapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Symbiosis Practice QuizDocument11 pagesSymbiosis Practice Quizapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- ConvergentboundariesDocument1 pageConvergentboundariesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Picture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To YoungestDocument2 pagesPicture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To Youngestapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bolin Creek - September 24, 2015Document4 pagesBolin Creek - September 24, 2015api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- AnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsDocument2 pagesAnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Station #1: Evaporation and TranspirationDocument6 pagesStation #1: Evaporation and Transpirationapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Waterqualityreadings 2015Document17 pagesWaterqualityreadings 2015api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Icecores 2015Document2 pagesIcecores 2015api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- BolincreekmealplanningDocument2 pagesBolincreekmealplanningapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- TakealookgraphtablesheetDocument1 pageTakealookgraphtablesheetapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- BBC Bitesize: IllustrateDocument2 pagesBBC Bitesize: Illustrateapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Symbiosis QuizDocument18 pagesSymbiosis Quizapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- HydrologylearningmapDocument3 pagesHydrologylearningmapapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
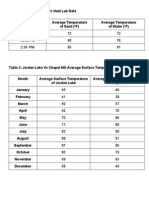
- SpecificheatdataDocument1 pageSpecificheatdataapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Food / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!Document4 pagesFood / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Hydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014Document5 pagesHydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Eogchemistryreviewnotes 2014Document4 pagesEogchemistryreviewnotes 2014api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Coral Reef Adventure Quiz: NameDocument2 pagesCoral Reef Adventure Quiz: Nameapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- EnergyflowpodcastnotesDocument8 pagesEnergyflowpodcastnotesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- SymbiosispodcastnotesDocument2 pagesSymbiosispodcastnotesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quest To Grow Human Organs Inside Pigs in JapanDocument2 pagesQuest To Grow Human Organs Inside Pigs in Japanapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- CellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabDocument7 pagesCellularrespirationandphotosynthesislabapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Three ParentbabiesDocument3 pagesThree Parentbabiesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Viruses Essential Questions NotesDocument3 pagesViruses Essential Questions Notesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Directions For Graphing Your Bacteria Data: Day Percent Bacteria Cover 0 0 1 2 3 6 7Document1 pageDirections For Graphing Your Bacteria Data: Day Percent Bacteria Cover 0 0 1 2 3 6 7api-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Date: - PeriodDocument1 pageName: - Date: - Periodapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- ElodealabmealparagraphDocument2 pagesElodealabmealparagraphapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- BacteriapodcastnotesDocument7 pagesBacteriapodcastnotesapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- P 4 Maple Syrup Urine DiseaseDocument9 pagesP 4 Maple Syrup Urine Diseaseapi-308145910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeDocument2 pagesComprehensive Drug Study Ketoanalogue PDF FreeYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Cell StructureDocument32 pagesChapter 1: Cell StructureAnneli MarshPas encore d'évaluation
- GST Gene Fusion System HandbookDocument132 pagesGST Gene Fusion System HandbookDaniela Gonzalez CaceresPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology LOsDocument31 pagesBiology LOsYoussef samehPas encore d'évaluation
- 106生物Document16 pages106生物德瑞克Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumDocument7 pagesPhytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumYogi PernandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8 Membrane Receptors & Cellular SignallingDocument23 pagesLecture 8 Membrane Receptors & Cellular SignallingDorama AikaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Teacher Grade Level 11 Learning Area Unit 2 How The Properties of MatterDocument5 pagesTeacher Grade Level 11 Learning Area Unit 2 How The Properties of MatterHelen Grace Llemos CabalagPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic RecombinationDocument55 pagesGenetic RecombinationRiyaniMartyasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Section 2Document3 pagesChapter 7 Section 2Pak RisPas encore d'évaluation
- Escherichia Coli DH10BDocument2 pagesEscherichia Coli DH10BSecc. 2 Marco Antonio Aviles RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 2 PDFDocument32 pagesChapter - 2 PDFnikhilPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitro Blue TetrazoliumDocument4 pagesNitro Blue TetrazoliumOsama Bakheet100% (1)
- Chapter - Biomolecules: One Mark QuestionsDocument1 pageChapter - Biomolecules: One Mark QuestionsPathan MohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Roles of Host Gene and Non-Coding RNA Expression in Virus InfectionDocument283 pagesRoles of Host Gene and Non-Coding RNA Expression in Virus InfectionFabricio HidalgoPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrophoresisDocument17 pagesElectrophoresisShilpaKamathamPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Lab 1Document4 pagesEnzyme Lab 1PrincessTPas encore d'évaluation
- Microarray Technology - A Brief Introduction - : Markus PanhuysenDocument38 pagesMicroarray Technology - A Brief Introduction - : Markus PanhuysenrashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Practice Test 01 Nucleic Acid (23-11-2023)Document4 pagesClass Practice Test 01 Nucleic Acid (23-11-2023)hemachaturvedi560Pas encore d'évaluation
- (NF) (MT6317) Introduction and Generalities of LipidsDocument14 pages(NF) (MT6317) Introduction and Generalities of LipidsJC DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids As Genetic Material PDFmanoj_rkl_07Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ in BiochemistryDocument6 pagesMCQ in Biochemistryvmshanes100% (1)
- 11 - Drug Design - Optimizing Target InteractionsDocument67 pages11 - Drug Design - Optimizing Target InteractionsNguyenHongThamPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Protein Based On CompositionDocument4 pagesClassification of Protein Based On CompositionHambaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Mind MapDocument1 pageClass 12 Biotechnology Principles and Processes Mind Mapupgratesleet704Pas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Document12 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: February 2017Farman MunawarPas encore d'évaluation
- BOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaDocument25 pagesBOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaNthabeleng NkaotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Osteoarthritis Role in Initiation and Progression of Cartilage DegenerationDocument10 pagesChondrocyte Hypertrophy and Osteoarthritis Role in Initiation and Progression of Cartilage DegenerationSTAF OSCEPas encore d'évaluation