Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mental Health
Transféré par
Jay VeeCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mental Health
Transféré par
Jay VeeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Arnel V. Hererra, M.D. (Sept.
2012) Mental Health Defined as The successful adaptation to stressors from the internal or external environment, evidenced by thoughts, feelings, and behaviours that are age-appropriate and congruent with local and cultural norms. Aspects of Mental Health: 1. Emotional Intelligence Feels comfortable about oneself. Have emotional self-control. Recognize emotions in others. Can handle relationships. Accepting people for what they are. 2. Resiliency Emerge and grow from negative life events 3. Enjoys life and contented with simple daily pleasures 4. Ambitious but sets realistic goals. 5. Accepts new challenges, new experiences and new ideas 6. Spirituality that are part of us that deals with relationships, values & addresses questions of purpose and meaning in life Mental Illness Defined as Maladaptive responses to stressors from the internal or external environment, evidenced by thoughts, feelings and behaviours that are incongruent with the local and cultural norms and interfere with the individuals social, occupational, or physical functioning. Impacts many people w/o regard for age, income, or profession. Dealing with people with mental illness is not anyones problem, it is everyones responsibility. Signs and symptoms of Mental Illness: 1. Change in behaviour, restlessness, irritability, talkativeness, depression & suspicion Persistence for >2 wks. predisposes you to develop mental illness Before Puberty: M=F (1:1) Adolescence & Adulthood: M<F (1:4) Treatment is usually 7 months 2. Alcohol abuse is a pattern of drinking that results in harm to ones health, interpersonal relationships, ability to work and linked with suicide 3. Impaired sleep or sleeplessness for a prolonged period 4. Getting tired easily, lowering of output 5. Impaired memory 6. Keeping away from family & friends Community Mental Health Refers to all activities undertaken in the community in the name of mental health In the context of Human Rights and Disability Current situation: in Institutions in Communities
Mental Health
A. Institutions Experience: Degrading treatment Neglect & lack of care Inhuman conditions Stripped of dignity INDISPUTABLE NEED FOR ALTERNATIVE B. Communities Experience for Majority: Neglect Rejection No access to treatment Poverty Stressed families Ridicule, Taunts Destitution Community as an alternative Is it possible? Mental Health help does not have to be in a hospital. Most patients living with a psychiatric disability can live a normal life with community support. Action Plan on Mental Health The Action Plan will: Focus on promotion, prevention & early intervention Improve access to services Build workforce capacity Better coordinate care & enable greater collaboration Provide a seamless and connected care system Two Key Concepts a. Institutionalize to place in a special location/house, lonely isolated but cannot live independently, lose individuality & ability to cope with life b. Community group of people, socially interdependent, participate together, relationships, share practices, collective action Experimentally almost opposite Treatment Process 1. Capacity Building breaking the silence of mental illness in communities 2. Treatment ensuring treatment for mentally ill people with the active involvement of their families, communities and using local resources, government facilities 3. Sustainable Livelihoods supporting practical projects that help mentally ill people to realise their potentials and contribute to their communities 4. Basic Needs Results people treated now productive members of their communities 5. Management & Administration to ensure work that is efficient and professional and satisfies the needs of mentally ill people and their families
Page 1 of 2
Caregivers & Mentors Take strengths-based, recovery approach to supporting people with severe mental illness Emphasis on community support and social connection as an integral component of recovery Coordination and integration of care o Multidisciplinary o intra- & inter-sectorial Referrals and links to appropriate services Individual recovery plans Care Coordination Provides for a clinical provider and a community coordinator Clinical providers psychiatrist, GP, Mental health nurse Community coordinator caregivers, barangay health workers, midwife These coordinators will manage referrals Major Obstacles Funding Stigma Infrastructure Leadership Financing Intersectoral (ex. DOH, PCSO) Department of Health Support Mobilizing International & Local Partners (Ex. WHO, UNICEF) Program Outcomes Increased access to appropriate support services at the right time Increased personal capacity & self-reliance Increased community participation How it will work? Talk to Community (Capacity Building) Treatment Self-Help Groups Livelihoods Acceptance Community
Page 2 of 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
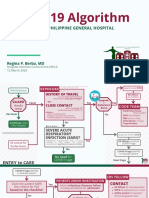
- COVID-19 Algorithm: For The Philippine General HospitalDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Algorithm: For The Philippine General HospitalJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Emergency DashboardDocument1 pageEmergency DashboardJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- BASic Life SOP TemplateDocument4 pagesBASic Life SOP TemplateJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- K1MTZDocument1 pageK1MTZJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Gym Work OutDocument19 pagesGym Work OutJay Vee100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- From Er To Ward 1, 3, Micu: ToopdàDocument2 pagesFrom Er To Ward 1, 3, Micu: ToopdàJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Sample Medical Guidelines: Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesSample Medical Guidelines: Congestive Heart FailureJohanna ShuulukaPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- RP Manual TemplateDocument9 pagesRP Manual TemplateJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Manual-R B-Medical ClearanceDocument2 pagesManual-R B-Medical ClearanceJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Department of Emergency Medicine: Philippine General Hospital University of The Philippines Manila Taft Avenue, ManilaDocument1 pageDepartment of Emergency Medicine: Philippine General Hospital University of The Philippines Manila Taft Avenue, ManilaJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Insert Facility/Institute Logo Here: TemplateDocument5 pagesInsert Facility/Institute Logo Here: TemplateJay Vee100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Annex 2: Laboratory Assessment Tool / Facility QuestionnaireDocument57 pagesAnnex 2: Laboratory Assessment Tool / Facility QuestionnaireJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Workout Set A:: Barbell Front Squat (If You Don'T Have Access, Use DBS)Document1 pageWorkout Set A:: Barbell Front Squat (If You Don'T Have Access, Use DBS)Jay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Final Covid Guideline PsmidDocument26 pagesFinal Covid Guideline PsmidJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Revised Clinical HX For NewbornDocument3 pagesRevised Clinical HX For NewbornJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Diseases of The Joint OutlineDocument1 pageDiseases of The Joint OutlineJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- ENT-Larynx by Dr. Nixon SeeDocument7 pagesENT-Larynx by Dr. Nixon SeeJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Near NCR (National Capital Region) - Quezon CityDocument1 pageNear NCR (National Capital Region) - Quezon CityJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- History Taking ExaminationDocument7 pagesHistory Taking ExaminationIndunil AnuruddhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- CK History Final W Pe Sample MentalDocument4 pagesCK History Final W Pe Sample MentalJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- CK History Final W Pe Sample MentalDocument4 pagesCK History Final W Pe Sample MentalJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Pediatric Clinical H&PDocument7 pagesPediatric Clinical H&PJay Vee100% (1)
- Census MayDocument8 pagesCensus MayJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia Finalsurgical AnestheisaDocument66 pagesAnesthesia Finalsurgical AnestheisaJay VeePas encore d'évaluation
- The ConceptDocument10 pagesThe ConceptJúlio C. Abdala FHPas encore d'évaluation
- SkilliZee Class 4 Journal Doodle Draft 3Document70 pagesSkilliZee Class 4 Journal Doodle Draft 3rashi sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Student Learning Basic ConceptsDocument5 pagesAssessment of Student Learning Basic Conceptsrujean romy p guisando67% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Managerial Counselling Module IIDocument50 pagesManagerial Counselling Module IIPrerana AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Group PresentationDocument11 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder Group Presentationapi-315727817Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rhetorical Analysis Through Music WorksheetDocument24 pagesRhetorical Analysis Through Music WorksheetRishi mPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare and Contrast Essay IIDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast Essay IIglamoc1987100% (1)
- Datavision OCDDocument6 pagesDatavision OCDYashwanth Varma100% (1)
- Principles Unit PlanDocument10 pagesPrinciples Unit Planapi-308317958Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal 3Document21 pagesJurnal 3Anonymous iWqYLBewyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Amr TohamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Collective BargainingDocument3 pagesCollective BargainingChhaya GahlotPas encore d'évaluation
- De THI CHINH THUC - Ma 401 Co Loi Giai Chi TietDocument11 pagesDe THI CHINH THUC - Ma 401 Co Loi Giai Chi TietTrịnh NamPas encore d'évaluation
- Execution SummaryDocument10 pagesExecution SummaryAnone SoreePas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- MILQ2 - LC3 August 21 - 2019Document3 pagesMILQ2 - LC3 August 21 - 2019Jose Ruel Rosello MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dari Program OverviewDocument5 pagesDari Program OverviewMichele EcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century CultureDocument2 pagesTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century CulturekbolorPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Assessment 2 Documentation Rubric p65-68Document6 pagesKey Assessment 2 Documentation Rubric p65-68api-215636357Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seeking Wisdom in The Age of (Mis) Information & Noise - Dec 2017Document59 pagesSeeking Wisdom in The Age of (Mis) Information & Noise - Dec 2017Vishal Safal Niveshak Khandelwal100% (3)
- Walcott Harry Potter Unit PDFDocument39 pagesWalcott Harry Potter Unit PDFapi-406263164100% (1)
- Nonmarket StrategyDocument27 pagesNonmarket StrategyMihaela GadircaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - 02-25-2021 - 16-19-14 - Master of Art 4th Sem (Only Re-Appear) Exams March, 2021Document3 pages4 - 02-25-2021 - 16-19-14 - Master of Art 4th Sem (Only Re-Appear) Exams March, 2021parteek 3636Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinesiology Info 1Document3 pagesKinesiology Info 1hwardell_oooPas encore d'évaluation
- Value EngineeringDocument51 pagesValue Engineeringjagfifa71% (14)
- Ethics and AccountabilityDocument46 pagesEthics and Accountabilityboniglai50% (1)
- Ap Psych SyllabusDocument30 pagesAp Psych Syllabusapi-261300427Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emotional or Transactional Engagement CIPD 2012Document36 pagesEmotional or Transactional Engagement CIPD 2012Maya Camarasu100% (1)
- Back StreetDocument2 pagesBack StreetNazwa DesfaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Organisation Structure: Activity 12.1 (Page 214) : Penang Valley Cars LTDDocument7 pagesOrganisation Structure: Activity 12.1 (Page 214) : Penang Valley Cars LTDNguyễn QuânPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effectiveness of Using Tongue Twister For ImprovingDocument11 pagesThe Effectiveness of Using Tongue Twister For ImprovingNophi'ez Zeth'iawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryD'EverandRewire Your Anxious Brain: How to Use the Neuroscience of Fear to End Anxiety, Panic, and WorryÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (157)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyD'EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)