Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Passive Voice
Transféré par
Hijatin Nur SpTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Passive Voice
Transféré par
Hijatin Nur SpDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Passive Voice
The passive voice is the phrase that the issue is not the perpetrators of an act. The subject is the recipient of the result of an action. Example: A tiger was killed by Eldy. (Here is indicated by the animal subject is a tiger, which suffered some Act by Eldy). In the Indonesian sentence using a verb that begins with "di". Formula to form a passive sentence is: Subject + be + Verb + by + Object + modifier 3 The sentences using the passive voice with modals: Can: Active: She can sell the car every time Passsive: The car can be sold by her every time May: Active: He may sell the car Passive: the house may be sold by him. Must: Active: She must open the gate every morning Passive: The gate must not be opened by her every mornig. Might: Active: He might meet Dewi Passive: Dewi might meet dewi. Could: Active: He could finish his duty last month Passive: His duty could be finished by him last month.
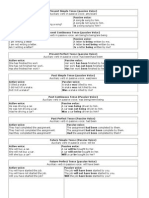
patterns of passive voice in each of tenses: a. If the active voice in Simple Present Tense, the to be is am or are . Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He meets them everyday. : They are met by him everyday. : She waters this plant every two days. : This plant is watered by her every two days.
b. If the active voice in Simple Past Tense, the to be is was or were . Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He met them yesterday : They were met by him yesterday : She watered this plant this morning : This plant was watered by her this morning .
c. If the passive voice in Present Perfect Tense, to be has been placed after the auxiliary have or has, so that 'has been' or 'have been' Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He has met them : They have been met by him : She has watered this plant for 5 minutes. : This plant has been watered by her for 5 minutes.
d. If the passive voice in Past Perfect Tense, the to be is been and has been placed after the auxiliary had, so that had been Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He had met them before I came. : They had been met by him before I came. : She had watered this plant for 5 minutes when I got here : This plant had been watered by her for 5 minutes when I got here.
e. If the active voice in Simple Future Tense, the to be be. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He will meet them tomorrow. : They will be met by him tomorrow. : She will water this plant this afternoon. : This plant will be watered by her this afternoon.
f. If the passive voice in Future Perfect Tense, the to be is been and has been placed after the auxiliary will have, so that will have been Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He will have met them before I get there tomorrow. : They will have been met by him before I get there tomorrow. : She will have watered this plant before I get here this afternoon. : This plant will have been watered by her before I get here this afternoon.
g. If the passive voice in Past Future perfect tense, the to be is been and has been placed after the auxiliary would have, so that would have been Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He would have met them. : They would have been met by him. : She would have watered this plant. : This plant would have been watered by her.
h. If the active voice in Present Continous Tense, the to be is, is, am, or are + being Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He is meeting them now. : They are being met by him now. : She is watering this plant now. : This plant is being watered by her now.
i. If the active voice in Past Continous Tense, the to be is, Was or Were + being Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He was meeting them. : They were being met by him. : She was watering this plant. : This plant was being watered by her.
j. If the active voice in Perfect Continous Tense, the to be is, (has/have) been + being Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He has been meeting them. : They have been being met by him. : She has been watering this plant. : This plant has been being watered by her.
k. If the active voice in Past Perfect Continous Tense, the to be is, had been + being. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He had been meeting them. : They had been being met by him. : She had been watering this plant. : This plant had been being watered by her.
l. If the active voice in Future Continous Tense, the to be is, will be + being. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He will be meeting them. : They will be being met by him. : She will be watering this plant. : This plant will be being watered by her.
m. If the active voice in Past Future Continous Tense, the to be is, would be + being. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He would be meeting them. : They would be being met by him. : She would be watering this plant. : This plant would be being watered by her.
n. If the active voice in Future Future Continous Tense, the to be is, will have been + being. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He will have been meeting them. : They will have been being met by him. : She will have been watering this plant. : This plant will have been being watered by her.
o. If the active voice in Past Future Future Continous Tense, the to be is, would have been + being. Example: Active Passive Active Passive : He would be meeting them. : They would be being met by him. : She would be watering this plant. : This plant would be being watered by her.
Conclucion: 1. Passive Voice is the subject of the sentence that the perpetrator did not act. The subject is the recipient of the result of an action. 2. To say a sentence in the passive voice, tenses do not change. Tenses must be the same if we say so in the active form. What changed verb only. 3. The verb has no object (intransitive verb) can not be converted into the passive voice, like, crying, boiling, rose, etc. 4. In addition to sentences that use tobe and additions, a sentence that uses the word capital can also be quiet. 5. To create a negative sentence add the words not after Tobe, auxiliary or modal verbs.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideD'EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesActive and Passive VoiceNurdIen Ibnu IdrusPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice: Was Atau WereDocument4 pagesPassive Voice: Was Atau Weresuci nurmalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument12 pagesActive and Passive VoiceAndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and PassiveDocument4 pagesActive and PassivealdowannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pola active dan passive voiceDocument6 pagesPola active dan passive voiceShertin Mooy MuskananPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE GUIDEDocument6 pagesACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE GUIDEIezma100% (2)
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument19 pagesActive and Passive VoicemedicalrecorderxxPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Modal Verbs PassiveDocument7 pagesPast Modal Verbs PassiveElva MarliahPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive SentencesDocument5 pagesActive and Passive SentencesAdi NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pola Active Dan Passive Voice Pada Tiap Tensis: Had BeenDocument3 pagesPola Active Dan Passive Voice Pada Tiap Tensis: Had Beenibnusurahman05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Future Tenses Active and Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesFuture Tenses Active and Passive VoicefauhanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Chapter 7: (19) (20) (21) (22) (23) (24) (25) (26)Document10 pagesGroup Chapter 7: (19) (20) (21) (22) (23) (24) (25) (26)Naila ShufaPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Passive VoiceDocument11 pagesMakalah Passive VoiceFebry Anto BakaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Dan Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesActive Dan Passive VoiceDella MitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice (Kalimat Pasif) Dan Active Voice (Kalimat Aktif)Document3 pagesPassive Voice (Kalimat Pasif) Dan Active Voice (Kalimat Aktif)Elisa HkannorPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Dan Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesActive Dan Passive VoiceDella Mitasari100% (2)
- Passive Voice Present 1. Simple Present TenseDocument14 pagesPassive Voice Present 1. Simple Present TenseZaskia Intan SaomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 Active and Passive Sentences: Abdul Wahid Ika Wulan Mia Kurniaty Nurul Aeni Siti RukmanaDocument20 pagesGroup 2 Active and Passive Sentences: Abdul Wahid Ika Wulan Mia Kurniaty Nurul Aeni Siti Rukmanamalika putri andriyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice To Active VoiceDocument19 pagesPassive Voice To Active VoiceAisyah LarasatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Om SwastyastuDocument14 pagesOm SwastyastuSri Apsari DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesActive and Passive VoiceMalik SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- SYMPATHY AND REPORTED SPEECHDocument7 pagesSYMPATHY AND REPORTED SPEECHNindhita Dyah SPas encore d'évaluation
- Language Description 1 - Tenses-Voice: Active and Passive: Prepared By: Deenadevy Jessica DebbieDocument15 pagesLanguage Description 1 - Tenses-Voice: Active and Passive: Prepared By: Deenadevy Jessica DebbieJessica Debbie PeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Future TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Future TenseBernadette NartePas encore d'évaluation
- Active Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesActive Passive VoiceS. Kathirvelu System AdministratorPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive Voice Lecture 7Document38 pagesActive and Passive Voice Lecture 7maheenshaikh119Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bab IDocument12 pagesBab IEko ServoPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument25 pagesPassive VoiceNikmatul Maula Nur RahmadaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice INGGRISDocument12 pagesPassive Voice INGGRISRafi RenaldyPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Active and Passive FormDocument4 pagesGrammar Active and Passive FormZenZaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice ExplainedDocument4 pagesPassive Voice ExplainedsifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive and ActiveDocument7 pagesPassive and Activeapi-304729893Pas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesPassive VoiceTianbestdionZaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Passive Voice GuideDocument2 pagesActive and Passive Voice GuideShailesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice Focuses New InfoDocument13 pagesPassive Voice Focuses New InfoDarcy DeeaPas encore d'évaluation
- WsActive and Passive Voice RulesDocument16 pagesWsActive and Passive Voice RulesLionel Carel Tchiendjo TchanagPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: - Class: - MarkDocument4 pagesName: - Class: - MarkLeslie VillalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDocument13 pagesE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Srtucture Passive Voice: Dosen Pengampu: Dara Ftri MarzukiDocument11 pagesSrtucture Passive Voice: Dosen Pengampu: Dara Ftri MarzukiFahruz zahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice 2023Document58 pagesPassive Voice 2023mudaneabdiwali157Pas encore d'évaluation
- Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesActive and PassiveDivya Rai SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity: UniversityDocument24 pagesAmity: UniversityRajat RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Beta Gustilawati NPM: 16310048 Class Perth in TuesdayDocument10 pagesName: Beta Gustilawati NPM: 16310048 Class Perth in TuesdayAzahrah Mawaddah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Changing Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveDocument4 pagesChanging Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveBernadette NartePas encore d'évaluation
- Changing Active Sentences to Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesChanging Active Sentences to Passive VoiceBernadette NartePas encore d'évaluation
- Active N Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesActive N Passive VoiceGintang PrayogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice 1Document2 pagesPassive Voice 1api-21516494Pas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesMakalah Passive VoiceSolehudin100% (1)
- Booklet c1 AdvancedDocument266 pagesBooklet c1 AdvancedSenteyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mood. Subjunctive Mood.Document8 pagesMood. Subjunctive Mood.Joel BradfordPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive and Active Voice (1) Passive and Active VoiceDocument5 pagesPassive and Active Voice (1) Passive and Active VoiceSergioPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Daily Exam-19 English - 9 - VoiceDocument17 pagesFree Daily Exam-19 English - 9 - Voiceroy chPas encore d'évaluation
- VOICE AND NARRATIONDocument15 pagesVOICE AND NARRATIONSukhwinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- La Voz Pasiva 2Document6 pagesLa Voz Pasiva 2Ines Rodri MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument16 pagesPassive VoiceJuan SpainPas encore d'évaluation
- AP VoiceDocument3 pagesAP VoiceHtun ThantPas encore d'évaluation
- BETAAMIRIN MASUK Der PHARMA ChemicaDocument14 pagesBETAAMIRIN MASUK Der PHARMA ChemicaHijatin Nur SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Lampiran IiiDocument6 pagesLampiran IiiHijatin Nur SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Dewan EtikDocument4 pagesTugas Dewan EtikHijatin Nur SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Hubungan Aktifitas Antioksidan Senyawa Fenolik Dalam Hipericum Pervoratum LDocument14 pagesHubungan Aktifitas Antioksidan Senyawa Fenolik Dalam Hipericum Pervoratum LHijatin Nur SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesPassive VoiceHijatin Nur SpPas encore d'évaluation
- ThesisDocument39 pagesThesisJeanine CristobalPas encore d'évaluation
- A Summary of Postmodern PhilosophyDocument3 pagesA Summary of Postmodern Philosophyjimpetree6090Pas encore d'évaluation
- The-Secret-of-Effective-Feedback Dylan William PDFDocument24 pagesThe-Secret-of-Effective-Feedback Dylan William PDFCésar SpotPas encore d'évaluation
- Santrock3 PPT Ch01Document35 pagesSantrock3 PPT Ch01Syarafina Abdullah67% (3)
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 4 Quarter: Kagawaran NG Edukasyon Sangay NG Lungsod NG DabawDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6 4 Quarter: Kagawaran NG Edukasyon Sangay NG Lungsod NG DabawEmmanuel Nicolo TaglePas encore d'évaluation
- Articles WorkbookDocument8 pagesArticles WorkbookrajisundarPas encore d'évaluation
- Презентация по стилистикеDocument17 pagesПрезентация по стилистикеIryna ShymanovychPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhythmic Activities Syllabus Outlines Course OutcomesDocument5 pagesRhythmic Activities Syllabus Outlines Course OutcomesTrexia PantilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Improvement Plan MatrixDocument3 pagesImprovement Plan MatrixJESSA MAE ORPILLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive Voice - Theory & Ex.Document4 pagesPassive Voice - Theory & Ex.Aleksandra SzyjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument12 pagesEmotional IntelligenceKritika PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive ScienceDocument2 pagesCognitive ScienceJetlin C PPas encore d'évaluation
- Erikson's 8 StagesDocument5 pagesErikson's 8 StagesAkhil KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sociolinguistic Research Proposal 202032001Document15 pagesSociolinguistic Research Proposal 202032001FitriaDesmayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ai Robocom: Mick G.D. Remmerswaal March 18, 2020Document11 pagesAi Robocom: Mick G.D. Remmerswaal March 18, 2020Mick RemmerswaalPas encore d'évaluation
- 5e Lesson Plan Perspectives Scientific NotationDocument5 pages5e Lesson Plan Perspectives Scientific Notationapi-509411193Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection LacDocument9 pagesReflection LacSTEPHEN MILANPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilinguals Social FlexibilityDocument13 pagesBilinguals Social FlexibilitySoumen DebPas encore d'évaluation
- Research MethodologyDocument4 pagesResearch MethodologySubrat RathPas encore d'évaluation
- "Recalls Chemical Formulas". What Is The Most Appropriate Objective Test Item To Use For Measuring It?Document89 pages"Recalls Chemical Formulas". What Is The Most Appropriate Objective Test Item To Use For Measuring It?Tony Santos100% (1)
- Practice Exercises For Pre-UnitDocument7 pagesPractice Exercises For Pre-UnitAmbar CarvajalPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Linguistics Lecture 1Document18 pagesApplied Linguistics Lecture 1Dina BensretiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To NLP - Part 1Document23 pagesIntroduction To NLP - Part 1Etsile KgosanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction On The Documentary "The Great Hack"Document1 pageReaction On The Documentary "The Great Hack"jyna77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Art Appreciation 3Document7 pagesArt Appreciation 3Asher SarcenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop Little Red Reading HoodDocument5 pagesWorkshop Little Red Reading HoodLoraine OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Project Intro ErnacioDocument4 pagesResearch Project Intro ErnacioJP Jayson TabiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Philo. Periodical 2nd Quarter PedofileDocument6 pagesPhilo. Periodical 2nd Quarter PedofileArwin NikkosPas encore d'évaluation
- Knotion Writing GuideDocument20 pagesKnotion Writing GuideSandra Torres100% (1)