Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Be Nazo Caine
Transféré par
dhungelsubhash8154Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Be Nazo Caine
Transféré par
dhungelsubhash8154Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
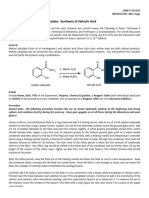
Preparation of Benzocaine by Acid-catalysed Esterification of a Carboxylic acid and Alcohol
(C9H11NO2 Mol.Wt. 165.2)
Theory:
When a carboxylic acid is heated with an alcohol in presence of mineral acid, e.g. sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid or hydrogen chloride gas, the hydrogen atom of the carboxyl group is replaced by an alkyl group in the resulting product is called an ester. Hence, the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to give an ester is known as esterification. When ethanol is heated with p-Amino benzoic acid in presence of Conc. sulphuric acid, Benzocaine (Ethyl p- amino benzoate) forms. This esterification is Fischer esterification.
H2N
p-Amino benzoic acid
+
Ethanol
H2SO4
+ H2 O Benzocaine(Ethyl p-amino benzoate)
Procedure:
Weigh and transfer 3.0g of p-Amino benzoic acid in a R.B. flask, then add 30ml of absolute ethanol. Shake well to dissolve the solid. Add 3ml of sulphuric acid dropwise into the ethanol-amino benzoic acid solution. A solid precipitates out of the solution. Attach a condenser to the round bottom flask , and set up the apparatus for heating under reflux. Connect the condenser to tap water supply. Heat the solution on a heating mantle under gentle reflux for approximately 30 minutes. Start heating slowly. Adjust the heat to keep the solution refluxing, but not boiling violently. Refluxing is confirmed when liquid droplets form at the tip of the condenser where the condenser is attached to the round bottom flask. If any solid precipitate remains after heating, take the condenser off of the round bottom flask and remove the round bottom flask from the heating mantle. Cool the solution at room temperature for 3-5 minutes. Add 9ml of absolute ethanol and 1.5ml of sulfuric acid (dropwise) to the round bottom flask containing the solution and precipitate. Reattach the condenser to the round bottom flask, and resume heating under gentle reflux until all of the solid has dissolved. It is very important for this experiment to succeed that ALL of the solids dissolve during this period. Once the solid is completely dissolved, continue heating the solution under gentle reflux for another 30 minutes.
Remove the round bottom flask from the heat source and allow the reaction mixture to cool to room temperature (7-10 minutes). Fill a 250mL beaker with 60ml of water and pour the cooled reaction mixture into the beaker. Basify the reaction mixture and water solution to a pH of about 8. To do this, calculate the approximate volume of 20% aqueous sodium carbonate required to neutralize the total amount of sulfuric acid you used (Usually between 27-36 ml). Slowly pour the calculated amount of 20% aqueous sodium carbonate into the beaker containing the reaction mixture and water solution. Be sure to add the sodium carbonate slowly as frothing occurs during neutralization . A solid should precipitate. This is crude benzocaine. Filter the mixture. Then transfer the crude benzocaine into a 125ml conical flask. Add about 60ml of water, then shake to mix properly. Heat the mixture to 60 C. Add minimum quantity of methanol (15-25ml) to dissolve the precipitates . Do not add more methanol than required. Then remove the flask from the heating source and allow the solution to cool to room temperature. It takes about 10 minutes. Cool the solution in an ice water bath for 15 minutes to complete crystallization of the benzocaine (white or colourless crystals) , then filter. Allow to dry the crystals. Finally calculate the yield and find out its m.p. (89.0 92)C.
Benzocaine
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Running The ReactionDocument3 pagesRunning The ReactionPaul ThiPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of Sodium Ethyl SulfateDocument2 pagesPreparation of Sodium Ethyl SulfateJoan Mas Torrent100% (2)
- Ph-C0 H + Meoh Ph.C0 Me + H 0: Methyl BenzoateDocument3 pagesPh-C0 H + Meoh Ph.C0 Me + H 0: Methyl BenzoateTrii SakttiPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Chemistry (CH258) Spring 2001 Gustavus Adolphus CollegeDocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry (CH258) Spring 2001 Gustavus Adolphus Collegefrankdebruin261Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of p-NitroacetanilideDocument5 pagesSynthesis of p-NitroacetanilideNuratiqah SalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs - How To Make Cocaine (Synthetically)Document5 pagesDrugs - How To Make Cocaine (Synthetically)jsssh80% (5)
- Synthesis of p-NitroacetanilideDocument5 pagesSynthesis of p-Nitroacetanilidechamanyusuff100% (2)
- Preparation of P-NitroanilineDocument11 pagesPreparation of P-NitroanilineRebecca Badour50% (2)
- 39. Dl-β-Phenylalanine - Gillespie - Organic Syntheses Collective 2 (1943) and Organic Syntheses 19 (1939)Document5 pages39. Dl-β-Phenylalanine - Gillespie - Organic Syntheses Collective 2 (1943) and Organic Syntheses 19 (1939)dextroenantiomer100% (1)
- Synthesis of p-Nitroaniline from AcetanilideDocument8 pagesSynthesis of p-Nitroaniline from AcetanilideMrinal SinghaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs - How To Make Cocaine Synthetically)Document4 pagesDrugs - How To Make Cocaine Synthetically)api-2618198977% (22)
- PCP Synthesis via Enamine IntermediateDocument24 pagesPCP Synthesis via Enamine Intermediatejolouis100% (2)
- Adipic Acid SynthesisDocument2 pagesAdipic Acid SynthesisPhạm Thành Lý100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Practical 301Document22 pagesOrganic Chemistry Practical 301geetesh waghela100% (1)
- BZP SynthesisDocument3 pagesBZP SynthesisScientology1Pas encore d'évaluation
- FL SopDocument45 pagesFL SopSara JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- CoAmm Procedures PDFDocument3 pagesCoAmm Procedures PDFtchoubzPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxidation of EthylbenzeneDocument1 pageOxidation of Ethylbenzeneaml_zgz82Pas encore d'évaluation
- AcetaminophenDocument4 pagesAcetaminophenSamushonga TendaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitration of Aniline in 3 StepsDocument4 pagesNitration of Aniline in 3 StepsvijpraPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Adrafinil & ModafinilDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Adrafinil & ModafinildjavahkPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter VII Organic Reagents in Inorganic and Organic Chemistry PDFDocument26 pagesChapter VII Organic Reagents in Inorganic and Organic Chemistry PDFtravellerfellowPas encore d'évaluation
- KokainDocument4 pagesKokainAhmet RecepPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnesium Stearate Analysis MethodsDocument7 pagesMagnesium Stearate Analysis MethodsAde YuLianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Sulfanilamide From NitrobenzeneDocument11 pagesSynthesis of Sulfanilamide From Nitrobenzenecrazybobblaskey33% (3)
- MacacDocument9 pagesMacacShawn NgPas encore d'évaluation
- MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY-I - Practicals PDFDocument25 pagesMEDICINAL CHEMISTRY-I - Practicals PDFAnit Dubey100% (1)
- Methylamine With EtohDocument16 pagesMethylamine With Etohjiskate77100% (1)
- AOAC 960.05-MolybdenumDocument1 pageAOAC 960.05-MolybdenumYến PhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Saponification of Methyl Salicylate 1Document2 pagesSaponification of Methyl Salicylate 1goyal8974Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mandelic Acid: 1. ProcedureDocument4 pagesMandelic Acid: 1. ProcedureKangal PothikPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1.6. Preparation of A Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin and Fabrication of A MouldingDocument2 pages5.1.6. Preparation of A Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin and Fabrication of A MouldingA MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving A Mystery Reaction, ReductionDocument3 pagesSolving A Mystery Reaction, ReductionEmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment One Preparation of Benzophenone Oxime: 1. ProcedureDocument5 pagesExperiment One Preparation of Benzophenone Oxime: 1. Procedurek uchePas encore d'évaluation
- Phenylacetic Acid From Benzyl CyanideDocument3 pagesPhenylacetic Acid From Benzyl CyanideriskobinskoPas encore d'évaluation
- Benzophenone OximeDocument20 pagesBenzophenone Oximek uchePas encore d'évaluation
- The Ex 3Document3 pagesThe Ex 3zFe 6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aim To Prepare and Submit Picric AcidDocument2 pagesAim To Prepare and Submit Picric Acidrajputanurag066Pas encore d'évaluation
- Recrystallization and Manufacture of Aspirin: The Practicum of Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesRecrystallization and Manufacture of Aspirin: The Practicum of Organic ChemistryEra MelaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2211 - Benzil From BenzoinDocument7 pages2211 - Benzil From Benzoindubstepo0% (1)
- Preparation of DibenzalacetoneDocument7 pagesPreparation of DibenzalacetoneHaiqal AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Redox TitrationDocument3 pagesRedox TitrationSubhamshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multistep Organic Synthesis from BenzaldehydeDocument4 pagesMultistep Organic Synthesis from BenzaldehydeNaveed SajidPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of 4-Amino-2,6-Dinitrophenol (Isopicramic Acid) and P-DDNP From Acetaminophen Version 1Document10 pagesSynthesis of 4-Amino-2,6-Dinitrophenol (Isopicramic Acid) and P-DDNP From Acetaminophen Version 1eduard morarPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020Document45 pagesCHEM F110 - Lab Manual - Nov 5-2020STUTI MATHUR100% (2)
- 2004 Chem 2OB3 Lab Manual - Experiment 4. Reactions of Carboxylic AcidsDocument4 pages2004 Chem 2OB3 Lab Manual - Experiment 4. Reactions of Carboxylic AcidsNstm3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of M-Nitroaniline From Sodium PolysulfideDocument2 pagesPreparation of M-Nitroaniline From Sodium Polysulfideprincesengar37Pas encore d'évaluation
- BenzoinDocument4 pagesBenzoinNurudeen IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Benzoic AcidDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Benzoic AcidVarun JogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Unit 3 NotesDocument12 pagesChem Unit 3 NotesMena Hashem100% (3)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresD'EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterD'EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisD'EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterD'EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidD'EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastD'EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastPas encore d'évaluation
- Recipes for Brewing Different Types of Beers and AlesD'EverandRecipes for Brewing Different Types of Beers and AlesPas encore d'évaluation
- FOOD & WINE Best Holiday Recipes: 100+ All-Time FavoritesD'EverandFOOD & WINE Best Holiday Recipes: 100+ All-Time FavoritesPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- ProverbDocument3 pagesProverbdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dissolution For PharmacyDocument4 pagesDissolution For Pharmacydhungelsubhash8154100% (1)
- Titration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate SolutionDocument3 pagesTitration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate Solutiondhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- ProverbDocument3 pagesProverbdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Document2 pagesTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Na CLDocument1 pageNa CLdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- TLCDocument3 pagesTLCdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determine Acetic Acid Content of Vinegar with TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermine Acetic Acid Content of Vinegar with Titrationdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Titration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate SolutionDocument3 pagesTitration of Iodine With Standard Thisulphate Solutiondhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fajans MethodDocument3 pagesFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- CopperDocument3 pagesCopperdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Properties of LiquidsDocument7 pagesPhysical Properties of LiquidsSubhamshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fajans MethodDocument3 pagesFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Document2 pagesTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Fajans MethodDocument3 pagesFajans MethodSubhash Dhungel50% (2)
- Determination of Aluminium Back TitrationDocument2 pagesDetermination of Aluminium Back Titrationdhungelsubhash8154100% (4)
- Na CLDocument1 pageNa CLdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Total Hardness of WaterDocument3 pagesTotal Hardness of Waterdhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- CompositionDocument3 pagesCompositiondhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChlorpromazineDocument3 pagesChlorpromazinedhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- CompositionDocument3 pagesCompositiondhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title:P: Reparation of Sodium CitrateDocument3 pagesTitle:P: Reparation of Sodium Citratedhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title:P: Reparation of Sodium CitrateDocument3 pagesTitle:P: Reparation of Sodium Citratedhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- CiproDocument2 pagesCiprodhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Title:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)Document2 pagesTitle:: To Prepare Calcium Carbonate (Precipitated)dhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fumar AteDocument3 pagesFumar Atedhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- P HmetryDocument4 pagesP Hmetrydhungelsubhash8154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essential organic compounds and their common namesDocument16 pagesEssential organic compounds and their common namesCheryl ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Ibadan Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesUniversity of Ibadan Chemistry Practice QuestionsOkhare PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Balluff Chemical ResistanceDocument17 pagesBalluff Chemical ResistanceHéctor Eduardo Hernández LópezPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Benzoic Acid Lab ReportDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Benzoic Acid Lab Reportstephanie damajPas encore d'évaluation
- FOOD Ingredients NUMBERS Numbers) - World of Islam - Halal & Haram FoodDocument11 pagesFOOD Ingredients NUMBERS Numbers) - World of Islam - Halal & Haram FoodAditya Rahman YaniPas encore d'évaluation
- OTC Ingredient List (Alphabetical by Ingredient) 9-21-10aDocument88 pagesOTC Ingredient List (Alphabetical by Ingredient) 9-21-10awindeleta0% (1)
- Potassium BisulphiteDocument16 pagesPotassium BisulphiteLalchandsahani SahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of Benzoic Acid from Benzyl ChlorideDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Benzoic Acid from Benzyl ChlorideBlakk Faraci100% (1)
- Sodium Benzoate in Soft DrinksDocument2 pagesSodium Benzoate in Soft Drinksapi-3771333Pas encore d'évaluation
- Potassium Bisulphite Preserves FoodDocument17 pagesPotassium Bisulphite Preserves FoodBiswajit Ghosh80% (5)
- Lab 1Document6 pagesLab 1Shatesh Kumar ChandrahasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Recrystallization of Benzoic AcidDocument3 pagesRecrystallization of Benzoic AcidbeaparmaPas encore d'évaluation
- European Pharmacopoeia reference standards guideDocument61 pagesEuropean Pharmacopoeia reference standards guideచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డి0% (1)
- Preservatives InformationDocument3 pagesPreservatives InformationNinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vdocuments - MX - Chem Proj Class 12 CbseDocument18 pagesVdocuments - MX - Chem Proj Class 12 CbseHimanshu GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of potassium bisulphite as a food preservativeDocument7 pagesEffect of potassium bisulphite as a food preservativesriramPas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium Benzoate Desciption MsdsDocument5 pagesSodium Benzoate Desciption MsdsmeccalamataPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Additive Info and Sources PDFDocument4 pagesFood Additive Info and Sources PDFirena34Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASEAN principles for additives and excipients in traditional medicinesDocument30 pagesASEAN principles for additives and excipients in traditional medicinesMelindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Important ConversionDocument3 pagesImportant ConversionAKVanugrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation and Optimization in The Process of Toluene Liquid-Phase Catalytic OxidationDocument3 pagesSimulation and Optimization in The Process of Toluene Liquid-Phase Catalytic OxidationSithambaran KamacheePas encore d'évaluation
- HSPi PData SetDocument210 pagesHSPi PData Setkamilo14100% (1)
- Anisole SynthesisDocument6 pagesAnisole SynthesisManoj Tiwari0% (1)
- Taiwan - RegulationDocument126 pagesTaiwan - RegulationArnaj MadyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multistep 2Document4 pagesMultistep 2bebo4gpaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - Study of Novel Aromatic Aminomethylenephosphonates As OilfieldScale InhibitorsDocument10 pages5 - Study of Novel Aromatic Aminomethylenephosphonates As OilfieldScale InhibitorsVinicius CarneiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectrophotometric analysis of caffeine and benzoic acid in soft drinksDocument2 pagesSpectrophotometric analysis of caffeine and benzoic acid in soft drinksFeras SwaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Organic Chemistry For Advanced StudentsDocument306 pagesPractical Organic Chemistry For Advanced StudentsSamuel DinizPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Distillation Isolation of EugenolDocument6 pagesSteam Distillation Isolation of EugenolRamsey Mora100% (1)
- Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulation, 2011 (Part II)Document81 pagesFood Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulation, 2011 (Part II)RAGHVENDRA PRATAP SINGHPas encore d'évaluation