Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Child Labour
Transféré par
Tanishq VarshneyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Child Labour
Transféré par
Tanishq VarshneyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
C
hild labour represent a fundamental abuse of children rights which are a violation of various
laws. Many working children are engaged in occupations that negatively affect there physical, mental and emotional wellbeing and are below their minimum age for employmentCHILD LABOUR IN INDIA According to the amendment in child labour act 1986, a ban is imposed on employing children Age group between 5-14 years More than 120 million childrens around the world 44million childrens in India U.P. has the highest number of child labours More than 80% are employed in villages, that also in agriculture and non-formal activities like livestock rearing, fishing etcCHILD ABUSE A recent study on Child Abuse: India 2007, conducted by Ministry of Women and Child development (GOI) revealed that across different kinds of abuse, it is young children, in the 5-12 year group, who are most at risk of abuse and exploitation. PHYSICAL ABUSE Two out of every three children were physically abused. Out of 69% children physically abused 54.68% were boys. Over 50% children were being subjected to one or the other form of physical abuse Out of those children physically abused in family situations, 88.6% were physically abused by parents. The State of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar and Delhi have almost consistently reported higher rates of abuse in all forms as compared to other states. 50.2% children worked seven days a week. FACTS According to the Indian census of 1991, there are 11.28 million working children under the age of fourteen years in India. Over 85% of this child labour is in the countrys rural areas, working in agricultural activities such as fanning, livestock rearing, forestry and fisheries. The worlds highest number of working children is in India. ILO estimates that 218 million children were involved inchild labour in 2004, of which 126 million were engaged in hazardous work. The Hindi belt, including Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh, account for 1.27 crore working children in the country, engaged in both hazardous and non-hazardous occupations and processes. Over 19 lakh child labourers in the 5-14 age group are in Uttar Pradesh. REASONS Poverty is the main push factor Parental illiteracy Absence of universal compulsory Primary education Ignorance of the parents about the adverse consequences of child labour Lack of educational facilities or poor quality of education Employers prefer children as they constitute cheap labour and they are not able to organize themselves against exploitation LAWS OF CHILD LABOUR IN INDIA The Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act 1986 prohibits employment of children below the age of 14 years in any factory or any hazardous employment Any person who employs child he is liable for punishment with imprisonment for 3 month which can be
extended to 1 year or 20,000Rs fine It Provides free and compulsory education for all children until they complete the age of 14 years Many beggar childrens and other similar forms of forced labour are prohibited and violation of this provision shall be an offence punishable in accordance with law. CONSEQUENCES Adult unemployment Depreciation in wages Increased abuse of children Increased bottlenecks in the development process Wasted human resources Wasted human talents and skills Suffer injuries and illness from work Not accessible to education ..
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lab Assignment-3: Rahul KataraDocument5 pagesLab Assignment-3: Rahul KataraTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Sneha Priya Enrollno.: 19114082: Part 1: Reading Datasheet (DONE)Document6 pagesName: Sneha Priya Enrollno.: 19114082: Part 1: Reading Datasheet (DONE)Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- RavjotDocument4 pagesRavjotTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
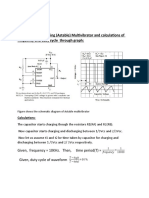
- Lab Assignment 3: Part-2: Design of Free-Running (Astable) Multivibrator and Calculations of Frequency and Duty Cycle Through GraphDocument8 pagesLab Assignment 3: Part-2: Design of Free-Running (Astable) Multivibrator and Calculations of Frequency and Duty Cycle Through GraphTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1: Ravjot SinghDocument4 pagesProblem 1: Ravjot SinghTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief Description About The Basic Operation of The IC:: NE555 PinoutsDocument12 pagesA Brief Description About The Basic Operation of The IC:: NE555 PinoutsTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Assignment-3: Rahul KataraDocument5 pagesLab Assignment-3: Rahul KataraTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- RavjotDocument4 pagesRavjotTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3 ReportDocument12 pagesLab 3 ReportTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Report DevanshuDocument4 pagesReport DevanshuTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1: Ravjot SinghDocument4 pagesProblem 1: Ravjot SinghTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhupendra MalakarDocument3 pagesBhupendra MalakarTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Part-2: Report On Lab 3 ECN-252-2021 19114002Document4 pagesPart-2: Report On Lab 3 ECN-252-2021 19114002Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- C.) Write Code For Stencil Pattern (A) Where One Value Approximates All The Other 8 Values of The Tile. A.)Document5 pagesC.) Write Code For Stencil Pattern (A) Where One Value Approximates All The Other 8 Values of The Tile. A.)Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab-6 ECN-252: Aman Sinha 19116007 Batch-O5 Part-1Document4 pagesLab-6 ECN-252: Aman Sinha 19116007 Batch-O5 Part-1Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhanu Prasanth BasavalaDocument7 pagesBhanu Prasanth BasavalaTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- HW1Document5 pagesHW1Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tcad Assignment: Submitted By: Tanishq Varshney (20534010) & Upadesh Kumar (20534011) Group 3Document7 pagesTcad Assignment: Submitted By: Tanishq Varshney (20534010) & Upadesh Kumar (20534011) Group 3Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Clean Room Is Required For Improving The Yield of A Fabricated ICDocument1 pageClean Room Is Required For Improving The Yield of A Fabricated ICTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- HW1 2Document7 pagesHW1 2Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Device 1 Plot 2Document1 pageDevice 1 Plot 2Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Signed Multiplier & Comparator: Arush SharmaDocument8 pagesSigned Multiplier & Comparator: Arush SharmaTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- ECN-252 Lab 6 - Lakshya Taragi (19111022 - O6) : Part 1: Implement The Bough-Wooley Multiplier CircuitDocument7 pagesECN-252 Lab 6 - Lakshya Taragi (19111022 - O6) : Part 1: Implement The Bough-Wooley Multiplier CircuitTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document3 pages1Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Logical EffortDocument22 pagesLogical EffortShekhar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial7 2ndnov2020Document1 pageTutorial7 2ndnov2020Tanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Institute of Technology RoorkeeDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Technology RoorkeeTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- IITR TemplateDocument5 pagesIITR TemplateTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial: CMOS Combinational Circuit DesignDocument6 pagesTutorial: CMOS Combinational Circuit DesignTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Set-B: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, RoorkeeDocument2 pagesSet-B: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, RoorkeeTanishq VarshneyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Myth of The Powerless State - Linda WeissDocument135 pagesThe Myth of The Powerless State - Linda WeissGabriel Furtado100% (1)
- Nationalizing Education in PakistanDocument24 pagesNationalizing Education in PakistanSuneel MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- SecretariesListEnglishl 18-05-2016Document4 pagesSecretariesListEnglishl 18-05-2016tipu1sultan_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Community DevelopmentDocument14 pagesCommunity DevelopmentAsim Fazal SubhanPas encore d'évaluation
- RA SocialWork Pagadian Aug2019 PDFDocument39 pagesRA SocialWork Pagadian Aug2019 PDFPhilBoardResultsPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Welfare EssayDocument1 pageAnimal Welfare EssayRovic MelladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Profile - Sarvoday Seva Charitable TrustDocument3 pagesProfile - Sarvoday Seva Charitable TrustKiran VyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 Reward SystemDocument26 pagesLesson 6 Reward Systemmark turbanadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Marxist Theory of Citizenship - Anthony GiddensDocument4 pagesMarxist Theory of Citizenship - Anthony GiddensRamita UdayashankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Urban Poverty in IndiaDocument11 pagesUrban Poverty in IndiaBushra HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Calalang V WilliamsDocument2 pagesCalalang V WilliamsRoby Ng100% (1)
- County Auditor Government Cod1Document3 pagesCounty Auditor Government Cod1Rodolfo BecerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Federalism Pros and ConsDocument4 pagesFederalism Pros and ConsNicole Bridjette AgordePas encore d'évaluation
- Women Have Been Tricked Into Living Like MenDocument17 pagesWomen Have Been Tricked Into Living Like MenIwpPas encore d'évaluation
- General Appropriations BudgetDocument14 pagesGeneral Appropriations BudgetMNCOOhioPas encore d'évaluation
- Bharat Nirman: Government of India Ministry of Rural DevelopmentDocument40 pagesBharat Nirman: Government of India Ministry of Rural DevelopmentMegha LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Police Injury Pensions - Home Office Circular 003/2004Document5 pagesPolice Injury Pensions - Home Office Circular 003/2004wdtkPas encore d'évaluation
- The African Report On Violence Against Children - FinalDocument134 pagesThe African Report On Violence Against Children - FinalsofiabloemPas encore d'évaluation
- Welfare StateDocument11 pagesWelfare StateMuhammad Majid Altaf100% (1)
- History of Social Work in Europe.Document34 pagesHistory of Social Work in Europe.enclonashynePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On EV:CVDocument13 pagesNotes On EV:CVlaraibPas encore d'évaluation
- Seasons Greetin S: Department of Children & Families Monthly UpdateDocument5 pagesSeasons Greetin S: Department of Children & Families Monthly UpdateMark ReinhardtPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity and Fairness in Health Care 2015Document35 pagesEquity and Fairness in Health Care 2015Mochamad Rizki FirmansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions On The Grant of Casual Leave and Special Casual LeaveDocument20 pagesInstructions On The Grant of Casual Leave and Special Casual Leaveshiva412199050% (2)
- Draft Parawise Reply Seeds CertificationDocument3 pagesDraft Parawise Reply Seeds CertificationmandarPas encore d'évaluation
- BCDA V COADocument3 pagesBCDA V COADanielle LimPas encore d'évaluation
- PHSO Update and Outcome 26 Feb 18Document8 pagesPHSO Update and Outcome 26 Feb 18Parliamentary Ombudsman (PHSO) TravestyPas encore d'évaluation
- HC WorkshopDocument27 pagesHC WorkshopVlad SandulescuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012fin MS307Document4 pages2012fin MS307Pa RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- JVW Welcome Poland Gazeta Wyborcza 131006Document3 pagesJVW Welcome Poland Gazeta Wyborcza 131006BruegelPas encore d'évaluation