Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
QUESTIONS 1) Connects With Myosin During Muscle Contraction 2)
Transféré par
api-25965241Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
QUESTIONS 1) Connects With Myosin During Muscle Contraction 2)
Transféré par
api-25965241Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
QUESTIONS ANSWERS
1) connects with myosin during muscle contraction 24) actin
2) oxygen is used to create lots of energy 25) atrophy
3) produces ATP quickly, but only a little bit 26) aerobic respiration
4) main energy source for muscle contractions 27) anaerobic respiration
5) muscle tissue in the heart 28) ATP
6) muscles locked in contraction 29) cardiac
7) muscle locked in contraction (won't relax again) 30) cramp
8) muscles that stretch out joints 31) cramp
9) muscle fibers that react quickly and fatigue quickly 32) extensors
10) muscles that bend joints 33) fast-twitch
11) place where muscle attaches to a bone that moves when the muscle flexes 34) flexors
12) chemical that causes muscle fatigue 35) insertion
13) microscopic fibers inside a muscle cell 36) lactic acid
14) thick protein that pulls on actin during muscle contraction 37) myofibrils
15) place where muscle attaches to a bone that doesn't move 38) myosin
16) muscles only ___, never push 39) origin
17) small cylinders of muscle proteins that can contract and relax 40) pull
18) the only voluntary muscle tissue; moves bones 41) sarcomeres
19) muscle fibers that work a long time without fatigue 42) skeletal
20) muscle cells that push food through esophagus and stomach 43) slow-twitch
21) connective tissue that connects muscles to bones 44) smooth
22) swelling and pain in tendons, due to overuse 45) tendon
23) muscle shrinks due to injury, disease, or lack of exercise 46) tendonitis
24) Running a marathon requires…
A) slow-twitch muscles B) aerobic respiration C) Both A & B
25) What starts a muscle contraction?
A) a nerve signal B) lactic acid enters sarcomeres C) myofibril absorbs ATP
26) Which of these is NOT a function of the integumentary system?
A) disease prevention B) UV protection C) moving bones D) waterproofing
27) How does skin help keep temperature balance?
A) senses the outside temperature C) sweats when too hot
B) changes blood flow (more or less) D) all the above
28) What causes baldness?
A) too much melanin B) hair follicles rest more than grow C) not enough lactic acid
Identify these skin features in the diagram:
29) dermis
30) epidermis
31) hair root
32) nerve
33) subcutaneous tissue
34) sweat gland
35) oil gland
36) hair shaft
QUESTIONS ANSWERS
37) bacterial infection of oil glands 1) acne
38) epidermis separates from the dermis 2) blisters
39) most common skin cancer 3) carcinoma
40) protein that strengthens the dermis 4) collagen
41) layer of skin with blood vessels, hair follicles, and sweat glands 5) dermis
42) top layer of skin 6) epidermis
43) epidermis is burned, as in a sunburn 7) first-degree burn
44) skin cells that surround hair root 8) follicle
45) skin spots made of melanin 9) freckles
46) protein found in epidermis, hair, and nails 10) keratin
47) place where fingernails grow 11) lunula
48) skin protein that absorbs UV radiation 12) melanin
49) most dangerous skin cancer 13) melanoma
50) clumps of melanin-producing cells 14) moles
51) produces sebum that moisturizes skin 15) oil gland
52) dermis is burned, which might cause scars 16) second-degree burn
53) dead part of hair, above the scalp 17) shaft
54) layer of fat cells that connects skin to the body 18) subcutaneous tissue
55) helps cool skin when body is hot 19) sweat gland
56) all skin layers die, may need a skin graft 20) third-degree burn
57) radiation that leads to skin cancer 21) UV
58) virus infection of skin 22) warts
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hematology in Practice, 2nd EditionDocument385 pagesHematology in Practice, 2nd Editionjaviergmar84% (19)
- 1.atlas Hematologi Diggs PDFDocument128 pages1.atlas Hematologi Diggs PDFPuspa YaNi100% (5)
- Lab 10 Blood and The HeartDocument6 pagesLab 10 Blood and The Heartcindy tranPas encore d'évaluation
- 90 423 0335 2 - Inh PDFDocument9 pages90 423 0335 2 - Inh PDFS GurumanickamPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled5 PDFDocument16 pagesUntitled5 PDFElizabeth LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Adr PlexusDocument9 pagesAdr PlexusNandha KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Test: Patterns of InheritanceDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Test: Patterns of Inheritanceapi-25965241100% (1)
- The Concept of Innocent Bystander in Blood Transfusion Medicine by Alhaji Bukar, ABDocument17 pagesThe Concept of Innocent Bystander in Blood Transfusion Medicine by Alhaji Bukar, ABAlhaji Bukar100% (4)
- Revision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFCattrainuhPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 5 Student Packet (ANP 1)Document8 pagesCh. 5 Student Packet (ANP 1)Alex ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular System Vocab1 2Document3 pagesMuscular System Vocab1 2api-305436791Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zani MCQs Zoo301Document10 pagesZani MCQs Zoo301mc190404891 ZAINAB ARSHADPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Study Question Chp3Document10 pagesAnatomy Study Question Chp3Hema JothyPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesCH 4take Home Test - Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemKatiePas encore d'évaluation
- LT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21Document6 pagesLT-23 SPL (G-1) Morphology of Animals - 04-09-21orisPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz IntegumentaryDocument44 pagesQuiz IntegumentaryMedShare100% (5)
- Untitled4 PDFDocument13 pagesUntitled4 PDFElizabeth LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Integuementary SystemDocument9 pagesInteguementary SystemDi DangPas encore d'évaluation
- Glosarium Modul IBDDocument6 pagesGlosarium Modul IBDAngki PerdiyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesThe Integumentary SystemLeona Marie Doctor100% (1)
- Elementary Anatomy (Q-Bank 2020)Document22 pagesElementary Anatomy (Q-Bank 2020)Muhammad AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 ExamDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Examraw4rillPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument14 pagesMultiple Choice Questions PDFMuhammad HaseebPas encore d'évaluation
- Histo FinalDocument10 pagesHisto FinalA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaiePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestDocument18 pagesChapt 4 5 6 7 Practice TestOregon190100% (6)
- Integumentary System NotesDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System NotesLeasxz ZxsaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio F4 Endterm ExamDocument7 pagesBio F4 Endterm ExamMoha abdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manualsamuelfintanult1jj100% (29)
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFhuonghuyen2cp9ez100% (11)
- PPSC Past Paper Lecturer Papaer Biology 15!06!2015Document6 pagesPPSC Past Paper Lecturer Papaer Biology 15!06!2015Kashmala Zia khanPas encore d'évaluation
- TC - Torax - 141018183553Document28 pagesTC - Torax - 141018183553Anonymous UmxvWIqIuPas encore d'évaluation
- A&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideDocument2 pagesA&P Exam 3 CH 3-5 Study GuideJoe ChounramanyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2401ModelKeys 2Document72 pages2401ModelKeys 2Threxsia SandePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrode Placement enDocument40 pagesElectrode Placement enRichard HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Yr ProffDocument17 pages2nd Yr ProffUsama HameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Integumentary System Terminology WorksheetDocument2 pagesIntegumentary System Terminology WorksheetfernandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesBiology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemNicole Athena CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled20 PDFDocument12 pagesUntitled20 PDFElizabeth LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Anat 2ND IaDocument6 pagesAnat 2ND IaSnehal SawantPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Review: TH TH TH THDocument7 pagesAnatomy Review: TH TH TH THNicole Xyza JunsayPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesodermal Tissue and Its Derivatives: MyocoelDocument62 pagesMesodermal Tissue and Its Derivatives: Myocoelytterbium101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Animal Tissues 22-05-2020Document8 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Animal Tissues 22-05-2020BLR PUNEETBHAVAN COLLEGEPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Year Important Question ListDocument17 pages1st Year Important Question ListMalsawma PolarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Integumentary SystemDocument77 pagesIntegumentary SystemAj MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular ExamDocument9 pagesMuscular Exam- マックスPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam Review SheetDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Review Sheetapi-264668182Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - 5 TESTDocument9 pagesUnit - 5 TESTmisgshlove1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Mo Ement MuscleDocument14 pagesTypes of Mo Ement MuscleChinmaya VastradPas encore d'évaluation
- Integumentary System OutlineDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System OutlinePIOZRPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument18 pagesCell The Unit of LifeNeptune Super-15 Science AcademyPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 3 Previous Years 2Document24 pagesPart 3 Previous Years 2mohamed fakhryPas encore d'évaluation
- 61th Continuous (Block 1)Document7 pages61th Continuous (Block 1)mahmoud ezzeldeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled10 PDFDocument14 pagesUntitled10 PDFElizabeth LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Biology 1 Final Fall 2021-2022Document3 pagesHuman Biology 1 Final Fall 2021-2022AmaanPas encore d'évaluation
- CTO 17 Form Assess Qus0910Document16 pagesCTO 17 Form Assess Qus0910becca_smith13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integumen SystemDocument22 pagesIntegumen Systemayu rahmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersDocument16 pagesMuscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersLinet HuchuPas encore d'évaluation
- XII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyDocument1 pageXII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyKishor KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Tissue - 1Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 1Kb AshishPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Year Paper-I PINK - RegularDocument4 pages1st Year Paper-I PINK - RegularMuhammad WaseemPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual 1Document12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual 1stevenbrownxockdjatwe100% (23)
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5Th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5Th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (15)
- Animal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionKb AshishPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 PDFDocument20 pages3 PDFRose Augustin100% (1)
- 9 - Integument System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pages9 - Integument System Anatomy and PhysiologyNickson OnchokaPas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument7 pagesNullapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between PathologyDocument1 pageINFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathologyapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument7 pagesNullapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between PathologyDocument1 pageINFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathologyapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Behavior Intro, Nervous System Intro To Animal BehaviorDocument19 pagesAnimal Behavior Intro, Nervous System Intro To Animal Behaviorapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ritchie Player School RD 1 RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6 Total Points Martacho Player School RD 1RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6total PointsDocument4 pagesRitchie Player School RD 1 RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6 Total Points Martacho Player School RD 1RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6total Pointsapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology Unit Test NAMEDocument5 pagesEcology Unit Test NAMEapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions in Communities: Section 2Document16 pagesInteractions in Communities: Section 2api-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
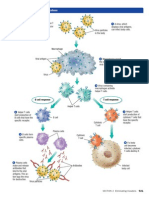
- The Immune Response System: Figure 7 Antigens (Small GreenDocument1 pageThe Immune Response System: Figure 7 Antigens (Small Greenapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument2 pagesNullapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tissue Identification QuizDocument1 pageTissue Identification Quizapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology Unit Test NAMEDocument5 pagesEcology Unit Test NAMEapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- A. Big Idea of Ecology-Interdependence: - Everything Is ConnectedDocument11 pagesA. Big Idea of Ecology-Interdependence: - Everything Is Connectedapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- QuickTime and A TIFF (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To SeeDocument2 pagesQuickTime and A TIFF (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To Seeapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name Class DateDocument2 pagesName Class Dateapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- 12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank WithDocument3 pages12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank Withapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Test: Cell ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter Test: Cell Reproductionapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- A&P Tissue Quiz 2008Document2 pagesA&P Tissue Quiz 2008api-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- A&P TISSUE TEST: 1,2. Tissues Are Made of Cells andDocument3 pagesA&P TISSUE TEST: 1,2. Tissues Are Made of Cells andapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- NameDocument3 pagesNameapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name Class DateDocument2 pagesName Class Dateapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 3 Bellringer AlternatelyDocument10 pagesSkeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 3 Bellringer Alternatelyapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" Cellsapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241Pas encore d'évaluation
- HematologyDocument6 pagesHematologyRian CopperPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Science NursingDocument15 pagesBlood Science NursingMaria Gloria Aquino BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Blood Typing Game DirectionsDocument3 pagesThe Blood Typing Game DirectionsMichael TownsendPas encore d'évaluation
- Rodaks Hema 2 Lec Chapter 39&40Document45 pagesRodaks Hema 2 Lec Chapter 39&40Ivory Mae Verona AndayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument14 pagesVenous ThromboembolismCélia BetkaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and BloodstainsDocument27 pagesBlood and BloodstainsPrincess Mae EstabilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument4 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsPavel MilenkovskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Group Testing: Hong-Yang Li and Kai GuoDocument11 pagesBlood Group Testing: Hong-Yang Li and Kai Guodkp rbmPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscular SystemDocument36 pagesMuscular SystemDeepak KdPas encore d'évaluation
- Thromboelastogram (TEG) - LITFL - CCC InvestigationsDocument10 pagesThromboelastogram (TEG) - LITFL - CCC InvestigationsMarcelliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Routine Laboratory ExamDocument8 pagesRoutine Laboratory Examthe studentPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic Coagulation DisordersDocument42 pagesHemorrhagic Coagulation DisordersGirum TesfayePas encore d'évaluation
- Jadual Graf Bacaan Tekanan DarahDocument2 pagesJadual Graf Bacaan Tekanan Darahsharimax06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of TransfusionDocument4 pagesRules of Transfusionapi-233414716100% (1)
- Chapter 2.2-2.3Document15 pagesChapter 2.2-2.3Gerard Bio100% (2)
- Interference in Coagulation Testing: Focus On Spurious Hemolysis, Icterus, and LipemiaDocument10 pagesInterference in Coagulation Testing: Focus On Spurious Hemolysis, Icterus, and LipemiaMichael John AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- A&P Replaced Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesA&P Replaced Cheat SheetNihal AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone DevelopmentDocument25 pagesBone DevelopmentZeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Thromboelastography: Clinical Application, Interpretation, and Transfusion ManagementDocument7 pagesThromboelastography: Clinical Application, Interpretation, and Transfusion ManagementMarcelliaPas encore d'évaluation
- S86 - F.PSC Trauma CentreDocument2 pagesS86 - F.PSC Trauma CentreSangita pandey100% (1)
- 127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Document4 pages127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Riri Andriani MinHoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Outlines - Abnormal PT and PTT - CausesDocument1 pagePathology Outlines - Abnormal PT and PTT - CausesShane AranetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood and Blood VesselsDocument10 pagesBlood and Blood Vesselsdiddi21Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Plant AnatomyDocument31 pages2 Plant AnatomyDipankar Roy100% (1)
- Laboratory Evaluation of FibrinolysisDocument14 pagesLaboratory Evaluation of FibrinolysisSusielyn Anne Tumamao Angobung100% (2)