Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Independence Day of All Country
Transféré par
arvindranganathanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Independence Day of All Country
Transféré par
arvindranganathanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Definining an Independent Country
Updated October 05, 2011 While the terms country, state, and nation are often used interchangeably, there is a difference. A State (note the capital "S") is a self-governing political entity. The term State can be used interchangeably with country. A nation, however, is a tightly-knit group of people which share a common culture. A nation-state is a nation which has the same borders as a State. States and Independent Countries Let's start with what defines a State or an independent country. An independent State:
Has space or territory which has internationally recognized boundaries (boundary disputes are OK). Has people who live there on an ongoing basis. Has economic activity and an organized economy. A country regulates foreign and domestic trade and issues money. Has the power of social engineering, such as education. Has a transportation system for moving goods and people. Has a government which provides public services and police power. Has sovereignty. No other State should have power over the country's territory. Has external recognition. A country has been "voted into the club" by other countries.
There are currently 196 independent countries or States around the world. Territories of countries or individual parts of a country are not countries in their own right. Examples of entities that are not countries include: Hong Kong, Bermuda, Greenland, Puerto Rico, and most notably the constituent parts of the United Kingdom. (Northern Ireland, Wales, Scotland, and England are not countries.) A "state" (with a lower-case "s") is usually a division of a federal State (such as the states of the United States of America). Nations and Nation-States
Nations are culturally homogeneous groups of people, larger than a single tribe or community, which share a common language, institutions, religion, and historical experience. When a nation of people have a State or country of their own, it is called a nation-state. Places like France, Egypt, Germany, and Japan are excellent examples of nation-states. There are some States which have two nations, such as Canada and Belgium. Even with its multicultural society, the United States is also referred to as a nation-state because of the shared American "culture." There are nations without States. For example, the Kurds are stateless people.
The vast majority of the countries on earth became independent after 1800. Only 20 were independent before the start of the 19th century, a mere 10%. By 1900, only 49 or 25% of the world's countries of today were independent. Many countries became independent following World War II when European powers granted independence to their vast colonial holdings, especially Africa. Here are the independence days for every country, from the oldest to the youngest... 660 BCE - Japan 221 BCE - China 301 CE - San Marino 843 CE - France 976 CE - Austria 10th Century CE - Denmark 1001 - Hungary 1143 - Portugal 1206 - Mongolia 1238 - Thailand 1278 - Andorra August 1, 1291 - Switzerland 1419 - Monaco 15th Century - Spain 1502 - Iran June 6, 1523 - Sweden January 23, 1579 - Netherlands 1650 - Oman May 1, 1707 - United Kingdom January 23, 1719 - Liechtenstein 1768 - Nepal July 4, 1776 - United States of America January 1, 1804 - Haiti
July 20, 1810 - Colombia Sept. 16, 1810 - Mexico Sept. 18, 1810 - Chile May 14, 1811 - Paraguay July 5, 1811 - Venezuela July 9, 1816 - Argentina July 28, 1821 - Peru Sept. 15, 1821 - Costa Rica Sept. 15, 1821 - El Salvador Sept. 15, 1821 - Guatemala Sept. 15, 1821 - Honduras Sept. 15, 1821 - Nicaragua May 24, 1822 - Ecuador Sept. 7, 1822 - Brazil August 6, 1825 - Bolivia August 25, 1825 - Uruguay 1829 - Greece October 4, 1830 - Belgium 1839 - Luxembourg February 27, 1844 - Dominican Republic July 26, 1847 - Liberia March 17, 1861 - Italy July 1, 1867 - Canada January 18, 1871 - Germany May 9, 1877 - Romania March 3, 1878 - Bulgaria 1896 - Ethiopia June 12, 1898 - Philippines January 1, 1901 - Australia May 20, 1902 - Cuba November 3, 1903 - Panama June 7, 1905 - Norway Sept. 26, 1907 - New Zealand May 31, 1910 - South Africa November 28, 1912 - Albania December 6, 1917 - Finland November 11, 1918 - Poland December 1, 1918 - Iceland August 19, 1919 - Afghanistan December 6, 1921 - Ireland February 28, 1922 - Egypt October 29, 1923 - Turkey February 11, 1929 - Vatican City Sept. 23, 1932 - Saudi Arabia October 3, 1932 - Iraq November 22, 1943 - Lebanon
August 15, 1945 - Korea, North August 15, 1945 - Korea, South August 17, 1945 - Indonesia Sept. 2, 1945 - Vietnam April 17, 1946 - Syria May 25, 1946 - Jordan August 14, 1947 - Pakistan August 15, 1947 - India January 4, 1948 - Burma February 4, 1948 - Sri Lanka May 14, 1948 - Israel July 19, 1949 - Laos August 8, 1949 - Bhutan December 24, 1951 - Libya November 9, 1953 - Cambodia January 1, 1956 - Sudan March 2, 1956 - Morocco March 20, 1956 - Tunisia March 6, 1957 - Ghana August 31, 1957 - Malaysia October 2, 1958 - Guinea January 1, 1960 - Cameroon April 4, 1960 - Senegal May 27, 1960 - Togo June 30, 1960 - Congo, Republic of the July 1, 1960 - Somalia July 26, 1960 - Madagascar August 1, 1960 - Benin August 3, 1960 - Niger August 5, 1960 - Burkina Faso August 7, 1960 - Cote d'Ivorie August 11, 1960 - Chad August 13, 1960 - Central African Republic August 15, 1960 - Congo, Dem. Rep. of the August 16, 1960 - Cyprus August 17, 1960 - Gabon Sept. 22, 1960 - Mali October 1, 1960 - Nigeria November 28, 1960 - Mauritania April 27, 1961 - Sierra Leone June 19, 1961 - Kuwait January 1, 1962 - Samoa July 1, 1962 - Burundi July 1, 1962 - Rwanda July 5, 1962 - Algeria August 6, 1962 - Jamaica
August 31, 1962 - Trinidad and Tobago October 9, 1962 - Uganda December 12, 1963 - Kenya April 26, 1964 - Tanzania July 6, 1964 - Malawi Sept. 21, 1964 - Malta October 24, 1964 - Zambia February 18, 1965 - Gambia, The July 26, 1965 - Maldives August 9, 1965 - Singapore May 26, 1966 - Guyana September 30, 1966 - Botswana October 4, 1966 - Lesotho November 30, 1966 - Barbados January 31, 1968 - Nauru March 12, 1968 - Mauritius Sept. 6, 1968 - Swaziland October 12, 1968 - Equatorial June 4, 1970 - Tonga October 10, 1970 - Fiji March 26, 1971 - Bangladesh August 15, 1971 - Bahrain Sept. 3, 1971 - Qatar November 2, 1971 - United Arab Emirates July 10, 1973 - Bahamas Sept. 24, 1973 - Guinea-Bissau February 7, 1974 - Grenada June 25, 1975 - Mozambique July 5, 1975 - Cape Verde July 6, 1975 - Comoros July 12, 1975 - Sao Tome and Principe Sept. 16, 1975 - Papua New Guinea November 11, 1975 - Angola November 25, 1975 - Suriname June 29, 1976 - Seychelles June 27, 1977 - Djibouti July 7, 1978 - Solomon Islands October 1, 1978 - Tuvalu November 3, 1978 - Dominica February 22, 1979 - Saint Lucia July 12, 1979 - Kiribati October 27, 1979 - Saint Vincent and the Grenadines April 18, 1980 - Zimbabwe July 30, 1980 - Vanuatu January 11, 1981 - Antigua and Barbuda Sept. 21, 1981 - Belize
Sept. 19, 1983 - Saint Kitts and Nevis January 1, 1984 - Brunei October 21, 1986 - Marshall Islands November 3, 1986 - Micronesia, Federated States of March 11, 1990 - Lithuania March 21, 1990 - Namibia May 22, 1990 - Yemen April 9, 1991 - Georgia June 25, 1991 - Croatia June 25, 1991 - Slovenia August 20, 1991 - Estonia August 21, 1991 - Kyrgyzstan August 24, 1991 - Russia August 25, 1991 - Belarus August 27, 1991 - Moldova August 30, 1991 - Azerbaijan Sept. 1, 1991 - Uzbekistan Sept. 6, 1991 - Latvia Sept. 8, 1991 - Macedonia Sept. 9, 1991 - Tajikistan Sept. 21, 1991 - Armenia October 27, 1991 - Turkmenistan November 24, 1991 - Ukraine December 16, 1991 - Kazakhstan March 3, 1992 - Bosnia and Herzegovina January 1, 1993 - Czech Republic January 1, 1993 - Slovakia May 24, 1993 - Eritrea October 1, 1994 - Palau May 20, 2002 - East Timor June 3, 2006 - Montenegro June 5, 2006 - Serbia February 17, 2008 - Kosovo July 9, 2011 - South Sudan
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 150 Interview QuestionsDocument167 pages150 Interview QuestionsPriyanka Kumari100% (2)
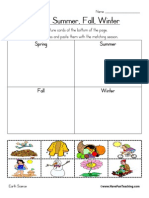
- Seasons of The Year MatchingDocument1 pageSeasons of The Year Matchingarvindranganathan100% (1)
- Outerspace DefinitionsDocument1 pageOuterspace DefinitionsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seasons EarthSunDistDocument10 pagesSeasons EarthSunDistarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seasons Arnolds Apple TreeDocument7 pagesSeasons Arnolds Apple Treearvindranganathan100% (1)
- Sentence Types: There Are 3 Types of Sentences. Can You Name Them All?Document10 pagesSentence Types: There Are 3 Types of Sentences. Can You Name Them All?arvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Precipitation EquilibriaDocument91 pages19 Precipitation EquilibriaarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths ActivitiesDocument85 pagesMaths ActivitiesarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructors GuideDocument55 pagesInstructors GuideskypaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy Lesson 4Document6 pagesAstronomy Lesson 4arvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Look Out There PowerpointDocument11 pagesLook Out There PowerpointarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Constellation Work BookDocument15 pagesConstellation Work BookarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kids Print SeasonsDocument1 pageKids Print SeasonsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Voyage G58 L1Document42 pagesVoyage G58 L1arvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- World War IDocument16 pagesWorld War IarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 35 Solar System ReasonsForTheSeasonsDocument4 pages35 Solar System ReasonsForTheSeasonsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Planet Sword SearchDocument1 pagePlanet Sword SearcharvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Seasons WheelDocument2 pages4 Seasons WheelarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ypes of MapsDocument8 pagesYpes of MapsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
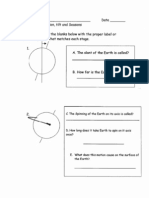
- Worksheet Rotation, Revolution, Tilt and SeasonsDocument2 pagesWorksheet Rotation, Revolution, Tilt and SeasonsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Outerspace DefinitionsDocument1 pageOuterspace DefinitionsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- World War IIDocument6 pagesWorld War IIarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Animals Which Kill Other AnimalsDocument1 pageAnimals Which Kill Other AnimalsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ypes of MapsDocument8 pagesYpes of MapsarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Voice and Accent Training MaterialDocument30 pagesVoice and Accent Training MaterialAnwar GaffPas encore d'évaluation
- The Number of Countries in TheDocument14 pagesThe Number of Countries in ThearvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is ISO 17712Document9 pagesWhat Is ISO 17712arvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Group DiscussionDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Group Discussionvinodh76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Training Needs AnalysisDocument11 pagesTraining Needs AnalysisarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thankyou LetterDocument18 pagesThankyou LetterarvindranganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- UK and US Forms of Government ComparisonDocument3 pagesUK and US Forms of Government ComparisonNikeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Social and Cutural History of Britain PDFDocument226 pagesSocial and Cutural History of Britain PDFThanh TranPas encore d'évaluation
- New Year Honours List 2015Document55 pagesNew Year Honours List 2015The New VisionPas encore d'évaluation
- WesDocument100 pagesWessegalcenterPas encore d'évaluation
- كتاب اللغة الإنجليزية (الدروس) - الصف الثانيDocument72 pagesكتاب اللغة الإنجليزية (الدروس) - الصف الثانيalbrtyhsam018Pas encore d'évaluation
- History - An Illustrated History of Britain - (David Mcdowall) Longman Pearson 2006Document194 pagesHistory - An Illustrated History of Britain - (David Mcdowall) Longman Pearson 2006eliarfzohal90% (21)
- Unit 5: Note/Summary Completion Practice 1Document4 pagesUnit 5: Note/Summary Completion Practice 1Nhan NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Europass CV in English PDFDocument2 pagesEuropass CV in English PDFNathan0% (1)
- RepresentationsDocument254 pagesRepresentationsWertonPas encore d'évaluation
- Irish Opinion and American Revolution PDFDocument378 pagesIrish Opinion and American Revolution PDFSerch González100% (1)
- A70 - Minh Tung - Pie ChartsDocument8 pagesA70 - Minh Tung - Pie ChartsMint TùnPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Reading .So Just Who Are The EnglishDocument5 pagesAdvanced Reading .So Just Who Are The Englishveronica barrosPas encore d'évaluation
- Shilpa Susan VishuDocument3 pagesShilpa Susan VishuShanoob TkPas encore d'évaluation
- A Broken Wave-Lionel EsherDocument39 pagesA Broken Wave-Lionel EsherChristian NoetzlyPas encore d'évaluation
- SSRN Id2292797Document14 pagesSSRN Id2292797scsew8332Pas encore d'évaluation
- Teachers Book Mosaic 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTeachers Book Mosaic 1 PDFInmaculada Macias33% (3)
- Barbados (In English)Document342 pagesBarbados (In English)DreamsAvenue.com100% (1)
- Unit I - Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceDocument3 pagesUnit I - Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceJay Karta0% (1)
- Curs Id Olaru VictorDocument102 pagesCurs Id Olaru VictorTE Iubesc TE IubescPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1.Supplementary A1-S Tiếng Anh 1Document20 pages4.1.Supplementary A1-S Tiếng Anh 1TúPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah - Kel 3 - British EducationDocument20 pagesMakalah - Kel 3 - British EducationFITRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Monochromatic and Polichromatic Cultures - Richard LewisDocument3 pagesMonochromatic and Polichromatic Cultures - Richard LewisGina AndreiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Most Secret List of Soe Agents: NDocument32 pagesThe Most Secret List of Soe Agents: NeliahmeyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Touching The MarginsDocument23 pagesTouching The MarginsTina DaveyPas encore d'évaluation
- BDT Toolkit - Country Nationality Codes April 2016Document12 pagesBDT Toolkit - Country Nationality Codes April 2016Matt BrumPas encore d'évaluation
- ESL - IrelandDocument2 pagesESL - IrelandTrill_MoPas encore d'évaluation
- Colonization and Colonialism, History OfDocument6 pagesColonization and Colonialism, History OfJacobin Parcelle100% (5)
- Ilyas Kahn, List of DirectorshipsDocument56 pagesIlyas Kahn, List of DirectorshipslifeinthemixPas encore d'évaluation
- Atestat La Engleza (Elena)Document10 pagesAtestat La Engleza (Elena)Lavinia MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Raw Material Prices Increase: March 2021Document30 pagesRaw Material Prices Increase: March 2021Shangeetha KumarPas encore d'évaluation