Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
16 ARDS - Nursing Care Management
Transféré par
Tisha CarretteDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
16 ARDS - Nursing Care Management
Transféré par
Tisha CarretteDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
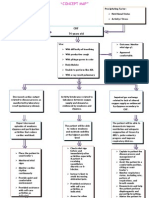
ARDS MANAGEMENT
1. Nurse patient in ICU as ARDS is a potentially life threatening complication and requires high quality one-on-one nursing care 2. Position client in a Semi or High Fowlers position (unless contraindicated) for maximum lung expansion 3. Assess respiration rate, rhythm and depth, presence of nasal flaring, use of accessory muscle of respiration as these are key indicators of clients inability to self-ventilate 4. Assess for signs such as cyanosis in lips, poor capillary refill, changes in level of consciousness as these would indicate a decrease in tissue perfusion 5. Auscultate for adventitious breath sounds such as crackles and rhonchi as they indicated the presence of fluid in air spaces and inability of lungs to adequately ventilate 6. Place client on pulse oximeter to monitor oxygenation saturation 7. Administer 100% humidified oxygen via a facemask to maintain PaO2 of 60mmHg and SaO2 of greater than 90% 8. Monitor CBC with emphasis on Hb as decreased Hb indicates need for blood replacement to prevent fatigue that will impact clients ability to self ventilate 9. Administer dopamine as prescribed to prevent hypovolemic shock 10.Assess client for low fluid levels in blood blood pressure, pulse, Monitor V/S with emphasis of blood pressure and pulse as an decrease in bp could indicate dopamine side effect along with headache 11.Administer bronchodilators such as Ventolin and epinephrine to increase the diameter of the airways an improved in air entry, exit 12.Administer corticosteroids such as methylprednisone to reduce and control inflammation 13.??Administer diuretics such as Lasix to help reduce pulmonary edema 14.Monitor electrolytes to assess serum levels and institute measures to correct imbalances which may be caused diuretic therapy
15.Place client on cardiac monitoring to monitor for any dysrhythmias 16.Maintain strict I/O monitoring as patient is at risk for hypovolemia due to movement of fluids from vascular to interstitial spaces of lungs 17.Assess ABGs PaO2 and PaCO2 and pH to monitor the adequacy of alveoli ventilation and gas exchange functions 18.Assist with moving client to mechanical ventilation if Pa02 is less than 60 mmHg and PaC02 is greater than 50 mmHg, pH is greater 7.30 19.Suction client as necessary to remove secretions and keep airway clear 20.Take patients weight daily to determine fluid and nutrition status 21.Ensure nutritive needs are met as indicated to maintain energy and muscle functions 22.Assist with obtaining chest x-rays of client to determine extent of lung involvement as the condition is made worse by increase alveoli damage 23.Stay with the patient and provide nursing care with a confident attitude at all times as nurses presence and attitude helps to allay clients anxiety which may intensify condition 24.Use aseptic techniques where necessary eg during suctioning to prevent cross contamination 25.Appropriate chest physiotherapy to loosen secretions and prevent stasis of fluid which is a medium for bacteria growth
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Clinical Log Term II PDFDocument9 pagesClinical Log Term II PDFPriscilla S100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureDocument5 pages2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureLovely CacapitPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map 2Document1 pageConcept Map 2lanrevoicePas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Geriatric Optometry and Pediatric OptometryDocument2 pagesGeriatric Optometry and Pediatric OptometryRony MathewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument31 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndromegretchen marie100% (1)
- Name: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaDocument2 pagesName: L.J.A AGE: 20 Years Old SEX: Male CC: Cough and DOB Admitting/Working Diagnosis: AsthmaMae Therese B. MAGNOPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument34 pagesCase StudyBSNNursing101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Document51 pagesLecture - 7 - Work - Capacity, - Stress - and - Fatigue (Autosaved)Aizat RomainoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Step PPD FormDocument1 page2 Step PPD FormWilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Med Surg (Oncology)Document169 pagesMed Surg (Oncology)DardarConstantinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Heart Failure ChronicDocument26 pagesNursing Care Plan For Heart Failure ChronicbrantPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pulmonary Edema PDFAsmaa100% (1)
- NCP1 CHFDocument2 pagesNCP1 CHFapi-27015740100% (5)
- Care of Ventilator PatientDocument10 pagesCare of Ventilator PatientNilesh JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7Document9 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output RM 7api-283470660Pas encore d'évaluation
- Child - AsthmaDocument2 pagesChild - AsthmaCleoanne Gallegos0% (1)
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Finished 2Document6 pagesConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPryzaimaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Cad ElectiveDocument1 pageNCP Cad ElectivejoegePas encore d'évaluation
- Premature Ventricular ContractionDocument17 pagesPremature Ventricular Contractiondr_jofrilPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map 360Document6 pagesConcept Map 360api-273469220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity Intoleranceravenshadow100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisPas encore d'évaluation
- Peds Concept MapDocument5 pagesPeds Concept Mapapi-496323326Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesNursing Care PlanjamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zaroxolyn MetolazoneDocument1 pageZaroxolyn MetolazoneCassiePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocument7 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahPas encore d'évaluation
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance-Nursing Care Plan For COPDRnspeakcom100% (1)
- DKA Concept MapDocument2 pagesDKA Concept MapJanetPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument41 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocument4 pagesAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingDocument3 pagesNCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingCedie BarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetDocument2 pagesCarla Hernandez Clinical WorksheetJasmyn RosePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykymsh_kimPas encore d'évaluation
- ThyroidectomyDocument11 pagesThyroidectomySherina W. EddingPas encore d'évaluation
- Course TaskDocument1 pageCourse TaskNestor CabacunganPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaPas encore d'évaluation
- CroupDocument10 pagesCroupEl Justinson Puspos100% (1)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasPas encore d'évaluation
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardGeevee Naganag VentulaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pages3 NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionSteffi MurielPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesPre-Lab Questions:: Deep Breathing & Coughing Exercises Oxygen TherapyaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxy Act 2Document5 pagesOxy Act 2Joshua DauzPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice (Kap) Study OnDocument52 pagesKnowledge, Attitude and Practice (Kap) Study OnQazi Muhammad IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Departm Ent of Education: R e P U B Lic of Tlje JH JilippineffDocument7 pagesDepartm Ent of Education: R e P U B Lic of Tlje JH JilippineffJoyce CarilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Characteristics of Intellectual Disabilities - Mental Disorders and Disabilities Among Low-Income Children - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesClinical Characteristics of Intellectual Disabilities - Mental Disorders and Disabilities Among Low-Income Children - NCBI BookshelfArhatya MarsasinaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Modified Supine Position Facilitates Bladder Function in Patient Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary InterventionDocument8 pagesA Modified Supine Position Facilitates Bladder Function in Patient Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary InterventionVelicia MargarethaPas encore d'évaluation
- Burt and Eklund's Dentistry, Dental Practice, and The Community - 7th EditionDocument5 pagesBurt and Eklund's Dentistry, Dental Practice, and The Community - 7th Edition鄭雅勻Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Souvenir GipsDocument143 pagesFinal Souvenir GipsSagar SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4D CT With Respiratory GatingDocument2 pages4D CT With Respiratory GatingLaura Karina Sanchez ColinPas encore d'évaluation
- Louela C. Acedera, RN, MANDocument18 pagesLouela C. Acedera, RN, MANelle seigdenPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech Language Pathology (SLP)Document6 pagesSpeech Language Pathology (SLP)Shariq MPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle:: Sample Considerations and Special ProceduresDocument97 pagesPrinciple:: Sample Considerations and Special Proceduresjustine anchetaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of Proteinuria in Preeclampsia and Its Predictive Role in Maternal and Neonatal OutcomesDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Proteinuria in Preeclampsia and Its Predictive Role in Maternal and Neonatal OutcomesimuhammadfahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rubella Quantitative IgG - IMMULITE 2000 SystemsDocument40 pagesRubella Quantitative IgG - IMMULITE 2000 SystemsMaria Ruth Moreno VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia Management For Pulmonary Hypertension PatientsDocument18 pagesAnesthesia Management For Pulmonary Hypertension PatientsAliNasrallahPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Deep Bite Using Myofunctional TrainerDocument3 pagesManagement of Deep Bite Using Myofunctional TrainerAmit SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- GRP2Document87 pagesGRP2Veronica ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Coma-Dr. AM IyagbaDocument53 pagesComa-Dr. AM IyagbaDr. Amb. Monday ZaccheausPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematoma: HaematomaDocument3 pagesHematoma: HaematomaBeeBeeSethPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis Treatment of Back Pain MedicationsDocument41 pagesDiagnosis Treatment of Back Pain Medicationsrabin1994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Receta Medica InglesDocument2 pagesReceta Medica InglesHannia RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Working With Addicted PopulationsDocument9 pagesWorking With Addicted PopulationsWhimsical BrunettePas encore d'évaluation
- WORKSHOP No 3Document21 pagesWORKSHOP No 3Jennifer Mabel Almeida BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Errors 2Document5 pagesErrors 2Anggun rahmi PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiopatias Congenitas FINALDocument17 pagesCardiopatias Congenitas FINALA.V.M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- HINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareDocument4 pagesHINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareHenie Louise HinanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash CartsDocument11 pagesCrash CartsJohanna AbellanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bell S Palsy Case StudyDocument4 pagesBell S Palsy Case StudyJAN ACCEL PAGADUANPas encore d'évaluation