Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Granite and Limestone
Transféré par
Tk Kendrick LauCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Granite and Limestone
Transféré par
Tk Kendrick LauDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
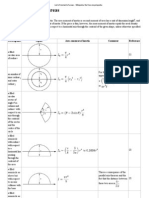
Granite versus limestone comparison notes 1) Characteristics (9m) 2) Weathering of the rocks (relates back to point 1 and causes
point 3) 3) Landforms associated [16m] Class: formation Limestone Sedimentary Non-clastic - Calcium from decomposition of marine organisms - Gaps filled in with mud and clay - Lithification: cementation and compaction and drying >50% generally calcite / calcium carbonate (carbonation and solution): homogenous (little regolith left behind) but pure limestone should be >90% 50-90%: impure limestone Calcite: natural cementing agent so not all rocks with calcite are limestones *Only for carboniferous limestone High secondary permeability - Bedding planes / joints / faults (selective weathering block disintegration) - Shrinkage joints: drying tensional (folding) / shear joints - Older: probability of experiencing tectonic forces Low primary permeability - Small pore spaces: water cannot penetrate through easily - Older: more compaction and cementation less pore spaces Hard (not prone to physical Granite Igneous (intrusive) (pressure release exfoliation) - Crystallisation of magma - Granitic (viscous) magma - Rock texture coarsegrained (phaneritic) because more time for crystals to grow before solidifies into rock Feldspar (hydrolysis clay), quartz (sand granular disintegration) (clay, sand and corestones due to spherodial weathering = residual debris): heterogenous (insolation weathering granular disintegration) (many types of elements) Mica, biotite High secondary permeability - Joints / faults (selective weathering block disintegration): sheet joints, shrinkage joints: during formation stage of rock cooling process during formation of granite Low primary permeability - Crystals close together and interlock during crystallization
Chemical compositi on
Rock structure
Physical
Hard (not prone to physical
hardness
weathering) compaction
weathering) feldspar and quartz hard minerals and interlock tightly
Words in red are how the characteristics link to weathering
Limestone landforms Tropical Closed Cockpit karst, tower karst depressi on Karren Pinnacles (spitzkarren) features Caves
Temperate Dolines, uvalas
Drainage
Limestone pavements (need glacial / lateral erosion) Less well-developed More well-developed (higher rainfall, but not (drizzle) much seeps in to form caves Stalagtite (more spread out) / enter ground. Most flow off to rivers) Stalagmite (more concentrated) Shallow holes (resurgence stream) + dry valleys + blind valleys *Cross question between geomo and hydro: drainage density falls because stream length falls but area of drainage still the same
Cockpit karst:
Cone
Cockpit Gullying / surface erosion Cave 200m plain If water table reached, then tower karsts protruding from water body
Tower karst: Cones
Granite landscape Etchplanation 1) Pluvial period (1000s of years) Wetter: higher rainfall Granite: breaks down to Slow regolith removal quartz, sand, clay, because dense corestones = residual vegetation: infiltration + debris percolation Fast regolith formation because rainfall amount high Regolith formation > regolith removal: accumulation of regolith Climate humid. Wet throughout whole year: no dry season. Similar to humid tropics. 2) Interpluvial period Former surface Etch plain Ruware Selective Basal surface weathering: weathering undulating due to different where joints depths of regolith: high are secondary + low primary concentrated permeability Regolith formation due to less rainfall, less chemical weathering < regolith removal because less vegetation: net loss of regolith Ruware: exposed part of basal surface of weathering Savanna Etch plain: isolated rock outcrop which rises abruptly from surrounding plain 3) Pluvial period + 4) Interpluvial period: repetition serves to increase height of ruware. If not cannot explain tall inselbergs.
Etch plain Former BSW
Pluvial period
Very little weathering at ruware, more weathering at sides 1) More joints 2) Shedding of water from ruware to sides 3 ) Regolith absorbs water vs solid rocks Former surface Regolit h remove d
Tall inselbergs
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- ParapetDocument26 pagesParapetTk Kendrick Lau50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Timber ManualDocument145 pagesTimber Manualspiderlance100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Construction SafetyDocument9 pagesConstruction Safetyngeel_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Government Expenditure: Economy of MalaysiaDocument17 pagesGovernment Expenditure: Economy of MalaysiaTk Kendrick LauPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- List of Moment of AreasDocument3 pagesList of Moment of AreasTk Kendrick LauPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Plate Bearing Load TestDocument1 pagePlate Bearing Load TestTk Kendrick Lau100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Fract Mechanics - de ZG514Document13 pagesFract Mechanics - de ZG514Umesh BhadalePas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Deere (1989) - Rock Quality Designation (RQD) After Twenty YearsDocument103 pagesDeere (1989) - Rock Quality Designation (RQD) After Twenty YearsKleyser CollazosPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Earth Science Q2 L1 Weathering Part 2Document27 pagesEarth Science Q2 L1 Weathering Part 2Cj PadataPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Channel Morphology: Geography With Sandeep SirDocument12 pagesChannel Morphology: Geography With Sandeep SirKedar BhasmePas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils !: Monument Valley, UtahDocument49 pagesChapter 5: Weathering and Soils !: Monument Valley, UtahUtkarshPraveenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- MEM333 Course Details, Summer - 2021Document4 pagesMEM333 Course Details, Summer - 2021William J. SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Liezl E. Valiente - Soil Chemistry and PollutionDocument37 pagesLiezl E. Valiente - Soil Chemistry and PollutionLiezl ValientePas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Quantification of Salt Weathering at Hot Deserts and Evaluation ofDocument11 pagesQuantification of Salt Weathering at Hot Deserts and Evaluation ofAmandita_geolPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM E1823 Standard Terminology Relating to Fatigue and Fracture Testing 한글Document22 pagesASTM E1823 Standard Terminology Relating to Fatigue and Fracture Testing 한글KALIDASS DPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Exogenic ProcessesDocument22 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Exogenic ProcessesJulius GamayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter SixDocument27 pagesChapter SixEphremPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Pulau Mawar Mersing, Johor PresentationDocument19 pagesHistory of Pulau Mawar Mersing, Johor PresentationFendy RoynPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Clay Mineral of SabahDocument10 pagesClay Mineral of SabahBandilung TzPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahram Farahmand, George Bockrath, James Glassco (Auth.) - Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics of High Risk Parts - Application of LEFM & FMDM Theory-Springer US (1997)Document385 pagesBahram Farahmand, George Bockrath, James Glassco (Auth.) - Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics of High Risk Parts - Application of LEFM & FMDM Theory-Springer US (1997)Pratiksha LohakarePas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Is 14496#2 Preparation of Landslide Hazard Zonation Maps inDocument22 pagesIs 14496#2 Preparation of Landslide Hazard Zonation Maps inv2299Pas encore d'évaluation
- ELS Quarter 1 REVIEWER ModifiedDocument3 pagesELS Quarter 1 REVIEWER ModifiedASh tabaogPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil MicromorphologyDocument735 pagesSoil MicromorphologyAlejandra Salamanca RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Efflorescence and The Discoloration of Concrete (1983)Document56 pagesEfflorescence and The Discoloration of Concrete (1983)Aurelian MusatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Vocabulary Fatigue FailureDocument2 pagesVocabulary Fatigue FailureZahi AekPas encore d'évaluation
- Chief Examiners Report Report For The Dec 2010 LshsceDocument85 pagesChief Examiners Report Report For The Dec 2010 LshscetimetconceptsPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - WeatheringDocument6 pagesModule 1 - WeatheringRayjan FormalejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth & Life Science TOSDocument9 pagesEarth & Life Science TOSkyn mairen rodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- HKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Suggested Answer Book 1Document76 pagesHKDSE Chemistry A Modern View Suggested Answer Book 1Chan Chun Hang Wesley OAOPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 5 Earth Science WeatherDocument19 pagesGrade 5 Earth Science WeatherJenny OsumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Geotechnical Investigation of SoilDocument67 pagesGeotechnical Investigation of SoilAbdullahi MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- A State-Of-The-Art Review On Fatigue Life Predicti PDFDocument15 pagesA State-Of-The-Art Review On Fatigue Life Predicti PDFAdnen LaamouriPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 331 Introductiom To Geotechnical Engineering - 2Document64 pagesCE 331 Introductiom To Geotechnical Engineering - 2HAB FFSPas encore d'évaluation
- Exogenic ProcessesDocument40 pagesExogenic Processesantonio Almiranes100% (1)
- SOIL - MECHANICS Rev.Document51 pagesSOIL - MECHANICS Rev.Nichols ManarangPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals and Energy Resources: Page No: 48 (Topic: Introduction)Document11 pagesMinerals and Energy Resources: Page No: 48 (Topic: Introduction)Monika JasujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)