Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stainless Steel DesignGuide (Euro)
Transféré par
Bergadamus0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
210 vues121 pagesStainless Steel Design
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentStainless Steel Design
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
210 vues121 pagesStainless Steel DesignGuide (Euro)
Transféré par
BergadamusStainless Steel Design
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 121
NUT OTILONKG
CRT Mee le
Structural Stainless Steel
-
;
NST emt
Th a |
tie | i. \ |
J (| Week| eva
EUROPEAN STAINLESS STEEL DEVELOPMENT & INFORMATION GROUP
This publication was sponsored by the Nickel Development Institute, NiDI, on behalf of the members of
the European Stainless Steel Development and Information Group (EURO INOX), whose locations are
shown on page i.
Enquiries and information on material supply should be directed to the appropriate Euro Inox member,
and advice on any aspect of stainless steel may be sought from either the advisory services provided by the
members or NiDI.
While every care has been taken to ensure that all data and information contained herein are accurate at
the time of publication, neither NiDI nor Euro Inox members assume responsibility for any errors in, or
misinterpretations of, such data, or any loss or damage arising from or related to their use.
© Nickel Development Institute April 1994
DESIGN MANUAL
FOR
STRUCTURAL
STAINLESS STEEL
‘SUMMARY
‘The contents of this manual relate to an in-depth study carried out
by the Steel Construction Institute on the structural application of
stainless steel for onshore and offshore structures. Expediency
dictated that the project would examine three grades of material only
namely austenitic grades 304L and 316L, and a high strength
austenitic-ferritic grade commonly known as Duplex 2205.
It should be emphasised that this does not however preclude the use
of standard 304 and 316 grades or other austenitic grades that
designers and manufacturers specify provided that the 0.2% proof
strength and the ultimate strength are not lower. In general, ‘L!
Brades are selected for highly aggressive corrosion conditions to
avoid intergranular corrosion from occurring, however since
modern stainless steels contain carbon levels of 0.05% and lower,
this phenomena is rarely encountered on thicknesses of material
up to 16mm.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Guide To Concrete RepairDocument168 pagesGuide To Concrete Repairhansen_zinck4751100% (11)
- Guide To Concrete RepairDocument168 pagesGuide To Concrete Repairhansen_zinck4751100% (11)
- Guide To Concrete RepairDocument168 pagesGuide To Concrete Repairhansen_zinck4751100% (11)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- ASCE 7-05 Code MasterDocument6 pagesASCE 7-05 Code Mastermark.taylor2962100% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Timber ManualDocument145 pagesTimber Manualspiderlance100% (1)
- Structural Design Bolted Welded ConnectionsDocument52 pagesStructural Design Bolted Welded ConnectionsBergadamus100% (1)
- Shallow Mount Bollard - Product Information - Barrier1 Systems - ASTM M40 (K8) - 09052017Document1 pageShallow Mount Bollard - Product Information - Barrier1 Systems - ASTM M40 (K8) - 09052017BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Shallow Mount Bollard - Product Information - Barrier1 Systems - ASTM M40 (K8) - 09052017Document1 pageShallow Mount Bollard - Product Information - Barrier1 Systems - ASTM M40 (K8) - 09052017BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Carpentry 1916Document199 pagesCarpentry 1916BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 07820 Acrylic Walkway CoverDocument3 pagesSection 07820 Acrylic Walkway CoverBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Morin Catalog 2015 WebDocument24 pagesMorin Catalog 2015 WebBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC 650 DrawingDocument1 pageDSC 650 DrawingBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Framing 1909Document359 pagesFraming 1909BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Municipal Engineering 1898Document470 pagesMunicipal Engineering 1898BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Brickwork & Masonry - A Practical Text Book For Students 1904Document483 pagesBrickwork & Masonry - A Practical Text Book For Students 1904BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Framing 1909Document359 pagesFraming 1909BergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Wood Design - CodeMasterDocument6 pagesWood Design - CodeMasterBergadamus100% (1)
- Architectural Terra CottaDocument177 pagesArchitectural Terra CottaBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Excavation and BackfillDocument1 pageExcavation and BackfillBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
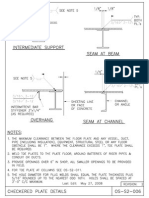
- Steel Checkered Plate Structural DetailsDocument1 pageSteel Checkered Plate Structural DetailsBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- CMU Detail With Double Steel Joist Over 8" WallDocument1 pageCMU Detail With Double Steel Joist Over 8" WallBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
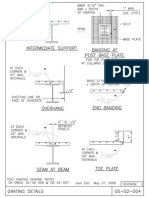
- Steel Grating DetailsDocument1 pageSteel Grating DetailsBergadamusPas encore d'évaluation
- Whiting Crane HandbookDocument205 pagesWhiting Crane HandbookShyam Murugesan100% (6)
- Whiting Crane HandbookDocument205 pagesWhiting Crane HandbookShyam Murugesan100% (6)
- Whiting Crane HandbookDocument205 pagesWhiting Crane HandbookShyam Murugesan100% (6)