Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
As Organic Chemistry 1
Transféré par
Ulee Abdul RaufDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
As Organic Chemistry 1
Transféré par
Ulee Abdul RaufDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
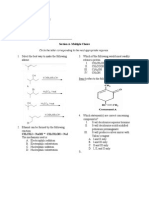
AS Organic Chemistry 1 1. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
H H H H C C H H H H C H H H H C C H
2-methyl butane Ethyl propane 3- Methyl butane Pentane
2. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? CH3 CH3 C CH2 CH3 3,3,4-trimethyl hexane 3,4,4- trimethyl hexane 4-Ethyl 3,4-dimethyl pentane 2-Ethyl-2,3-dimethyl pentane 3. Identify the functional group present in HCOCH2CH3 O HC CH3 CH C H2 CH3
O C O C O R
4. How many structural isomers are possible with molecular formula C6H14? 4 5 6 7 5. Which compound is a member of the same homologous series as 1-chloropropane? 1-Chloropropene 1-bromopropane 1-Chloropropane 1,1-Dichloropropane 6. Propane ,C3H8, undergoes incomplete combustion in a limited amount of air. Which products are most likely to be formed during this reaction? Carbon monoxide and water. Carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Carbon dioxide and water. 7. Which are characteristics typical of a free radical? I. II. It has lone pair of electrons. It can be formed by the homolytic fission of a covalent bond?
III.
It is uncharged. I and II only. I and III only. II and III only. I, II and III .
8. When bromine water is shaken with a liquid organic compound, it is rapidly decolourised. What can be determined from this test? The compound is an alcohol. The compound is an alkane. The compound is an alkene The compound is an iodoalkane
9, What structural feature must a molecule have in order to undergo addition polymerization? Two functional groups. A carbon-carbon double bond. Carbon atoms singly bonded together. A polar covalent bond.
10. What type of reaction does the equation below represent? CH2==CH2 + Br2 Substitution Condensation Reduction Addition BrC H2C H2Br
11. Which reactions can ethene undergo? I. II. III. Addition Esterification Polymerization. I and II only. I and III only. II and III only. I, II and III . 12. Which statement about alcohols is correct? Primary alcohols can be obtained by the reduction of carboxylic acids or aldehydes. Secondary alcohols can be obtained by the oxidation of ketones. Tertiary alcohols can be obtained by the reduction of carboxylic acids or aldehydes. Alcohols can be obtained by the addition of water to alkanes using acid as catalyst, 13. Which of the following products could be formed from the oxidation of ethanol? I. II. III. Ethanal. Ethanoic Acid. Ethane. I and II only. I and III only. II and III only. I, II and III . 14. Which compound can not be easily oxidized using acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution? CH3CH2CH2OH CH3CH(OH) CH3 (CH3 )2 CHCH2OH
(CH3 )3 C OH 15. Consider the following compounds; I. II. III. CH3 CH2CH(OH) CH3 CH3CH(CH3) CH2 OH (CH3 )3 C OH
The compounds are treated separately with acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution. Which will produce a colour change from orange to green? I and II only. I and III only. II and III only. I, II and III . 16. Which compound is a tertiary halogenoalkane? (CH3 CH2 )2 CHBr CH3 (CH2)3 CH2 Br (CH3 )2 CHCH2 CH2 Br CH3 CH2 C (CH3)2Br !7. Which statement best describes the reaction mechanism involved in the single step conversion of chloroethane to ethanol? The reaction involves removal of HCl, followed by the addition of H2O. The reaction involves heterolytic fission of the CCl bond, followed by a reaction with H2O. The reaction involves nucleophilic attack of OH- in a bimolecular mechanism. The reaction mechanism involves a carbocation.
18. What is the reaction type when (CH3)3CBr reacts with aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form (CH3)3COH and NaBr.? Addition Elimination SN1 SN2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- POGIL - Strength of Acids PDFDocument6 pagesPOGIL - Strength of Acids PDFAmy Tony0% (13)
- BCH 4th Year Course SeminarDocument9 pagesBCH 4th Year Course SeminarbrianbobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- TVL Cookery: Quarter 1 - Module 2: (WEEK 2)Document17 pagesTVL Cookery: Quarter 1 - Module 2: (WEEK 2)BiZayangAmaZona100% (6)
- Project Report - Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesProject Report - Organic ChemistryJosh ChiuPas encore d'évaluation
- OutlineDocument1 pageOutlineKalfakPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDocument34 pagesBio Molecules PPT For P AP BiologyDivineDoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- Enoolate Chemistry ExcerciesDocument15 pagesEnoolate Chemistry ExcerciesClara CarreraPas encore d'évaluation
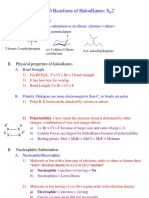
- Chapter 6 Reactions of Haloalkanes: S 2Document8 pagesChapter 6 Reactions of Haloalkanes: S 2Roberto SIlvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bkf1323-Organic Chemistry 21213 PDFDocument8 pagesBkf1323-Organic Chemistry 21213 PDFrushdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistryawais gujjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Formal Report in Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesSample Formal Report in Organic ChemistryAudrey CobankiatPas encore d'évaluation
- Recrystallization in Organic Chemistry LabDocument5 pagesRecrystallization in Organic Chemistry Labrc865Pas encore d'évaluation
- College of Arts and Sciences: CHM 215 Organic Chemistry IDocument3 pagesCollege of Arts and Sciences: CHM 215 Organic Chemistry INajmul Puda PappadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Revista Boliviana de Química: Short Review Peer-ReviewedDocument18 pagesRevista Boliviana de Química: Short Review Peer-ReviewedBolivian Journal of ChemistryPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry: Prepared By: Goce, Ivan Rei LDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Prepared By: Goce, Ivan Rei LReiVanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageOrganic ChemistryPybRajeshKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Execises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Document2 pagesExecises - Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 Part 1Michelle ChicaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry PDFDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry PDFAli AyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesOrganic ChemistryErroel Rodel SaquilabonPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistryapi-233187566Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW11 - Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesHW11 - Organic ChemistryMichael NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- SiklusDocument63 pagesSiklusdasninkdaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic PlansDocument2 pagesAcademic Plansapi-318263897Pas encore d'évaluation
- Side Chain: IUPAC DefinitionDocument2 pagesSide Chain: IUPAC DefinitionspiraldaoPas encore d'évaluation
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3362.001 06s Taught by Sandhya Gavva (Sgavva)Document2 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol3362.001 06s Taught by Sandhya Gavva (Sgavva)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry: Additional Support Materials I.E. Animations, Quizzes, Pictures, WorksheetsDocument26 pagesBiochemistry: Additional Support Materials I.E. Animations, Quizzes, Pictures, WorksheetsnikkikeswaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsGideon CavidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem 323-Final 2005Document1 pageBiochem 323-Final 2005api-3763291Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryNivas KaruppananPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Excersice Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesChapter 12 Excersice Organic ChemistryGerardo Luis RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 - DNA Affinity Screening of Plants, BJC. v.27, n.2, 2010Document4 pages15 - DNA Affinity Screening of Plants, BJC. v.27, n.2, 2010Bolivian Journal of ChemistryPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument45 pagesOrganic ChemistryAnubhav Sinha0% (1)
- rr212304 Bio ChemistryDocument4 pagesrr212304 Bio ChemistrySrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem 322-Final 2005Document1 pageBiochem 322-Final 2005api-3763291Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesOrganic ChemistryVanessa Marie IrizPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry 2 - Syllabus - USTHDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 - Syllabus - USTHMinh MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebulizer Therapy PitfallsDocument8 pagesNebulizer Therapy PitfallskemalahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemistryDocument60 pagesOrganic ChemistryPavani PrabhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsJan RubiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Organic ChemistryDocument37 pagesAssignment Organic ChemistryJoshua Lacerna PelagioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2.1 Refraction 91-01Document16 pages3.2.1 Refraction 91-01Murray PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument28 pages07 Introduction To Organic ChemistryM BPas encore d'évaluation
- M.sc. - II, Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesM.sc. - II, Organic ChemistryDeepak50% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Syllabus Final VersionYseemaz AzeeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal-1-Molecular Modeling in Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesJournal-1-Molecular Modeling in Organic ChemistryRochelle Joyce Olmilla BersaminPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument34 pagesChemistryrishank guptasPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro-Syllabus of CSIT Physics: NumericalDocument5 pagesMicro-Syllabus of CSIT Physics: NumericalBhanubhakta poudelPas encore d'évaluation
- OrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFDocument19 pagesOrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFJuliet Tatiana CumbePas encore d'évaluation
- Health Ethics Master Copy 2Document159 pagesHealth Ethics Master Copy 2Ong Fuentes II100% (1)
- College PhysicsDocument21 pagesCollege PhysicsAve de GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesJeneshaPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistrytesting namePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocument17 pagesNotes Organic Chemistry and Alkanessrk78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry TestDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Testron971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conduction of Electricity in SolidsDocument11 pagesConduction of Electricity in SolidsDallas BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher Incharge: Ms - Priyal Jain Name: Vaibhav Sharma Roll No: CLASS: 12 BDocument16 pagesTeacher Incharge: Ms - Priyal Jain Name: Vaibhav Sharma Roll No: CLASS: 12 BSanjay SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOETICS - IN - NURSING - PPTX Filename UTF-8''BIOETICS IN NURSINGDocument31 pagesBIOETICS - IN - NURSING - PPTX Filename UTF-8''BIOETICS IN NURSINGBanaag Jay100% (1)
- JP XII Organic Chemistry (01) - 1Document4 pagesJP XII Organic Chemistry (01) - 1Ashish RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Madonna H S Physics TutorialsDocument174 pagesMadonna H S Physics TutorialsMHS_Physics_2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- SCH4C Organic Chemistry Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesSCH4C Organic Chemistry Cheat SheetSteve M HallPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic ChemDocument116 pagesOrganic ChemNidhi Sisodia100% (1)
- JHDLKLJLKDJLKDocument1 pageJHDLKLJLKDJLKUlee Abdul RaufPas encore d'évaluation
- Stefanie Ellis - The Gray Area Series 02 - IllusionsDocument214 pagesStefanie Ellis - The Gray Area Series 02 - IllusionslifeturntodustPas encore d'évaluation
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Physics (6PH05) Paper 01Document14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Physics (6PH05) Paper 01areyouthere92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jade Parker - To Catch A PirateDocument79 pagesJade Parker - To Catch A Piratecutelilmonkie930Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 7 Notes - FinalDocument7 pagesPaper 7 Notes - FinalUlee Abdul RaufPas encore d'évaluation
- EdexcelASPhysicsRG 9781846905957 Pg70-78 WebDocument9 pagesEdexcelASPhysicsRG 9781846905957 Pg70-78 WebSabrizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics: Guidance Notes On Experimental Work (Edexcel New Spec AS & A2)Document11 pagesPhysics: Guidance Notes On Experimental Work (Edexcel New Spec AS & A2)arya12391% (33)
- Mark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Physics (6PH05) Paper 01Document14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) June 2011: GCE Physics (6PH05) Paper 01areyouthere92Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring The Rate of Oxygen UptakeDocument2 pagesMeasuring The Rate of Oxygen UptakeSachitra WijethungaPas encore d'évaluation
- (BIO) Probability, Chance and Null HypothesisDocument1 page(BIO) Probability, Chance and Null HypothesisUlee Abdul RaufPas encore d'évaluation
- Between Friends Cowen AmandaDocument159 pagesBetween Friends Cowen AmandaNaina GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Afterlife - Isabella KrugerDocument120 pagesAfterlife - Isabella KrugerUlee Abdul RaufPas encore d'évaluation
- LME Special Contract Rules For Copper GRADE ADocument4 pagesLME Special Contract Rules For Copper GRADE Aadelafuente2012Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8.7 Dipole Moments: Suggested ReadingDocument4 pagesLesson 8.7 Dipole Moments: Suggested Readingrosalie halePas encore d'évaluation
- STPM 2019 Sem 2 Mock AnsDocument2 pagesSTPM 2019 Sem 2 Mock AnsNicholson NicholsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Benedicto Et Al 2017 - REVIEW Tech Economic Environmental The LubriCooling in Machining ProcessesDocument18 pagesBenedicto Et Al 2017 - REVIEW Tech Economic Environmental The LubriCooling in Machining ProcessesPaulo ResendePas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Citric Acid: Asessment 1Document7 pagesProduction of Citric Acid: Asessment 1kindenewPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chem 2 by HaftomDocument285 pagesOrganic Chem 2 by Haftomdereje dawitPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit PDS - Vasilgrit Technical DatasheetDocument1 pageGrit PDS - Vasilgrit Technical DatasheetNelson IzorPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Chemistry Paper 2Document2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Paper 2Naveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Asid Dan Bes Kimia Ting 4Document74 pagesAsid Dan Bes Kimia Ting 4Wan Azzura Wan Ismail100% (1)
- SS Pipe Weld PurgingDocument5 pagesSS Pipe Weld Purging888ddbPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry ProjectSriVathsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Deterjent Powder PDFDocument9 pagesDeterjent Powder PDFMrutunjay PatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Curent LiabilitiesDocument106 pagesCurent Liabilitiesapi-19931483Pas encore d'évaluation
- wch13 01 Que 20231018Document20 pageswch13 01 Que 20231018zainab zeinPas encore d'évaluation
- Foam ConcentratesDocument5 pagesFoam ConcentratesSureshKumar DevulapallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Elektroliticko NiklovanjeDocument17 pagesElektroliticko NiklovanjeStefan RadojevicPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry Q4 M4Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q4 M4roxan clabria100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Pyrolysis UnitDocument3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Pyrolysis UnitInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis and Kinetics Study of Vinyl Ester Resin PDFDocument9 pagesSynthesis and Kinetics Study of Vinyl Ester Resin PDFMamoon ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Management: Yan Xu, Jinhui Li, Quanyin Tan, Anesia Lauren Peters, Congren YangDocument9 pagesWaste Management: Yan Xu, Jinhui Li, Quanyin Tan, Anesia Lauren Peters, Congren YangMinh TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Term 1 Science PaperDocument32 pagesCBSE Term 1 Science PaperSAI ARAVINDPas encore d'évaluation
- Nickel Revolution Has Indonesia Chasing Battery Riches Tinged With Risk - BloombergDocument10 pagesNickel Revolution Has Indonesia Chasing Battery Riches Tinged With Risk - Bloombergandrew hendersonPas encore d'évaluation
- CLE ModuleDocument47 pagesCLE ModuleMark Lawrence GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionpaper Paper1C January2015 PDFDocument36 pagesQuestionpaper Paper1C January2015 PDFChahinese FahsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Am SteelDocument28 pagesAm Steelyogesh v100% (1)
- HPM Steel For MoldDocument15 pagesHPM Steel For MoldcadcamtaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.DIARY-VITAMINS and MINERALS-ESPINO, PAULA BIANCA C. BSN2-BDocument2 pages3.DIARY-VITAMINS and MINERALS-ESPINO, PAULA BIANCA C. BSN2-BPaulaBiancaC.EspinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laundry StarchDocument2 pagesLaundry StarchfaizPas encore d'évaluation