Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NWS Cloud Chart
Transféré par
Mathew Gray0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
407 vues2 pagesCloud chart from NWS
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCloud chart from NWS
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
407 vues2 pagesNWS Cloud Chart
Transféré par
Mathew GrayCloud chart from NWS
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
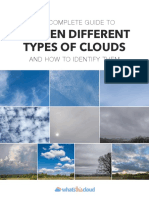
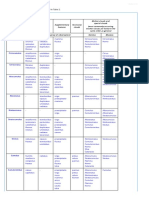
NOAA/NWS AND NASAS SKY WATCHER CHART
High Clouds
Typical Types: Cirrus (Ci), Cirrostratus (Cs), Cirrocumulus (Cc)
H1: Cirrus In the form of filaments, strands, or hooks
H2: Cirrus Dense, in patches or sheaves, not increasing, or with tufts
H3: Cirrus Often anvil shaped remains of a cumulonimbus
H4: Cirrus In hooks or filaments, increasing, becoming denser
H5: Cirrostratus Cirrus bands, increasing, veil below 45 elevation
H6: Cirrostratus Cirrus bands, increasing, veil above 45 elevation
H7: Cirrostratus Translucent, completely covering the sky
H8: Cirrostratus Not increasing, not covering the whole sky
H9: Cirrocumulus Alone or with some cirrus or cirrostratus
Middle Clouds
Typical Types: Altostratus (As), Altocumulus (Ac), Nimbostratus (Ns)
M1: Altostratus Mostly semi-transparent, sun or moon may be dimly visible
M2: Altostratus or Nimbostratus Dense enough to hide the sun or moon
M3: Altocumulus Semi-transparent, one level, cloud elements change slowly
M4: Altocumulus M5: Altocumulus M6: Altocumulus Lens-shaped, or continually One or more bands or layers, From the spreading of changing shape and size^ expanding, thickening cumulus or cumulonimbus
M7: Altocumulus One or more opaque layers, w/ altostratus or nimbostratus
M8: Altocumulus With cumulus-like tufts or turrets
M9: Altocumulus Chaotic sky, usually at several layers, maybe w/ dense cirrus
Low Clouds
Typical Types: Stratus (St), Stratocumulus (Sc), Cumulus (Cu), Cumulonimbus (Cb)
L1: Cumulus With little vertical extent
L2: Cumulus Moderate/strong vertical extent, or towering cumulus
L3: Cumulonimbus Tops not fibrous, outline not completely sharp, no anvil
L4: Stratocumulus From the spreading and flattening of cumulus*
L5: Stratocumulus Not from the spreading and flattening of cumulus
L6: Stratus In a continuous layer and/or ragged shreds
L7: Stratus Fractus and/or Cumulus Fractus Of bad weather
L8: Cumulus & Stratocumulus Not spreading, bases at different levels
L9: Cumulonimbus With fibrous top, often with an anvil
Mammatus Drooping underside of heavy, rain-saturated clouds
Tornado Formed by rotation of up and down drafts within thunderstorm
Wall Cloud Hanging from cumulus, possible tornado formation
Shelf Cloud Leading edge of fast moving frontal system
Wave Cloud Formed by strong horizontal winds over uneven terrain
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
http://www.nasa.gov http://education.nasa.gov/ http://scool.larc.nasa.gov
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service
www.noaa.gov www.weather.gov www.srh.noaa.gov/jetstream
*Photo copyright Kevin Larman ^Photo copyright Leigh R. Hilbert All other photos courtesy of NASA and Jim W. Lee, NWS.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cloud Formation and ImagesDocument10 pagesCloud Formation and ImagescontroladoraereoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading the Clouds: How You Can Forecast the WeatherD'EverandReading the Clouds: How You Can Forecast the WeatherÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- WMO, No. 407 International Cloud Atlas, Volume IIDocument212 pagesWMO, No. 407 International Cloud Atlas, Volume IIcavrisPas encore d'évaluation
- International Cloud Atlas Wmo PDFDocument212 pagesInternational Cloud Atlas Wmo PDFChirca Florentin100% (1)
- 2019 - Fly B - Step 4 - Quiz 1 - ATSC 113 PDFDocument7 pages2019 - Fly B - Step 4 - Quiz 1 - ATSC 113 PDFManan ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud ChartDocument2 pagesCloud Chartaitormr100% (1)
- Cloud ChartDocument2 pagesCloud ChartmcwoodlandsPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossary of Terms For Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageDocument23 pagesGlossary of Terms For Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageLee Yiu FaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloudwise RightDocument1 pageCloudwise RightSteven PentonPas encore d'évaluation
- CloudDocument7 pagesCloudphyu57457Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud FormationsDocument35 pagesCloud FormationsAbel MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- CloudsDocument84 pagesCloudsIoana IoanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Cloud Names, Shapes, and AltitudesDocument13 pagesCommon Cloud Names, Shapes, and AltitudesAshraf MambalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloudchart PDFDocument2 pagesCloudchart PDFvannaviettelPas encore d'évaluation
- Science - Types of Clouds BookletDocument16 pagesScience - Types of Clouds Bookletfayroozb100% (1)
- CumulusDocument4 pagesCumulusमान तुम्साPas encore d'évaluation
- Tab 3 PMI Cloud FormationsDocument40 pagesTab 3 PMI Cloud FormationsAhmed ElgoharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds and Precipitation NewDocument16 pagesClouds and Precipitation NewAkash GujjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Meteorology Module 5Document14 pagesMeteorology Module 5George AntonescuPas encore d'évaluation
- ABE 137 CloudsDocument12 pagesABE 137 CloudsJackielou PachesPas encore d'évaluation
- CloudsDocument20 pagesCloudsRagini khargPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Clouds. Stratus Stratocumulus NimbostratusDocument28 pagesTypes of Clouds. Stratus Stratocumulus NimbostratusMircea PetcuPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Security - Types of Clouds - Assignment - FinalDocument5 pagesWater Security - Types of Clouds - Assignment - FinalHrushikesh Pawar 10thBPas encore d'évaluation
- Project in Science IV: Chloe Gabriel B. Advincula Grade 4 - YttriumDocument7 pagesProject in Science IV: Chloe Gabriel B. Advincula Grade 4 - YttriumRiz Bolofer AdvinculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud FormationDocument19 pagesCloud FormationBe Len DaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Identification PowerpointDocument28 pagesCloud Identification Powerpointapi-298791525Pas encore d'évaluation
- CloudsDocument29 pagesCloudshp.harsh.patil.09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds: by Jevelyn SumalinogDocument36 pagesClouds: by Jevelyn SumalinogBe Len DaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds Types and ExtentDocument5 pagesClouds Types and ExtentzoePas encore d'évaluation
- CloudsDocument14 pagesCloudsPilot MrPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Classification1Document33 pagesCloud Classification1WORADA DUANGJAIPas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds DR - BnsDocument96 pagesClouds DR - BnsBharath BhosePas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Content PicsDocument26 pagesCloud Content PicsShriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds: General SummaryDocument26 pagesClouds: General SummaryShriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Meteo PPLDocument4 pagesMeteo PPLFahmi PrayogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds: The Airline Pilots Forum & ResourceDocument10 pagesClouds: The Airline Pilots Forum & ResourceTanvir HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud, Types & Its Formation: Introduction To CloudsDocument14 pagesCloud, Types & Its Formation: Introduction To CloudsUsama UsamaArqemPas encore d'évaluation
- 'Clouds' With YouDocument21 pages'Clouds' With YouMamunPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Week 29 - 20231102 - 044925 - 0000Document11 pagesScience Week 29 - 20231102 - 044925 - 0000aaron.lima736Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clouds How To Distinguish The Different Types of CloudsDocument11 pagesClouds How To Distinguish The Different Types of CloudsMahesh IngalePas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring WeatherDocument40 pagesMeasuring WeatherLinda StrydomPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Read CloudsDocument6 pagesHow To Read CloudsSherryPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Cloud Names, Shapes, and AltitudesDocument13 pagesCommon Cloud Names, Shapes, and AltitudesFabo GrPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Characteristics Among The Various Types of CloudsDocument2 pagesDifferent Characteristics Among The Various Types of CloudsmarkderekcharwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrus Clouds: Fibrous, Threadlike, White Feather Clouds of Ice Crystals, Whose Form Resembles Hair CurlsDocument9 pagesCirrus Clouds: Fibrous, Threadlike, White Feather Clouds of Ice Crystals, Whose Form Resembles Hair CurlsFelix Baracena Endico Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Formation & Its Types With Pictures-Meaning PDF-Geography NotesDocument9 pagesCloud Formation & Its Types With Pictures-Meaning PDF-Geography NotesSanjay Kumar ShahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Formation & CharacteristicDocument22 pagesCloud Formation & CharacteristicPaulo LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate Change and Risk ReductionDocument2 pagesClimate Change and Risk ReductionAQUINO ALODIA NOREENPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Types and RecognitionDocument11 pagesCloud Types and RecognitionBen KleinPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Cloud Information and Questions 1Document6 pages03 - Cloud Information and Questions 1api-292000448Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cirro Alto Nimbo Nimbus: Cloud TypeDocument2 pagesCirro Alto Nimbo Nimbus: Cloud TypeDjustine Faith Garcia RosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Clouds & Precipitation LectureDocument29 pagesChapter 6 - Clouds & Precipitation LectureGf MilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Assignment PDFDocument13 pagesCloud Assignment PDFhudabdullah95Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Cloud ClassificationsDocument3 pagesCommon Cloud ClassificationsGeorge AntonescuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Types of CloudsDocument7 pagesThe Types of CloudsChristopher Enriquez100% (1)
- CloudsDocument2 pagesCloudskarasuilyas123Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Nimbus Cloud Is A Cloud That Produces PrecipitationDocument2 pagesA Nimbus Cloud Is A Cloud That Produces PrecipitationMarianne FelixPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Identification GuideDocument40 pagesCloud Identification Guidemark twain100% (1)
- Types of Clouds4791649Document17 pagesTypes of Clouds4791649PhftPas encore d'évaluation
- Arlenes Cloud Types SlideshowDocument37 pagesArlenes Cloud Types SlideshowRiza Cloud100% (2)
- Zoia Zaidi 045 (IV)Document32 pagesZoia Zaidi 045 (IV)MaleehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Clouds4791649Document17 pagesTypes of Clouds4791649PhftPas encore d'évaluation
- Wmo Classification of Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageDocument68 pagesWmo Classification of Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageIrfan KuljuhPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud ClassificationDocument1 pageCloud ClassificationGustavo FerollaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wmo Classification of Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageDocument68 pagesWmo Classification of Clouds: Skystef'S Weather PageRyō SumyPas encore d'évaluation
- NWS Cloud ChartDocument2 pagesNWS Cloud ChartMathew GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Ist Utc Ist Utc Ist UtcDocument11 pagesIst Utc Ist Utc Ist UtcBharat BhushanPas encore d'évaluation
- CloudsDocument84 pagesCloudsIoana IoanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud WorksheetDocument3 pagesCloud Worksheetapi-234224768Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cloudwise LeftDocument1 pageCloudwise Leftsidadams2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas de NubesDocument220 pagesAtlas de NubesJuan Pablo Cortes GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation