Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Transféré par
E0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues1 pageGlyburide Lowers blood sugar by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity to insulin at receptor sites. May also decrease hepatic glucose production. Normal dosage range 2.5-5 mg once daily initially (range 1.25-20 mg / day)
Description originale:
Titre original
Micronase (glyburide)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentGlyburide Lowers blood sugar by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity to insulin at receptor sites. May also decrease hepatic glucose production. Normal dosage range 2.5-5 mg once daily initially (range 1.25-20 mg / day)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues1 pageClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Transféré par
EGlyburide Lowers blood sugar by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity to insulin at receptor sites. May also decrease hepatic glucose production. Normal dosage range 2.5-5 mg once daily initially (range 1.25-20 mg / day)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
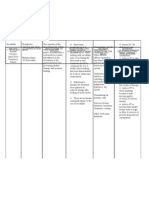
Clinical Medications Worksheets
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Glyburide Micronase Antidiabetics 5mg PO Q day
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
1.5-3 hr 45-60 24hr 2.5-5 mg once daily initially (range 1.25-20 mg/day)
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Gestational DM N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Lowers blood sugar by stimulating the release of insulin from Hypersensitivity, hypersensitivity to sulfonamides, uncontrolled
the pancreas and increasing the sensitivity to insulin at receptor infection, serious burns, or trauma. Use cautiously in pregnancy or
sites. May also decrease hepatic glucose production. lactation (safety not established; insulin recommended during
pregnancy)
Common side effects
Photosensitivity, hypoglycemia, APLASTIC ANEMIA
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) Monitor serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin periodically
None known for this patient during therapy to evaluate effectiveness. Monitor CBC periodically
during therapy. Report ↓ in blood counts promptly. May cause an ↑ in
AST, LDH, BUN, and serum creatinine.
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication
Instruct patient to take medication at same time each day. Take missed
doses as soon as remembered unless almost time for next dose. Do not
take if unable to eat. Review signs of hypoglycemia and
hyperglycemia with patient. If hypoglycemia occurs, advise patient to
drink a glass of orange juice or ingest 2-3 tsp of sugar, honey, or corn
syrup dissolved in water or an appropriate number of glucose tablets
and notify health care professional. May occasionally cause dizziness
or drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities
requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Insulin is
the recommended method of controlling blood sugar during pregnancy.
Counsel female patients to use a form of contraception other than oral
contraceptives and to notify health care professional promptly if
pregnancy is planned or suspected. Advise patient to carry a form of
sugar (sugar packets, candy) and identification describing disease
process and medication regimen at all times. Advise patient to notify
health care professional promptly if unusual weight gain, swelling of
ankles, drowsiness, shortness of breath, muscle cramps, weakness, sore
throat, rash, or unusual bleeding or bruising occurs.
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving
Observe for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemic Overdose is manifested by symptoms of Blood glucose level maintained
reactions (sweating, hunger, weakness, dizziness, hypoglycemia. Mild hypoglycemia may be WNL
tremor, tachycardia, anxiety). Patients on treated with administration of oral glucose.
concurrent beta-blocker therapy may have very Severe hypoglycemia should be treated with
subtle signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. IV D50W followed by continuous IV infusion
Assess patient for allergy to sulfonamides. of more dilute dextrose solution at a rate
sufficient to keep serum glucose at
approximately 100 mg/dl
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonPas encore d'évaluation
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG SpirivaDocument1 pageDRUG SpirivarholiboiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study on CelecoxibDocument11 pagesDrug Study on CelecoxibPrincess Brigitte R. PATE�APas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJam CorrosPas encore d'évaluation
- MotiliumDocument5 pagesMotiliumAkram KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- New DS3Document3 pagesNew DS3dakiePas encore d'évaluation
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoPas encore d'évaluation
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD Treatment Spiriva Handihaler Drug StudyDocument1 pageCOPD Treatment Spiriva Handihaler Drug Studylivewithoutgoals0% (1)
- AcarboseDocument1 pageAcarboseHanna SePas encore d'évaluation
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP EsrfDocument9 pagesNCP EsrfKen RegalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study2Document2 pagesDrug Study2Haifi HunPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarPas encore d'évaluation
- Simethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDocument1 pageSimethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDivine Dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studymegreen GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Levofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticDocument2 pagesLevofloxacin: A Potent Fluoroquinolone AntibioticEliza Rahardja100% (1)
- Methylprednisolone AlphapharmDocument5 pagesMethylprednisolone AlphapharmMarthin TheservantPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isPas encore d'évaluation
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyRai D. MacapantonPas encore d'évaluation
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (1)
- Drug PepcidDocument2 pagesDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- Ipratropium BromideDocument20 pagesIpratropium BromideAngelique Ramos PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimenhydrinate PDFDocument2 pagesDimenhydrinate PDFWindy SengiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosPas encore d'évaluation
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanDocument1 pageDrug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanVoid LessPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug Studyabulan100% (1)
- Nursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneDocument7 pagesNursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneAlvin LimPas encore d'évaluation
- AmlodipineDocument1 pageAmlodipineHsintan HsuPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatPas encore d'évaluation
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkPas encore d'évaluation
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayPas encore d'évaluation
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studypopoyoio100% (2)
- Pioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, ActonelDocument3 pagesPioglitazone (Actos, Lilly) : May Be Confused With Actidose, Actonelshidyakg100% (1)
- Paracetamol Biogesic Analgesic AntipyreticDocument8 pagesParacetamol Biogesic Analgesic AntipyreticGian Era100% (1)
- Azithromycin, Cefixime, Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAzithromycin, Cefixime, Paracetamol Drug StudyAzizah VillaminPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study HydrocodoneDocument1 pageDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study CHDCDocument1 pageDrug Study CHDCIannBlancoPas encore d'évaluation
- PlasilDocument1 pagePlasilernestjohnPas encore d'évaluation
- LortabDocument1 pageLortabSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaroneanindiawPas encore d'évaluation
- F&E Drug StudyDocument2 pagesF&E Drug Studychelle_asenjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Ssalbutamol7Document3 pagesDrug Study Ssalbutamol7Gorgeouschelle FeriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug GlucotrolDocument1 pageDrug GlucotrolSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lantus (Insulin Glargine)Document3 pagesLantus (Insulin Glargine)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISDocument4 pagesPyelonephritis 1 Running Head: PYELONEPHRITISEPas encore d'évaluation
- Left-Side CHF PathoDocument5 pagesLeft-Side CHF PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureEPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Burns PathoDocument2 pagesChemical Burns PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Influenza B PathoDocument4 pagesInfluenza B PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Short PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia Short PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperparathyroidism PathoDocument2 pagesHyperparathyroidism PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Deficiency Anemia PathoDocument6 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyponatremic Dehydration PathoDocument4 pagesHyponatremic Dehydration PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart Failure-ABDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure-ABEPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Pancreatitis PathoDocument5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bowel Resection PathoDocument7 pagesBowel Resection PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Subluxation c6c7 Short PathoDocument1 pageSubluxation c6c7 Short PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Autonomic DysreflexiaDocument2 pagesAutonomic DysreflexiaEPas encore d'évaluation
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Geodon (Ziprasidone)Document2 pagesGeodon (Ziprasidone)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Pancreatitis Short PathoDocument2 pagesPancreatitis Short PathoEPas encore d'évaluation
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgEPas encore d'évaluation
- Zosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)Document2 pagesZosyn (Piperacillin/tazobactram)E67% (3)
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Document1 pageSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)EPas encore d'évaluation
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Darvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDarvocet (Propoxyphene Napsylate/Acetaminophen)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Reglan (Metoclopramide)Document3 pagesReglan (Metoclopramide)E100% (1)
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 pagesLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- Keppra (Levetiracetam)Document2 pagesKeppra (Levetiracetam)E100% (1)
- Jawaban UASDocument3 pagesJawaban UASJaclin Awuy SalembaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Design BriefsDocument62 pagesMedical Design Briefsneto512Pas encore d'évaluation
- History, Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Removable Partial DenturesDocument96 pagesHistory, Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Removable Partial DenturesPriya BagalPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Disorder ProjectDocument10 pagesEnzyme Disorder Projectria wuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hipopresivos y Dolor Lumbar Cronico 2021Document9 pagesHipopresivos y Dolor Lumbar Cronico 2021klgarivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Goals and principles of community health nursingDocument4 pagesGoals and principles of community health nursingNoemiPas encore d'évaluation
- D.O School InformationDocument102 pagesD.O School Informationkape1onePas encore d'évaluation
- CAMTC Certified Massage Therapist Chuck LeeDocument1 pageCAMTC Certified Massage Therapist Chuck LeeChuck LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Malignant Hyperthermia: Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Recommendations Recommendations For Hospital Emergency DepartmentsDocument6 pagesMalignant Hyperthermia: Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Recommendations Recommendations For Hospital Emergency DepartmentsHelend Ndra TaribukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lazy Leucocyte SyndromeDocument2 pagesLazy Leucocyte SyndromeDragos BourosPas encore d'évaluation
- Labor Pain ManagementDocument1 pageLabor Pain ManagementKenneth Sy100% (5)
- OutputDocument1 pageOutputmsenthamizharasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dental BS Delta 1500 PPO Benefit Summary 2018Document4 pagesDental BS Delta 1500 PPO Benefit Summary 2018deepchaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Medical Engineer On Contract BasisDocument3 pagesBio Medical Engineer On Contract BasisSreedhar RajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Package-Nursing Practicum I STUDENTDocument36 pagesInformation Package-Nursing Practicum I STUDENTPui Pui LamPas encore d'évaluation
- German Gov't Bombshell - Alarming Number of Vaccinated Are Developing AIDS' - News PunchDocument8 pagesGerman Gov't Bombshell - Alarming Number of Vaccinated Are Developing AIDS' - News PunchKarla VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sush Unity Haemotology-1700Document51 pagesSush Unity Haemotology-1700Dr-Jahanzaib GondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar ON: Birth InjuriesDocument38 pagesSeminar ON: Birth Injuriesvishnu100% (1)
- Practices of Self-Medication Among Tribal Population North Maharashtra (Khandesh)Document5 pagesPractices of Self-Medication Among Tribal Population North Maharashtra (Khandesh)Latasha WilderPas encore d'évaluation
- CCIM MD Siddha Syllabus for Nanju Maruthuvam SpecialtyDocument16 pagesCCIM MD Siddha Syllabus for Nanju Maruthuvam SpecialtyJithinPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For SchizoDocument6 pagesNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEAPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Present IllnessDocument4 pagesHistory of Present IllnessJehangir KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital Information Management System - Cover PageDocument15 pagesHospital Information Management System - Cover Pageapi-1946401583% (6)
- Prasugrel and RosuvastatinDocument7 pagesPrasugrel and RosuvastatinMohammad Shahbaz AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ijmrhs Vol 2 Issue 1Document110 pagesIjmrhs Vol 2 Issue 1editorijmrhs100% (1)
- Green White Minimalist Modern Real Estate PresentationDocument8 pagesGreen White Minimalist Modern Real Estate Presentationapi-639518867Pas encore d'évaluation
- FIKY NISWATI YUSLIHAH P17250193025 (Morning Breafing)Document3 pagesFIKY NISWATI YUSLIHAH P17250193025 (Morning Breafing)Fiky NiswatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved Private Hospitals List for CG Govt EmployeesDocument12 pagesApproved Private Hospitals List for CG Govt Employeesm_asitPas encore d'évaluation
- Malnutrition in Critical Illness and Beyond A Narrative Review PDFDocument9 pagesMalnutrition in Critical Illness and Beyond A Narrative Review PDFEsteban DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalence of Soil Transmitted Helminths infection in adults in North SulawesiDocument4 pagesPrevalence of Soil Transmitted Helminths infection in adults in North SulawesiSahrul hamidPas encore d'évaluation