Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Evidence Based Medicine
Transféré par
lianazulakCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Evidence Based Medicine
Transféré par
lianazulakDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
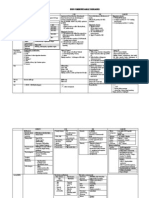
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE Definition: integrating best research evidence with clinical expertise % patient values to achieve best
possible patient management. Component: 1. Evidence: relevant, valid & easy to obtain (information mastery) for diagnosis & therapy 2. Experience 3. Expectation Important: 1. Stay up-to-date with current literature 2. Communication effectively with each other 3. Make best use of different sources of information: infor mastery Usefulness of medical info = 4. 5. Take sound clinical decision based in valid research evidence Reducing variation in practice Steps EBM process 1. Formulate answerable clinical question PICO 1. Population/ Problem Descript grp patient belong Age Gender Race Ethnicity Stage of disease diagnostic test Prognostic marker Exposure factor Treatment Alternative Usually conversion Sometimes no comparison Improve fx Relieve symptoms Increase survival Improve quality of life
Most sensitive: 1. Systemic review & meta analyses 2. RCT 3. Cohort 4. Case control 5. Case series 6. Case report 7. Ideas, editorials, opinion 8. Animal research 9. In vitro research
2. Intervention
3. Comparison 4. Outcome
Type of studies 1ry (original research) 1. Experimental- randomized control trial 2. Observational cohort, case control, cross- sectional Type of question Therapy Diagnosis Etiology / harm Prognosis Prevention Clinical exam Cost 1. MEDLINE 2. PUDMED 1. 2. 3. 2ry 1. Review original research (systemic preview) 2. Meta analysis 3. Practice guidelines
Suggested best type of study RCT > Cohort > Case control > case series Prospective. Blind comparison to gold standard RCT > Cohort > Case control > case series Cohort > Case control > case series RCT > Cohort > Case control > case series Prospective. Blind comparison to gold standard Economic analysis
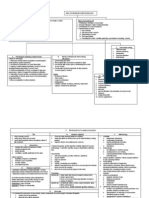
2. Literature search select appropriate resources conduct a search 3. Appraise evidence for its validity (closeness to truth) & applicability (usefulness in clinical
Randomization Patient follow up Blinding
Was the assignment of patient to treatment randomized? Were all patients who enter trial properly accounted & attributed for at its conclusion? Were patients, health workers & study personnel
practice) 4. 5. Baseline characteristic of patients Treatment
blind to treatment? Were grps similar at starting of trial? Aside from experimental intervention, were grps treated equally?
4. Apply evidence: Return to patient, integrate with clinical expertise, patient preference & apply it to practice 5. Asses outcome: evaluate performance
Result of validity: 1. Magnitude 2. Relative risk reduction 3. No need to treat (NNT): No of patient who need to be treats in order to prevent 1 additional bad outcome Absolute Risk Reduction (AAR) = control grp event rate (CER) experimental grp event rate (EER) NNT = 4. Confidence intervals 1. INTERNAL: Is valid result important? 2. EXTERNAL: are valid & important result applicable RR = 1 NO RISK RELATION <1 NO >1 HARMFUL
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 6 DiseasesDocument2 pages6 DiseaseslianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual OffencesDocument52 pagesSexual Offenceslianazulak100% (1)
- Cholera Enteric Food PoisoningDocument1 pageCholera Enteric Food PoisoninglianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy AbortionDocument45 pagesPregnancy AbortionlianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 5th and 6th WeekDocument3 pages5th and 6th WeeklianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Viral HepatitisDocument2 pagesPrimary Viral HepatitislianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV MalariaDocument2 pagesHIV MalarialianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy AbortionDocument45 pagesPregnancy AbortionlianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Communicable DsDocument3 pagesNon Communicable DslianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesHealth Research MethodologylianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Module 12Document1 pageAssignment Module 12lianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Tahun 5 IkhwahDocument3 pagesTahun 5 Ikhwahlianazulak0% (1)
- Pharmacology Final Exam ILODocument3 pagesPharmacology Final Exam ILOIqbal BearPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Week 2nd Year IumpDocument3 pages4th Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Week 2nd Year IumpDocument3 pages4th Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDlianazulak100% (2)
- Assignment Groups For Cardiovascular Module International)Document2 pagesAssignment Groups For Cardiovascular Module International)lianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Week 2nd Year IumpDocument3 pages3rd Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Senarai Tazkirah Lecture BDocument1 pageSenarai Tazkirah Lecture BlianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Final Exam ILODocument3 pagesPharmacology Final Exam ILOIqbal BearPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For AnatomyDocument1 pageAssignment For AnatomylianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Week 2nd Year IumpDocument2 pages2nd Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharma AssignmentDocument1 pagePharma AssignmentlianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument56 pagesIntroduction To ParasitologylianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Histo AssignmentDocument3 pagesHisto AssignmentlianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 71 MicrosDocument40 pages71 MicroslianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Groups For Neuroscience Module 0001Document2 pagesAssignment Groups For Neuroscience Module 0001lianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 in Vitro Antigen Antibody ReactionsDocument81 pages6 in Vitro Antigen Antibody Reactionslianazulak100% (2)
- 5-Major His To Compatibility Complex (MHC)Document12 pages5-Major His To Compatibility Complex (MHC)lianazulakPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Health Workers Regarding Nosocomial Infection at Selected Hospitals of Birtamode Municipality, JhapaDocument5 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Health Workers Regarding Nosocomial Infection at Selected Hospitals of Birtamode Municipality, JhapaIJCRM Research JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Rate LabDocument6 pagesHeart Rate LabSteve RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- My Path to Becoming a Childhood Trauma PsychologistDocument2 pagesMy Path to Becoming a Childhood Trauma PsychologistThivyana ShrreePas encore d'évaluation
- Penguins Medicine August-SeptumberDocument215 pagesPenguins Medicine August-SeptumberKhattabPas encore d'évaluation
- BPH Zinc GreenTea Papaya LeafDocument13 pagesBPH Zinc GreenTea Papaya Leafteddy_shashaPas encore d'évaluation
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument14 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderAngie McaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 2013 Couzin Frankel 68 9Document2 pagesScience 2013 Couzin Frankel 68 9Ricardo ChavarriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Occlusal Contacts RetentionDocument9 pagesOcclusal Contacts RetentionRockey ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Patient Support and Regional Cancer ServicesDocument76 pagesGuide To Patient Support and Regional Cancer Servicesgiovanna2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lumbosacral Plexus # 6Document6 pagesLumbosacral Plexus # 6Arcel De Luca G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write A Review Article PRISMA GuidelinesDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Review Article PRISMA GuidelinesPuneeth RaghavendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Timing of Antimicrobial Prophylaxis and Infectious Complications in Pediatric Patients Undergoing AppendicectomyDocument3 pagesTiming of Antimicrobial Prophylaxis and Infectious Complications in Pediatric Patients Undergoing AppendicectomyJuan J. Acosta VelásquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatrics QuestionsDocument22 pagesPediatrics QuestionsShaik AmreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bag-Mask Ventillation PDFDocument6 pagesBag-Mask Ventillation PDFHaris PapadopoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone Marrow Biopsy SheetDocument2 pagesBone Marrow Biopsy SheetSouvik BairagyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Beyond The Bloody Mess: Hematologic Assessment: Carol A. RauenDocument7 pagesBeyond The Bloody Mess: Hematologic Assessment: Carol A. RauenAgoo AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Sumit Garg Projec-IECDocument10 pagesDR Sumit Garg Projec-IECkamlesh yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Modification of The Treatment Protocol As A Strategy in The Control of The Cholera Epidemic in Haiti 2016-2017Document3 pagesModification of The Treatment Protocol As A Strategy in The Control of The Cholera Epidemic in Haiti 2016-2017Carlos Efraín Montúfar SalcedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Katz Activities of Daily LivingDocument2 pagesKatz Activities of Daily LivingGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBAPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesInterview QuestionsRitesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding M. tuberculosis Morphology, Diagnosis and PropertiesDocument17 pagesUnderstanding M. tuberculosis Morphology, Diagnosis and Propertiesيارا المزيدPas encore d'évaluation
- Meniscus Disorders, Knee: The Medical Disability Advisor: Workplace Guidelines For Disability DurationDocument5 pagesMeniscus Disorders, Knee: The Medical Disability Advisor: Workplace Guidelines For Disability DurationStephen Nathaniel100% (1)
- 2008 Polyflux R Spec Sheet - 306150076 - HDocument2 pages2008 Polyflux R Spec Sheet - 306150076 - HMehtab AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Paediatrica Indonesiana: Fereza Amelia, Muhammad Ali, Syahril PasaribuDocument5 pagesPaediatrica Indonesiana: Fereza Amelia, Muhammad Ali, Syahril PasaribuAnonymous rKbaHFEPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 WHLP 5Document14 pagesGrade 6 WHLP 5Benj AlejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cek List Mini ICUDocument4 pagesCek List Mini ICUmichelle chiajungPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The MouthDocument4 pagesDiseases of The MouthAhmed Gh Al-zechrawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Caesarean Section Performing Caesarean SectionDocument13 pagesCaesarean Section Performing Caesarean SectionBlablabla BlablablaPas encore d'évaluation
- NHS LA - Duty of Candour 2014 - SlidesDocument10 pagesNHS LA - Duty of Candour 2014 - SlidesAgnieszka WaligóraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertension - Management in Pregnancy Guideline (GL952) : ApprovalDocument55 pagesHypertension - Management in Pregnancy Guideline (GL952) : ApprovalhestiPas encore d'évaluation