Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Human Growth Hormone
Transféré par
Michael BriscoeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Human Growth Hormone
Transféré par
Michael BriscoeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Human Growth Hormone: effects on Growth and Development HGH is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction
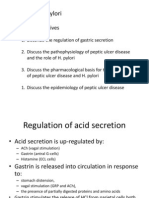
and regeneration in humans and other animals. It is a mitogen specific to only some kinds of cells. It is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. Secretion of HGH in the APG is regulated by neurosecretory neuclei in the hypothalamus. These cells release the peptides growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH aka somatocrinin) and growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH aka somatostatin) into the hypophyseal portal venous blood surroining the pituitary. The release of HGH Is primarily determined by the balance of these two hormones which is in turn affected by physiological stimulators including diet, exercise and sleep) and inhibitors such as fatty acids ..(significance of somatostatin with FFA digestion) Somatotropic cells in the lateral wing of the APG secrete GH in a pulsatile manner in response to these stimulatory compounds facilitated through the hypothalamus. The largest and most predictable of these GH peaks about an hour after onset of sleep. Otherwise large variation between days and individuals. A number of factors affect GH secretion: Age ie increased glandular secretion throughout onset and durstion of puberty 700micrograms/day and 400 in adults Gender Diet Exercise Stress Interplay with other hormones Stimulators of growth hormone secretion: 1. GHRH somatocrinin 2. Ghrelin 3. Sex hormones increased androgens (testis in males and adrenal cortex in females) also estrogen 4. Deep sleep 5. Fasting 6. Vigorous exercise Inhibitors of growth hormone secretion include: 1. GHIH somatostatin 2. Circulating concentrations of IGF-1 3. Hyperglycemia 4. Dihydrotestosterone
Function Effects are general described as anabolic. Increased height during childhood is the most recognized effect of GH and appears to be stimulated by two mechanisms: Binds to receptors on target cells and activates the MAP/ERK pathway thereby stimulating division and multiplication of chondrocytes in cartilage. Though JAK-STAT signaling pathway: production of IGF-1 by specifically targeting the liver where this is produced. IGF-1 has a variety of growth stimulating effects on a variety of tissues. Other effects: Increased calcium retention, strengthening and increasing bone mineralization Increased muscle mass through sarcomere hyperplasia Increased protein synthesis stimulates growth of all internal organs excluding the brain stimulates immune system
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Physiology GrowthhormoneDocument7 pagesPhysiology GrowthhormoneAndrianna NastasyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior PituitaryDocument41 pagesAnterior Pituitaryhamid100% (1)
- Notes For Lecture 9Document11 pagesNotes For Lecture 9BelPas encore d'évaluation
- Physio 5Document15 pagesPhysio 5amjadPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology, Growth Hormone: February 2018Document7 pagesPhysiology, Growth Hormone: February 2018Tom HollandPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1: The Endocrine System: Growth HormoneDocument1 pageModule 1: The Endocrine System: Growth HormoneZeina SharkasPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth Hormone AssignmentDocument2 pagesGrowth Hormone AssignmentIsabelle Ruth HawkePas encore d'évaluation
- Growth HormoneDocument2 pagesGrowth HormoneEvi Marina SiraitPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Pituitary Hormonesthis.8732849.PowerpointDocument24 pages1 Pituitary Hormonesthis.8732849.Powerpointmustafa aliPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument27 pagesBSC Anterior Pituitary HormonesThalapathy PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IV CompleteDocument116 pagesUnit IV CompleteAlok RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 HZ Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones HZDocument20 pages2 HZ Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones HZAmirabbas SaffariPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology 1STDocument10 pagesPhysiology 1STGW LEGENDPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior Pituitary (Autosaved)Document33 pagesAnterior Pituitary (Autosaved)BABLU GAMINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Pro Life GHRDocument16 pagesPro Life GHRHewr HawarPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.0 Pitutitary Gonadotrophin and ProlactinDocument46 pages5.0 Pitutitary Gonadotrophin and ProlactinHomeground entertainmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormonal Regulation of Growth: Prof. Dr. Supartono, M.S Department Chemistry Semarang State UniversityDocument63 pagesHormonal Regulation of Growth: Prof. Dr. Supartono, M.S Department Chemistry Semarang State UniversityBella FebrianPas encore d'évaluation
- SomatotrophinDocument42 pagesSomatotrophinSaqib SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Growth: Normal PhysiologyDocument41 pagesDisorders of Growth: Normal Physiologyal3qeelahPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Growth HormoneDocument28 pagesDisorders of Growth Hormoneamachreeobomate90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Growth HormonesDocument42 pagesGrowth Hormonessaputra tri nopianto100% (1)
- Pharmacology: EndocrineDocument210 pagesPharmacology: EndocrineSharifa Darayan100% (1)
- Endocrine DrugsDocument172 pagesEndocrine DrugsAlvim Tiel FactorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pituitary Gland: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument14 pagesPituitary Gland: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec-3 The Pituitary Gland-IDocument37 pagesLec-3 The Pituitary Gland-IMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaalePas encore d'évaluation
- Function of Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesFunction of Endocrine SystemCeelin RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Caso 50Document4 pagesCaso 50Laura ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Peptide Hormone Growth Cell Mitogen Amino Acid Polypeptide Somatotropic Cells Anterior Pituitary Stress Hormone IGF-1 Prescription DrugDocument1 pagePeptide Hormone Growth Cell Mitogen Amino Acid Polypeptide Somatotropic Cells Anterior Pituitary Stress Hormone IGF-1 Prescription DrugIoana PiticarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.GH Use UseDocument23 pages6.GH Use UseRuvarashe MutadzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - Hormonal AgentsDocument64 pages10 - Hormonal Agentsnica velanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 9 - Stomatostatin...Document11 pagesLec 9 - Stomatostatin...rajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Growth Hormone GuideDocument18 pagesHuman Growth Hormone GuidemgmgmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of Growth and Growth Factors Alrashid SU 2023 AKADocument26 pagesPhysiology of Growth and Growth Factors Alrashid SU 2023 AKARaghad AlPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth Hormone: Kartika PrahasantiDocument11 pagesGrowth Hormone: Kartika PrahasantiAlfi SyahrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 6.1 and 6.2 Ant Pituitary GH and Post Pituitary NOTESDocument7 pagesPhys 6.1 and 6.2 Ant Pituitary GH and Post Pituitary NOTESsine summsun PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- endocrine فسيولوجياDocument49 pagesendocrine فسيولوجياAUDEH AHMADPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Pituitary HormonesDocument18 pages4 Pituitary HormonesRana AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)Document31 pagesBiochemistry of Hormones (Part 1)arun231187100% (1)
- Endocrine 3Document14 pagesEndocrine 3Abdikadir XaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Growth HormoneDocument31 pagesHuman Growth HormoneGhadeer Jad100% (2)
- Hormones and Nutrient PartitioningDocument36 pagesHormones and Nutrient Partitioningbwade2_916499061Pas encore d'évaluation
- k.3b Hormone Control of GrowthDocument22 pagesk.3b Hormone Control of GrowthJane Andrea Christiano DjianzoniePas encore d'évaluation
- K9, FL, Hormone Control of Growth GDS-K9-2Document23 pagesK9, FL, Hormone Control of Growth GDS-K9-2Mari BelajarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fazio Log YeDocument31 pagesFazio Log YeBianca NegrutPas encore d'évaluation
- Pituitary and ThyroidDocument54 pagesPituitary and ThyroidSaif AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormone Control of Growth: Dedi Ardinata Yetty MachrinaDocument23 pagesHormone Control of Growth: Dedi Ardinata Yetty MachrinaAgus Salim BhrPas encore d'évaluation
- Hormone Control of GrowthDocument23 pagesHormone Control of GrowthFira TasyaPas encore d'évaluation
- k.3b Hormone Control of GrowthDocument22 pagesk.3b Hormone Control of GrowthWinson ChitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physio Endo 5Document32 pagesPhysio Endo 5Hoth HothPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulation of Growth Hormone SecretionDocument4 pagesRegulation of Growth Hormone SecretionIbrahim Sugiyono100% (1)
- The Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument27 pagesThe Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewEdelrose LapitanPas encore d'évaluation
- HormonesDocument29 pagesHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- Igh 1Document4 pagesIgh 1Aisle Malibiran PalerPas encore d'évaluation
- Anterior and Posterio Pituitary GlandDocument7 pagesAnterior and Posterio Pituitary GlandAnny AlvrzPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Glands Are Glands of TheDocument9 pagesEndocrine Glands Are Glands of ThextinebadzPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Growth Hormone Secretagogue Stack: Special Report: by Gareth ThomasDocument13 pagesHuman Growth Hormone Secretagogue Stack: Special Report: by Gareth ThomasAdiantoWinataTjiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine SystemDocument69 pagesEndocrine SystemDivya JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and ReleaseDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and Releasedr_saleh77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hormone Balance: How To Reclaim Hormone Balance , Sex Drive, Sleep & Lose Weight Now: The Blokehead Success SeriesD'EverandHormone Balance: How To Reclaim Hormone Balance , Sex Drive, Sleep & Lose Weight Now: The Blokehead Success SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Grow Taller After Puberty Exercise Routine to Follow 4th EditionD'EverandGrow Taller After Puberty Exercise Routine to Follow 4th EditionÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Workshop On PharmacokineticsDocument3 pagesWorkshop On PharmacokineticsMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- (Nor) Is The (Murky-Side) (North of The Hamptons) of (Northwards), (Nor Your) (Oxygen) (Sloppy) inDocument1 page(Nor) Is The (Murky-Side) (North of The Hamptons) of (Northwards), (Nor Your) (Oxygen) (Sloppy) inMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Describe How Cells GrowDocument1 pageDescribe How Cells GrowMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Hip and ThighDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Hip and ThighMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- A Diagnosis of Diabetes Is Made If The Fasting PlasmaDocument1 pageA Diagnosis of Diabetes Is Made If The Fasting PlasmaMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Countercurrent MultiplicationDocument4 pagesCountercurrent MultiplicationMichael Briscoe100% (1)
- H PyloriDocument20 pagesH PyloriMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Food IdeasDocument1 pageFood IdeasMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 - Week 4 - Cell CycleDocument3 pagesPhase 1 - Week 4 - Cell CycleMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 - Week 4 - Bleeding and ShockDocument2 pagesPhase 1 - Week 4 - Bleeding and ShockMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Describe How Cells GrowDocument1 pageDescribe How Cells GrowMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Medical MnemonicsDocument2 pagesMedical MnemonicsMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 - Week 1 - The Skin PPPDocument15 pagesPhase 1 - Week 1 - The Skin PPPMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- BP CaseDocument3 pagesBP CaseMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- The Clotting Cascade - Responses To Vascular InjuryDocument1 pageThe Clotting Cascade - Responses To Vascular InjuryMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Describe How Cells GrowDocument1 pageDescribe How Cells GrowMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Public Health PBLDocument18 pagesPublic Health PBLMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Hip and ThighDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Hip and ThighMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Common Methods of Contraception Methods With No User Failure Method Effectiveness How It Works Advantages DisadvantagesDocument5 pagesCommon Methods of Contraception Methods With No User Failure Method Effectiveness How It Works Advantages DisadvantagesMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Limbs and BackDocument1 pageLimbs and BackMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 RevisionDocument3 pagesPhase 1 RevisionMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 RevisionDocument3 pagesPhase 1 RevisionMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- The Volume of Blood in An Average Sized Person Is Approximately 5.5LDocument2 pagesThe Volume of Blood in An Average Sized Person Is Approximately 5.5LMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 1 RevisionDocument3 pagesPhase 1 RevisionMichael BriscoePas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPclaidelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Unilever Lifebuoy in India Implementing The Sustainability PlanDocument14 pagesUnilever Lifebuoy in India Implementing The Sustainability PlanMira Sesaria50% (2)
- Angina PectorisDocument17 pagesAngina PectorisRakesh Reddy100% (1)
- Cell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell Types Animal Tissue ReviewerShane LaluPas encore d'évaluation
- HED 2007 Cellular Molecular, Microbiology & GeneticsDocument16 pagesHED 2007 Cellular Molecular, Microbiology & Geneticsharyshan100% (1)
- Systema Let Every BreathDocument82 pagesSystema Let Every BreathB Agel100% (1)
- Hemorrhoid - Pathophysiology and Surgical ManagementA LiteratureDocument7 pagesHemorrhoid - Pathophysiology and Surgical ManagementA LiteratureIndra YaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Chapter of Assessment Made Incredibly Easy! 1st UK EditionDocument28 pagesSample Chapter of Assessment Made Incredibly Easy! 1st UK EditionLippincott Williams and Wilkins- Europe100% (1)
- Adobe Scan Jul 28, 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 28, 2023Krishna ChaurasiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Retention of Maxillofacial Prosthesis Fayad PDFDocument7 pages11 Retention of Maxillofacial Prosthesis Fayad PDFMostafa Fayad50% (2)
- Tobacco Cessation PlanDocument11 pagesTobacco Cessation PlanEsteban García EcheverryPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Meeting Brochure 2016 PDFDocument4 pagesLiver Meeting Brochure 2016 PDFManas GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- A Color Atlas of Poultry Diseases by J.L VegadDocument131 pagesA Color Atlas of Poultry Diseases by J.L VegadAbubakar Tahir Ramay95% (63)
- Clinical Practice Guidelines - 2017Document54 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines - 2017Cem ÜnsalPas encore d'évaluation
- LAN Party Skate Park by Shane Jesse ChristmassDocument91 pagesLAN Party Skate Park by Shane Jesse ChristmassPatrick TrottiPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Johannesburg MPH Reasearch Questionnaire Final Version JMDocument9 pagesUniversity of Johannesburg MPH Reasearch Questionnaire Final Version JMYvonne MankolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantifying The Health Economic Value AsDocument1 pageQuantifying The Health Economic Value AsMatiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of CENTRAL VENOUS PRESSURE Via A TransducerDocument22 pagesMeasurement of CENTRAL VENOUS PRESSURE Via A TransducerJasleen KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifying Giant Cell Lesions A Review.21Document5 pagesClassifying Giant Cell Lesions A Review.21shehla khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nowadays Young People Spend Too Much of Their Free Time in Shopping MallsDocument3 pagesNowadays Young People Spend Too Much of Their Free Time in Shopping MallsYacine BenHmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hempseed As A Nutritional Resource: An Overview: J.C. CallawayDocument8 pagesHempseed As A Nutritional Resource: An Overview: J.C. CallawayCarmen Yuliana GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Surgical Rescue in Medical PatientsDocument11 pages2018 Surgical Rescue in Medical PatientsgiseladlrPas encore d'évaluation
- Bentonite MSDSDocument10 pagesBentonite MSDSkhai rulePas encore d'évaluation
- Conduction Blocks in Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective StudyDocument6 pagesConduction Blocks in Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective StudyJack JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- 8mkebook PDFDocument300 pages8mkebook PDFVanja Vujovic100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputRy Pablo83% (41)
- Full Text of RA 7719Document4 pagesFull Text of RA 7719camz_hernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Hydroxide, Root ResorptionDocument9 pagesCalcium Hydroxide, Root ResorptionLize Barnardo100% (1)
- Beauty Care 1st Summative TestDocument4 pagesBeauty Care 1st Summative TestLlemor Soled SeyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Tendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesTendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsSylvia GracePas encore d'évaluation