Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PracProb2 - 2004
Transféré par
SoonyamCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PracProb2 - 2004
Transféré par
SoonyamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pharmacy 331 Problem Set #2
Thompson: Spring 2004
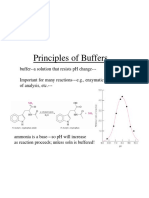
pH, pKa and Henderson-Hasselbalch Calculations (corrections 2/5/04) 1. Calculate the concentration of benzoic acid and benzoate in a solution whose pH = 5.2. The pKa of benzoic acid is 4.20 and the solution was prepared to be 0.005 M benzoic acid. (Connors, p. 164) pH = pKa + log[A-/HA] 5.20 = 4.20 + log[A-/HA] 1.0 = log[A-/HA] 10 = [A-]/[HA] says the concentration of benzoate is ten times that of benzoic acid or the fractional amount is: [A-]/([HA] + [A-]) or 1/11 [HA] and 10/11 [A-]. The fractional amount of [HA] is: 0.005 M x 1/11 = .0004545 M (4.5 x 10-4 M) The fractional amount of [A-] is: 0.005 M x 10/11 = .004545 M (4.5 x 10-3 M) 2. From class Calculate the pH of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 242.2 mg of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane in 10.0 mL of 0.170 M HCl and diluting it to 100 mL with water. The mw of tris = 121.1 and has a pKa = 8.08. Connors p. 170 Tris: 242.2 mg/121.1 g/mol = 2.00 mmol (or 0.002 M). HCl: 10 mL x 0.170 M/L = 1.7 mmol or 0.0017 M) If 1.7 mmol HCl is added to 2.0 mmol of tris then 1.7 mmol of tris-HCl forms but leaves 0.3 mmol HCl tris unreacted (tris HCl is as the conjugate acid). And. Note: My narrative error from discussion section is denoted in blue (vs. red strikeout) above thanks to those of you who caught it. The numbers are correct. pH = pKa + log[A-/HA] or pH = pKa + log[tris/trisHCl] (tris is equivalent to the ionized A- and trisHCl is equivalent to the acid HA. pH = 8.08 + log [0.3/1.7) = 7.32 3. Ephedrine (pKa = 9.6) reacts with hydrochloric acid to afford the ephedrine hydrochloride salt. If you react 1 M ephedrine with 1 M HCl what is the pH? (Cairnes p. 22) The key is to remember is that when you add 1.0 M ephredrine to 1.0 M HCl the result is a 0.5 M solution. For example, adding 10 mL of 1 M ephedrine to 10 mL of 1.0 M HCl gives you 20 mL from the same molarity but a net dilution of two-fold or 0.5 M. So. pH = pKa log C = (9.6) log (0.5 M) = 4.8 (-0.15) = 4.95
4. What is the pH of 0.05 M sodium acetate given that acetic acid pKa = 4.66. Although sodium acetate is a weak base, we can use the weak acid equation to calculate and then substract from 14. Sodium acetate is a weak base so we substitute for pKa using the equation: pKw = pKa + pKb or pKw pKb = pKa if then pH = pKa log C pH = (pKw pKb) log C = (14 - 4.66) log (0.05 M) = 4.67 (-0.65) = 5.32 14 - 5.32 = 8.68 5. An antilog calculation!! Calculate the concentration of acetic acid needed to be added to a 0.1 M solution of sodium acetate to give a buffer of pH 5 (pKa of acetic acid= 4.66). (Cairns, p. 24) pH = pKa + log[A-/HA] 5.0 = 4.66 + log (0.1/HA) 0.34 = log 0.1 log[HA] 1.34 = -log[HA] 0.045 M [acetic acid] 6. Calculating the fractional amount of a compound in the ionized and unionized forms. Pentobarbitone (pKa 8.0) is a weak acid. Calculate the percentage of a dose of this drug in the plasma (pH 7.4). First, since the pH is lower than the pKA, the higher proportion of the drug will be unionized!!! pH = pKa + log[A-/HA] 7.4 = 8.0 + log[A-/HA] -0.6 = log[A-/HA] 0.25 = = [A-]/[HA] or there are four HAs for every one A-. 4 + 1 = 5 total. So the fractional amounts are 4/5 x 100% pHA] and 1/5 x 100% [A-] 80% pentobarbitone and 20% pentobarbitone anion (conjugate base).
and
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mechanical Aptitude Test 080609Document63 pagesMechanical Aptitude Test 080609Soonyam100% (11)
- Machinist Course - Lathe Operation ManualDocument140 pagesMachinist Course - Lathe Operation Manualmerlinson1100% (16)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisD'EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Buffers and Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation ExamplesDocument49 pagesBuffers and Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation ExamplesABDUL HANANPas encore d'évaluation
- Spirituality and Science - Bridging The GapDocument154 pagesSpirituality and Science - Bridging The GapMartin Euser100% (27)
- Belt, Rope & Chain Drives - PDF PDFDocument36 pagesBelt, Rope & Chain Drives - PDF PDFabhisar100% (3)
- Fruit and Vegetable ChartDocument8 pagesFruit and Vegetable ChartVishal VithalpuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer PreparationDocument5 pagesBuffer PreparationJULLIENE IVES BUQUIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of AyurvedaDocument35 pagesOverview of Ayurvedaravi_chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of AyurvedaDocument35 pagesOverview of Ayurvedaravi_chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of AyurvedaDocument35 pagesOverview of Ayurvedaravi_chandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Naming CompoundsDocument60 pagesNaming CompoundsLoriliePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 7Document10 pagesExperiment 7Jay Jay50% (2)
- COMMON-ION EFFECT TITRATIONDocument24 pagesCOMMON-ION EFFECT TITRATIONMothi KarunaPas encore d'évaluation
- 17bufferkspap 100308200536 Phpapp01Document235 pages17bufferkspap 100308200536 Phpapp01Isabelle AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 - P-Block Elements PDFDocument27 pages9 - P-Block Elements PDFthinkiit86% (7)
- Delta Lake Definitive Guide Early ReleaseDocument104 pagesDelta Lake Definitive Guide Early ReleaseWF1 Hackathon1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit X - Database Recovery TechniquesDocument55 pagesUnit X - Database Recovery TechniquesNirjal DhamalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Ka of Unknown AcidDocument23 pagesDetermination of Ka of Unknown AcidShasha0% (1)
- Vasant LadDocument19 pagesVasant LadAnonymous JE7uJR47% (19)
- Review On Chemical Stimulation Techniques in Oil IDocument35 pagesReview On Chemical Stimulation Techniques in Oil IJessePas encore d'évaluation
- IBHL Investigations: Investigating Acids Aim: Claudia Braganza IBHL Chemistry Grade 12Document13 pagesIBHL Investigations: Investigating Acids Aim: Claudia Braganza IBHL Chemistry Grade 12tennisrox94100% (1)
- BioChem ReviewerDocument32 pagesBioChem ReviewerLester ManiquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Notes Full PDFDocument55 pagesAqa A Level Chemistry Notes Full PDFRS JPas encore d'évaluation
- Accurate pH titration curvesDocument23 pagesAccurate pH titration curvesDavidPas encore d'évaluation
- 1AA3 T1 2011 SolDocument19 pages1AA3 T1 2011 SolDavidPas encore d'évaluation
- KUNCI Jawaban LKS Ekcellent Bahasa Inggris Kelas XIIDocument16 pagesKUNCI Jawaban LKS Ekcellent Bahasa Inggris Kelas XIIXerxes Xanthe Xyza74% (23)
- Buffer Calculation Examples Explained Step-by-StepDocument4 pagesBuffer Calculation Examples Explained Step-by-StepSajeewa PemasinghePas encore d'évaluation
- BuffersDocument22 pagesBufferslana alarnabPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffers KeyDocument5 pagesBuffers KeyHasantha PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Quimica BufferDocument4 pagesQuimica BufferJassan ArtetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 Sample Problem AnswersDocument2 pagesLecture 3 Sample Problem AnswerssonicdragonPas encore d'évaluation
- LSM1101 Tutorial 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesLSM1101 Tutorial 1 AnswersJasmine TohPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffers PDFDocument28 pagesBuffers PDFrxpturousPas encore d'évaluation
- BuffersDocument28 pagesBuffersRicky Justin NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- BuffersDocument5 pagesBuffersDiana ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid and Base Chemistry LabDocument7 pagesAcid and Base Chemistry LabChrist EllePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrolysis:: Calculation of The PH of Solutions of SaltsDocument9 pagesHydrolysis:: Calculation of The PH of Solutions of Saltsحسين عمار محسن سالمPas encore d'évaluation
- Julia Burdge and Jason Overby: Chemistry: Atoms FirstDocument22 pagesJulia Burdge and Jason Overby: Chemistry: Atoms FirstEunice LeePas encore d'évaluation
- HW11 F06 KeyDocument6 pagesHW11 F06 KeySOFIA MELENDEZ RODRIGUEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Carroll Lab Chap 3Document8 pagesCarroll Lab Chap 3Aya Karlmela LangresPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyDocument14 pagesBuffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyRadhika RaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer CalculationsDocument3 pagesBuffer CalculationsJessie MorgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffers AnswersDocument2 pagesBuffers AnswersKharisma N. PuspitasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Weak AcidDocument22 pagesWeak AcidMazlia MazlanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHY 47.1 Procedure Factors Affecting Buffers Capacity 1st Sem 2021-2022Document5 pagesCHY 47.1 Procedure Factors Affecting Buffers Capacity 1st Sem 2021-2022Kathryne May JinonPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Test 8 Notes - Acids, Bases and BuffersDocument7 pagesA2 Test 8 Notes - Acids, Bases and BuffersJane PernesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - PHDocument26 pagesLecture 3 - PHapi-249972919Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 - Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument59 pagesChapter 15 - Acid-Base EquilibriaPatel MswaziPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaChem Conjugate Acid Base Pairs 3Document3 pagesAnaChem Conjugate Acid Base Pairs 3Jei HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 AbequilDocument29 pages18 AbequilSam H. SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of BuffersDocument10 pagesPrinciples of BuffersLuluin Latifa NissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 1220 Assignment 2Document4 pagesChem 1220 Assignment 2KathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Henderson Hasselbalch Equation QuestionsDocument7 pagesHenderson Hasselbalch Equation Questionsmisganamarcos10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution of ProblemsDocument4 pagesSolution of ProblemsVIHIKA ENGINEERINGPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaChem Conjugate Acid Base Pairs 3 RevisedDocument3 pagesAnaChem Conjugate Acid Base Pairs 3 RevisedJei HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Buffer Calculation 0Document31 pages8 Buffer Calculation 0Ahmed ZakyPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.8 BuffersDocument16 pages8.8 BuffersMia PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- pH CALCULATIONS AND BUFFERSDocument2 pagespH CALCULATIONS AND BUFFERSParamjit KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Henderson Hasslebach PDFDocument21 pagesHenderson Hasslebach PDFJesseca Calaunan QuintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer solutions: pH regulation through weak acids and basesDocument2 pagesBuffer solutions: pH regulation through weak acids and basesDhairya GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- VinegarDocument14 pagesVinegarLynn HeimatotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Review For Solving PH Problems: Acid IonizationDocument5 pagesReview For Solving PH Problems: Acid IonizationtvvsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyprotic Acids Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesPolyprotic Acids Practice QuestionsStephanie LeePas encore d'évaluation
- PHCM223 Midterm Revision SS16 443Document20 pagesPHCM223 Midterm Revision SS16 443Michelle MenciasPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid Base CH 16 ComprehensiveDocument4 pagesAcid Base CH 16 ComprehensiveAidah AmirPas encore d'évaluation
- Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Chapte R17Document92 pagesAdditional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria: Chapte R17api-683027695Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of Buffers: An Experiment in pH ControlDocument6 pagesPreparation of Buffers: An Experiment in pH ControlGladys CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 03b - Buffer Ws Answers and Titration NotesDocument47 pages03b - Buffer Ws Answers and Titration NotesTushar RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - Acid Base ConceptsDocument27 pagesLecture 5 - Acid Base ConceptsThomas JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer CapacityDocument40 pagesBuffer CapacityDrAmit VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Not MineDocument27 pagesChapter 12 Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonPas encore d'évaluation
- Concentration)Document3 pagesConcentration)CoibaPas encore d'évaluation
- Materialscience Metallurgy May June 10 PDFDocument2 pagesMaterialscience Metallurgy May June 10 PDFSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- CE336 09 Civil CorrosionDocument26 pagesCE336 09 Civil CorrosionSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- LatheDocument16 pagesLathepuneet28vPas encore d'évaluation
- AcupressureDocument3 pagesAcupressureravi_kumar_bokkaPas encore d'évaluation
- RTP Practitioner 10 07Document6 pagesRTP Practitioner 10 07moovitchPas encore d'évaluation
- Knuckle Joint & Cotter JointDocument10 pagesKnuckle Joint & Cotter JointSanthosh SekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Fasteners - Part IIDocument24 pagesMechanical Fasteners - Part IIsaded05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forge WeldingDocument3 pagesForge WeldingSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- HR Interview QuestionsDocument38 pagesHR Interview QuestionsSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Staff ProfileDocument1 pageStaff ProfileSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsDocument11 pagesInductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsDocument11 pagesInductive Reasoning Test1 SolutionsSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of CoscurveDocument3 pagesUse of CoscurveSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Reasoning Test1 QuestionsDocument0 pageNumerical Reasoning Test1 QuestionsSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Reasoning Test1 Questions 1Document6 pagesInductive Reasoning Test1 Questions 1SoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbal Reasoning Test1 QuestionsDocument0 pageVerbal Reasoning Test1 QuestionsSoonyam0% (1)
- Numerical Reasoning Test1 SolutionsDocument0 pageNumerical Reasoning Test1 SolutionsSoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Light Microscopy HandoutDocument24 pagesLight Microscopy HandoutDevaprakasam DeivasagayamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansys Labmanual Mech460 - 07Document41 pagesAnsys Labmanual Mech460 - 07SoonyamPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class X Science Chap 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts - BasicsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class X Science Chap 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts - BasicsMd RabbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3 HH EquationDocument34 pages4.3 HH EquationAdinda Nur AdilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Protolytic ReactionDocument8 pagesProtolytic ReactionRobo KnapPas encore d'évaluation
- Carboxylic Acids and Their SaltsDocument2 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their SaltsfaithPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry SQP PDFDocument8 pagesChemistry SQP PDFÀĺťhàf AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 21 Ec Lab Manual Student VersionDocument141 pages2020 21 Ec Lab Manual Student Versionتسليم الدينPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of Class X BBOSEDocument8 pagesSyllabus of Class X BBOSEFaisal AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Adam1992 Hypochlorous Acid Decomposition in The PH 5-8 RegionDocument8 pagesAdam1992 Hypochlorous Acid Decomposition in The PH 5-8 RegionGregorio ValeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Amicon Ultra-4 10K Centrifugal Filter Devices: User GuideDocument10 pagesAmicon Ultra-4 10K Centrifugal Filter Devices: User GuideDainius JakubauskasPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C TabletsDocument2 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C TabletsNoel NeumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Size Control of Gold Nanocrystals in Citrate ReductionDocument10 pagesSize Control of Gold Nanocrystals in Citrate ReductionJosé Adriano SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of Period 3 Elements With Chlorine, Oxygen and WaterDocument13 pagesReactions of Period 3 Elements With Chlorine, Oxygen and WaterTony GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tit RationDocument7 pagesTit RationgautamahujaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9701 s07 QP 5Document11 pages9701 s07 QP 5G M Ali KawsarPas encore d'évaluation
- ResistanceofNickelandHigh NickelAlloystoCorrosionbyHydrochloricAcid HydrogenChlorideandChlorine 279 PDFDocument31 pagesResistanceofNickelandHigh NickelAlloystoCorrosionbyHydrochloricAcid HydrogenChlorideandChlorine 279 PDFLambertWaynePas encore d'évaluation
- Detail Estimate O1T2 29092023Document15 pagesDetail Estimate O1T2 29092023Masud95Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 BIOCHEMDocument50 pagesChapter 2 BIOCHEMDentist_2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- January 2015 (IAL) MS - Unit 4 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument27 pagesJanuary 2015 (IAL) MS - Unit 4 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelIbrahim SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- (Raymond Chang) Chemistry by Raymond Chang (B-Ok - Org) Compressed (1) - 682-688Document7 pages(Raymond Chang) Chemistry by Raymond Chang (B-Ok - Org) Compressed (1) - 682-688Hikma AinazzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Year Chemistry Full Book MCQs TitleDocument52 pages2nd Year Chemistry Full Book MCQs TitleMalaika MinerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 4 - Mat Bal 03-1Document79 pagesChap 4 - Mat Bal 03-1Alina AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- MC Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesMC Acids and Alkalisapi-3826629100% (1)