Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RPT Math Yr4 2013
Transféré par
Nour Janna FahruddinDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RPT Math Yr4 2013
Transféré par
Nour Janna FahruddinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
WE EK
DATE
TOPIC/UNI T UNIT 1: WHOLE NUMBERS
LEARNING AREA
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
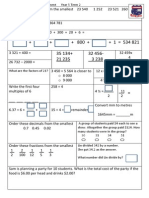
LEARNING OURCOMES (i) Name and write numbers up to 100 000. (ii) Determine the place value of the digits in any whole number up to 100 000. (iii) Compare value of numbers to 100 000. (iv) Round off numbers to the nearest tens, hundreds and thousands. (i) Add any two to four numbers to 100 000. (ii) Solve addition problems. (i) Subtract one or two numbers from a bigger number less than 100 000. (ii) Solve subtraction problems. (i) Multiply three-digit numbers with o 100, o two-digit numbers. (ii) Multiply four-digit numbers with o one-digit numbers, o 10, o two-digit numbers. (iii) Multiply two-digit numbers with 1 000. (iv) Solve multiplication problems. (i) Divide four-digit numbers by o one-digit numbers, o 10, 100 and 1000, o two-digit numbers. (ii) Divide five-digit numbers by o one-digit numbers, o 10, 100 and 1000, o two-digit numbers. (iii) Solve division problems.
REMARKS
2/1- 4/1
1.1 NUMBERS TO 100 000
1.1.1 Develop number sense involving numbers of up to 100 000.
7/1 11/1
1.2 ADDITION WITH THE HIGHEST TOTAL OF 100 000 1.3 SUBTRACTION WITHIN THE RANGE OF 100 000
2.1 Add numbers to the total of 100 000 3.1 Subtract numbers from a number less than 100 000.
14/1 18/1
1.4 MULTIPLICATION WITH THE HIGHEST PRODUCT OF 100 000
1.4.1 Multiply any two numbers with the highest product of 100 000.
21/1 25/1
1.5 DIVISION WITH THE HIGHEST DIVIDEND OF 100000
1.5.1 Divide a number less than 100 000 by a twodigit numbers.
28/1 1/2
1.6 MIXED OPERATIONS
1.6.1 Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction.
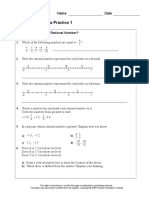
(i) Perform mixed operations involving addition and subtraction with numbers less than o 100, o 1 000, o 10 000. (ii) Solve mixed operation problems. (i) Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10. (ii) Compare the value of two proper fractions with o the same denominators, o the numerator of 1 and different denominators up to 10. (i) Express and write equivalent fractions for proper fractions. (ii) Express equivalent fractions to its simplest form. (i) Add two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o with different numerators. (ii) Add two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o with different numerators. (iii) Solve problems involving addition of proper fractions. (i) Subtract two proper fractions with the same denominator up to 10 to its simplest form with 1 as the numerator for both fractions,
UNIT 2: FRACTION S 2.1 PROPER FRACTIONS 6 4/2 - 8/2
2.1.1 Name and write proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
2.2 EQUIVALENT FRACTIONS
2.2.1 Express equivalent fractions for proper fractions.
11/2 15/2
2.3 ADDITION OF FRACTIONS
2.3.1 Add two proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
18/2 22/2
2.4 SUBTRACTION OF FRACTIONS
2.4.1 Subtract proper fractions with denominators up to 10.
25/2 1/3
UNIT 3: DECIMALS
3.1 DECIMAL NUMBERS
3.1.1 Understand decimal numbers,
with different numerators. (i) Subtract two proper fractions with different denominators up to 10 to its simplest form o with 1 as the numerator for both fractions, o with different numerators. (ii) Solve problems involving subtraction of proper fractions. (i) Name and write decimals with o one decimal place, o two decimal places. (ii) Recognise the place value of o tenths, o hundredths, o tenths and hundredths. (iii) Convert fraction to decimals of o tenths, o hundredths, o tenths and hundredths, and vice versa (i) Add any two to four decimals of one decimal place involving o decimals only, o o whole numbers and decimals, mixed decimals.
10 11
4/3 - 8/3 11/3 15/3 UNIT 3: DECIMALS 3.2 ADDITION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS
UJIAN 1 3.2.1 Add decimals up to two decimal places.
(ii) Add any two to four decimals of two decimal places involving o decimals only, o o whole numbers and decimals, mixed decimals.
(iii) Solve problems involving addition of decimal numbers.
(i) Subtract one to two decimals from a decimal of one decimal place involving o decimals only, 12 18/3 22/3 3.3 SUBTRACTION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS 3.3.1 Subtract decimals up to two decimal places. o mixed decimals, o whole numbers and decimals (mixed decimals). (ii) Subtract one to two decimals of one or two decimal places. (iii) Solve problems involving subtraction of decimals.
23/3 31/3
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1 (i) Multiply any decimal of one decimal place with o one-digit number, 3.4 MULTIPLICAITION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS 3.4.1 Multiply decimals up to two decimal places with a whole number. o 10, 100 and 1000. (ii) Multiply any decimals of two decimal places with o one-digit number, o UNIT 3: DECIMALS 10, 100 and 1000. (iii) Solve problems involving multiplication of decimals. by 3.5.1 Divide decimals up to two decimal places by a whole number. (i) Divide decimals of one decimal place
13
1/4 - 5/4
14
8/4 12/4
3.5 DIVISION OF DECIMAL NUMBERS
o one-digit number, o 10. (ii) Divide decimals of two decimal places by one-digit number. (iii) Divide decimals by a whole number with the dividend value of up to two decimal places. (iv) Solve problems involving division of decimals. (i) Read and write the value of money up to RM10 000.
15
15/4 19/4
UNIT 4: MONEY
4.1 MONEY UP TO RM10000
4.1.1 Understand and use the vocabulary related to money.
(i) Add money up to RM10 000. (ii) Subtract money from up to RM10 000. (iii) Multiply money to the highest product of RM10 000. (iv) Divide money with dividend not more than RM10 000. (v) Perform mixed operation involving addition and subtraction involving money up to RM10 000. (vi) Round off money to the nearest ringgit. (vii) Solve problems involving money up to RM10 000 (i) Read time in hours and minutes according to the 12 hours system. (ii) Write time in hours and minutes according to the 12 hours system. (i) Construct, read and extract information from a simple schedule. (i) Extract information from a calendar. (ii) Solve simple real life problems involving reading the calendar.
4.1.2 Use and apply knowledge of money in real life. 16 22/4 26/4
5.1 READING AND WRITING TIME 17 29/4 3/5 UNIT 5: TIME 5.2 TIME SCHEDULE 6/5 10/5 UNIT 5: TIME 13/5 17/5 5.3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF TIME
5.1.1 Understand, read and write time in hours and minutes. 5.2.1 Construct a simple schedule. 5.2.2 Read a calendar. PKSR 1 5.3.1 Understand the relationship between units of time.
18
(i) State the relationship between units of time:o 1 day = 24 hours, o o o 1 year = 365 / 366 days, 1 decade =10 years. years to days, and vice versa, decades to years, and vice versa, years to months, and vice versa,
19
(ii) Convert 20 20/5 24/5 o o
o o
hours to days, and vice versa. hours to minutes, and vice versa,
(iii) Convert time from o hours and minutes to minutes, and vice versa, 25/5 9/6 UNIT 5: TIME 21 10/6 14/6 5.4 BASIC OPERATION INVOLVING TIME CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN 5.4.1 Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time. 5.4.1 Add, subtract, multiply and divide units of time. (i) Add time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
(ii) Subtract time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o years and months, decades and years. o
22
17/6 21/6
23
24/6 28/6
(iii) Multiply time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units of : o hours and minutes, o years and months, o decades and years. (iv) Divide time involving conversion of units with answers in compound units for time duration of : o hours and minutes, o o years and months, decades and years.
(v) Solve problems involving basic operations of time: o hours and minutes, o years and months,
decades and years.
(i) Read and state the start and end of an event from a schedule. (ii) Calculate the duration of an event from a schedule in 24 1/7 - 5/7 5.5 TIME DURATION 5.5.1 Use and apply knowledge of time to find the duration. o o o and two minutes, hours, hours and minutes within a day consecutive live days.
(iii) Calculate the start or the end of an event from a given duration of time and read the start or end of an event. UNIT 6: LENGTH (i) Read measurement of length using units of milimetre. (ii) Write measurement of length to the nearest scales of tenth division for: 25 8/7 12/7 6.1 MEASURING LENGTH 6.1.1 Measure lengths using standard units. centimetre, metre. (iii) Measure and record lengths of objects using units of o millimetre, o centimetre and milimetre, o metre and centimetre. (iv) Estimate the lengths of objects in o millimetre, o metre and millimetre, o centimetre and millimetre. (i) State the relationship between centimetre and milimetre. (ii) Convert units of length from: milimetres to centimetres and vice versa, o o
26
15/7 21/7
6.2 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN UNITS OF LENGTH
6.2.1 Understand the relationship between units of length.
compound units to a single unit. (i) Add units of length, involving conversion of units in; o millimetre, o 27 22/7 26/7 6.3 BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING LENGTH 6.3.1 Add and subtract length. o metre and centimetre, centimetre and millimetre.
(ii) Subtract units of length, involving conversion of units in; o millimetre, o o metre and centimetre centimetre and millimetre
(i) Multiply units of length, involving conversion of units, by; o a one-digit number, 6.3.2 Multiply and divide length. o 10, 100, 1000. (ii) Divide units of length, involving conversion of units, by; o a one-digit number; 10, 100, 1000. (i) Measure of masses using in units of kilogram and gram. (ii) Read measurement of masses to the nearest scales division of kilograms and grams. (iii) Estimate the masses of objects using kilograms and grams. (i) Convert units of mass from o kilograms to grams, o kilograms and grams to grams, o kilograms and grams to kilograms.
28
29/7 2/8
7.1 MEASURING MASS 29 5/8 - 9/8 UNIT 7: MASS 7.2 RELATONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF MASS 10/8 18/8
7.1.1 Measure mass using standard units.
7.2.1 Understand the relationship between units of mass.
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2
30
19/8 23/8
7.3.1 Add and subtract involving units of mass.
UNIT 7: MASS
7.3 BASIC OPERATIONS INVOLVING MASS
31
27/8 31/8
7.3.2 Multiply and divide units of mass.
UNIT 8: VOLUME OF LIQUID 8.1 MEASURING VOLUME OF LIQUID 8.1.1 Measure and compare volume of liquid using standard units.
(i) Add mass involving units of mass in; o kilograms, o grams, o kilograms and grams. (ii) Subtract mass involving units of mass in; o kilograms, o grams, o kilograms and grams. (iii) Multiply mass involving conversion of units, with o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. (iv) Divide mass involving conversion of units : o one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. (v) Solve problems involving basic operations with mass. (i) Read measurement of volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. (ii) Write measurement of volume of liquid to the nearest scales of tenth division for o litre, o mililitre. (iii) Measure and record the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. (iv) Estimate the volume of liquid in litres and mililitres. (i) Convert units of volume, from o litres to mililitres, o mililitres to litres, o litres and mililitres to litres, o litres and mililitres to milillitres. (i) Add volume of liquid involving
32
3/9 - 7/9
33
10/9 14/9 17/9 -
8.2 RELATONSHIP BETWEEN UNITS OF VOLUME OF LIQUID 8.3 BASIC
8.2.1 Understand the relationship between units of volume of liquid. 8.3.1 Add and
34
21/9
subtract units of volume.
OPERATIONS INVOLVING V0LUME OF LIQUID 8.3.2 Multiply and divide units of volume.
35
24/9 28/9
36
30/9 4/10
UNIT 9: SHAPE AND SPACE
9.1 TWODIMENSIONAL SHAPES
9.1.1 Understand the perimeter of a twodimensional shape.
conversion of units in; o litre, o mililitre, o litre and mililitre. (ii) Subtract volume of liquid involving conversion of units in : o litre, o mililitre, o litre and mililitre. (i) Multiply volume of liquid involving conversion of units by : o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. (ii) Divide volume of liquid involving conversion of units by: o a one-digit number, o 10, 100, 1000. (iii) Solve problems involving volume of liquids. (i) Identify the sides of a: o square, o rectangle, o triangle. (ii) Measure and record the perimeter of a: o square, o rectangle, o triangle. (i) Identify the dimensions of a: o square, o rectangle. (ii) Compare with unit squares the size of a: o rectangle,
37 38
7/10 11/10 14/10 18/10
PKSR 2 UNIT 9: SHAPE AND SPACE 9.1 TWODIMENSIONAL SHAPES 9.1.2 Understand the area of a twodimensional shape.
square.
(iii) Measure and record the dimensions of squares and rectangles. 9.1.3 Find the area and perimeter twodimensional shapes. 39 21/10 25/10 UNIT 9: SHAPE AND SPACE 28/10 1/11 9.2.1 Understand the volume for cubes and cuboids. 9.2 THREEDIMENSIONAL SHAPES (i) Calculate the area of squares and rectangles. (ii) Solve problems involving perimeter and area of two-dimensional shapes. (i) Identify the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. (ii) Compare with a unit cube: o cuboid o cube (iii) Measure and record the dimensions of cubes and cuboids. (i) Calculate the volume of cubes and cuboids. (ii) Solve problems involving volume of cubes and cuboids. (i) Describe a pictograph featuring o the picture used to represent data, o the title of the graph, o what the axes represent, o What one unit of picture represent. (ii) Extract and interpret information from pictographs. (iii) Construct pictographs to illustrate given information. (iv) Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in pictographs. (i) Describe a bar graph featuring o the title of the graph, o what the axes represent, (i) Extract and interpret information
40
9.2.2 Find the volume for cubes and cuboids.
UNIT 10: DATA HANDLING
41
4/11 8/11
10.1 PICTOGRAPH
10.1.1 Use a pictograph to read and display data.
42
11/11 15/11
10.2 BAR GRAPH
10.2.1 Use bar graphs to read and display data.
from bar graphs. (ii) Construct bar graphs to illustrate given information. (iii) Solve a given problem by organising and interpreting numerical data in bar graphs. 10/11 31/12 CUTI AKHIR TAHUN
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Ixl Nwea Map Growth 6 PlusDocument18 pagesIxl Nwea Map Growth 6 Plusapi-232904428Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan 4 - Equivalent FractionsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 4 - Equivalent Fractionsapi-251663017100% (1)
- Base Rate Percentage + Ratio and ProportionDocument15 pagesBase Rate Percentage + Ratio and Proportionrommel legaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 8 Maths Worksheet Set-1Document45 pagesClass 8 Maths Worksheet Set-1singh vijay0% (1)
- Bulan MatematikDocument10 pagesBulan MatematikSarol St XavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test 1 2 3 - Math 6 - q1Document11 pagesSummative Test 1 2 3 - Math 6 - q1Jennet Perez100% (3)
- Vedic MathematicsDocument26 pagesVedic MathematicsMs100% (1)
- The Procurement Law No. 26 (2005) PDFDocument27 pagesThe Procurement Law No. 26 (2005) PDFAssouik NourddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mtap Math Math Challenge Oral Grade IDocument5 pagesMtap Math Math Challenge Oral Grade Ikharl larano100% (1)
- Tenambit Ps Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 t2Document3 pagesTenambit Ps Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 t2api-267136654Pas encore d'évaluation
- Platinum Mathematics Grade 5 Lesson PlansDocument48 pagesPlatinum Mathematics Grade 5 Lesson PlansLerato50% (2)
- Abdulai Sakina 1Document44 pagesAbdulai Sakina 1Mohammed Abu Shaibu90% (10)
- Key Answers To Word Analogy Questions in 2017 Civil Service ExamDocument2 pagesKey Answers To Word Analogy Questions in 2017 Civil Service ExamJeffrey Lois Sereño MaestradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Index Laws RevisionDocument4 pagesIndex Laws RevisionMaria Rajendran M100% (1)
- Operator Overloading L7Document58 pagesOperator Overloading L7vipin sainiPas encore d'évaluation
- ST ST: WWW - Careerpower.inDocument5 pagesST ST: WWW - Careerpower.inDavinder Singh KhalsaPas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument11 pagesPDFVijayChaganamPas encore d'évaluation
- Iemh 101Document27 pagesIemh 101rajyar1994Pas encore d'évaluation
- PythagDocument3 pagesPythagapi-454894356Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asmworkbook PDFDocument77 pagesAsmworkbook PDFShakila ShakiPas encore d'évaluation
- (M) Ymtg5b 08 PDFDocument80 pages(M) Ymtg5b 08 PDFMark Anthony Seballa TubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 4 Math Test Item SpecificationsDocument62 pagesGrade 4 Math Test Item Specificationsapi-290541111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Extra Practice BLMDocument12 pagesUnit 3 Extra Practice BLMlsmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress READING RESPONCE 5 FRACTIONS PART 1Document13 pagesProgress READING RESPONCE 5 FRACTIONS PART 1Karoki Francis KagombePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 + Year-7-Maths-Specimen-Paper-ChesterDocument17 pages11 + Year-7-Maths-Specimen-Paper-ChesterGary ChestersPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Surds and Indices PDFDocument28 pages15 Surds and Indices PDFashnaPas encore d'évaluation
- New York State Testing Program Grade 6 Common Core Mathematics TestDocument45 pagesNew York State Testing Program Grade 6 Common Core Mathematics TestramjdPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplifying Square RootsDocument15 pagesSimplifying Square RootsAnonymous w23lTWPas encore d'évaluation
- Phoresis Extended Eng Rel. 5.6 (For SQL Database) PDFDocument31 pagesPhoresis Extended Eng Rel. 5.6 (For SQL Database) PDFoscar senaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Frequency Domain Method For Tuning Hydro GovernorsDocument4 pagesA Frequency Domain Method For Tuning Hydro GovernorsadinamartinsPas encore d'évaluation