Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sonic Boiler
Transféré par
xreader0Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sonic Boiler
Transféré par
xreader0Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
02/05/08 - More on the Sonic Boiler
The photos shown to date reminded me of a website I found a couple of years ago describing a similar thing. Here are my notes from that find; "As a sensitive musician Mr Davey noticed, that there was such a frequency of the motor and propeller buzzing, when the aeroplane cabin and his body were getting into a resonance. At this unique resonance frequency he always was experiencing an influx of heat in his aeroplane cabin. He did not know yet, that in future this phenomenon will be utilised in ultrasonic weapon systems for effective and undetected killing of people. But he decided to test whether the same phenomenon is to appear, if a metal hemisphere which simulates his pilot cabin is submerged in water and is excited into a resonance frequency. So he found two tops from old bicycle bells, joined them together, tuned one of them to 50 Hz frequency, attached electricity wire to each one of them, and thrown them into water. Surprisingly, water started to boil extremely fast. So he made his first heater patent based on this observation. This patent was already registered in 1944. After a hero return from the war, he had a device, which repetitively proved to everyone who measured it, that it has the efficiency decisively exceeding 100%. Realising this, he believed that the world is going to pounce on the opportunity of production and use of this technical miracle. After all, people are full of declarations about apparent saving on energy, resources, about protection of our natural environment, etc. However, the reality turned out to be completely opposite. Immediately after it was experimentally confirmed that the device has unexplainably high efficiency, the heater and the inventor fell into disfavour of various institutions that are interested in selling electricity and that protect the monopoly on electrical power. In the result, this extraordinary invention received an extraordinary treatment! Namely authorities were doing everything in their powers to disallow the production and sale of this heater in New Zealand. One of legal tricks that were used against this heater, was that it was declared officially to be "unsafe to health and life of users". (Please notice that practically every electrical device working on 220 Volts can be declared unsafe, if someone in the position of authority wishes to put it down.) In turn in New Zealand it is impossible to undertake the production and sale of anything, that is not officially approved by the government. In the result, Mr Davey was fighting for almost 50 years to receive a permit for the industrial production of this heater. And during these almost 50 years, the permission was continually refused to him, no matter what research outcomes he submitted to please authorities, and no matter how hard he tried. But it is interesting, that in Australia an electric jug with a heating element of the design very similar to the Daveys heater was put in mass production (this Australian jug most probably is produced in there still even today). This Australian jug is working on the principle of electrical resistance of water (i.e. not telekinesis as the heater of Mr Davey does). Water that it heats is a resistor, in which heat is generated because of the electric current flows through this water. This Australian jug is exactly the same "dangerous to the health and lives", like the telekinetic heater of Mr Davey. Only that it did not encountered in Australia similar bureaucratic resistance because the energy efficiency of it is "normal". When I met Mr Davey for the first time in 1990, he still was appealing to authorities, and still had a hope to receive a permit for the production of his heater - in spite of these almost 50 years of lost battles with bureaucrats. He was even showing to me a large stock of components he gathered to start a production immediately after the permit is granted
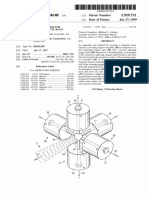
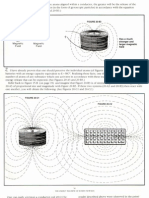
to him. However, he gave up the experimental production of research copies of his heater. The design of the Davey's sonic heater is extremely simple. It actually is composed of two major parts only - see Figure K8 (3) from monograph [1/4]. The most important out of these two parts is a resonating hemispherical bowl (1) made of a sound inducing metal plate. The second part is a buffering hemispherical bowl (2) almost identical in shape to the bowl (1). This second bowl has the radius around 4 mm larger than the resonating hemispherical bowl (1). Both bowls are assembled symmetrically one around the other, means the hemispherical bowl (1) is placed inside of the hemispherical bowl (2). Coin is 32 mm wide = 1.25984 inches / Big bowl approximately 1.75 inches wide and .75 inches thick / Small bowl approximately 1 3/8 inches wide. Of course, apart from these two bowls, the heater also includes a long rod, nuts, washers, and electrical wires. These are to hold it together, to supply electricity to both bowls, and to allow the heater to be submerged into water that it heats. But these other parts are marginal additions only. The major parts are the bowls. During experimental production of this heater, the resonating hemispherical bowl (1) usually is made from an old cover for a bicycle bell. The dimensions of this hemispherical bowl are not important. It is only vital that it falls into a sonic resonance at the frequency of 50 Hertz, and that it has the outer surface which is parallel and equidistant from the external buffering hemispherical bowl (2). To each of these two bowls a different wire of the household electricity supply (i.e. 220 V, 50 Hz) is connected. The heater must be submerged in water that it heat. It brings water to the boiling point extremely fast. More details about the design and operation of this sonic heater is provided in subsection K3.3 from volume 10 of monograph [1/4]. After being constructed, the Davey's telekinetic heater must be "tuned" in two different manners. The first tuning depends on providing the hemispherical bowl (1) with such frequency of the own oscillations, that makes this bowl to resonate acoustically when a sound of the frequency 50 Hertz is emitted nearby. The second tuning of the heater depends on appropriate selecting the distance "L" between both bowls (1) and (2). On this distance depends the formation of the standing wave between both bowls. Thus it decides about the energy efficiency of the entire heater. From the information that the inventor repeated to me, I gather that the measurements carried out by New Zealand scientists suggested that this heater may consume even less than the equivalent for around 5% of the energy that it generates in form of heat. This would indicate, that the electrical efficiency of this heater is around 2000%. (Means, that the heater produces over 20 times more heat than it consumes electrical energy.)" - from Private Files
02/03/08 - Video - Sonic Boiler
It looks like a desk lamp, is cool to the touch and appears not to be doing anything, until it comes into contact with water. Former spitfire pilot Peter Davey claims his invention uses the power of sound to boil water. Mr Davey believes high frequency sonic vibrations emitted from within the silver bulb cause the water to boil. He says the idea came to him 50 years ago when he noticed different saxophone notes caused different household items to rattle. The mains-powered gizmo has experts intrigued. Ive never seen anything like it in my live, Professor Arthur Williamson said. The Professor has his doubts about Mr Daveys acoustic theory and suspects there are two simple electrodes inside the boiler. Im careful that I dont divulge everything, Mr Davey said. Im waiting to get a manufacturer that is prepared to put some money into it. -
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Easy Stretching PosturesDocument118 pagesEasy Stretching Postures김종빈100% (3)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Donna Eden - Wired For Joy - Secret of Radiant CircuitsDocument11 pagesDonna Eden - Wired For Joy - Secret of Radiant CircuitsDaniel Wallach100% (10)
- How To Be The Golden Egg in The Trading Game PrintDocument68 pagesHow To Be The Golden Egg in The Trading Game PrintNagy100% (1)
- Edible Cell WorksheetDocument3 pagesEdible Cell Worksheetm_frajman100% (4)
- The Stubblefield PapersDocument18 pagesThe Stubblefield PapersDan Beeson100% (2)
- Build A 3-Band Shortwave Converter For Your CarDocument2 pagesBuild A 3-Band Shortwave Converter For Your CarbobbyunlockPas encore d'évaluation
- Schauberger Implosion TechnologyDocument10 pagesSchauberger Implosion TechnologyFatima FróisPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Cultur IDocument47 pagesElectro Cultur Isicedaca212100% (2)
- Experiment of The Biefield-Brown Effect Using Symmetric Plate Capacitors Charged Below 35kVDocument8 pagesExperiment of The Biefield-Brown Effect Using Symmetric Plate Capacitors Charged Below 35kVLuis Alberto MiglioreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Grebennikov's Mystery Revealed !!!Document13 pagesGrebennikov's Mystery Revealed !!!jamjam_95678853Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nineteenth-Century Aether Theories: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsD'EverandNineteenth-Century Aether Theories: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Live Blood AnalysisDocument6 pagesLive Blood Analysisxreader0100% (1)
- Dayton Miller's Ether-Drift ExperimentsDocument33 pagesDayton Miller's Ether-Drift Experimentsxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vimanika ShastraDocument134 pagesVimanika ShastraSilvio ŠarunićPas encore d'évaluation
- World of Free EnergyDocument8 pagesWorld of Free EnergyLilian B M FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasonic ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesUltrasonic ElectrolysisBirdy MadPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitors That Recharge ThemselvesDocument10 pagesCapacitors That Recharge Themselvesdakkid100% (1)
- Nikola Tesla's Flying Saucer - Electromagnetic Field Lift ExperimentsDocument2 pagesNikola Tesla's Flying Saucer - Electromagnetic Field Lift Experimentsfairymouse100% (1)
- Water ChargerDocument15 pagesWater ChargerKWojtek100% (1)
- How Honeycombs Can Build Themselves - Nature News & CommentDocument5 pagesHow Honeycombs Can Build Themselves - Nature News & CommentProf C.S.PurushothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nikola Tesla's Black Magic Touring CarDocument23 pagesNikola Tesla's Black Magic Touring CarJorge AmaralPas encore d'évaluation
- Ray Guns 101: (Part I - History)Document20 pagesRay Guns 101: (Part I - History)CyrrexPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalar Wave PDFDocument7 pagesScalar Wave PDFBibiz999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To John Bedini S Web PagesDocument590 pagesWelcome To John Bedini S Web PagesKatamba Rogers100% (1)
- Teal NewspaperDocument3 pagesTeal NewspaperkishbudPas encore d'évaluation
- The Keshe Plasma Electric GeneratorDocument21 pagesThe Keshe Plasma Electric GeneratorCuauhtemoc EspinoPas encore d'évaluation
- J C D U: Oe Ell Own NderDocument72 pagesJ C D U: Oe Ell Own NderRuddyMartiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Carlo Splendore MSC Orgone MotorDocument28 pagesCarlo Splendore MSC Orgone Motorgrewa153Pas encore d'évaluation
- Boyd Magnetic Beam PDFDocument7 pagesBoyd Magnetic Beam PDFShannon BentleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mueller Experiments Kromrey Brandt Tesla Bedini!!!!!Document30 pagesMueller Experiments Kromrey Brandt Tesla Bedini!!!!!d4nk4rPas encore d'évaluation
- BEDINI DRAWNS Report On 4 Battery SwitchDocument31 pagesBEDINI DRAWNS Report On 4 Battery SwitchMANNAJANELAGUNA0% (1)
- The Problem of Increasing Human Energy - Nikola Tesla PDFDocument27 pagesThe Problem of Increasing Human Energy - Nikola Tesla PDFKarhys100% (2)
- Adams Motor DetaljerDocument18 pagesAdams Motor DetaljerGeorg LidtveitPas encore d'évaluation
- Peter Lindemann, Aaron Murakami - Save On Home Energy-A&P Electronic Media (2009)Document94 pagesPeter Lindemann, Aaron Murakami - Save On Home Energy-A&P Electronic Media (2009)Ganugio MirianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tapping Into 200 Volts Positive of FreeDocument7 pagesTapping Into 200 Volts Positive of Freeaccime24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hubbard Amplifying TransformerDocument8 pagesHubbard Amplifying TransformerTomislav JovanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Impulse Power Secrets-3docDocument8 pagesImpulse Power Secrets-3doc77nicuPas encore d'évaluation
- Schapellern Rex ResearchDocument16 pagesSchapellern Rex Researchmrhemped100% (1)
- THB Invbi (Tion of Hans Colbr, Rblating To An Source of PowerDocument35 pagesTHB Invbi (Tion of Hans Colbr, Rblating To An Source of PoweromkarPas encore d'évaluation
- As Works (Devays) of (Tarielya) To (Kapanadze) .: Moral AspectDocument64 pagesAs Works (Devays) of (Tarielya) To (Kapanadze) .: Moral AspectchigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Peter Markovich - Apparatus To Rectify Ether Energy (ATREE)Document21 pagesPeter Markovich - Apparatus To Rectify Ether Energy (ATREE)Sean ReevesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Case For AntiGravity-bookletDocument48 pagesThe Case For AntiGravity-bookletJerry DoughertyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tesla's Hairpin Circuit - TransformacommDocument9 pagesTesla's Hairpin Circuit - Transformacommfsilassie8012100% (1)
- Resonant Gravity Field Coil PDFDocument16 pagesResonant Gravity Field Coil PDFClover1897Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newman Machine VerDocument136 pagesNewman Machine Vercaius999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Discharges, Waves and ImpulsesDocument170 pagesElectric Discharges, Waves and Impulseselectrosci100% (1)
- The Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston BurridgeDocument6 pagesThe Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston BurridgepboserupPas encore d'évaluation
- Alex Schiffer UpdatesDocument204 pagesAlex Schiffer UpdatesRuddyMartiniPas encore d'évaluation
- KeelyNet 2009 - The Clem Engine Reborn - 11-08-09Document11 pagesKeelyNet 2009 - The Clem Engine Reborn - 11-08-09overyounityPas encore d'évaluation
- "THE ENERGY MACHINE OF JOSEPH NEWMAN" (2 of 5) (Fully Searchable Text)Document56 pages"THE ENERGY MACHINE OF JOSEPH NEWMAN" (2 of 5) (Fully Searchable Text)Zachary Riles Conner100% (5)
- Electromag and ElectrostaticsDocument29 pagesElectromag and ElectrostaticsChristine MalibiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Breaking News Egyptian Inventor Invents A New Source of Clean EnergyDocument5 pagesBreaking News Egyptian Inventor Invents A New Source of Clean EnergyMohamed KhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2Document2 pages2Aman SodhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicola Tesla Electroradiant EffectDocument16 pagesNicola Tesla Electroradiant Effectrodolfo barbosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Space Radiant Energy ReceiverDocument5 pagesSpace Radiant Energy ReceiverfghjhgfPas encore d'évaluation
- Nikola Tesla's 4-Battery SwitchDocument22 pagesNikola Tesla's 4-Battery SwitchDr_ZeusPas encore d'évaluation
- Testament of Eric P DollardDocument6 pagesTestament of Eric P Dollardacuonaut100% (1)
- Abbreviated Report On Prof. Seiki About The Use of The G-EnergyDocument9 pagesAbbreviated Report On Prof. Seiki About The Use of The G-EnergyAndrew Bellon50% (2)
- Some Homemade ElectricityDocument4 pagesSome Homemade Electricitycirrus12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Non Ferrous Magnet OcrDocument24 pagesNon Ferrous Magnet Ocrchadj10600% (1)
- Cold Electricity Circuit Diagram With Capacitors - by UFOpolitics - Tír Na Saor Land of The FreeDocument6 pagesCold Electricity Circuit Diagram With Capacitors - by UFOpolitics - Tír Na Saor Land of The FreeSadegh Simorgh100% (4)
- The Hamel Spinning DiscDocument3 pagesThe Hamel Spinning DiscWilhelm HartmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stanley Meyer Big Bobbin Builders Guide 2019 v1: Very Rare Guide for How to Assemble Water Fueled injector tri-filar bobbinD'EverandStanley Meyer Big Bobbin Builders Guide 2019 v1: Very Rare Guide for How to Assemble Water Fueled injector tri-filar bobbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla: Including Tesla's AutobiographyD'EverandInventions, Researches and Writings of Nikola Tesla: Including Tesla's AutobiographyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Magnetic Pulse of Life: Geomagnetic Effects on Terrestrial LifeD'EverandThe Magnetic Pulse of Life: Geomagnetic Effects on Terrestrial LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Japan ElectretsDocument5 pagesJapan Electretsxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Garlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization DestroyerDocument6 pagesGarlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization Destroyerxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Rockefeller File (1976) by Gary AllenDocument12 pagesThe Rockefeller File (1976) by Gary Allenxreader0100% (1)
- Lodge Oliver - Pioneers - of - ScienceDocument258 pagesLodge Oliver - Pioneers - of - Sciencexreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Popular Science - Vibrational Energy HarvestingDocument3 pagesPopular Science - Vibrational Energy Harvestingxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bolinas Incident by Eric DollardDocument54 pagesBolinas Incident by Eric Dollard~ScaLaR~100% (1)
- Breathing For Voic 00 Hul Bu of TDocument90 pagesBreathing For Voic 00 Hul Bu of Txreader0100% (1)
- Orgone GeneratorsDocument19 pagesOrgone Generatorsxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics of AdvaitaDocument6 pagesPhysics of AdvaitaparahexavoctalePas encore d'évaluation
- Bachschorals 01 TerruoftDocument100 pagesBachschorals 01 Terruoftxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Star Light Aerial Space Secrets (1941 - 2009)Document39 pagesStar Light Aerial Space Secrets (1941 - 2009)Unwanted Publicity Intelligence100% (7)
- X RaysMachinesyouneverseenDocument26 pagesX RaysMachinesyouneverseenxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Fallacy of Conductors and Proof of The Aether by Eric DollardDocument17 pagesThe Fallacy of Conductors and Proof of The Aether by Eric Dollardxreader0100% (2)
- Vedic Maths in Digital Signal ProcessingDocument6 pagesVedic Maths in Digital Signal ProcessingSwanand RaikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Implosion - Viktor - SchaubergerDocument134 pagesImplosion - Viktor - SchaubergerGilgames Ex100% (1)
- Dna Secret - Harun YahyaDocument61 pagesDna Secret - Harun YahyamehdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Basis of Music - StoneDocument80 pagesScientific Basis of Music - Stonejue2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 15 KW Induction ManualDocument5 pages15 KW Induction Manualxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cook OnRadiantMatterDocument24 pagesCook OnRadiantMatterxreader0Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Occult Masonic Temple GodDocument226 pagesThe Occult Masonic Temple GodOnyx God96% (51)
- Sacred Geometry StudyDocument18 pagesSacred Geometry Studykundalini2009100% (26)
- Mason Book MagnetismDocument22 pagesMason Book Magnetismwayne thompson0% (1)
- Esp QuestionnaireDocument9 pagesEsp QuestionnaireMarivic SolijonPas encore d'évaluation
- Brainstorming WhahahDocument20 pagesBrainstorming WhahahJohnrey V. CuencaPas encore d'évaluation
- User fc20 PDFDocument34 pagesUser fc20 PDFjesus diasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohammed Shamsuddin CVDocument2 pagesMohammed Shamsuddin CVmohammed shamsuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Socsc 03Document24 pagesSocsc 03Emon Espejo100% (1)
- Penyelarasan Instrumen Pentaksiran PBD Tahun 2 2024Document2 pagesPenyelarasan Instrumen Pentaksiran PBD Tahun 2 2024Hui YingPas encore d'évaluation
- Geodetic Engineer's Report On Relocation SurveyDocument5 pagesGeodetic Engineer's Report On Relocation SurveyMalson GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- AQUINAS de Motu Cordis LAT - ENGDocument9 pagesAQUINAS de Motu Cordis LAT - ENGOta FlegrPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Portfolio B1 Tak 1 To 4Document2 pagesWriting Portfolio B1 Tak 1 To 4DUAIZ TORRESPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Indian Astrology, Indian Vedic Astrology, Future Predictions, Horoscopes, Astrological Remedies, Astrological Solutions 271015Document5 pagesOnline Indian Astrology, Indian Vedic Astrology, Future Predictions, Horoscopes, Astrological Remedies, Astrological Solutions 271015jaithilagarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista de Paineis LCD Atualizacao 26 04 2013 PDFDocument412 pagesLista de Paineis LCD Atualizacao 26 04 2013 PDFHfssSilva100% (4)
- The Reading The Mind in The Eyes Test: Testretest Reliability and Preliminary Rsychometric Rroperties of The German VersionDocument9 pagesThe Reading The Mind in The Eyes Test: Testretest Reliability and Preliminary Rsychometric Rroperties of The German VersionSEP-PublisherPas encore d'évaluation
- Pass Microsoft 74-343 Exam: Number: 74-343 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 40.2Document26 pagesPass Microsoft 74-343 Exam: Number: 74-343 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 Min File Version: 40.2tapera_mangeziPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization StructureDocument11 pagesOrganization StructureKaran RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Penerapan Prinsip Prinsip Koperasi Dalam UUDDocument10 pagesAnalisis Penerapan Prinsip Prinsip Koperasi Dalam UUDSaikhudinPas encore d'évaluation
- English Practice 1: C. Carried D. Sugar B. Underline A. Danger A. CharacterDocument3 pagesEnglish Practice 1: C. Carried D. Sugar B. Underline A. Danger A. CharacterKeisaPas encore d'évaluation
- KMSC Mystery School of Self Spiritual MasteryDocument7 pagesKMSC Mystery School of Self Spiritual MasteryRalphPas encore d'évaluation
- ID Analisis Tingkat Kesehatan Perusahaan BeDocument7 pagesID Analisis Tingkat Kesehatan Perusahaan BeAjna RossaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aniket CV NewDocument2 pagesAniket CV NewRajreddy ChamawarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Menstrual Cycle Remedies Amenorrhea HandoutDocument3 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle Remedies Amenorrhea HandoutRoger AugePas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Screening-PostedDocument16 pagesConcept Screening-PostedCintia NurliyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- KG 2 Week 5 - (133089689484163457) - 0Document3 pagesKG 2 Week 5 - (133089689484163457) - 0Nahdat Al Ghad International SchoolPas encore d'évaluation
- The Philosophical Foundations of Educational Research: A Beginner's GuideDocument6 pagesThe Philosophical Foundations of Educational Research: A Beginner's GuideGlorie RoxasPas encore d'évaluation
- CNC Unit 1Document4 pagesCNC Unit 1chandiran88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Educational Planning (Felipe)Document102 pagesEducational Planning (Felipe)Felipe Beranio Sullera Jr.100% (4)
- GIS Thermografie Audits PDFDocument2 pagesGIS Thermografie Audits PDFkhalidfarooq009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Developing Training Program For Effective and Quality Volleyball PlayersDocument13 pagesDeveloping Training Program For Effective and Quality Volleyball PlayersDeogracia BorresPas encore d'évaluation