Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Starch
Transféré par
Logan ElengkoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Starch
Transféré par
Logan ElengkoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
8Starch a polysaccharide carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose monosaccharide units joined together by glycosidic bonds.
All plant seeds and tubers contain starch which is predominantly present as amylose and amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25 percent amylose and 75 to 80 percent amylopectin. Starch is produced as granules in most plants cells. Native starches from different botanical sources vary widely in structure and composition, but all granules consist of two major molecular components, amylose (20-30%) and amylopectin (70-80%), both of which are polymers of -D-glucose units in the 4C1 conformation. In amylose (Figure 1), these are linked -(1 4)-, with the ring oxygen atoms all on the same side, whereas in amylopectin about one residue in every twenty is also linked -(1 6)- forming branch-points. Function - Starch is the main source of energy form in plants. Cellulose Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C6H10O5)n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand (14) linked D-glucose units. function - Cellulose is the structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most common organic compound on Earth. About 33 percent of all plant matter is cellulose (the cellulose content of cotton is 90 percent and that of wood is 50 percent).
Glycogen Glycogen is a highly branched polymer. Most of Glc units are linked by -1,4 glycosidic bonds, approximately 1 in 12 Glc residues also makes alpha-1,6 glycosidic bond with a second Glc, which results in the creation of a branch. Glycogen does not possess a reducing end: the 'reducing end' glucose residue is not free but is covalently bound to a protein termed glycogenin as a beta-linkage to a surface tyrosine residue. function - Glycogen is a short term storage energy molecule in animals. It is a polysaccharie made out of glucose. Glucose is are our primary source to produce ATP. And ATP is our primary source for energy. Muscle cell glycogen appears to function as an immediate reserve source of available glucose for muscle cells. Other cells that contain small amounts use it locally as well. Muscle cells lack glucose-6phosphatase enzyme, so they lack the ability to pass glucose into the blood, so the glycogen they store internally is destined for internal use and is not shared with other cells, unlike liver cells.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- MLS 014 - Sas 3Document4 pagesMLS 014 - Sas 3Ylia MastarsPas encore d'évaluation
- Platelet Physiology: Thomas Gremmel, MD Andrew L. Frelinger Iii, PHD Alan D. Michelson, MDDocument14 pagesPlatelet Physiology: Thomas Gremmel, MD Andrew L. Frelinger Iii, PHD Alan D. Michelson, MDRochnald PigaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of A Low-Cost Two-Stage Technique For Production of Low-Sulphur Purified Konjac FlourDocument12 pagesDevelopment of A Low-Cost Two-Stage Technique For Production of Low-Sulphur Purified Konjac Flouregdgh ghhdfhPas encore d'évaluation
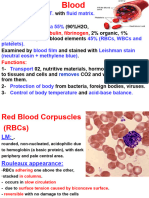
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallDocument25 pagesMechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallelhierofantePas encore d'évaluation
- Banana LabDocument6 pagesBanana Laboofnivlak550% (2)
- Chapter 3 Subcellular Fractionation and Isolation of OrganellesDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Subcellular Fractionation and Isolation of OrganellesrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 12-Peripheral Blood: Zone of Best Morphology (4x)Document8 pagesModule 12-Peripheral Blood: Zone of Best Morphology (4x)Faye AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- TRANS PPT TOPIC - PlateletDocument4 pagesTRANS PPT TOPIC - PlateletPaul LesterPas encore d'évaluation
- Production of Platelet CountsDocument9 pagesProduction of Platelet CountsJack KayatPas encore d'évaluation
- NursingDocument13 pagesNursingGo IdeasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015-Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis PDFDocument997 pages2015-Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis PDFnikospapaioannouPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Lecture 2023fallDocument18 pagesBlood Lecture 2023falldodomrmr205Pas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Test Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition by Harmening PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition by Harmening PDF Full Chapterenvynedplungeyuyz77100% (19)
- 223 FullDocument27 pages223 FullAlberto HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Physiology Week 2 Revised Tabrez Specialized Organels-Cytoplasm 1445 HDocument40 pagesCell Physiology Week 2 Revised Tabrez Specialized Organels-Cytoplasm 1445 H6258c7pxkjPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema2 Lec 2 TransDocument159 pagesHema2 Lec 2 TransJPPas encore d'évaluation
- Volutin Granule StainingDocument2 pagesVolutin Granule StainingRajeev PotadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesChapter 13 - Platelet Production, Structure and FunctionAira UsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Protective Effect of Curcumin On Histopathology and Ultrastructure of Pancreas in The Alloxan Treated Rats For Induction of DiabetesDocument11 pagesProtective Effect of Curcumin On Histopathology and Ultrastructure of Pancreas in The Alloxan Treated Rats For Induction of DiabetesJhoel Zuñiga LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- BD - Bulk Density of Corn StarchDocument6 pagesBD - Bulk Density of Corn Starchsinta putri karismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Detergent EnzymesDocument2 pagesDetergent EnzymesAmer KasidehPas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Lysosome-Related Organelle BiogenesisDocument34 pagesDisorders of Lysosome-Related Organelle BiogenesisMaria AnggiePas encore d'évaluation
- Morphology Internationaljournalplantsciences2011Document14 pagesMorphology Internationaljournalplantsciences2011wenagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition by HarmeningDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition by Harmeningthricechessesmd1m6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hema 2Document35 pagesHema 2Angela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Platelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESDocument7 pagesPlatelets: o Serotonin, ADP & ATP o Destroyed by RESEunice AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Transes MidtermDocument13 pagesHistology Transes MidtermblessganzoncandariPas encore d'évaluation