Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Kom Paper
Transféré par
Vivek PatelTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Kom Paper
Transféré par
Vivek PatelDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Seat No.
: ________
Enrolment No.___________
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
BE - SEMESTERIV EXAMINATION SUMMER 2013
Subject Code: 141902 Subject Name: Kinematics of Machines Time: 10.30 am - 01.00 pm
Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Date: 14-06-2013 Total Marks: 70
Q.1
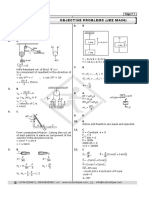
(a) Define : (1) Lower Pair (2) Kinematics Chain (3) Completely Constrained Motion (4) Angle of friction (b) Derive the equation for finding out the ratio of angular velocities of two shafts of Hookes joint. (a) What is straight line motion mechanism? Explain Harts straight line motion mechanism with neat sketch. (b) What is inversion? Explain the inversions of double slider crank chain with neat sketch. OR (b) What is steering gear mechanism? Derive the relation for correct steering for Devis steering gear mechanism. (a) Fig-1 shows the mechanism of a radial valve gear. The crank OA turns uniformly at 150 rpm and is pinned at A to rod AB. The point C in the rod is guided in the circular path with D as centre and DC as radius. The dimensions of various links are: OA = 150 mm; AB = 550 mm; AC = 450 mm; DC = 500 mm; BE = 350 mm. Determine velocity and acceleration of the ram E for the given position of the mechanism. OR (a) Explain the terms used in cam. (1) Trace point. (2) Pressure angle (3) Pitch circle. (b) Determine a cam for operating the exhaust valve of an oil engine. It is required to give simple harmonic motion during opening and closing of the valve each of which corresponds to 60o of cam rotation. The valve must remain in the fully open position for 30o of cam rotation. The lift of the valve is 40 mm and the least radius of the cam is 40 mm. The follower is provided with a roller of radius 15 mm and its line of stroke passes through the axis of cam. Find out the maximum value of velocity and acceleration of follower if the cam rotates at 120 rpm. (a) Derive the equation for finding out the torque required to lift the load by a screw jack. (b) A belt 100 mm wide and 100 mm thick is transmitting power at 900 m/min. the driving tension is 2.8 times the tension on the slack side. If the safe permissible stress for the belt is 1.8 N/mm2, calculate the maximum power that can be transmitted at this speed. Assume the density of leather belt is 1000 kg/m3. Consider the initial tension in the belt; also calculate the greatest power that can be transmitted by this belt and its corresponding speed. OR (a) Derive the equation for maximum efficiency of a screw jack for raising a load.
07
07 07 07
Q.2
07 14
Q.3
Q.3
07 07
Q.4
07 07
Q.4
07
1
(b) In an epicyclic gear train, the internal wheels A and B and compound wheels C and D rotate independently about axis O. The wheels E and F rotate on pins fixed to the arm G. E gears with A and C and F gears with B and D. All the wheels have the same module and the numbers of teeth are: TC = 28, TD = 26, TE = TF = 18. (1) Find the number of teeth on A and B. (2) If the arm G makes 100 rpm clockwise and A is fixed, find the speed of B. (3) If the arm G makes 100 rpm clockwise and wheel A makes 10 rpm counterclockwise, find the speed of wheel B. Q.5 (a) Derive the equation for finding out the length of path of contact for a pair of involute gears. (b) A pair 20o involute gears has module of 5 mm. The pinion has 20 teeth and gear has 60 teeth. Addendum on the pinion and gear wheel in terms of module is one. Find the followings: (1) Number of pairs in contact. (2) Angle turned through by the pinion and gear wheel for one pair in contact. OR (a) Derive equation for finding out the limiting tension ratio in a belt drive. (b) An open belt drive connects two pulleys 1.2 m and 0.5 m diameter, on parallel shafts 3.6 m apart. The mass of the belt is 1 kg/m length and the maximum tension is not to exceed 2000 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.3. The 1.2 m pulley, which is the driver, runs at 200 rpm. Due to slip on one of the pulleys, the velocity of the driven shaft is only 450 rpm. Calculate (1) The torque on each of the two shafts, (2) The power transmitted, and (3) Power lost in friction.
07
07 07
Q.5
07 07
Figure 1
Figure 2
*************
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Structure: J-Car: Automatic Transmission Participant HandoutDocument10 pagesStructure: J-Car: Automatic Transmission Participant HandoutRajuna Dalimunthe33% (3)
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetAgare Tube0% (1)
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesFRANCISCO JERHYL KEITH G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric Velocity Analysis - III: Anirvan DasguptaDocument20 pagesGeometric Velocity Analysis - III: Anirvan Dasguptarahul srivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematic SimilitudeDocument7 pagesKinematic SimilitudeP. SuhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Guidance and Control Systems For Tactical Missles - Zaikang, Qi PDFDocument255 pagesDesign of Guidance and Control Systems For Tactical Missles - Zaikang, Qi PDFrvpilotPas encore d'évaluation
- AccelerationandFreeFall EditedDocument37 pagesAccelerationandFreeFall EditedDarcy EvansPas encore d'évaluation
- L1 Cams and FollowersDocument28 pagesL1 Cams and FollowersDhayane RedoquerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Gear: The Standard Values and Equations Taken From Text Book of Machine Design byDocument4 pagesDesign of Gear: The Standard Values and Equations Taken From Text Book of Machine Design byLemi Chala BeyenePas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Axis Post ProcessorDocument9 pages5 Axis Post ProcessorDUONGTAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Double Class 1 LeverDocument4 pagesDouble Class 1 Levernurlisa khaleedaPas encore d'évaluation
- PS 312fDocument1 pagePS 312fNick MargiePas encore d'évaluation
- Cb7b170c 080e 465f A881 60caacc97670N.L.M Exercise With Solution DoneDocument24 pagesCb7b170c 080e 465f A881 60caacc97670N.L.M Exercise With Solution DoneShuvanshu GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 Trib IntroDocument58 pagesCh1 Trib IntroJaime BerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Contact Detection and Force Estimation During Compliant ManupulationDocument7 pagesHybrid Contact Detection and Force Estimation During Compliant ManupulationRodrigo Murillo ArandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics SeaDocument464 pagesPhysics SeaMaheshwar Kumar100% (1)
- Course Descriptions Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 pagesCourse Descriptions Mechanical Engineeringmasrizal_khairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument227 pagesKinematics of Machinesborchec100% (2)
- Lab 3 ME352Document9 pagesLab 3 ME352Ethan CoynePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Kinematics One DimensionDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - Kinematics One DimensionCuca Lordwin Y SobiorPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Ratio DTC'S, TCC SlippageDocument2 pagesGear Ratio DTC'S, TCC Slippageacmemail583100% (1)
- Automotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesDocument10 pagesAutomotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesMohammad YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic1-Introduction To Gears PDFDocument55 pagesTopic1-Introduction To Gears PDFimranPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Engineering Departmental Seminar Presented By: Tukesh Soni 2013MEZ8475Document38 pagesMechanical Engineering Departmental Seminar Presented By: Tukesh Soni 2013MEZ8475Tukesh SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanisms: Prof - Dr.ing. Csaba AntonyaDocument67 pagesMechanisms: Prof - Dr.ing. Csaba AntonyaGabriel IulianPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Design of An Elliptical Trainer With RiDocument12 pagesInnovative Design of An Elliptical Trainer With RiSilvana AiadPas encore d'évaluation
- Abs, TRC, VSCDocument13 pagesAbs, TRC, VSCĐức LêPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 12 Lecture 1 Rectilinear and Curvilinear MotionDocument51 pagesES 12 Lecture 1 Rectilinear and Curvilinear MotionMarian Galvez-Luis100% (1)
- Basic Biomechanics Hall 7th Edition Test BankDocument14 pagesBasic Biomechanics Hall 7th Edition Test BankjoelalmayowxuPas encore d'évaluation