Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Emm 213-3 - Strength of Meterials
Transféré par
saifulhaffiziCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Emm 213-3 - Strength of Meterials
Transféré par
saifulhaffiziDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
[EMM 213/3] -1-
UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA First Semester Examination Academic Session 2010/2011
November 2010
EMM 213/3 Strength of Materials Kekuatan Bahan
Duration : 3 hours Masa : 3 jam
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATE: ARAHAN KEPADA CALON: Please check that this paper contains EIGHT (8) printed pages, TWO (2) pages appendix and SIX (6) questions before you begin the examination. Sila pastikan bahawa kertas soalan ini mengandungi LAPAN (8) mukasurat bercetak, DUA (2) mukasurat lampiran dan ENAM (6) soalan sebelum anda memulakan peperiksaan. Answer FIVE (5) questions. Jawab LIMA (5) soalan. Appendix/Lampiran: 1. Table of Average Mechanical Properties of Typical Engineering Materials (SI Units) [1 page/mukasurat] 2. Beam Deflection Formulae [1 page/mukasurat]
You may answer all questions in English OR Bahasa Malaysia OR a combination of both. Calon boleh menjawab semua soalan dalam Bahasa Malaysia ATAU Bahasa Inggeris ATAU kombinasi kedua-duanya. Answer to each question must begin from a new page. Jawapan untuk setiap soalan mestilah dimulakan pada mukasurat yang baru. In the event of any discrepancies, the English version shall be used. Sekiranya terdapat sebarang percanggahan pada soalan peperiksaan, versi Bahasa Inggeris hendaklah diguna pakai.
2/-
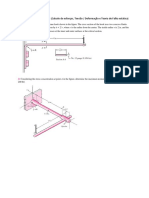
[EMM 213/3] -2Q1. [a] (i) For the hollow shaft and loading shown in Figure Q1[a], determine the maximum shear stress. Bagi shaf berlubang dan bebanan seperti dalam Rajah S1[a], tentukan tegasan ricih maksimum. (ii) Determine the diameter of a solid shaft for which the maximum shear stress under the loading shown is the same as part (i) above. Tentukan diameter shaf padu di mana tegasan ricih maksimum bagi bebanan yang ditunjukkan adalah sama seperti bahagian (i) di atas.
Figure Q1[a] Rajah S1[a] (40 marks/markah) [b] The 304 stainless steel hollow shaft is 3 m long and has an outer diameter of 60 mm. When it is rotating at 60 rad/s, it transmits 30 kW of power from the engine E to the generator G as shown in Figure Q1[b]. The allowable shear stress of the shaft is 150 MPa and the shaft is restricted not to twist more than 0.08 rad. If the inner diameter of shaft is 29.0 mm, determine the possible cause of failures. Then, explain the failure of the shaft. Syaf rongga keluli tahan karat 304 adalah 3 m panjang dan berdiameter luar 60 mm. Apabila berputar pada 60 rad/s, ia menghantar kuasa 30 kW dari enjin E ke penjana G seperti ditunjukkan dalam Rajah S1[b]. Tegasan ricih terizin bagi shaf adalah 150 MPa dan kilasan shaf dihadkan tidak melebihi 0.08 rad. Jika diameter dalam syaf adalah 29.0 mm, tentukan kemungkinan sebab-sebab kegagalan syaf tersebut. Seterusnya, terangkan kegagalan bagi syaf tersebut.
3/-
[EMM 213/3] -3-
Figure Q1[b] Rajah S1[b] (60 marks/markah) Q2. The 304 stainless steel beam ABCD is subjected to a uniform load w as shown in Figure Q2. (i) Determine the shear force and bending moment in the beam as functions of x, where 0 x 2a+l. Then, draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam. Determine the placement a of the supports so that the bending stress in the beam is as small as possible. Then, calculate the bending stress in term of w, a, b, d and l. In the bending testing experiment where the objectives is to determine the beam's deflection and to calculate the modulus of elasticity E of the beam, a point load P is being applied at the middle of the two supports. By using the equation below, E can be calculated. If the own weight of the beam must be considered, discuss and compare the result of E with material properties of beam in Appendix 1. P(2a + l )3 = 48EI
(ii)
(iii)
Rasuk tahan karat 304, ABCD dikenakan beban taburan seragam w seperti dalam Rajah S2. (i) Tentukan daya ricih dan momen lenturan untuk rasuk sebagai fungsi x, di mana, 0 x 2a+l. Seterusnya lukis rajah daya ricih dan momen lenturan bagi rasuk tersebut. Tentukan kedudukan a bagi penyokong-penyokong di mana tegasan lentur dalam rasuk adalah sekecil mungkin. Seterusnya, kirakan tegasan lentur tersebut dalam sebutan w, a, b, d dan l. Di dalam ujian lenturan yang bertujuan untuk menentukan pesongan dan mengira modulus elastik bagi rasuk, daya berpusat P dikenakan pada tengah antara dua penyokong. Dengan menggunakan persamaan di bawah, E dapat dikira. Jika berat sendiri rasuk perlu diambilkira, bincang dan bandingkan keputusan E dengan sifat bahan dalam Lampiran 1.
(ii)
(iii)
4/-
[EMM 213/3] -4-
P(2a + l )3 48EI
Figure Q2 Rajah S2 (100 marks/markah) Q3. [a] Determine the equation of the elastic curve for the beam that is subjected to moment M as shown in the Figure Q3[a] using the x coordinate. Calculate the slope at A and the maximum deflection of the beam. EI is constant. Tentukan persamaan lengkungan elastik untuk rasuk yang dikenakan momen M seperti dalam Rajah S3[a] menggunakan koordinat x. Kirakan kecerunan pada A dan pesongan maksimum bagi rasuk. EI adalah malar.
Figure Q3[a] Rajah S3[a] (60 marks/markah) [b] The box frame ABCD in the Figure Q3[b] is subjected to a uniform distributed loading w along each of its sides. Determine the moment developed in each corner. Neglect the deflection due to axial load. EI is constant and use formulae in Appendix 2 to solve this problem. Kerangka ABCD dalam Rajah S3[b] dikenakan daya taburan seragam w pada setiap sisinya. Tentukan momen yang terhasil pada setiap sudut. Abaikan pesongan yang terhasil akibat daya paksi. EI adalah malar dan sila gunakan persamaan dalam Lampiran 2 untuk menyelesaikan masalah ini.
5/-
[EMM 213/3] -5-
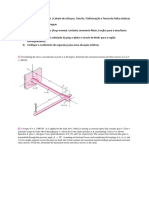
Figure Q3[b] Rajah S3[b] (40 marks/markah) Q4. [a] Define the following term and cite an example for each case together with a sketch showing the condition reflecting such case (iv) Plane stress (v) Plane strain (vi) Principal plane Berikan definisi istilah berikut dan nyatakan satu contoh bagi setiap kes dengan lakaran yang menggambarkan contoh tersebut (i) Tegasan satah (ii) Terikan satah (iii) Satah utama (40 marks/markah) [b] For the loading condition shown in the component below calculate the principal stresses and the maximum shear stress at the point A and draw the Mohrs circle representing the stress condition at that point Bagi keadaan tegasan yang ditunjukkan di dalam unsur-unsur di bawah, kirakan tegasan utama dan tegasan riceh utama A dan lakarkan Bulatan Mohr yang mewakili keadaan tegasan bagi setiap unsur.
6/-
[EMM 213/3] -6Diameter of shaft = 100 mm (solid) 100 mm
Z Y X
A
1800 mm
3000 mm
= 2 + 2 4
Figure Q4[b] Rajah S4[b] (60 marks/markah) Q5. An electric drill is shown in Figure Q5. The drill bit is subjected to a compressive axial force of 500 N, an end bending moment of 20 Nm (in the y-z plane) and a torque of 4 Nm (in the x-z plane). The length of the drill from the bit end to the support at the shank is 100 mm. Based on the stress level at point A determine the suitable diameter of the drill bit made of solid high speed steel if the allowable normal stress is 200 MPa and the allowable shear stress is limited to 60 MPa. Sebuah gerudi elektrik ditunjukkan di dalam Rajah S5. Mata gerudi itu mengalami daya paksi mampatan 500 N, momen lentur hujung 20 Nm (di dalam satah y-z) dan kilas 4 Nm (di dalam satah x-z). Panjang mata gerudi dari hujung gerudi ke bahagian disangga ialah 100 mm. Berdasarkan keadaan tegasan di titik A tentukan diameter yang sesuai untuk mata gerudi yang diperbuat daripada keluli kelajuan tinggi jika tegasan normal yang dibenarkan ialah 200 MPa dan tegasan riceh yang dibenarkan ialah 60 MPa.
7/-
[EMM 213/3] -7-
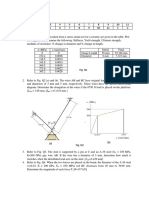
Figure Q5 Rajah S5 (100 marks/markah) Q6. Figure Q6[a] shows three different level of fit between the hole and the shaft. [a] For each case determine the maximum and minimum force needed to push the shaft through the disc given the thickness of the disc is 20 mm and the outer diameter is 70 mm. Both the shaft and the disc are made of steel (E=200 GPa, = 0.28) and the friction coefficient is 0.3.
Rajah S6[a] menunjukkan tiga paras padanan antara lubang dan syaf. [a] Bagi setiap kes padanan tentukan daya maksimum dan minumum yang diperlukan untuk menolak syaf menerusi lubang cakera jika ketebalan setiap cakera adalah 20 mm dan diameter luaran adalah 70 mm. Keduadua syaf dan cakera diperbuat daripada keluli (E=200 GPa, = 0.28) dan pekali geseran ialah 0.3.
8/-
[EMM 213/3] -8-
Figure Q6[a] Rajah S6[a] (70 marks/markah) [b] Cite an example of the use of each type of fit in machine design and comment on the manufacturing challenges to produce each type of fit. Bagi setiap kes padanan nyatakan contoh aplikasi di dalam rekabentuk mesin dan berikan komen anda tentang cabaran proses pembuatan bagi menghasilkan setiap jenis padanan. (30 marks/markah)
-oooOOooo-
9/-
[EMM 213/3] APPENDIX 1/LAMPIRAN 1
Table of Average Mechanical Properties of Typical Engineering Materials (SI Units)
Coef. of Therm. Expansion (10-6)/C
Materials
Density (Mg/m3)
Modulus of Elasticity E (GPa)
Modulus of Rigidity G (GPa)
Yield Strength (MPa)
Metallic Aluminum Wrought Alloys Cost Iron Alloys 197 Copper Alloys 2014-T6 6061-T6 2.79 2.71 7.19 7.28 8.74 8.83 1.83 7.85 7.86 8.16 4.43 73.1 68.9 67.0 1.72 101 103 44.7 200 193 200 120 27 26 27 68 37 38 18 75 75 75 44 70.0 345 152 400 517 800 1000 414 255 23 24 12 12 18 17 26 12 17 12 9.4
Gray ASTM 20 Malleable ASTM ARed Brass C83400 Bronze C86100 [Am 1004-
Magnesium Alloy T61] Steel Alloys Titanium Alloy
Structural A36 Stainless 304 Tool L2 [Ti-6A 1-4V]
Nonmetallic Concrete Low Strength High Strength Kevlar 49 30% Glass 2.38 2.38 1.45 1.45 22.1 29.0 131 72.4 11 11 -
Plastic Reinforced
[1/1]
[EMM 213/3] APPENDIX 2/LAMPIRAN 2
Beam Deflection Formulae
[1/1]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanics of MaterialDocument3 pagesMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsD'EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsPas encore d'évaluation
- AMMDocument3 pagesAMMRajesh Kumar PPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFDocument8 pagesMechanical Eng Ses Main 2016 First PDFSumeet TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Special Mid Term Exam CET204Document3 pagesSpecial Mid Term Exam CET204zPas encore d'évaluation
- BFC 20903Document10 pagesBFC 20903Priyaah KarunakaranPas encore d'évaluation
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech Sol - 2020 - Compre Part A&bDocument4 pagesMech Sol - 2020 - Compre Part A&brohit BindPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2021Document2 pagesMarch 2021AshokPas encore d'évaluation
- CCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023Document7 pagesCCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023aaschlysebakisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Questions 4523Document29 pagesTutorial Questions 4523Toby Joseph ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruPas encore d'évaluation
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDocument3 pagesS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakPas encore d'évaluation
- March 2021Document2 pagesMarch 2021Visal.RPas encore d'évaluation
- UTM Final Exam - Mechanics Sab 2223 Sem 1 2012-13Document10 pagesUTM Final Exam - Mechanics Sab 2223 Sem 1 2012-13Nurhafizah AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMDocument13 pagesSoalan Final Analisis Struktur UTHMliyana2030Pas encore d'évaluation
- Answer ALL Questions Part A (5 2 10 Marks)Document4 pagesAnswer ALL Questions Part A (5 2 10 Marks)rameshbabu_1979Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lista Exercicios PDFDocument8 pagesLista Exercicios PDFLeonardo NecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercícios Elementos de MáquinasDocument8 pagesExercícios Elementos de MáquinasThomas AlmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Elasticity Question PaperDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity Question PaperDESHMUKH ANKIT PRAKASHRAOPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jntu Anan I Year Enggmecha Set 2Document9 pagesJntu Anan I Year Enggmecha Set 2prasaad08Pas encore d'évaluation
- L-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013Document18 pagesL-2/T-2/WRE Date: 06/07/2013MuradPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet No.2 (Simple Stress)Document3 pagesSheet No.2 (Simple Stress)elhalawanyh46Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final ExamSOMFinal 2016 FinalDocument11 pagesFinal ExamSOMFinal 2016 Finalkhalil alhatabPas encore d'évaluation
- JNTUH B.Tech II Year I Semester Mechanics of Solids Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesJNTUH B.Tech II Year I Semester Mechanics of Solids Exam Questionsmahendra babu mekalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument6 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruPas encore d'évaluation
- 9EH EoC Test 2013 No SolsDocument11 pages9EH EoC Test 2013 No SolsDanny EtievePas encore d'évaluation
- Assign I MD IDocument3 pagesAssign I MD IAtharva KPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No 8Document2 pagesAssignment No 8saurabhpatankar5Pas encore d'évaluation
- MAE 635 Advanced Mechanics AssignmentDocument4 pagesMAE 635 Advanced Mechanics Assignmentawsmith1938Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Strength of Materials Paper ModelDocument3 pagesAdvanced Strength of Materials Paper ModeldurgaraokamireddyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3B3 Mechancis of Solids Exam 23Document7 pages3B3 Mechancis of Solids Exam 23Emer DuffPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Analysis Exam PapersDocument3 pagesStructural Analysis Exam Papersfesada1100% (1)
- Theory of Machines & Machine DesignDocument3 pagesTheory of Machines & Machine DesignAvilash JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Define Factor of SafetyDocument3 pagesDefine Factor of SafetySunil AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- CH6 PDFDocument45 pagesCH6 PDFAguero AgueroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesMechanics of SolidsKhaista RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunPas encore d'évaluation
- SFD, BMD and Deflection of beams questionsDocument4 pagesSFD, BMD and Deflection of beams questionsSai Krishna SKPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2-2Document4 pagesTutorial 2-2nageshPas encore d'évaluation
- Mom Sem 1 (09-10)Document12 pagesMom Sem 1 (09-10)Jenylex KumilPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 ME Som Model Examination 2013Document3 pages4 ME Som Model Examination 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- L-2/T-1/CE Date: 31/01/2012: Section - ADocument17 pagesL-2/T-1/CE Date: 31/01/2012: Section - AMahmudul Hasan PathikPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel bar fatigue strength and shaft design calculationsDocument15 pagesSteel bar fatigue strength and shaft design calculationsDaniel RuedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mace 60035Document7 pagesMace 60035eng_ayman_H_MPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Chapter 3 ProblemsNEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng2032-N 2022-2023 Eca First SitDocument21 pagesEng2032-N 2022-2023 Eca First SitSajid MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Previous Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesPrevious Exam QuestionssallyreffatPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of The Toggle JackDocument30 pagesDesign of The Toggle Jackkoanakist91% (11)
- Torsional Analysis of Steel MembersDocument6 pagesTorsional Analysis of Steel MembersasdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Tesla TurbineDocument15 pagesTesla TurbineJY GDPas encore d'évaluation
- Damjanovic Piezoelectricity ECMPDocument10 pagesDamjanovic Piezoelectricity ECMPTimmy LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Sheet-Pile WallsDocument10 pagesDesign of Sheet-Pile WallsbarouniaminePas encore d'évaluation
- Astm d638 99 CompressDocument7 pagesAstm d638 99 CompressJonel UrbonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Ship Design - Ship Motion & Wave LoadDocument203 pagesInnovative Ship Design - Ship Motion & Wave Loadtran phamPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Parameters For Hyperbolic Model of SoilsDocument13 pagesDetermination of Parameters For Hyperbolic Model of SoilsRamiro ChairezPas encore d'évaluation
- Thin Cylinder Experiment: Apparatus We Have Used A Thin Cylinder SM1007Document8 pagesThin Cylinder Experiment: Apparatus We Have Used A Thin Cylinder SM1007Rohan Kumar0% (1)
- 1Document227 pages1api-3838442Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shear Flow in MembersDocument9 pagesShear Flow in MembersMax NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Approach For Bursting Cracking Analysis of Post-Tensioned Anchorage ZoneDocument10 pagesAnalytical Approach For Bursting Cracking Analysis of Post-Tensioned Anchorage ZoneMyat NoePas encore d'évaluation
- AISC 1971 v02Document16 pagesAISC 1971 v02Ignacio Hiram M RoquePas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Elements in Fracture Mechanics Theory Numerics ApplicationsDocument464 pagesFinite Elements in Fracture Mechanics Theory Numerics Applicationscvc100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Practical Column Base Details in Steel StructuresDocument135 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Practical Column Base Details in Steel Structuressom_bs79100% (1)
- FACADE MODELING Structural AnalysisDocument39 pagesFACADE MODELING Structural AnalysisGodino Christian100% (3)
- Basics of Stress Analysis of Underground Piping in Caesar IIDocument4 pagesBasics of Stress Analysis of Underground Piping in Caesar IIiaftPas encore d'évaluation
- Irc 24 2010# PDFDocument258 pagesIrc 24 2010# PDFsuphalPas encore d'évaluation
- Deep - Drawing - Mechanism - Parameters - Defects - and - Rece (1) - DikonversiDocument11 pagesDeep - Drawing - Mechanism - Parameters - Defects - and - Rece (1) - DikonversiEko Andrianto100% (1)
- Damage and Cracking of Concrete Structures From Theory To PracticeDocument299 pagesDamage and Cracking of Concrete Structures From Theory To PracticeMartin RogićPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation on Roll-Over Crashworthiness of an Intercity CoachDocument18 pagesInvestigation on Roll-Over Crashworthiness of an Intercity CoachsibiePas encore d'évaluation
- STAAD Pro - Lesson 07 - SpecificationsDocument7 pagesSTAAD Pro - Lesson 07 - SpecificationsEBeePas encore d'évaluation
- TensorDocument20 pagesTensoremma698Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4130-2009 (A1)Document37 pages4130-2009 (A1)Vardhan100% (1)
- Machdes Project Group ScrewDocument6 pagesMachdes Project Group ScrewSecret SecretPas encore d'évaluation
- Is226 1975Document16 pagesIs226 1975suja ramPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaft Design: Example: Line Shaft (Main), Spindle Shaft (Short), Countershaft (Intermediate)Document9 pagesShaft Design: Example: Line Shaft (Main), Spindle Shaft (Short), Countershaft (Intermediate)Rs SumitPas encore d'évaluation
- M TECH Structural and Construction PDFDocument55 pagesM TECH Structural and Construction PDFniteshPas encore d'évaluation
- Nortje Desiree 2002 PDFDocument328 pagesNortje Desiree 2002 PDFAtul KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- B.tech Mechatronics PDFDocument106 pagesB.tech Mechatronics PDFSandeep KotaPas encore d'évaluation
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindD'EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureD'EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastD'EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (76)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityD'EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (115)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationD'EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessD'EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsD'EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceD'EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkD'EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryD'EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityD'EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.D'EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksD'EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Design and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsD'EverandDesign and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsMarco CecarelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCD'EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceD'EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligencePas encore d'évaluation
- Visions Of Technology: A Century Of Vital Debate About Machines Systems AD'EverandVisions Of Technology: A Century Of Vital Debate About Machines Systems AÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsD'EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Distributed Process Control ReportD'EverandDistributed Process Control ReportPas encore d'évaluation
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!D'EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Modeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesD'EverandModeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: Data Analytics and Innovation for BeginnersD'EverandArtificial Intelligence: Data Analytics and Innovation for BeginnersÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Building Server-side and Microservices with Go: Building Modern Backends and Microservices Using Go, Docker and KubernetesD'EverandBuilding Server-side and Microservices with Go: Building Modern Backends and Microservices Using Go, Docker and KubernetesPas encore d'évaluation